L3 Innate Immunity, inflammation and complement
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
characteristics innate immunity
present in invertebrates and vertebrates
fast response (hours)
non-specific (no antigen specific receptors involved)
no memory
precedes and directs specific immunity
training (epigenetic modifications, memory)
functions innate immunity
prevention of infection
degradation of microbes
cleaning of waste
responds to danger signals
first line of defense, gaining time
activation of specific immunity
effector of specific immunity
no specific memory, but training
always present
physical and biochemical barriers
anatomic, physiologic, phagocytic (cellular) barriers, inflammatory barriers
anatomic barriers
skin and (mucosal) epithalia (large surface exposed to outside world)
cilia
mucus(gut), surfactant proteins(lung)
physiologic barriers
temperature (fever)
low pH in the stomach (HCl)
peristaltic action gut, pooping, coughing, vomiting
enzymes such as lysozyme, phspholipase A
antimicrobial peptides (defensins and catelicidins)
phagocytic (cellular) barriers
specialized cells (monocytes, neutrophils, tissue resident macrophages)
inflammatory barriers
tissue damage and infection lead to influx of phagocytic cells
macrophage - function
phagocytosis, antigen presentation to cells
neutrophil - function
phagocytosis, degranulation (discharge of contents of a cell)
eosinophil
degranulation, release of enzymes, growth factors, cytokines
basophil - function
degranulation, release of histamine, enzymes, cytokiens
mast cell - functions
degranulation, releae of histamine, enzymes, cytokines
monocyte - function
differentiate into macrophages and dendritic cells to elicit an immune response
natural killer (NK) cells
tumour rejection, destruction of infected cells, release of perforin and granzymes which induce apoptosis
T helper (Th) cells, CD4+
function
immune response mediators
Cytotoxic T cells, CD8+
function
cell destruction
pattern recognition receptors and PAMPS/MAMPS
to detect stranger and danger
differntiation between self and foreign
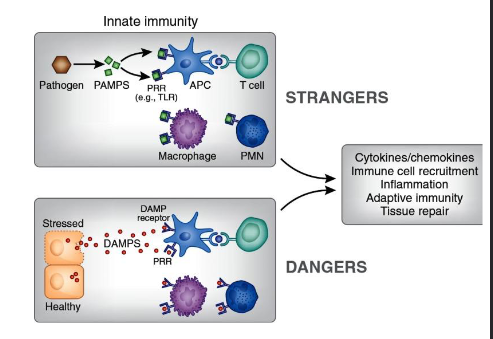
how does the innate immune system recognize pathogens
danger theory polly matzinger (2002)
PAMP: pathogen associated molecular patterns
MAMP: microbial associated molecular patterns
DAMP: danger associated molecular patterns
Pattern recognition receptors (PRRS)
toll like receptors
DC-sign
NLR’s
nod like receptors(nulcoetiding binding oligomerizatoin domain receptors)
RIG-like receptors etc
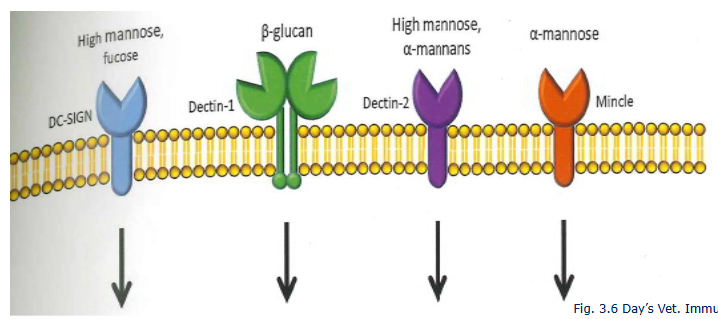
Dectin 1 and 2
NF-kB, IRF3 at the end
Pattern Recognition Receptors (PRRs) are crucial immune system sensors that detect conserved molecular patterns on pathogens (PAMPs) or damaged cells (DAMPs) to initiate innate immune responses, bridging to adaptive immunity, and coordinating inflammation, anti-infection, and tissue repair by activating signaling pathways like NF-κB, leading to pathogen clearance or anti-tumor activities.

C-type lectins on innate immune cells detect
procaryotic carbohydrate molecules
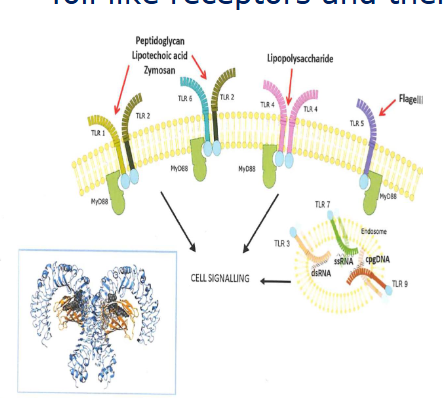
Toll like receptors and their ligans
pathogen associated molecular pathogens
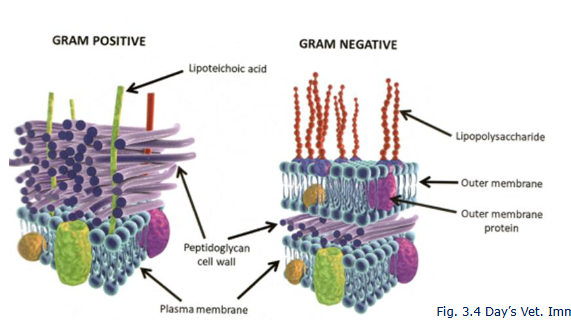
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)
lipoteichoic acid (LTA)
peptidoglycan
Bacterial flagella
Bacterial CpG DNA
Viral ssRNA and dsRNA
LPS AND LTA PRESENT IN THE BARN ETC
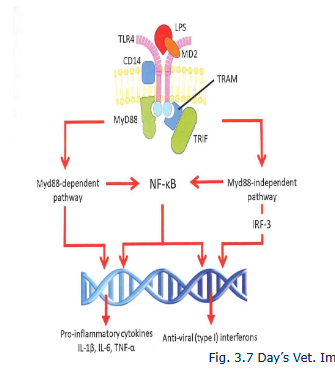
TLR4 signalling by LPS
NF-kB is a key nuclear transcription facot in M1 macrophages
Myd88 dependent and independent pathways
fast and long term inflammatory responses
chicken lack TRAM (TLR4 signalling is less orbust
IRF-3 is interferon response facotr
Pathogen associated molecular patterns (PAMP)
gram positive
gram negative bacteriaS
PAMPS and DAMPS can act synergistically
true
Danger Associated Molecular Patterns
Mitochondrial DNA and ATP
Histone proteins
Necrotic cells
Heat shock proteins
Uric acid crystals
High mobility group box 1 (HMBG1)
extracellular matrix breakdown products
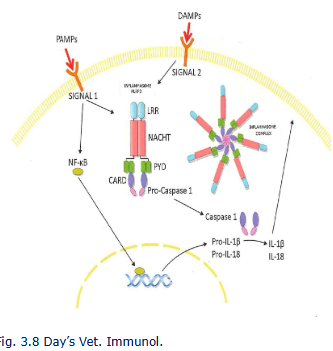
Inflammasome
cytosolic multiportein complexes
type of inflammasome dependent on nature stimulating agen
caspase 1 converts inactive IL-IB and IL-18 in bioacgive forms
Caspace1 induces pyroptosis, which has features of apoptosis and necrosis
Phagocytes
Monocytes and neutrophils migrate to sites of infection (e.g. bovine mastitis)
use of adhesion molecules : integrins LFA-1 (CD11a/CD18)
chemotaxis along cytokine gradient (e.g. IL-8 (CXCL-8)) and macrophage inflammatory protein1a (MIP-1a)
activation pahgocyte via PAMP and PRR
Phagocytosis and killing pathogen
Macrophages produce nitric oxide (NO) radicals to kill bacteria
Neutrophil extravasation at the site of infection
tethering
rolling
activation
adhesion
transmigration
chemotaxis
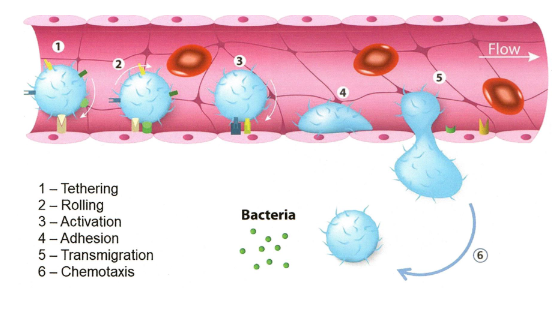
Somatic cell count
ase line in healthy cows or height of the response in infected cows
differentiation of cell types - monocytes vs neutrophils
genetics
the SCC may reflect the vulnerability for udder infections
Neutrophil extracellular traps(NETs)
NETs trap bacteria
Nuclear DNA with bound histone proteins, lactoferine, myeloperoxidase, cthepsis etc to kill bacteria
may cause trombosis like problems, probably also in covid infections
Innate lymphoid cells
ILCs and Natural killer cells
Morphologically similar to T cells, but lack antigen specific receptors (TCR)
Thus no MHC restriction
Present at barriers like mucosa
Tissue resident cells, no circulation
ILCs regulate immune responses via cytokine secretion
Detect symptoms of infection, but not the infectious agent itself early sentinels
Groups of innate lymhoid celles (deze nog verder uitsplitsen, zodat ik het goed kan otnhoudne)
ILC 1, NK CELLS, ILC1, IFN-Y, TNF, viral defense, tumour surveillance, infammation
ILC2, ILC2, IL-4, IL-5, IL-9, IL-13, defense against parasites, allergy, tissue repair
ILC3, LTi cells, IL-17 IL22, defencse against bacteria/fungi, lymphoid organ development

NK cells
kill infected or unwanted cells sometimes together with antibodies (ADCC)
inhibitory receptor detect self MHC class I on healthy cells
Cells with down regulated MHCI molecules are targets for NK cells - is called missing self recognition
Down regulation of MHCI can be caused by viruses and in tumor cells
NK-cells: early detection of infected cells
IFN-gamma causes enhanced expression of MHCI
Inflammation
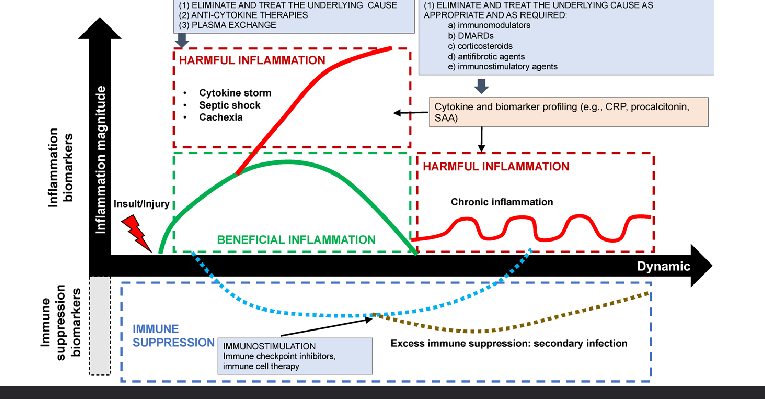
increasing evidence that chronic inflammation is related to diseases on the long term
Stimuli of acute inflammation
pathogens (bacteria, viruses, parasites)
microbial associated molecular patterns (MAMP)
danger associated molecular patterns (DAMP)
necrotic cells/tissues
chemical agents/poisons
Heat or cold
Injury (cut, needle, splinter)
Sequence of events in acute inflammation
Stinulus
mediators
vascular
cellular
repair/resolution
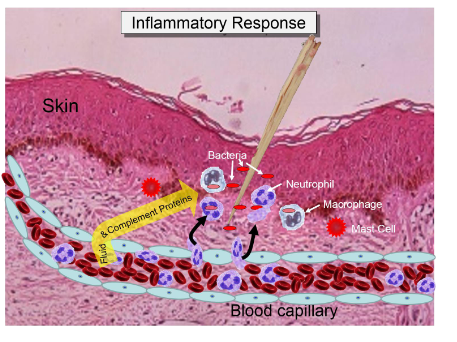
mediators of inflammation
pro and anti-inflammatory components
pro-ifnlamamtory components
proinflammatory cytokines (interferon-y, il-1b, il-6, TNFa, IL8
complement facotors C5a
Acute phase proteins (CRP, haptoglobin)
prostaglandins
reactive oxygen species (ROS)
anti-inflammatory components → downregulated autoimmune response
anti-inflammaotry cytokines (IL-19, TGFB)
Interleukin 1 receptor anatonis (IL1Ra)
Natural (auto) antibodies
Prostaglandins
prostocyclin, thromboxane
phospholipase A2 → COX1, COX2 (NSAIDs) → prostaglandins
NSAIDs (e.g. ibuprofen, aspirin) block COX enzymes, reducing prostaglandin synthesis, reduce pain, reduce fver, reduce inflammation
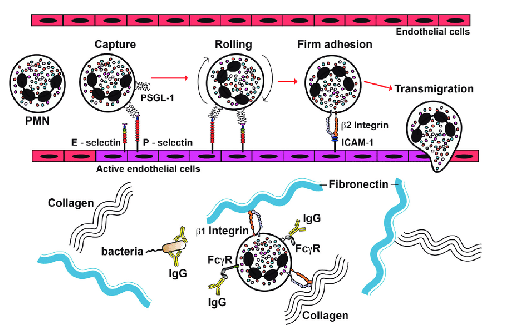
Adhesion, rolling and diapedesis of neutrophils
Adhesion molecules involved in rolling adhesion and diapedesis:
E-selectin and P-selectin
ICAM
Integrins
Extracellular matrix proteins
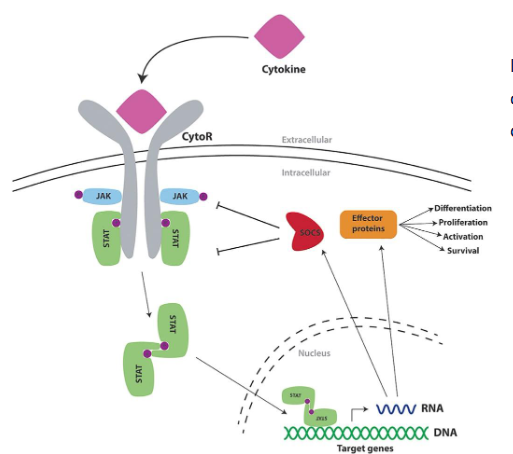
SOCS: suppressors of cytokine signaling
negative feedback regulation of cytokine signalig by 8 different SOC proteins
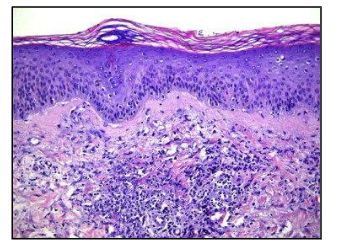
what kind of inflammation is this
acute - neutrophils (macrophages)
No T/B cells
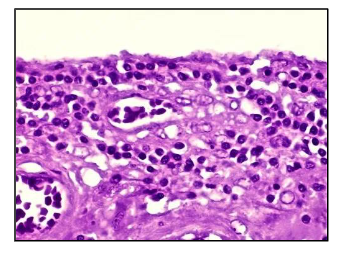
what kind of inflammation is this
chronic
mononuclear cells, macrophages/monocytes, lymphocytes, palsma cells
T/B cells
in chronic infoammaiton is specific immunity involved
five symptoms of acute inflammation
heat (color)
redness (rubor)
swelling (tumor)
pain (dolor)
funciton loss (functio laesa)
Acute phase response
positive acute phase protines: their levels increase in response ot inflammation (e.g. CRP, SAA, haptoglobin)
Function of positive acute phase:
enahcning immune function, modulating the inflamamtory response, promoting tissue repair
negative acute phase proteins: their levels decrease during inflammation (e.g. albumin)
function of negative acute phase proteins:
regulating inflmmation to maintain homeostasis
produced in the liver
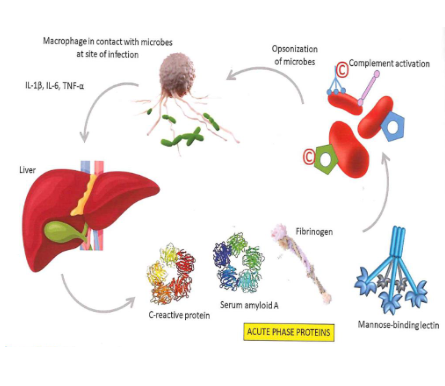
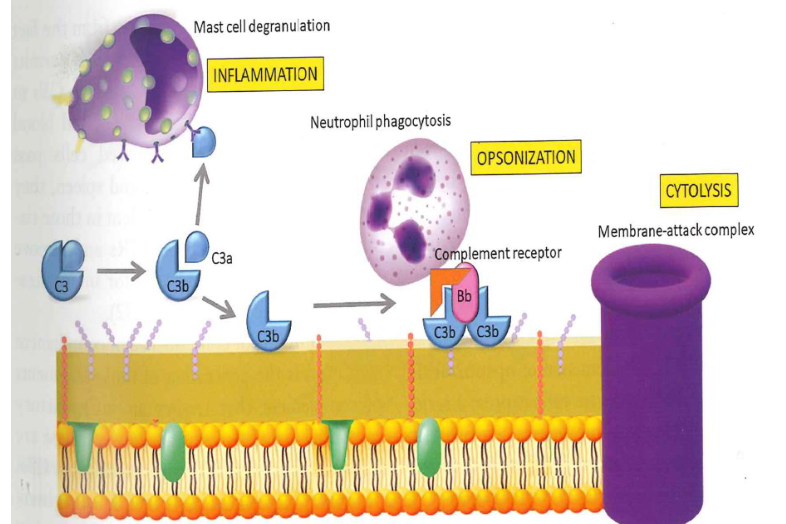
Complement system
functions
Opsonisation of bacteria and unwanted cells (C3b) resulting in clearance of immune complexes
stimulating inflammation (C3a, C5a)
increase vascular permeability
release of histamine from mast cells and basophils
cell lysis (membrane attack complex)
Complement deficiencies
vulnerable for infectious diseases
autoimmune diseases (e.g. systemic lupus erythmeatosus (SLE), renal failure kidneh)
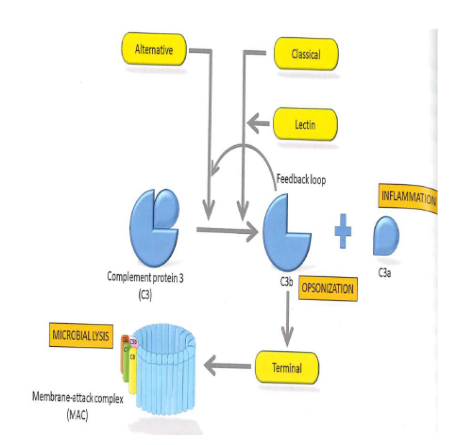
3 complement pathways
classical - via antigen-antibody complexes
lectin pathway - via MBL-MASP complexes
Altenative pathway - via spontaenous C3 hydrolysis
C3a - pro-inflammatory action
C3b - opsonization
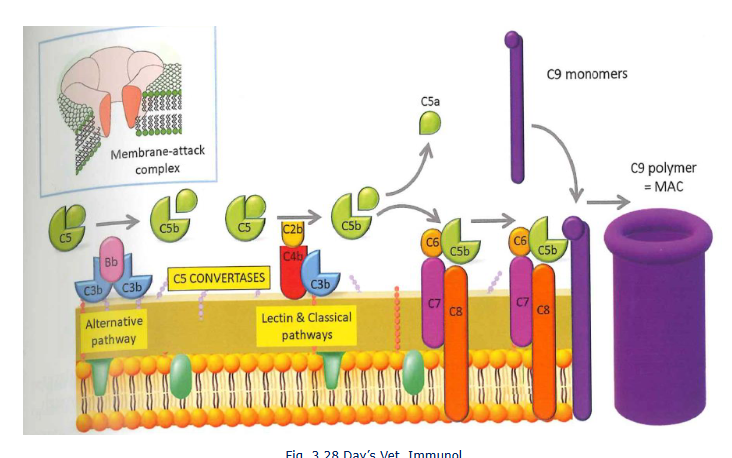
C5B - membrane attack complex
Around 30 plasma proteins, self assembling csacase
all 3 pathwasy end up in C3 convertase, which is the start of the terminal pathway, the membrane attack complex (MAC)

3 complement pathways + opsonization
T
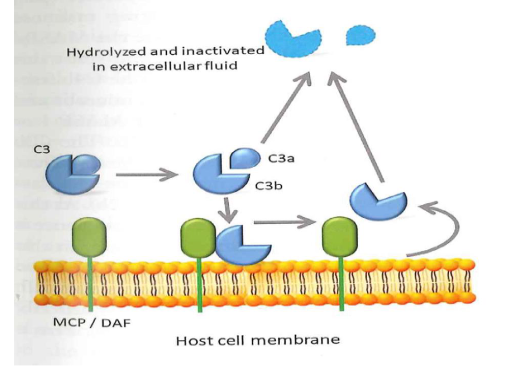
Tick over phase: to prevent killing of healthy host cells
C3 produced in the liver
In extracellular fluid C3 is cleaved sponataneously in C3b and C3a
C3b deposited on healhty cell surface is removed by MCP and DAF
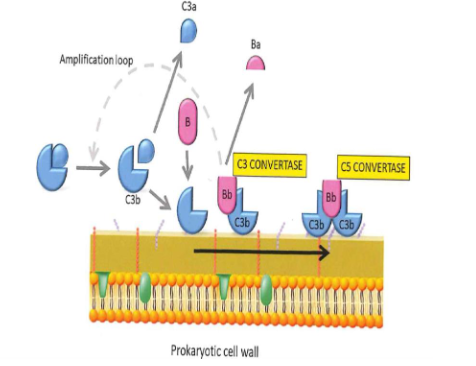
The alternative pathway
Trigger surface (e.g. bacterial cell wall) permits deposition from C3b
C3b is generated form the thick over phase
C3 in extracellular fluid is hydrolized spontaenously in C3b + C3a
C3b on healthy cells inactived by MCP(CD46) and DAF(CD59)
C3 convertase: factor B binds C3b. B is cleaved by factor D into Bb and Ba. C3bBb is formed
Properdin stabilizes the C3bBb complex
endproduct is C5 convertase: C3bBbC3b
C5 convertase cleaves C5 in C5a and C5b
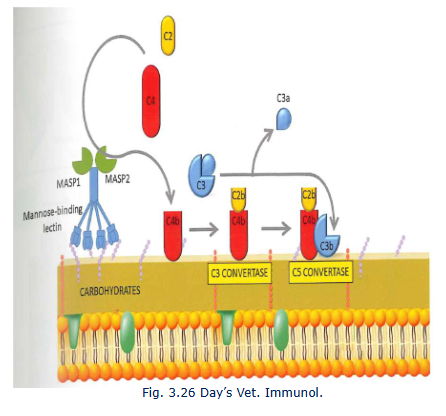
The lectin pathway
Mannose binding lectin (MBL) is acute phase protien
ACtives C4 (C4a and C4b)
C4b binds to pathogen surface and binds C2
C2 is cleaved into C2a and C2b
C4bC2b = classival C3 convertase
C4bC2bC3b = C5 convertase
The classical pathway
antigen specific antibodies form immune complexes
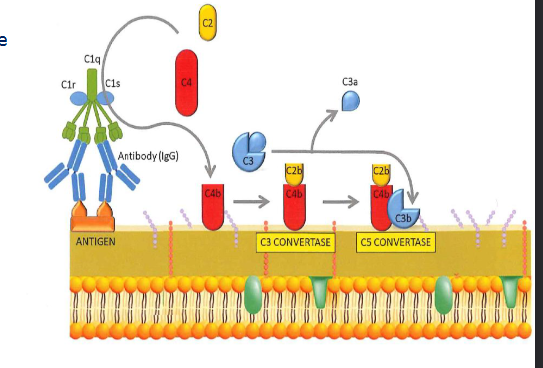
The terminal pathway
C3a and C5a have a clear role in local inflammatory responses
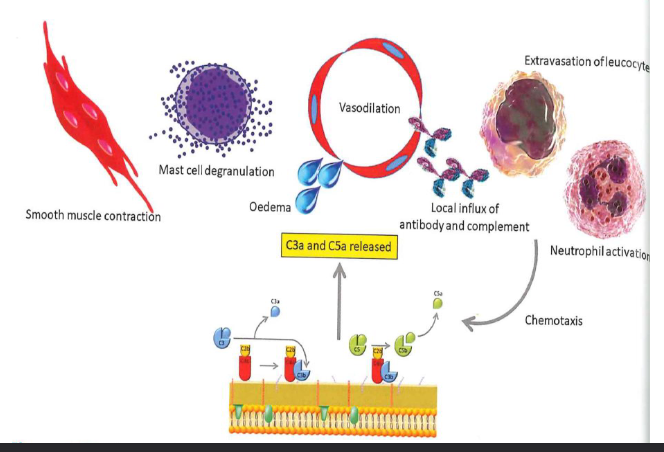
Which complement is involved in inflammation and opsonization?but alos cytolysis?