RAT 5 - Human Physiology
1/46
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chs 24 and 26
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
What is a pathogen?
Any substance capable of causing diseases
What is innate immunity?
The nonspecific responses of the body to invasion by foreign substances, responds within minutes to hours
What is acquired immunity?
Immune responses directed at specific invades mediated by antibodies, takes days or weeks to respond
What is a leukocyte?
White blood cells that defend the body against foreign invaders
What is a phagocyte?
Immune cell that ingests material by phagocytosis
What is phagocytosis?
The process by which a cell engulfs a particle into a vesicle by using the cytoskeleton to push the membrane around the particle
What is a lymphocyte?
A white blood cell responsible primarily for the acquired immune response
What is an antigen?
Substances that trigger an immune response from the body and that can react with products of that response
What are plasma cells?
Type of lymphocyte that secretes antibodies
What are memory cells?
Lymphocytes responsible for creating stronger and more rapid immune response following second exposure to an antigen
What is an antibody (immunoglobulin)?
A molecule keyed to a particular pathogen that helps target it for destruction
What is a cytotoxic T cell?
A lymphocyte that kills its target cells
What is an autoimmune disease?
Diseases in which the immune system creates antibodies against the body’s own tissues
What is an allergy?
Inflammatory immune response to a nonpathogenic antigen
What is malfunctioning in autoimmune diseases and allergies?
The immune system, not adaptive responses
What are the differences between the acquired and innate defense systems?
Acquired:
a) Highly specific
b) Develops memory using memory B and T cells
c) Slow initial response, fast on repeat exposures
d) Relies on antibody (B cells) and cytotoxic (T cell) responses
e) Relies on antigen presentation with MHC to activate T cells or specific antigens binding to activate B cells
Innate:
a) Non-specific
b) No memory
c) Rapid first-line response
d) Relies on general mechanisms such as phagocytosis, inflammation, and complement proteins
e) Relies on common pathogen associated molecular patterns (PAMPs)
Where do most immune cells originate from?
The bone marrow
Where do immune cells go when they are mature?
In lymphoid tissue such as the spleen, lymph nodes, and tonsils
What is the function of helper T cells?
Bind to immune cells that display antigens on MHC-II and influence other immune cells
What is the function of cytotoxic T cells?
Defend the body against intracellular pathogens by attacking cells with MHC-I antigen.
How does a vaccine work to produce immunity to a pathogen?
A vaccine has an altered pathogen that can’t harm the body but can be recognized by our immune system. This allows our body to develop antibodies for this pathogen and memory B cells that are specific to that pathogen which will help the body produce a stronger and more rapid response upon future infection.
What are gonads?
The organs (ovaries and testes) that produce gametes
What are gametes?
The reproductive cells that unite to form a new individual
What are the testes?
The male gonads
What is internal genitalia?
The internal reproductive structures (uterus and testis)
What is external genitalia?
The external reproductive structures (penis and vagina)
What are the seminiferous tubules?
Region of the testes where sperm and hormones are produced
What is spermatogenesis?
Process by which sperm cells are produced in the testes
What are ovaries?
The female gonad
What is an oocyte?
Developing female germ cells that have started meiosis
What is ovulation?
Release of a mature egg from its follicle in the ovary
What is oogenesis?
Process by which a female’s ovaries produce eggs
What is human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG)?
Hormone secreted by the developing placenta
What is the placenta?
Organ that forms in the womb during pregnancy
What is the chromosomal difference between males and females?
Males are XY while females are XX
How does the chromosomal difference between males and females trigger sex-specific development?
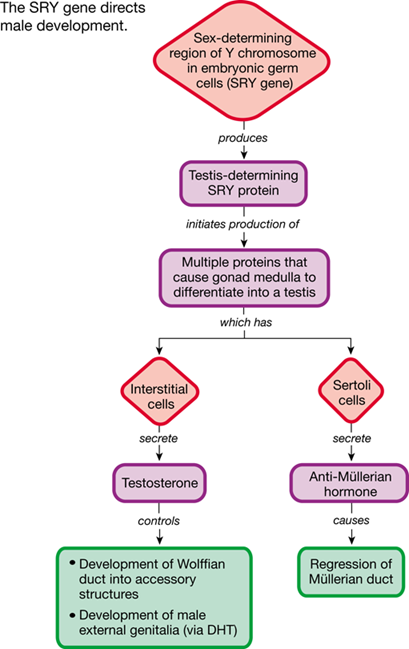
The Y chromosome contains the SRY gene which facilitates development of testes and inhibits development of the uterus
What is the structure of gametes and how are they produced?
Haploid, produced by meiosis
What is the major function of the testes?
To produce sperm
What is the major function of the ovaries?
To produce eggs
What is the major function of the penis?
To place sperm in the receptacle (vagina)
What is the major function of the uterus?
Muscular organ where fertilized eggs implant and develop during pregnancy
What is the major function of the vagina?
The cavity that acts as a receptacle for the penis during intercourse
What is the major function of the mammary glands?
Glands in the chest that produce and secrete milk during lactation
What is the major function of LH in males and females?
Triggers testosterone production in males and triggers estrogen production in females
What is the major function of FSH in males and females?
Stimulates gamete production (sperm and eggs) in the gonads
Where and how long does spermatogenesis occur?
In the seminiferous tubules of the testes, and takes around 10-12 weeks
Where does fertilization usually occur?
In the fallopian tubes