rr1 biology gas exchange in humans
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
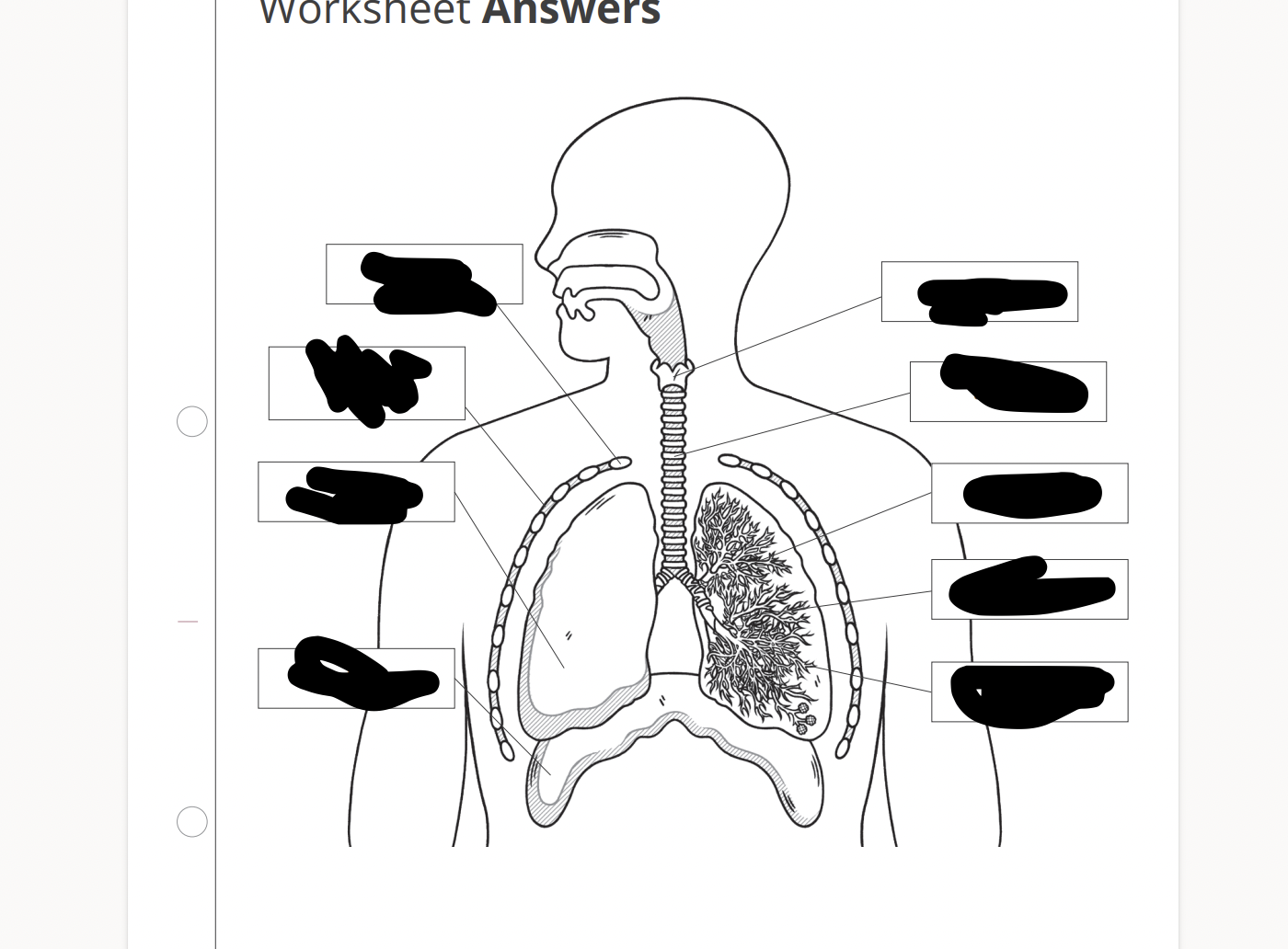
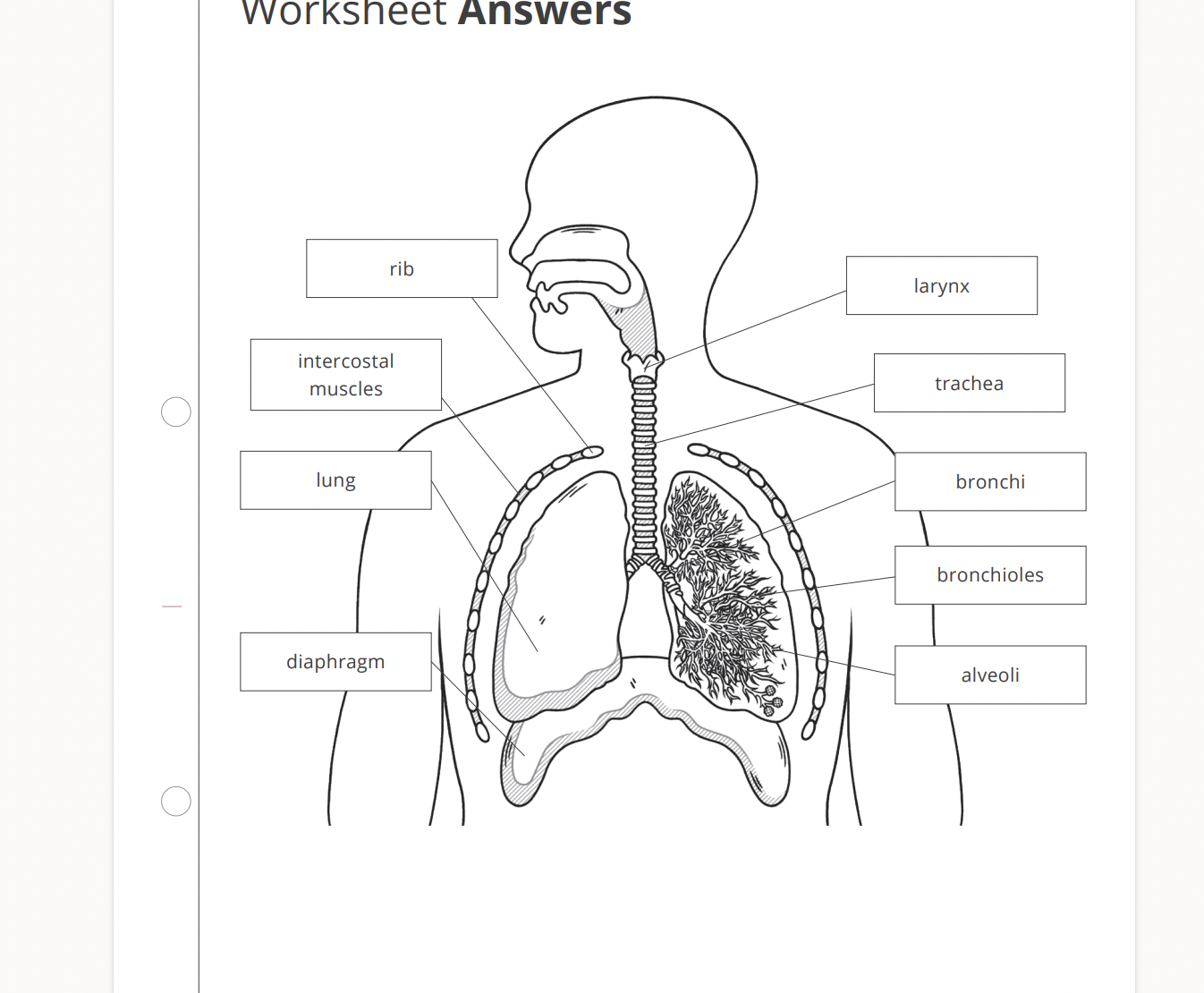
all gas exchange surfaces have features in common. name the 4 features.
large surface area
thin walls
good ventilation
good blood supply
explain the set up used to investigate the difference between inspired and expired air
list the difference in percentages between inspired and expired air of the following: oxygen, carbon dioxide, nitrogen and water vapor
Inspired air contains approximately 21% oxygen, 0.04% carbon dioxide, 78% nitrogen, and a minimal amount of water vapor. Expired air contains about 16% oxygen, 4% carbon dioxide, 78% nitrogen, and a higher percentage of water vapor due to humidification in the lungs.
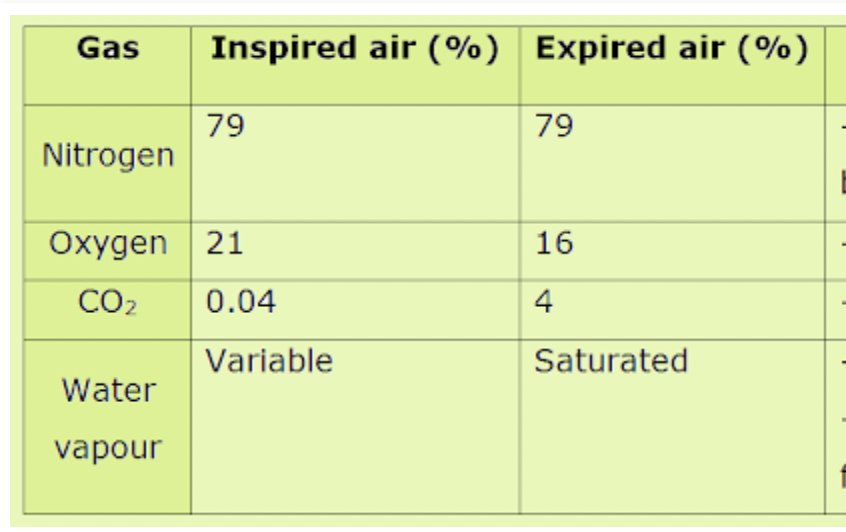
explain why there was a change in percentage for each.
nitrogen gas is very stable and so cannot be used by the body, for this reason its concentration does not change.
oxygen is taken into the blood and used in the process of respiration
co2 is a by-product produced in respiration therefore it diffuses into the blood by respiring cells which then are transported to the lungs.
water evaporates from the moist lining of the alveoli into the explired air as a result of warmth in the body
why does your breathing rate increase when you exercise?
during exercise your breathing rate increases as your body needs more oxygen to supply your muscles and remove the carbon dioxide the produce.
explain how to investigate your breathing rate increaseduring exercise
for this experiment all you will need is a stopwatch and a volunteer.
count how many breaths the participant took in 1 minute(before exercise)
exercise (could be as simple as jumping jacks)
right after concluding physical activity count the number of breaths taken by the participant (should be more)
comare the two counts and observe the increase in breathing rates
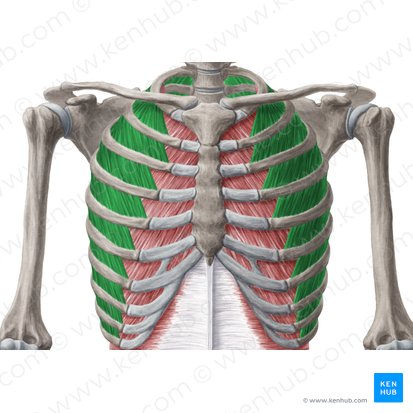
label the internal and external intercostal muscles and and describe the function of intercostal muscles.
function of the cartilage
rings of cartilage surround the trachea (and bronchi). their function is to support the airway and keep it open during breathing. without the cartilage the trachea could colapse inwards therefore allowing the air preassure inside the tubes to drop.
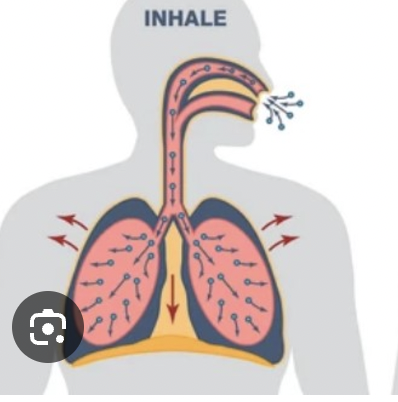
describe what happens to the body during inhalations
air is drawn in
ribcage moves up and down
diaphragm contracts and flattens (pulling down)
volume of thorax increases
preassure inside thorax decreases
intercostal muscles contract
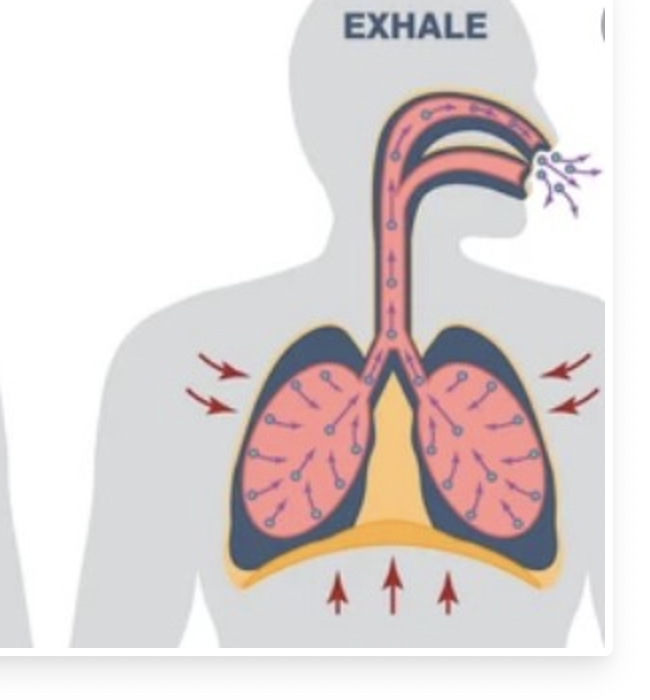
describe what happens to the body during exhalations
air is forced out
intercostal muscles relax
ribcage moves down and in
diaphragm relaxes and becomes dome shaped
volume of thorax decreases
preassure inside thorax increases
thoroughly explain the link between physical activity and breathing.
when you exercise your muscles work harder and need more energy, which they get using oxygen and the production of co2 in the process of aerobic respiration.
to supply the oxygen demand and remove the extra co2 produced your breathing rate turns faster and deaper.
if your muscles cant get enough oxygen, the body switches to anaerobic respiration which produce lactic acids in the muscles. after exercise you need more oxyge to break down the lactic acid. this is known as “repaying the oxygen dept”
As co2 levels rise in your blood during exercise, they make the blood slightly acidic. sensors in you brain detect this and sent signals to your breathing muscles (such as the diaphragm) to work harder. This increases the ammount of oxygen you take in and co2 you exhale, helping youe muscles keep up with the demand of energy.
what are cilliated epithelial cells and what are their function?
the passages down the lungs are lined with cilliated epithelial cells. these cells have tiny hairs which push mucus up where it can be removed (nose and mouth).
what are goblet cells and what are their function.
goblet cells produce mucus. mucus traps pathogens, particles and dust therefore preventing them from reaching the lungs.