A level economics theme 2
1/113
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
114 Terms
What is economic growth?
Is the rate of change of output
-Increase in the productive potential of the country
How is economic growth measured?
By the percentage change in real GDP per annum
What does GDP stand for? What is it an indicator of?
Gross Domestic Product
-The total value of finished goods and services produced in a country within a year
-GDP is an indicator of standard of living
what's the difference between Total GDP and GDP per capita
-total GDP represents the overall GDP for the country
-GDP per capita represents the total GDP divided by the total population ( average output per person)
What is the difference between real and nominal GDP?
-Real GDP is adjusted for inflation, shows the Volume of national income .
- whereas nominal GDP is not adjusted and shows the Value of national income
what is the distinction between 'value' and 'volume' ?
- value : the monetary worth of goods and services
- volume: the physical quantity of goods and services produced
What is Gross National Product?
The value of goods and services over a period of time through labour or property supplied by citizens of a country both domestically (GDP) and overseas.
- the total value of finished goods and services produces by citizens whether they live in the country or not
What is Gross National Income?
The total value of goods and services produced by a country over a period of time plus net overseas interest payments and dividends.
- total amount of income earned by a nation's people and businesses.
How can comparisons about growth be made over time?
- growth figures can be compered against similar countries to see whether a country has done well or not
- judgements on national welfare can be made ( rise in GDP can show rise in living standards)
why should we use Real, per capita figures?
- per capita : a rise in population without a rise in living standards would increase total GDP
- real : inflation can give the impression of GDP growing without any more goods and services being produces
Was are Purchasing Power Parities?
An exchange rate of one countries currency for another , which compares how much a typical basket of goods in the country costs compared to one in another country
what are the benefits of PPP's ?
- provide an alternative to using exchange rates ( exchange rates don't reflect how much people can actually buy with the money in different countries )
- takes cost of living into account , so better to compare living standards with
- the difference between the highest and lowest GDP's will be smaller when PPP is used - PPP takes into account how far people's money goes
What are the problems of using GDP to compare standards of living?
1) Inaccuracy of data:
-some countries may be inefficient at collecting data
-Black markets
- home-produced services aren't taken into account
- transfer payments must be taken away
2) Inequalities: growth in GDP may be due to only certain group of people- living standards haven't improved everywhere
3) Quality if goods and services : technological improvements means higher quality services can be produced at a cheaper cost. This may show a lower GDP whereas living standards have actually improved
4) comparing different currencies : US dollar is used , some argue PPP should be used to take cost of living into account
5) spending: some expenditure maybe increase GDP but not cost of living. E.g. GDP higher is Second World War that 1930's greater spending on defence
explain UK national well being
- 2010 Measuring National Wellbeing report was launched.
self-reported health, relationship status and employment status most affect personal well being
Explain the relationship between real incomes and subjective happiness
-Easterlin Paradox: an increase in consumption of material goods will increase happiness if basic needs aren't met, but once they are met, an increase in consumption wont increase long term happiness
- happiness depends on people you surround yourself with and social status
What is inflation?
the rate of increases in prices over a given period of time
What is deflation
a sustained decrease in the general price level of goods and services within an economy
What is disinflation?
A reduction in the rate of inflation
How is the consumers price index calculated?
- a household basket of 700 goods/services that an average family would purchase is compiled on an annual basis, surveys are taken to determine what enters and leaves
-items are weighed based on the proportion of household spending
-prices of these items are collected from 150 location every month and averaged out
-final values ( price x average ) Are added together to get total basket's value
How can inflation rate for the period be calculated using CPI?
(cost of basket in year x )/ (cost of basket in base year ) x 100
What are the limitations of CPI
- not completely representative, all goods and services aren't included.
- Ignores regional differences in inflation ( lodon vs Harrogate )
- Difficult to make comparisons with historical figures, it is a recent figure
- errors in data collection : small sample, respondents have no incentive to fill the survey carefully and accurately
What is the Retail Price Index? (RPI)
- calculated the same as CPI but also includes housing costs ( e..g mortgage, council tax)
- RPI inflation is higher than CPI inflation due to extra inclusions
What are the causes of inflation?
demand pull inflation, cost push, Growth of money supply
What is demand pull inflation?
When demand exceeds the economy's ability to produce goods & services.
- Increase in AD
What is cost push inflation?
A rise in the general price level resulting from an increase in the cost of production
-Reduction of Aggregate Supply
What is growth of money supply?
- Too much money in the economy. people will spend more , if there is no increase in goods and services, prices rise
What are the effects of inflation on Consumers?
- if incomes don't rise with inflation, then they will have less to spend , so fall in living standards
-those in debt pay it off at a price of cheaper value, this who are owed money receive money of cheaper value
-consumers who saved lose out as money is now worth less
What are the effects of inflation on firms?
-If inflation is higher in Britain , goods are more expensive, become less competitive in foreign market , difficult to export, also effects balance of payments
- deflation , leads to fall in demand , falling investment , falling profit
- inflation / deflation difficult to predict so difficult to plan for the future
- changing prices, firms must change menus , labelling etc...
How does inflation affect governments?
- if government doesn't change excise ( fixed ) taxes in line with inflation , then real government revenue falls
-if they fail to change personal income tax allowances in line with inflation, more income becomes taxable , real government income increases and taxpayers have less money
What are the effects of inflation on workers?
- living standards decrease when workers don't reactive yearly pay rises of the rate of inflation
- those in weaker unions are worse off , unable to win wage rises
-deflation could cause some staff to lose their jobs, due to a lack of demand
-issue can be solved through indexation , when wages rise in line with inflation
What is the definition of unemployment?
when individuals are willing to work but cannot find a job, they are actively seeking employment
What is the labour force and non- labour force?
Labour force- consists of all workers actively working and the unemployed
Non-Labor force - includes those not seeking work , economically inactive
What are the measures of unemployment?
1) Claimant count
2) International Labor Organisation and UK Labor Force Survey
What is the Claimant Count?
- the number of people receiving benefits for being unemployed
What is the Labour force survey?
A survey sent to a random sample of 60,000 UK households
- respondents self- determine if they are unemployed based on ILO criteria
- same survey is used globally so used to make comparisons
What are the International Labor Organisation's criteria for unemployed
- ready to work in next to weeks
- Has actively looked for work in the past one month
Compare the Claimant count and the LFS
- Some people would may not be included in the LFS unemployment measure, but would be claimant in the claimant count --> hidden economy / fraudulently claim benefits
- some aren't eligible for benefits but are classed as unemployed --> so appear in LFS but not claimant count
Why is it argued that both underestimate the figure?
-They don't include those :
- working part time but would like to work full time
-on government training schemes who would prefer employment
-classed as sick or disabled
- who aren't actively seeking jobs but would take a job If offered , or in education as they cant get a job
(hidden unemployed )
define economically active and workless
- Economically active: the employed and unemployed
- Workless : unemployed and inactive
What is underemployment?
when a person’s job does not fully utilise their skills, abilities or time
- People who want to work more hours than they currently work
-Working in a job that requires lower skills than they have
- Increases during recessions, costs rise, high skill workers made redundant
What is frictional unemployment?
- when people are moving between jobs
- takes a while to locate and gain a new job the are willing to accept
- only short term
What is structural unemployment?
-- long term decline in demand for an industry leading to unemployment
A worker's job skills do not match those necessary to get a job so they need education or training
What is seasonal unemployment?
- industries that are prominent during certain times of the year
- only demand large number of workers at specific times
What is Cyclical unemployment?
Unemployment due to a general lack of demand of goods and services in the country
- during recessions
-firms lay off worker
What is real wage inflexibility?
- when wages don't fall, even during high unemployment / recession
- so firms can't afford to hire new workers
-wages don't fall due to minimum wage laws, unions, worker contracts
Migration and employment
- increased net inward migration , lead to increased jobs
-take low skilled jobs
-less likely to claim benefits
- increases employment
-migrant workers can fill shortages
- can lead to lower wages , as supply go labor is increased
- increased completion for low skilled jobs, can reduce motivation
Skills and employment
- higher skills are needed to work
What are the impacts of unemployment on workers?
- loss of income
-long term unemployed can lose skills making it difficult to find jobs
-workers can face low job security
what are the impacts of unemployment o
What is aggregate demand ?
Total demand for all goods and services produced in an economy at any given price level
How is AD calculated ( formula) ?
AD = Consumption ( C) + Investment (I) + Government spending( G) + Exports - Imports ( X-M )
What are expansions and contractions?
- a fall in price causes an expansion in demand
- a rise in price causes a contraction in demand
What are the three reasons the AD curve is downwards sloping?
1) high prices lead to fall in real income , so less goods and services are less affordable
2) high inflation in UK so prices are high , foreign goods would seem cheaper, there would be more imports , increased current account deficit, AD falls
3) High inflation means high interest rates,
, saving increases and spending is discouraged , AD falls
What is consumer spending?
How much consumers spend on goods and services
- Larges component of AD
What is disposable income
The amount of income left over after taxes and social security charges have been removed. it is what consumers can choose to spend
What is the marginal propensity to consume?
and what is the marginal propensity to save?
How much a consumer changes their spending following a change in income. a measure of the proportion of an increase in income that a person or household is likely to spend on consumption (goods and services) rather than save
- the proportion of each additional pound of household income that is used for saving
Explain the relationship between the marginal propensity to consume and the marginal propensity to save
MPC + MPS = 1
What factors influence consumer spending?
1) Interest rates : high interest rates --> less spending, low interest rates --> more spending
2) Consumer confidence
3) Wealth effect:
- when prices of home- owners houses rise they ' feel wealthier ' , spend more.
- rise in equity -> more spending
4) distribution of income
5) tastes/trends
What is the difference between gross investment and net investment?
gross investment: the amount of investment carried out and ignores the level of depreciation
net investment: gross investment - level of depreciation
What is investment?
the total spending on capital goods by firms
- helps increase capacity of an economy
-increasing potential economic growth
What is depreciation?
The decrease in monetary value of a capital good( asset ) over time
- old capital goods are replaced
What is the difference between gross investment and net investment?
Gross Investment: The Total amount spent on capital goods in an economy over a period of time
-includes new investments to expand production
-includes replacing old capital ( depreciation )
- if depreciation > gross investment , no economic growth and decrease in value of capital in economy
Net investment:
The actual increase in the economy's capital stock
- net investment = gross investment -
depreciation
-shows how much new capital is ADDED after replacing worn out capital
What factors affect Investment?
1) Economic growth
2) Business confidence / expectation -->Keynes animal spirits
3) Demand for exports
4) Interest rates —>can also influence firms that use retained profits rather than borrowing —> higher interest rates increase opportunity costs of keeping retained profits in bank and earning from interest
5) Access to credit
6) Influence of government and regulations
7) Technological change
8) costs
What influences government expenditure?
Trade cycle
Fiscal policy
age and distribution of the population
Name the stages in the trade cycle
Boom: fast economic growth, could be inflationary or unsustainable
Recession: real output in economy falls, negative economic growth
slump: lowest point, high unemployment , no growth
recovery: periods of economics growth
How does trade cycle affect government spending?
Recessions: government might increase spending to stimulate economy e.g. welfare payments , cutting taxes --> increases government deficit
economic growth: gov receives more tax revenue, may spend less , less people claim benefits
Fiscal policy
What is the net trade balance?
The difference between exports (X) - imports (M)
- postive = surplus
- negative = deficit
What factors influence the net trade balance
1) Real income
2) Exchange rates
3 )State of the world economy
4) degree of protectionism
5) non-price factors ( competitiveness bases on quality , marketing etc..)
What is aggregate supply?
The total supply of goods/ services produced within an economy at a specific price level at a given time
Why is the SRAS curve upward sloping?
at a higher price level, producers are willing to supply more as they can make more profit
What is the difference between Long run aggregate supply and short run aggregate supply
- SRAS covers the period immediately after a change in the price level
-covers the time when at least one factor of production is fixed ( can't change capital as of now, need more money)
-LRAS shows potential supply in the economy in the long run
-All factors of production are variable
( factors of production can be changed, firm can afford to)
What factors affect SRAS?
1) changes in costs of raw materials and energy
high cost - shifts left
low costs - shifts right
2) changes in exchange rates
appreciates - shifts right ( firms can buy foreign goods and raw materials cheaper ) vice versa
3) changes in tax rates
higher tax , higher costs , SRAS shifts left
What factors affect Long- run AS
1) advancements in technology
2) changes in relative productivity
3) changes in education/ skills
4) changes in government legislation
5) demographic changes and migration
6) competition policy
What is national income?
The value of the output of an economy over a given period of time
Explain the circular flow of income
-Firms and household interact and exchange resources in economy
- household provide firms with land, labour ,capital, enterprise ( factors of production ), in return they can receive goods/ services
Households can provide consumer spending in return they receive wages, rent , dividends, profit
what are injections and withdrawals
injections: add money to the circular flow of income and increase its size :
-increased government spending, increased investment, increased exports --> money comes into economy as it's sold to other countries
Withdrawals/ leakages: remove money from the circular flow of income, reduce it's size:
-increased savings by households
-increased taxation by government
-increased import purchases
What is the difference between income and wealth?
-income is a flow of money that goes to the factors of production, the money a person earns regularly
- wealth is a value of assets
How do injections and withdrawals impact the circular flow of income?
- economy reaches a state of equilibrium when rate of injections = rate of withdrawals
--> this is show when AD = AS
- if there are net injections into the economy, there will be an expansion in national output
-if there are net withdrawals from the economy, there will be a contraction of production , output decades
What is the multiplier ratio?
The ratio of the change in real income to the injection that created the change
Explain the multiplier process
- occurs when there is new demand in an economy
-leads to an injection of more income into the circular flow of income , leads to economic growth
- more jobs created, higher avg salary, more spending, more income is created
- This causes a secondary movement of AD to the right
- size of multiplier depends on the size of withdrawals
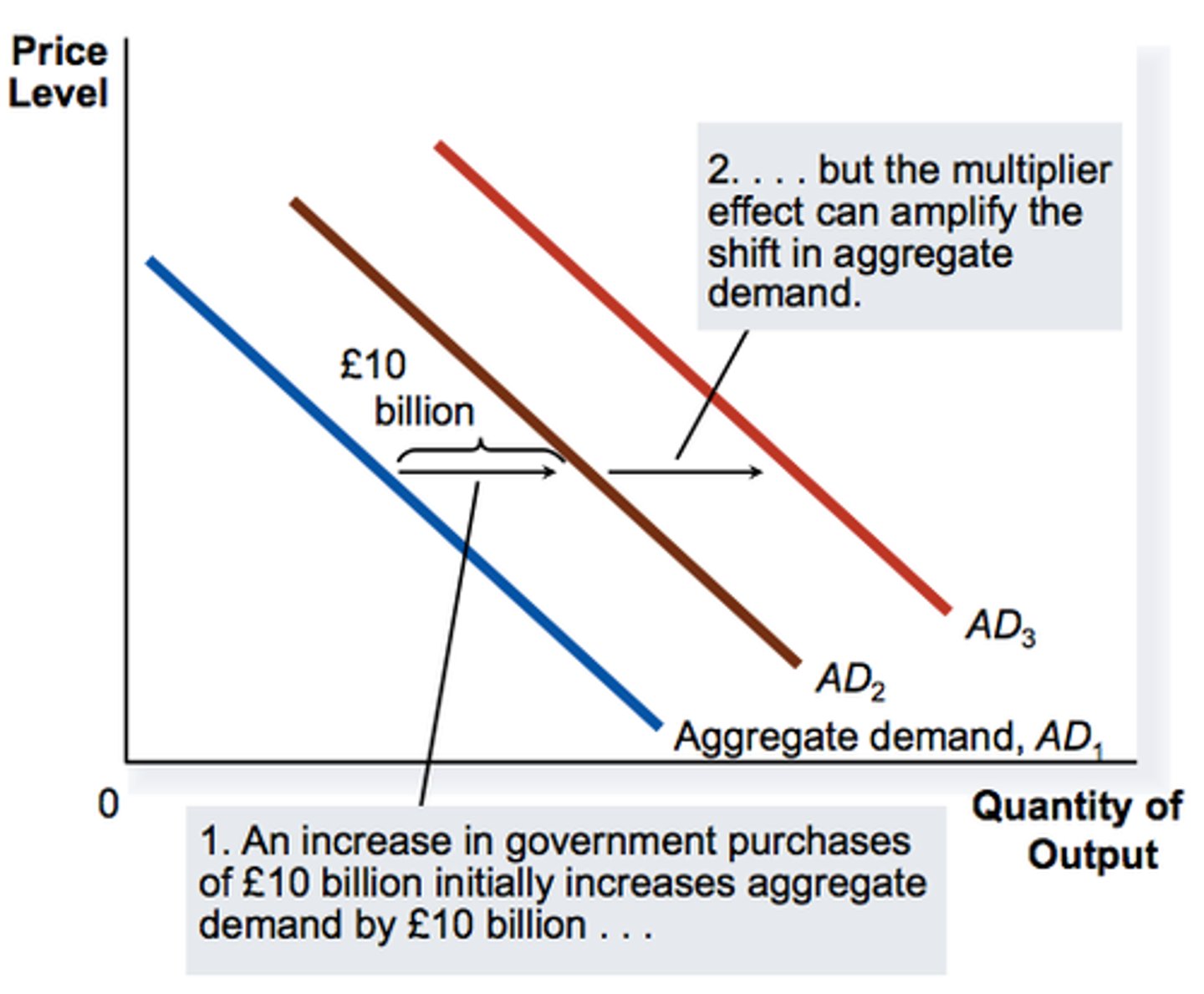
How do the marginal propensities affect the multiplier
- higher MPC, bigger multiply
- government can reduce direct tax, consumers have more disposable income, MPC increase
- increases tax and increased imports reduce multiplier
How do you calculate the Multiplier?
1 / ( 1 -MPC )
1 / MPW
-MPW = marginal propensity to withdraw
- MPW = Marginal propensity to save + marginal propensity to tax + marginal propensity to import
Explain the significance of the multiplier to shifts in AD
- if AS is elastic ,multiplier is larger , small increase in AD = large multiplier
-If AS inelastic, multiple effect is smaller , as AD rises prices rise
What factors cause economic growth
- anything that increase quality / quality of factors of production
- anything that causes increased efficacy in the use of factors of production
E.g., better quality eduction improves quality of labour force, migration increases labour force, technology investment , higher efficiency.
What is actual growth and potential growth?
Annual growth: percentage increase in a country's real GDP, measured annually . caused by increased AD
Potential growth: long run expansion of productive potential of an economy. what the economy could produce if resources were fully employed. caused by increased AS
What is the important of international trade for economic growth?
- countries can specialise where they have a comparative advantage
-increases world output and lowers average costs
- initially rise AD, causing short term growth, but can encourage firms to invest bringing about long term growth by improving the supply- side of the economy . ( meaning ability of economy to produce goods and services increases
what are the issues of international trade for economic growth?
- unbalanced economy , current account surplus
- net injections aren't really sustainable , over time high inflation
-however growth may lead to increased imports, balancing the current account
-countries cannot be over reliant , if recession in major export market occurs, exports fall, fall in economic growth
What are output gaps?
When there is a difference between the actual level of output and the potential level of output
what is a negative output gap?
when the actual level of output is less than the potential level of output, lots of spare capacity
what's a positive output gap?
when actual level of output is greater than potential level of output
- resources are used beyond normal capacity , inflationary pressures
What are the possible macroeconomic objectives?
1. Economic growth
2.low and Stable rate of inflation
3. Low unemployment
4. Balance of payments equilibrium on current account
5. Balanced Government budget - keeps control of borrowing so national debt doesn't escalate
6. Protect environment
7. Greater income equality - income and wealth should be distributed equally
What are demand side policies?
Policies designed to increase consumer demand , so that total production in the economy increases
What is the difference between monetary and fiscal policy?
Monetary policy:
-controls the money flow of the economy
- aims for low inflation and stable economic growth
Fiscal policy:
-uses government spending and revenues from taxation to influence AD
Explain the monetary policy instruments
Interest rates:
- Monetary Policy Committee alters base rate, which controls interest rates across the country
--> decrease interest rates , increase AD
--> Increase interest rates, decrease AD
Quantitative easing:
- QE is used when inflation is low and it's not possible to lower interest rates further
- pumps money directly into economy
- MPC creates only electronically, uses this money to purchase assets from private sector business ( e.g. insurance companies, high street banks) , most assets purchased are government bonds ( you lend money to the government in exchange fir fixed interest payments) , increases cash flowing in financial system . interest rates fall and cheaper brewing for firms
What are the limitations of monetary policy?
1) banks may not pass base rate onto consumers, won't have intended effects
2) even if cost of borrowing is low, banks may not be willing to lend, low confidence
3) Liquidity trap : interest rates are more effective at stimulating spending when confidence is high . low confidence = low spending
4) Time lags
-it can take up to 18 months after BoE changes interest rates for effect to filter through
What are the fiscal policy instruments?
government spending and taxation
Explain expansionary fiscal policy
- boosts economic growth after recession/ economic downturn
-increase spending ( e.g. on welfare) and reduce taxes
-worsens budget deficit
explain deflationary fiscal policy
- aims to decrease AD
- gov cuts spending, raises tax to reduce spading
-improvement of budget deficit
- AD falls, income lower, less purchasing of imports , reduces current account deficit
-higher taxation on wealthy : re distribution of income
what is government budget surplus and deficit?
budget deficit : expenditure is greater than receipts in a financial year
budget surplus; tax receipts exceed expenditure