Matter and Energy
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
What is a pure substance? What are the two categories of pure substances?
It contains only one type of matter. (ex: pure water)
It is either an element or a compound
What is a mixture? What are the two categories of mixtures?
It contains two or more types of matter. (ex: pool water). It is a physical blend of two or more substances.
It is either a heterogeneous mixture or a homogenous mixture (aka solution)
What are examples of common mixtures?
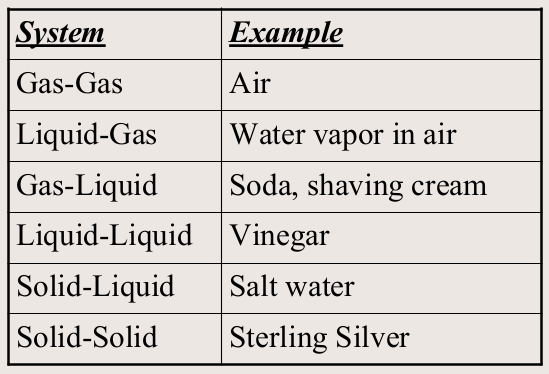
What are homogenous mixtures?
A mixture in which the components of the mixture are uniform throughout.
ex: salt water, air, iced tea, colors such as green and purple, copper sulfate

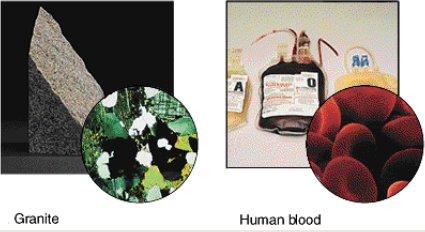
What are heterogeneous mixtures?
A mixture in which there is no uniform composition.
ex: salad, granite, human blood, soup
What does aqueous mean?
A homogenous mixture that is mixed with water.
What are the separation techniques?
Can be done based on properties such as boiling point, magnetism, solubility, etc.
Evaporation
Filtration
Distillation
Chromatography
Gel Electrophorisis
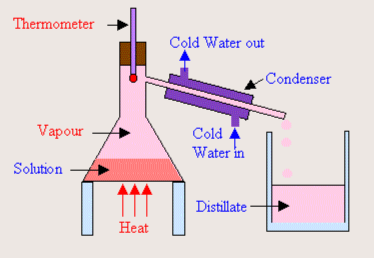
What is distillation?
It is a separation technique that purifies water and makes fuel for alcoholic drinks. It separates mixtures of liquids by boiling point.
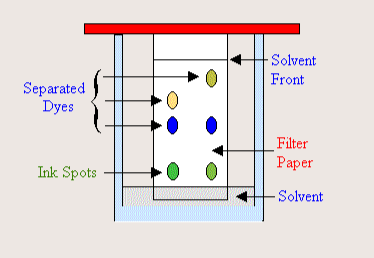
What is chromatography?
A separation technique that separates substances, pigments, and colors. It separates based on polarity (separation of electric charge - positive and negative) and solubility (the ability of a substance to form a solution with another substance)
What is filtration?
It is a separation technique that separates things that dissolve in water from things that do not dissolve in water.
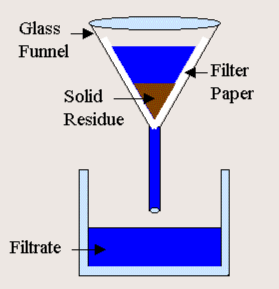
What is evaporation?
It is a separation technique that can separate water from whatever is put into it.
What is gel electrophoresis?
It is a separation technique that separates based on size.
What is an element?
It is a pure substance and is also the smallest amount of matter. It can not be broken down and still be considered its original substance.
It can not be broken down by chemical means.
It can be either an atom or a molecule.
What are compounds?
They are pure substances that are two or more different types of elements chemically combined to form a stable substance in a fixed ratio.
They can be broken down by chemical means.
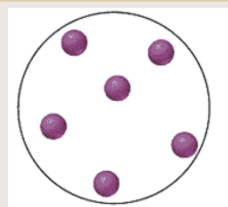
Is it an element, compound, or mixture? Is it a solid, liquid, or gas?
Element, gas

Is it an element, compound, or mixture? Is it a solid, liquid, or gas?
Diatomic element, can be either a solid, liquid, or gas.
Only seven types:
Br (liquid), I (solid), N, Cl, H, O, & F (gases)
What are the diatomic elements?
Br, I, N, Cl, H, O, & F
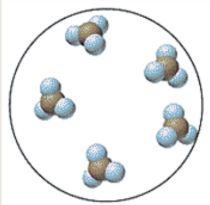
Is it an element, compound, or mixture? Is it a solid, liquid, or gas?
Compound, liquid
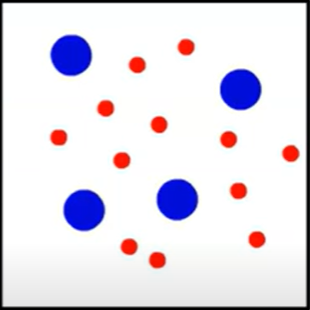
Is it an element, compound, or mixture? Is it a solid, liquid, or gas?
Mixture
Sometimes you can’t tell if it is homogenous or heterogenous
What are words that describe chemical properties?
combination
decomposition
exchange
displacement
precipitation
gas-forming
neutralization
acid/base
oxidation/reduction
redox
charge transfer
proton transfer
electron transfer
rotting
sours
cooks
grows
digested

What are words that describe physical properties?
vaporization
mixing
evaporation
condensation
crushing
cutting
dissolving
breaking
liquefy
shredding
Which can be decomposed, an element or a compound?
Compound
Which varies, compounds or mixtures?
Mixtures
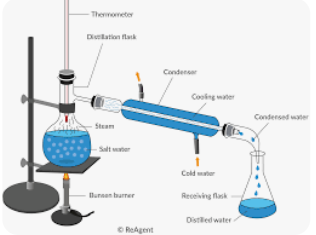
What process is shown in this diagram?
Distillation
As you move down any group of metals, they…
get more reactive because they want to get rid of their last valence electrons
Metals vs nonmetals
Metals have high/low electronegativity.
low electronegativity.
They want to get rid of electrons, not gain one
Metals vs nonmetals
Nonmetals have high/low electronegativity.
high electronegativity.
Metals vs nonmetals
Metals only form positive/negative ions.
positive ions.
This is because they lose their valence electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration.
Metals vs nonmetals
Nonmetals only form positive/negative ions. Why?
negative ions.
This is because they gain electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration. They have a high number of valence electrons and a high electronegativity.
Metals vs nonmetals
Metals have a high/low conduction of heat and electricity.
high conduction of heat and electricity.
Metals vs nonmetals
Nonmetals have a high/low conduction of heat and electricity.
low conduction of heat and electricity.
Metals vs nonmetals
Metals have high/low ionization energy.
low ionization energy.
Metals vs nonmetals
Nonmetals have high/low ionization energy.
high ionization energy.
Metals vs nonmetals
Metals are ductile and malleable/brittle.
ductile and malleable.
Metals vs nonmetals
Nonmetals are ductile and malleable/brittle.
brittle.
Metals vs nonmetals
Metals have high/low densities, melting points, and boiling points.
high densities, melting points, and boiling points
Metals vs nonmetals
Nonmetals have high/low densities, melting points, and boiling points.
low densities, melting points, and boiling points.
Metals vs nonmetals
Metals are lustrous/not lustrous.
lustrous.
Metals vs nonmetals
Nonmetals are lustrous/not lustrous.
not lustrous.
Metals vs nonmetals
Metals will/will not react with acid to produce hydrogen
will react.
Metals vs nonmetals
Nonmetals will/will not react with acid to produce hydrogen.
will not react.
Which does not change chemical identity: physical or chemical changes?
physical changes
Which changes chemical identity: physical or chemical changes?
chemical changes
What breaks and reforms bonds?
Chemical changes
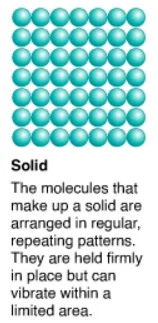
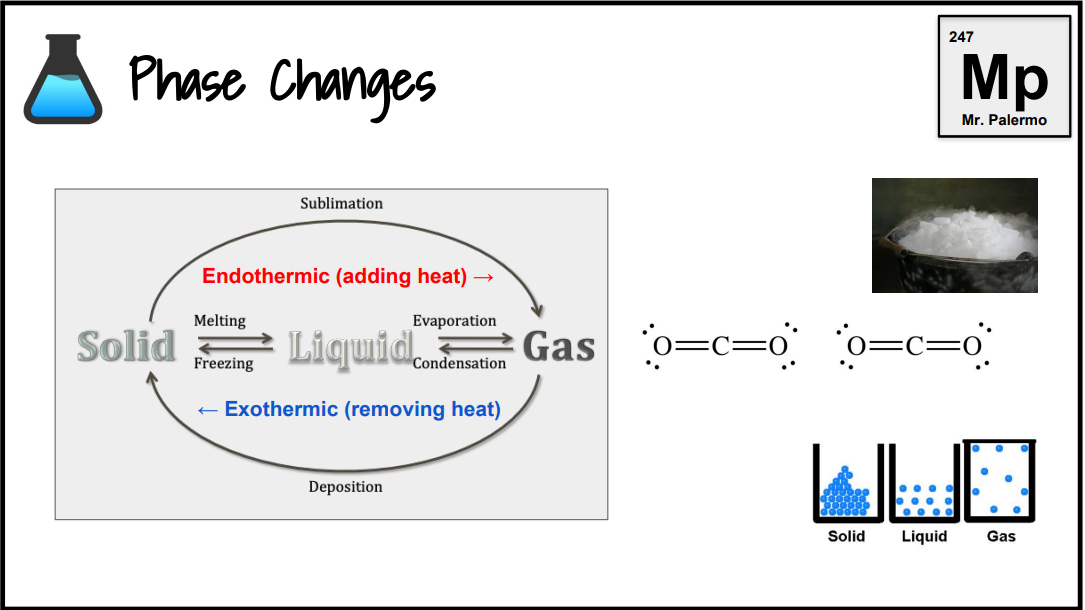
What are solids?
They have a definite shape (regular geometric pattern), and have a definite volume. They can be metals, nonmetals, or metalloids.
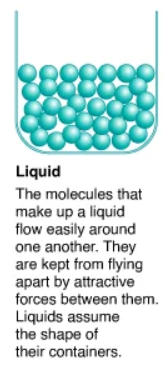
What are liquids?
They do not have a definite shape, they just take the shape of the container they are in. They have a definite volume.
They can also conduct energy if it is a liquid metal or if you dissolve salts, acids, or bases in water (they are ions).
What are gases?
The particles are far apart but can be compressed. They do not have a definite volume, but you can change it through temperature or pressure. The shape is not definite either.
Every reaction is…
exothermic or endothermic
What is an endothermic change?
Endo: inside. Any reaction where heat gets absorbed. Boiling and photosynthesis are endothermic. If heat is shown on the left side of the arrow, the reaction is endothermic.
What is an exothermic change?
Energy is released from the reaction. If heat is shown on the right side of the arrow, the reaction is exothermic.
What is the phase change of melting/fusion?
Endothermic
S → L
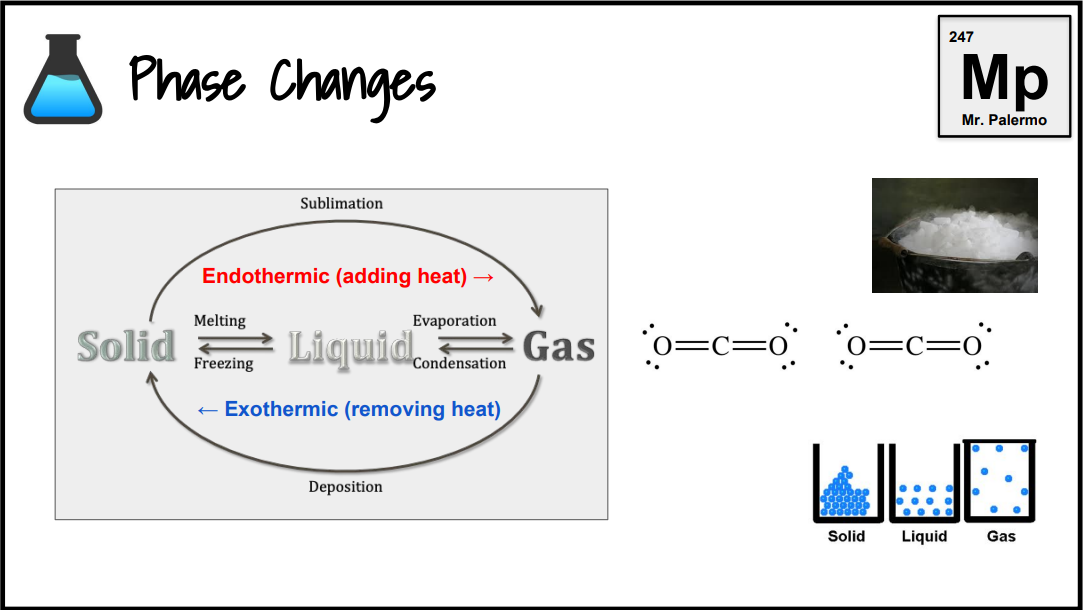
What is the phase change of evaporation/vaporization?
Endothermic
L → G
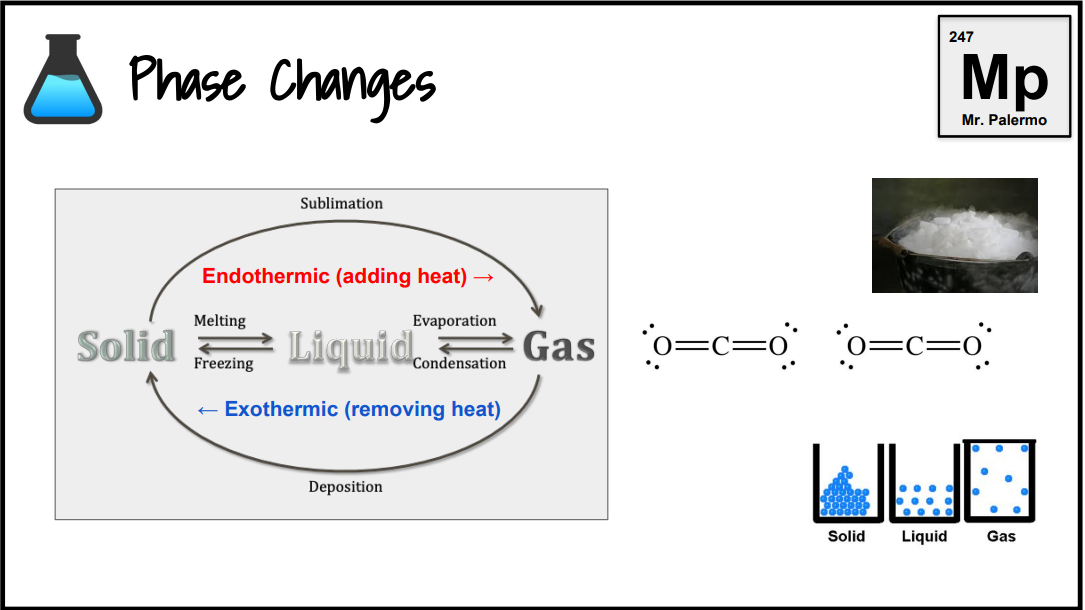
What is the phase change of sublimation? (dry ice, solid iodine)
Endothermic
S → G
Which is the system?
NaOH(s) → NaOH(aq) + energy
Water
NaOH(s) → NaOH(aq) + energy
Which is the surroundings?
NaOH(s) → NaOH(aq) + energy
Water
Water
When water dissolves exothermically, it gets…
hotter
When water dissolves endothermically, it gets…
colder
What is kinetic energy?
Energy of motion. Synonymous with heat (heat makes things faster) and temperature. Particles are always moving so they would have kinetic energy. If a particle is not moving, it is at absolute zero. (0k)
What is Celsius equal to in Kelvin?
K-273
What is Kelvin equal to in Celsius?
C+273
What is the boiling point of water?
100oC, 373K
What is the freezing point of water?
0oC, 273K
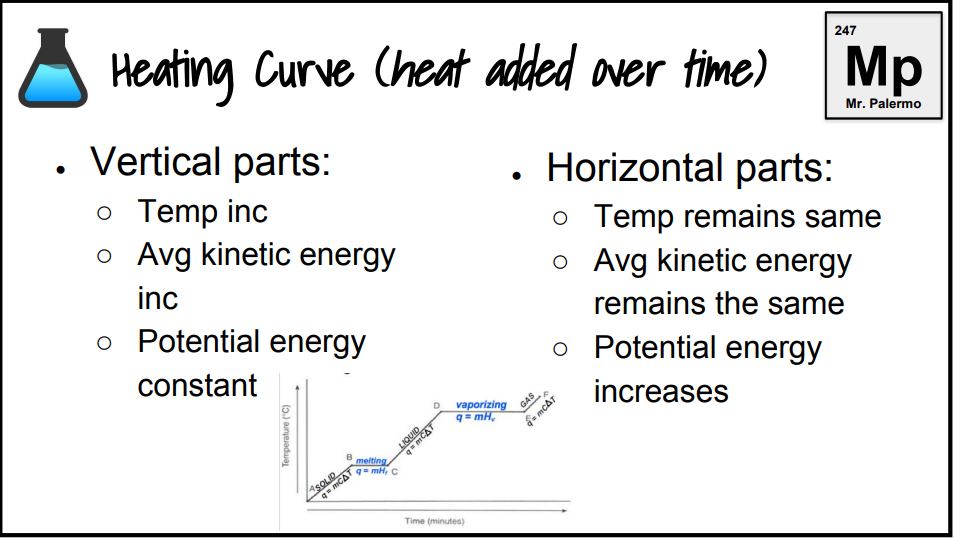
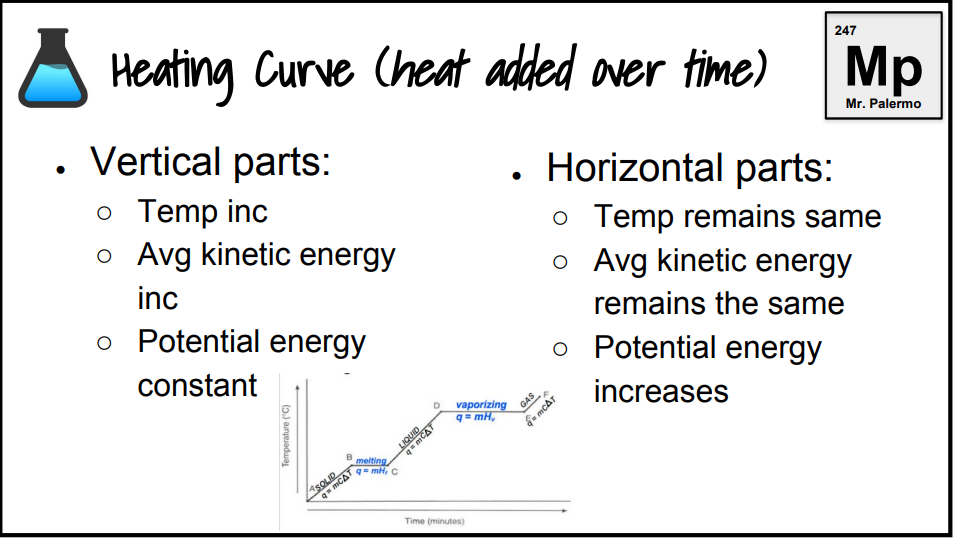
What is the heating curve?
What happens to a substance that is increasing in temperature when it goes through all 3 phases.
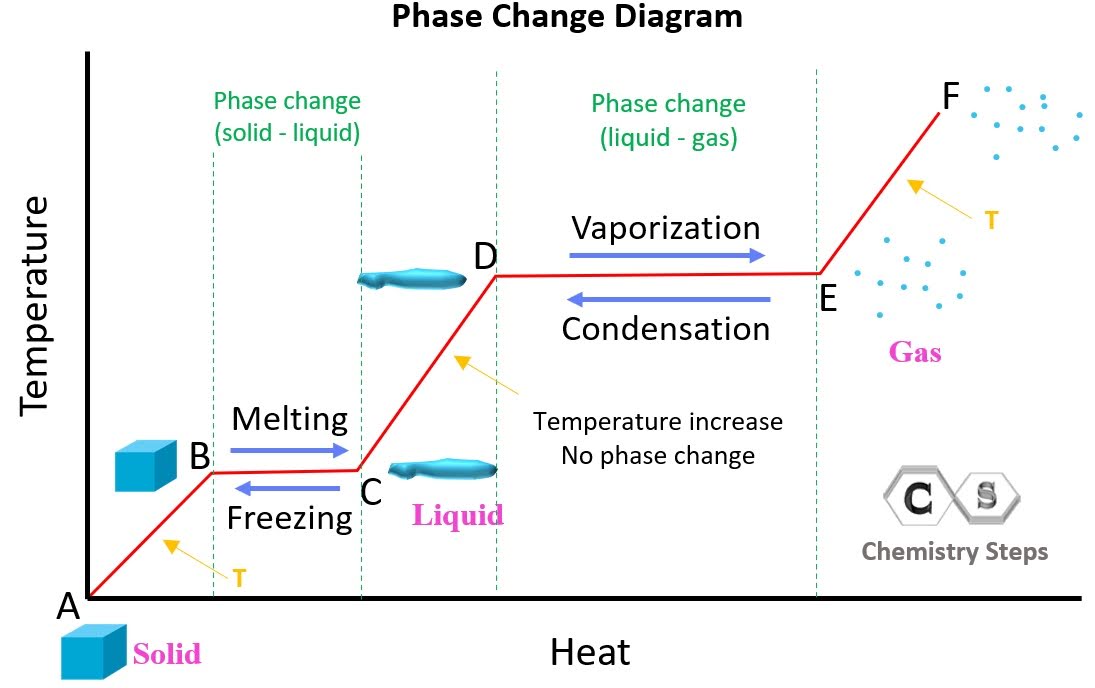
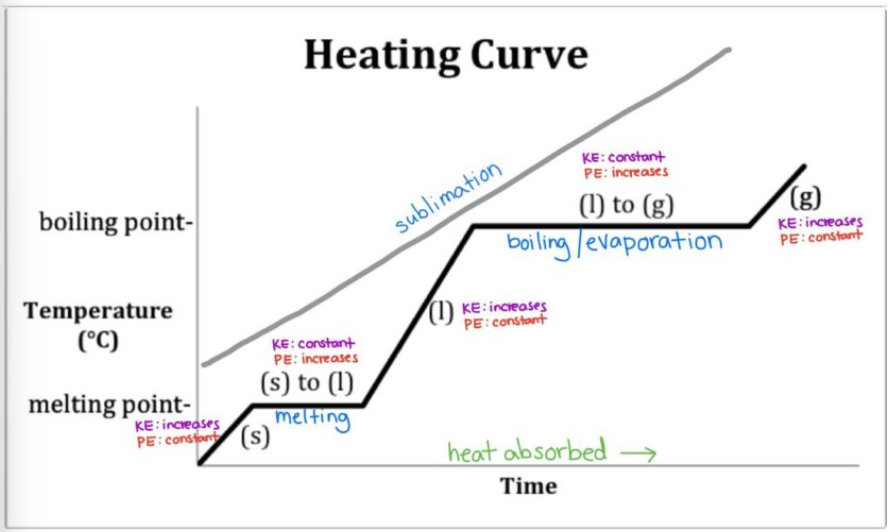
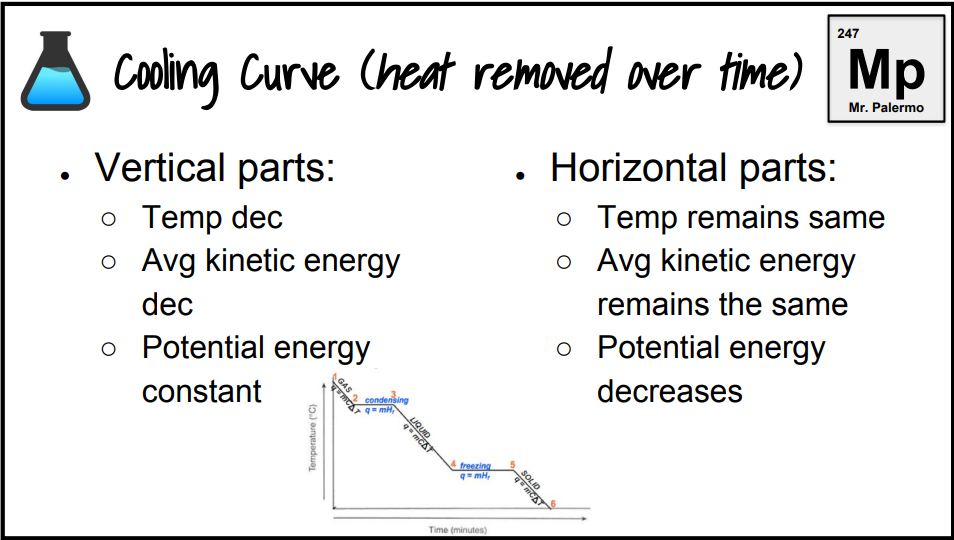
What is the cooling curve?
What happens to a substance that is decreasing in temperature when it goes through all 3 phases.
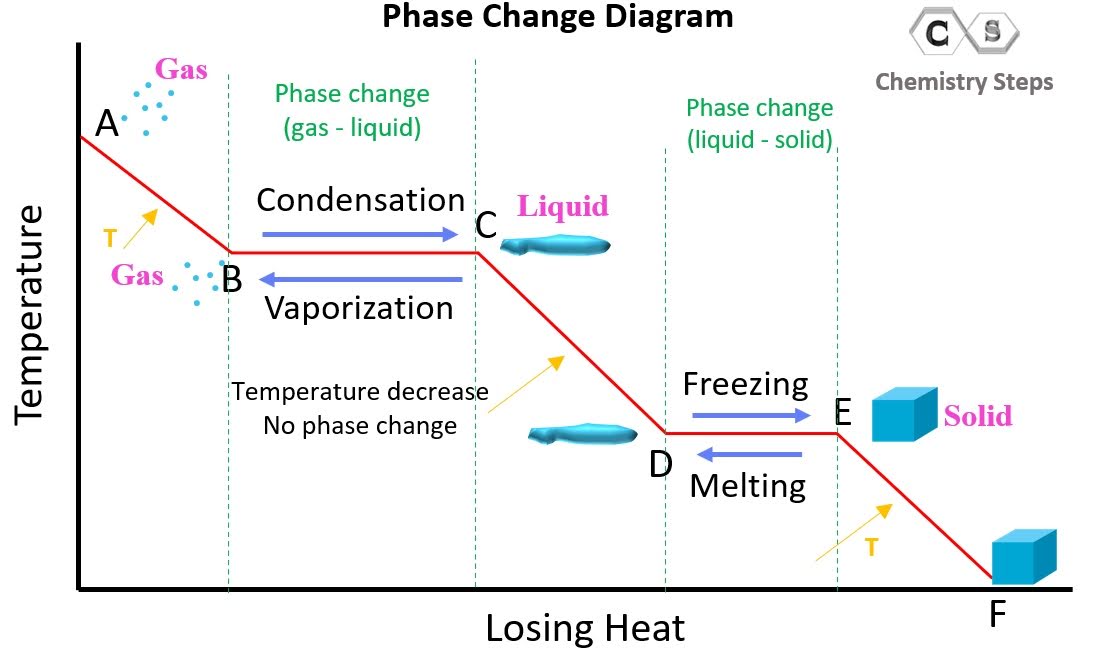
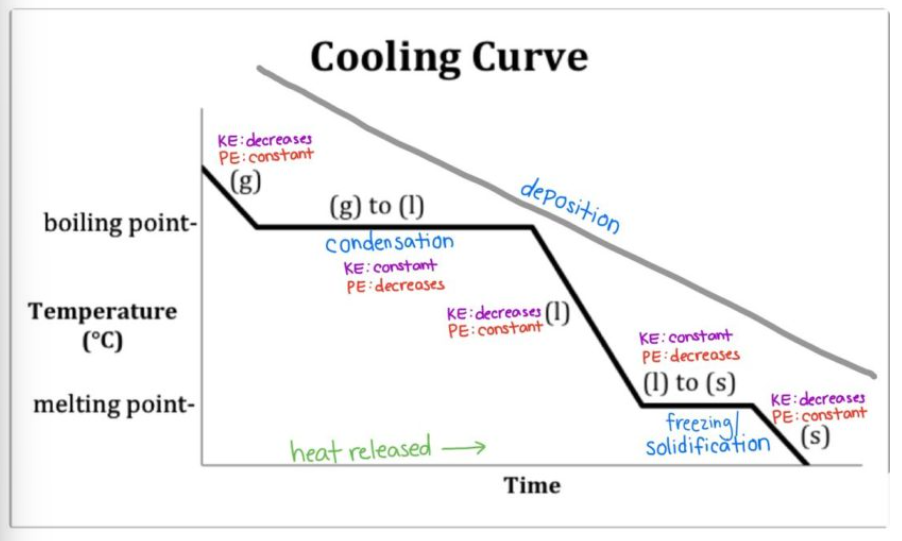
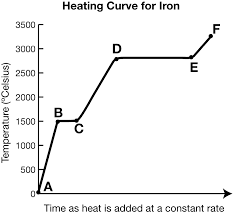
What is represented by segment ab?
Solid
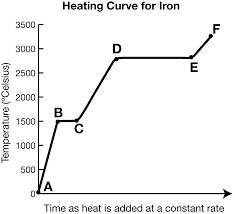
What is represented by segment cd?
Liquid
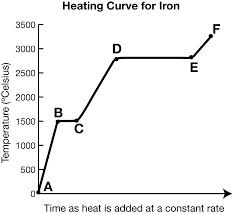
What is represented by segment ef? (f is supposed to be above e)
Gas
In a heating curve, the phases of matter are increasing/decreasing in temperature and kinetic energy.
increasing
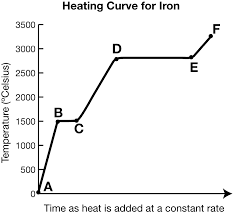
What exists at segment bc?
S ⇄ L (equilibrium)
This equilibrium occurs at a fixed temperature, the melting/freezing point.
The melting point for water is at B, 20o.
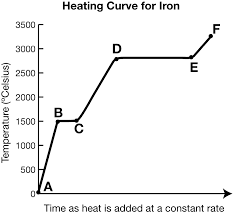
What is Hf and where is it?
It exists at segment bc. It is the heat of fusion (amount of energy needed to melt the substance)
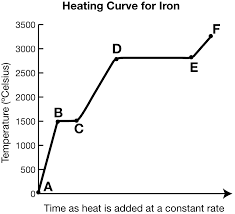
What exists at segment de?
Vaporization. The boiling point of this substance is between 2500-3000oC.
The liquid and gas phases are in equilibrium.
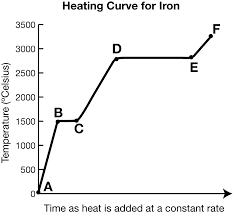
What is Hv and where is it?
It exists at segment de. It is the amount of energy needed to evaporate the substance.
What is potential energy?
Energy of position. Stored energy
On a heating curve, kinetic and potential energy increases/decreases or stays the same.
increases
On a cooling curve, kinetic and potential energy increases/decreases or stays the same.
decreases
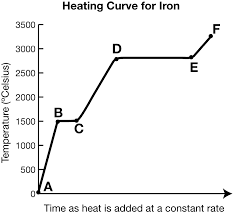
What is the trend of kinetic/potential energy for segments ab, cd, and ef?
kinetic energy increases, potential energy stays the same.
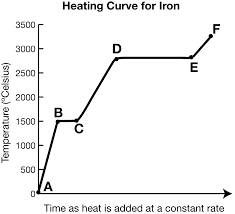
What is the trend of kinetic/potential energy for segments bc and de?
potential energy increases, kinetic energy stays the same
What is the heat of fusion?
334 J/g
What is the heat of vapor?
2260 J/g
What is the heat of specific heat capacity?
4.18 J/gk
What are the formulas?
q=mHf
q=mHv
q=mCΔT
A student adds 7,250 J of energy to a sample of ice at 0oC. What is the mass of the sample?
21.7g
A substance requires 112000J to vaporize a 60g sample. What is the heat of vaporization?
1867 J/g
How much energy is released when 320g of water is cooled from 90.0oC to 60oC.
40,128 J
16,250 J of energy is added to a sample of water at 26oC and is raised to 89oC. What is the mass of the water?
61.707g
32,675 J of energy is added to a sample of water at 10oC until it reaches 35oC. What is the mass of the sample?
313g
42.6g of water absorbs 8350 J at 12oC. What is the change in temperature?
46.89
17,525 J of energy is released from 350g of water at 75oC. What is the final temperature?
x=12oC
A 36g sample of water has an initial temperature of 22oC. After the sample absorbs 1200 J of heat energy, the final temperature of the sample is…
8oC change, so 30oC
68,800 J of energy is absorbed into 182g of water until its final temperature reads 99oC. What is the initial temperature?
9oC
Solids have low/moderate/high kinetic energy and low/moderate/high potential energy.
low kinetic energy, high potential energy
Liquids have low/moderate/high kinetic energy and low/moderate/high potential energy.
moderate kinetic energy, moderate potential energy
Gases have low/moderate/high kinetic energy and low/moderate/high potential energy.
high kinetic energy, low potential energy
What are the properties of matter that never change?
Boiling point, melting point, density
Heat flows from…
hot → cold
What separation technique can be used to separate the following:
NaCl(aq) + C6H12O6 (aq)
Distillation
What separation technique can be used to separate the following:
KCl(aq) + SiO2(s)
Filtration
A 7.5g piece of lead (C=0.128) at 125oC is placed into a beaker of 60g of water at 25oC. What is the eq temperature?
≈ 25.38oC
What does C stand for?
Q=mC∆T
specific heat capacity (amount of heat needed to raise the temp. of the substance)
What does ∆T stand for?
Q=mC∆T
change in temperature