Nitrogen Cycle
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
Processes in the Nitrogen cycle
1) Nitrogen fixation
2) Nitrification
3) Ammonification
4) Denitrification
What is Nitrogen fixation?
A process of combining nitrogen gas and hydrogen to produce ammonia.
Ammonia is a form of nitrogen that can be absorbed and used by plants.
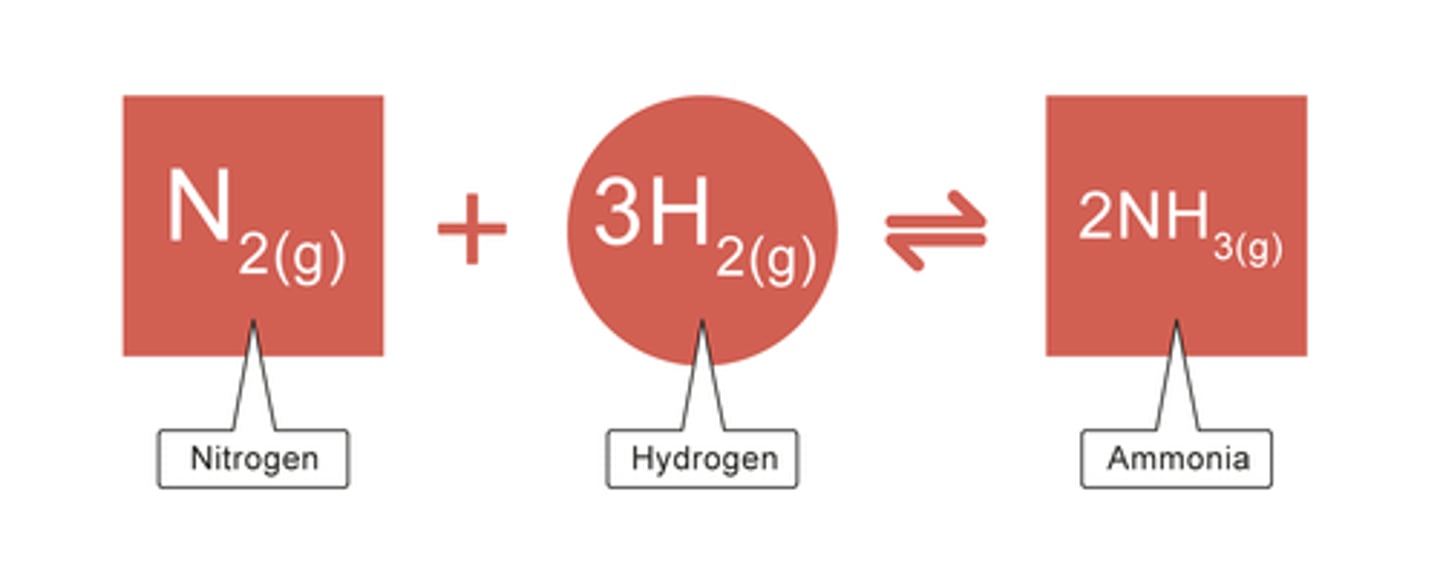
Nitrogen fixation methods?
- Non living processes - Lightning, and the Haber process
- Living processes - Rhizobium, and azotobacter
Azotobacter
- Free living soil bacterium
- Converts nitrogen to ammonia
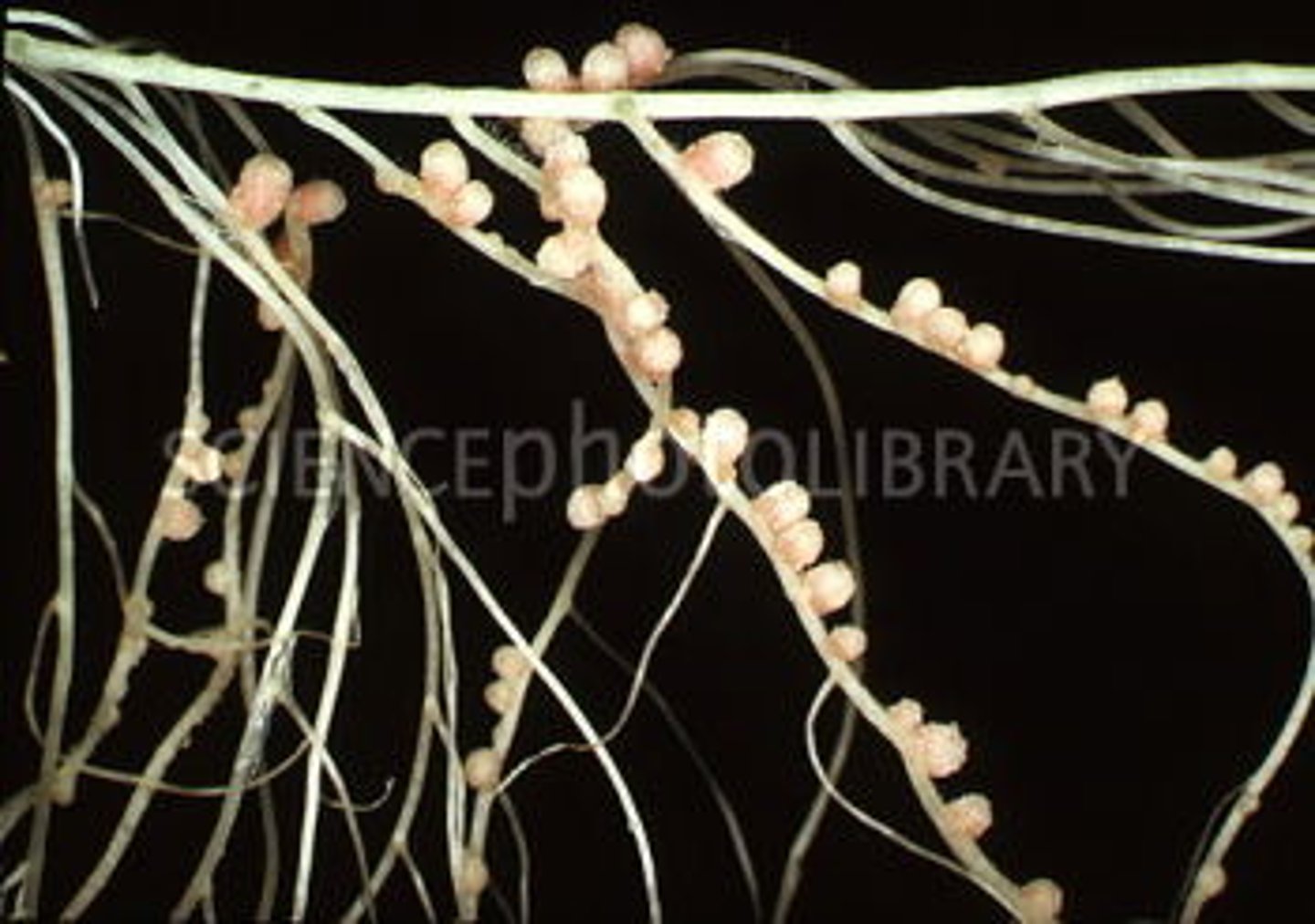
Rhizobium
- Nitrogen fixing bacteria that live inside root nodules
- They have a symbiotic relationship with the plant, like how the plant gains amino acids from Rhizobium, which are produced by fixing nitrogen gas in the air into ammonia in the bacteria. The bacteria gain carbohydrates produced by the plant during photosynthesis, which they use as an energy source.
What's nitrification?
A process by which ammonium compounds in the soil are converted into nitrogen containing molecules that can be used by plants.
Free-living nitrifying bacteria are involved
An oxidation reaction
Nitrifying bacteria
Nitrosomonas
Nitrobacter
Nitrosomonas
Oxides ammonium to nitrites
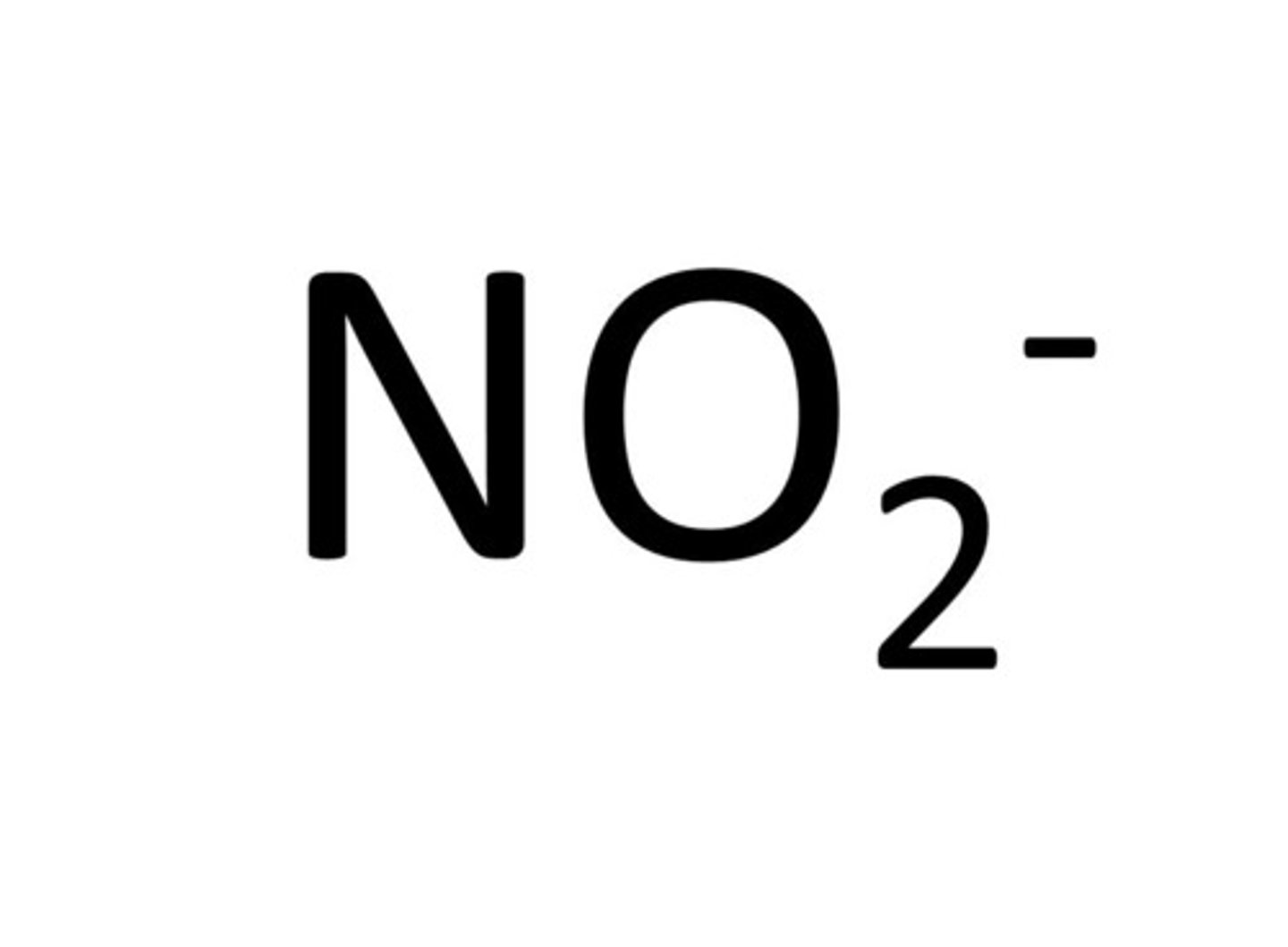
Nitrobacter
Oxides nitrites to nitrates
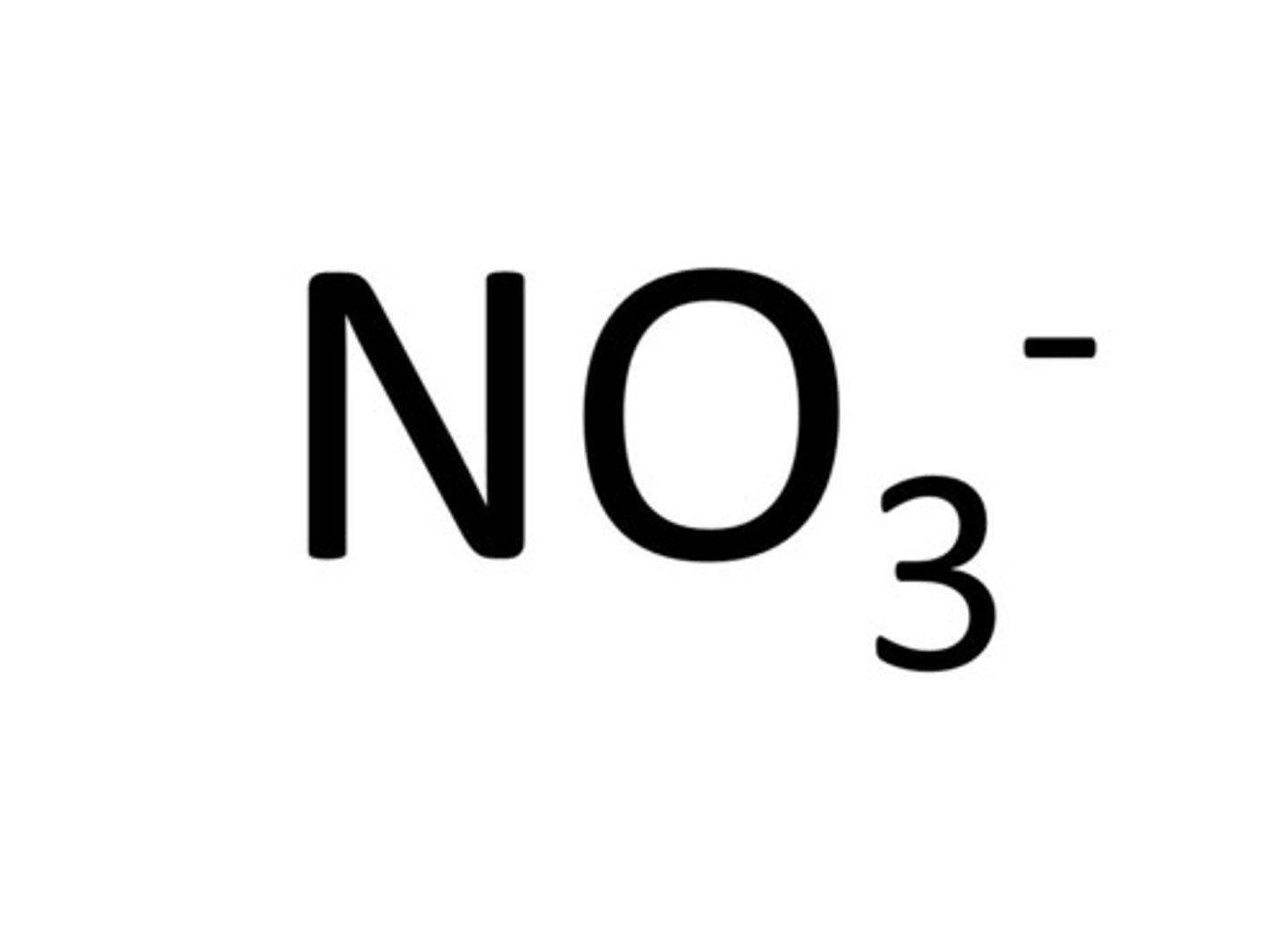
What's denitrification?
- In the absence of oxygen, denitrifying bacteria convert nitrates in the soil back to nitrogen gas (N2)
- Only occurs under anaerobic conditions, such as waterlogged soils
- The bacteria use nitrates as a source of energy for respiration, and nitrogen gas is released
Denitrificans
Pseudomonas
What's ammonification?
A process by which decomposers convert nitrogen containing molecules in dead organisms, faeces, and urine, into ammonium compounds.