Forensic blood spatter
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
What are the components of blood
Blood is composed of red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, and plasma.
Define Antigens
Antigens are proteins that can be foreign to the body (parasites, bacteria, pollen).
Define Antibodies
Antibodies identify and label foreign antigens/materials so they can be destroyed.
Are blood types classified as class evidence or individual evidence? Explain.
Blood types are classified as class evidence because it is not specific to one individual like DNA. Instead, blood types can be shared among many individuals, making them useful for narrowing down a suspect pool to a group of people.
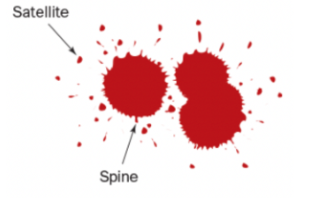
Define blood spatter spines
Blood hits and adheres to a porous surface
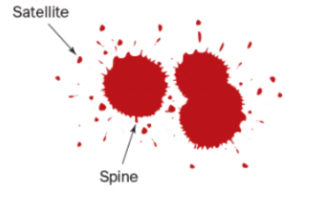
Define blood spatter satellites
Blood overcomes cohesion and separates from the main drop
Define how cohesion affects blood spatter patterns
Cohesion affects blood spatter patterns by causing droplets to remain intact as they fall, influencing their shape and distribution on impact surfaces.
Define how adhesion affects blood spatter patterns
Adhesion affects blood spatter patterns by allowing blood droplets to stick to surfaces upon impact, altering their shape and creating distinctive patterns.
Explain why a passive drop of blood will be circular in appearance
The molecules in blood are attracted to one another so as they fall due to gravity only, this cohesion isn’t disrupted so the blood drop remains circular.
Explain why most of the blood will remain a drop where it first strikes a surface, but some of the blood will continue to move forward creating a spine/tail.
Blood falling at an angle less than 90 degrees will drop and adhere to the surface with most of it staying together due to cohesion but some will have momentum in the direction away from the person bleeding.
What happens to the shape of a blood drop when dropped from angles less than 90 degrees
The blood drop will become elongated and may form a tail or spine the smaller the angle of impact, resulting in a more elongated shape rather than remaining circular.
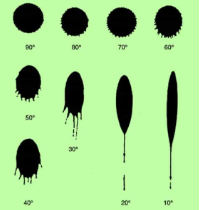
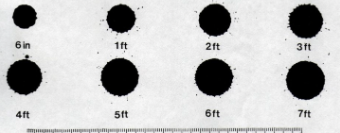
Describe the difference in size of a blood spatter when dropped from 30 cm vs 100 cm.
The drop size increases with height
What would cause blood spatter patterns produced by high velocity
A gunshot

What would cause blood spatter patterns produced by medium velocity
A stabbing

What would cause blood spatter patterns produced by low velocity
An open wound

How would two blood spatter patterns differ if one came from a gun fired at close range and the other came from a gun fired from a distance
Less force with greater distance, so the spatter pattern would be larger and cover less area.
Passive trail of blood drops

Transfer Pattern
Bloodstain created when a bloody object touches another surface
Expired Blood
Blood blown out of the nose, mouth, or wound as a result of air flow

Shadowing or Void
Created when an object blocks the deposition of blood spatter onto a target surface or object
Cast Off Pattern
Blood stains created when blood is released from a moving, bloody object (ex. a bloody knife being swung through the air)

Wipe
Occurs when a bloody object, like a hand, clothing, or hair, is wiped across a surface

Swipe
Occurs when a bloody object transfers blood onto a surface that is not bloody.

What is the overall pattern of an arterial gush
Arching pattern with large individual stains
Why do arterial gushes have high points and low points
The blood gushes out with the rhythm of the heart
Define area of convergence
Shows where a person was standing or sitting when they were bleeding
Define area of origin
The location where an injury occurred
How is blood spatter evidence used to '“tell a story” of what happened at the crime scene
Number of people at the scene, movement and positions of people at the crime scene, type of weapon used, type of injuries incurred, number of blows delivered to the injured party, and level of violence.
What methods are used to document blood and blood-spatter evidence
Note taking, videotaping, photography, and sketches.
How is blood identified in an area devoid of visible blood
Investigators spray the area with luminol or BlueStar®, chemical reagents that react with hemoglobin the iron-containing molecule in the blood that transports oxygen. When viewed under a UV light, previously invisible blood produces light for approximately 30 seconds.
What procedures should be completed prior to collection of blood evidence at the crime scene
CSI conducts color tests on the stains to determine if it is blood and if its human blood
What is the procedure for collecting dried blood from small areas
Packaged in a paper bag. If item is large, samples are collected from a section with blood and a negative control section, a sample without blood.
What is the procedure for collecting dried blood from large, wet, blood-soaked surfaces
Can be packaged in a paper bag and brought to evidence collection site where it’ll be removed, thoroughly air dried, and repackaged in a paper bag.
What is the procedure for collecting and packaging liquid blood evidence
Clean unused sealed plastic containers at the scene and refrigerated if possible. Must be stored for less than two hours to prevent contamination.
What four things can we determine from blood spatter analysis
Direction, distance, angle, and speed
What is pattern analysis
The examination of physical characteristics such as size, shape, distribution, and overall appearance.
What is crime scene reconstruction
Based on the physical evidence found at a crime scene such as angle of impact, area of convergence, area of origin, transfer patterns, swipes, wipes, cast off patterns, and more
Consistency of scientific evidence
Determines if the eyewitness accounts seem consistent with the blood evidence