General Chemistry 7: Thermochemistry
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Standard conditions are [...] K, [...] atm, [...] M
273 k
1 atm
1 M

[...] is the phase change from solid to liquid
Fusion
also known as melting
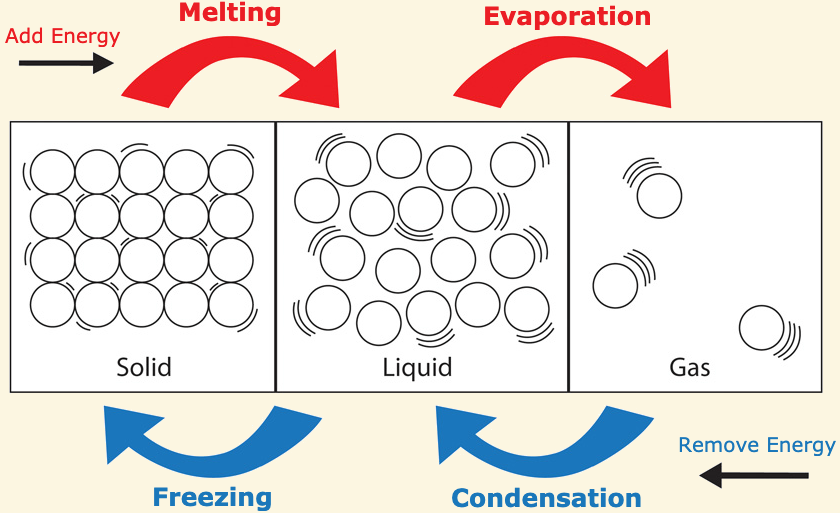
[...] is the phase change from liquid to solid
freezing
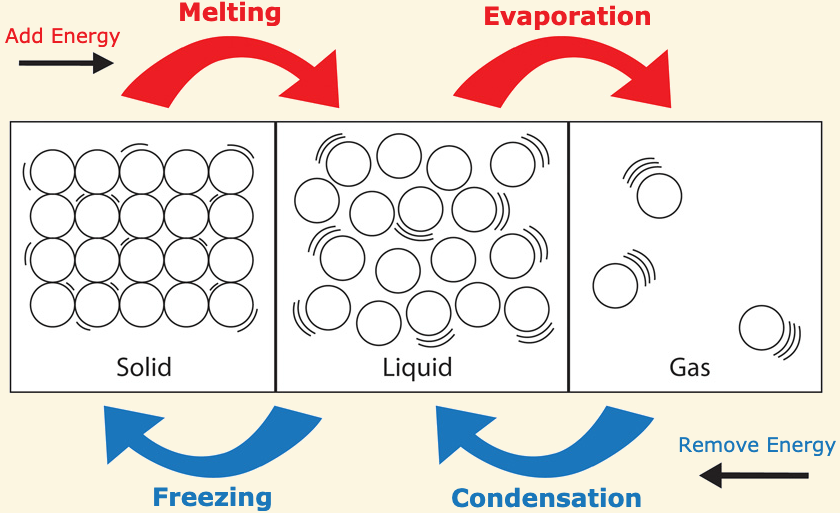
[...] is the phase change from liquid to gas
vaporization
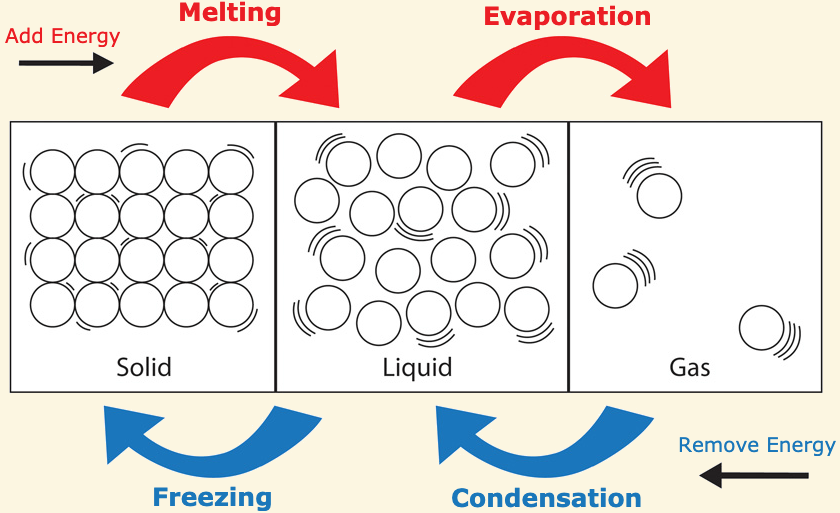
[...] is the phase change from solid to gas
sublimation
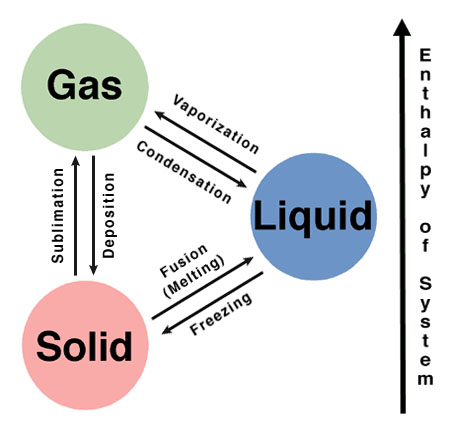
[...] is the phase change from gas to solid
deposition
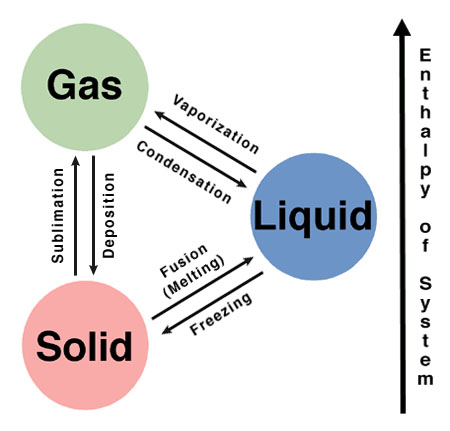
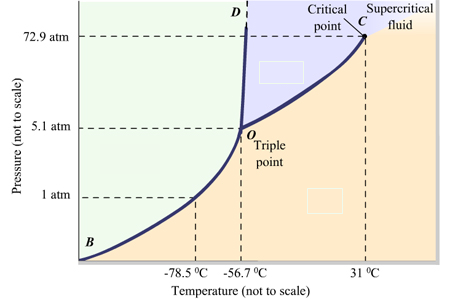
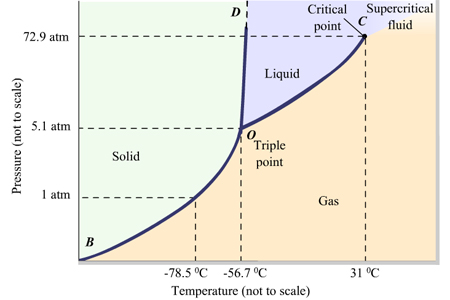
label the phases in the phase diagram
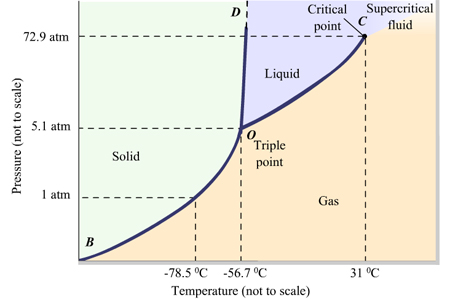
The point in phase diagram where all 3 phases exist is known as the [...]
triple point
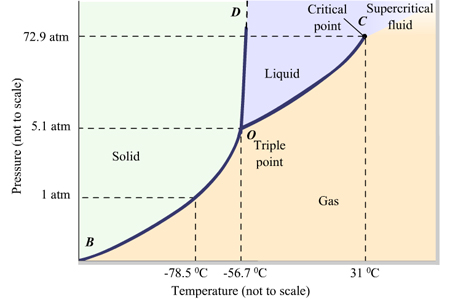
A/an [...] fluid is one in which the density of gas = density of liquid
supercritical
no distinction between those two phases
[...] combines enthalpy and entropy into a single value and is used to determine the spontaneity of a reaction
Gibbs free energy
we only concerned with changes in G, rather than its absolute value
gibbs free energy = (change enthalpy) - (temperature X change in entropy)

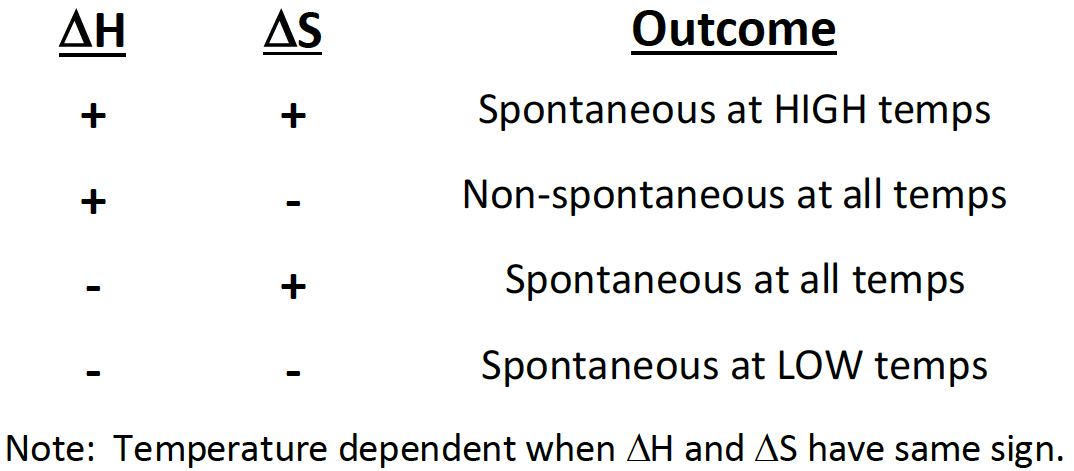
If a reaction has a positive ∆H and positive ∆S, then it will be [spontaneous or nonspontaneous] at [high, low, or all] temperatures
spontaneous at high temperatures
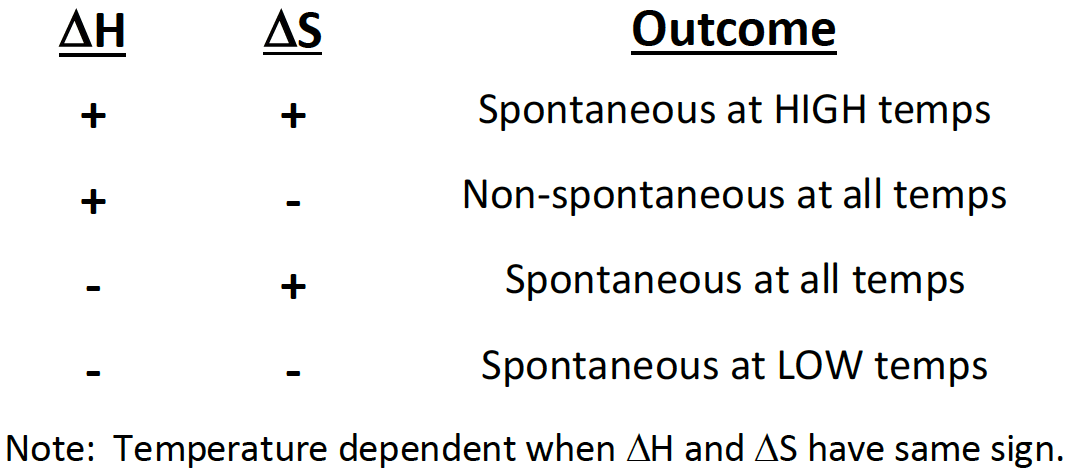
If a reaction has a positive ∆H and negative ∆S, then it will be [spontaneous or non-spontaneous] at [high, low, or all] temperatures
non-spinatanours at all temperatures
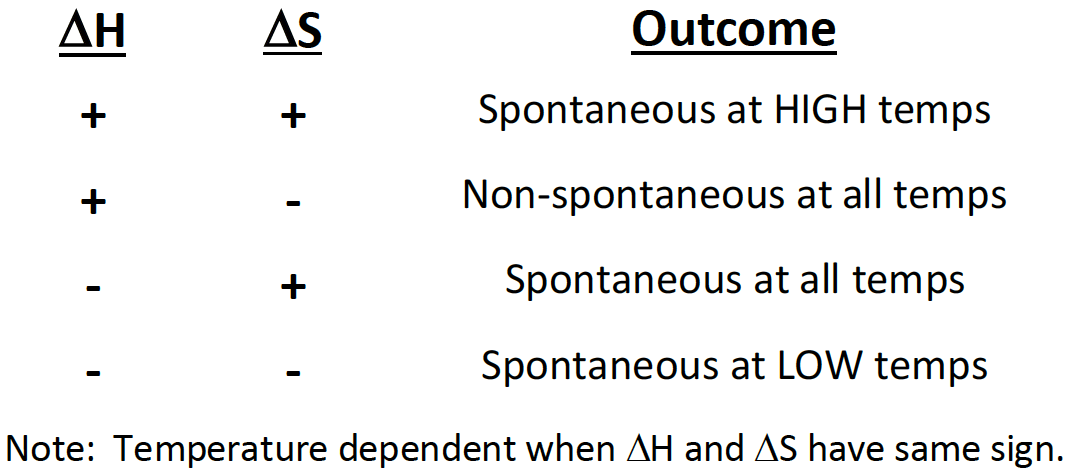
If a reaction has a negative ∆H and positive ∆S, then it will be [spontaneous or non-spontaneous] at [high, low, or all] temperatures
spontaneous at all temperatures
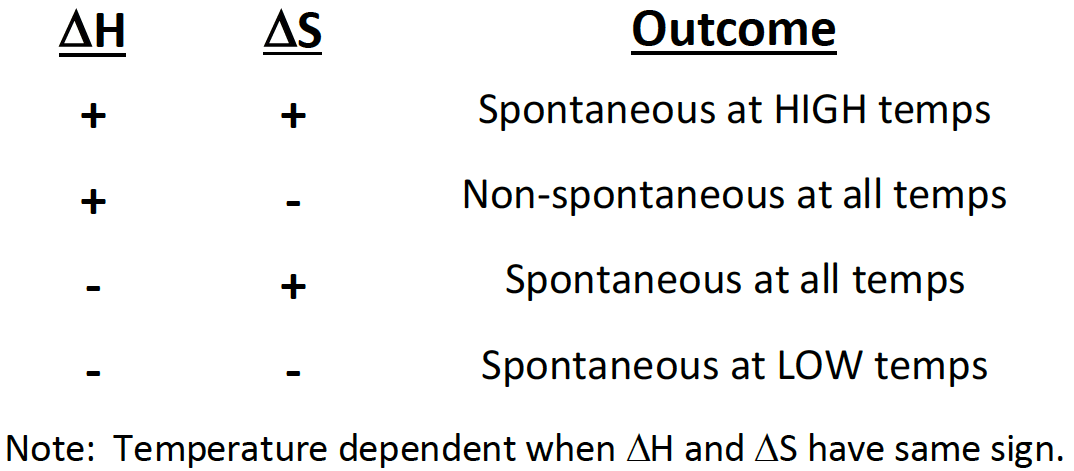
If a reaction has a negative ∆H and negative ∆S, then it will be [spontaneous or non-spontaneous] at [high, low, or all] temperatures
spontaneous at low temp
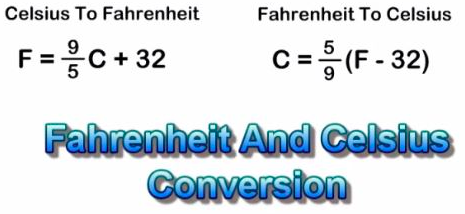
Room temperature is approximately [...] Celsius
25
25 c= 75 f
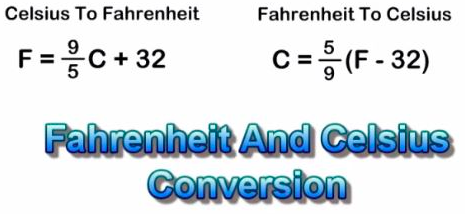
Body temperature is approximately [...] Celsius
37 c to 98.6 f
[...] is a measure of the potential energy of a system found in intermolecular attractions and chemical bonds
enthalpy (H)
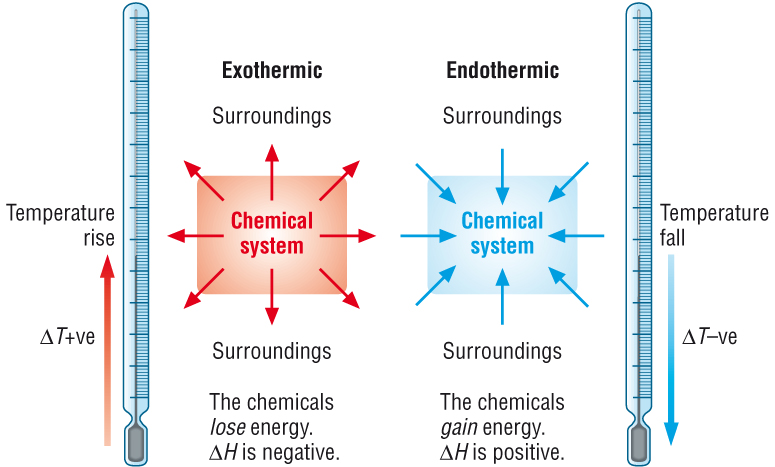
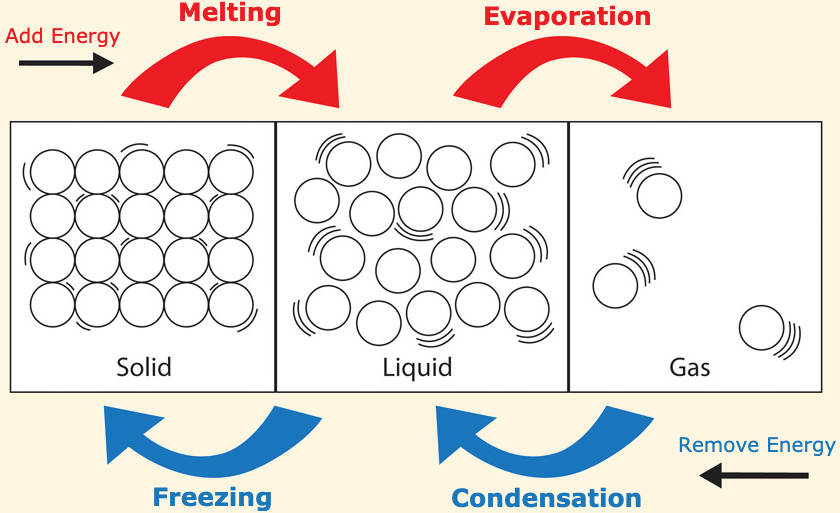
Phase changes from solid → liquid → gas are [endothermic or exothermic]
endothermic
gasse have more heat energy than liquids and liquids have more heat energy than solids
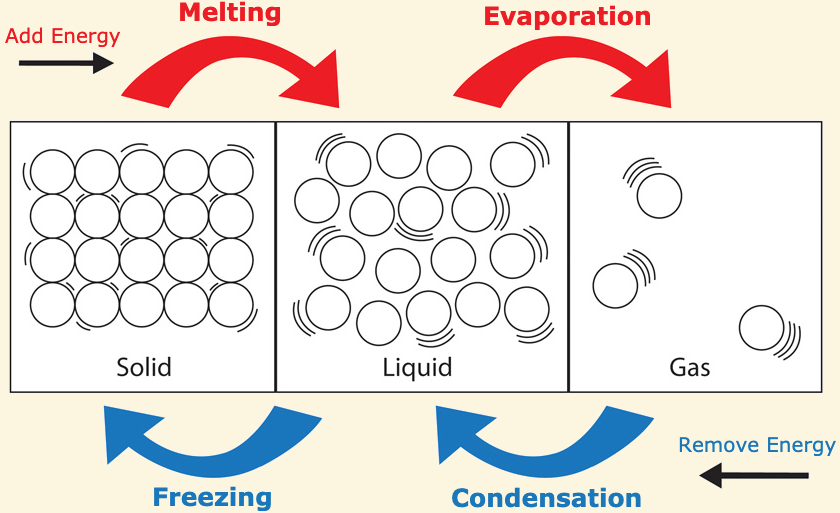
Phase changes from gas → liquid → solid are [endothermic or exothermic]
exothermic
these reactions release heat energy
Give the formula for ∆H when using heat of formations

Give the formula for ∆H when using bond dissociation energies

[...] is a measure of how much energy has spread out or how spread out energy has become
entropy
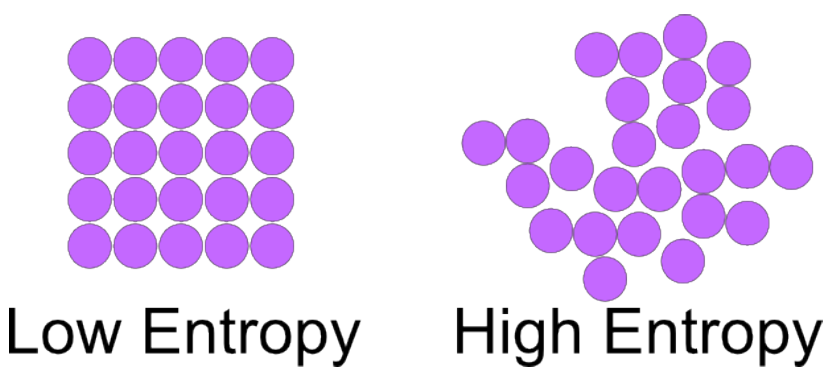
Give the formula for the standard entropy of reaction

Give the Gibbs Free Energy equation that uses the equilibrium constant Keq

Give the Gibbs Free Energy equations that use the reaction quotient Q
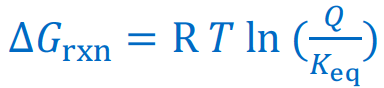
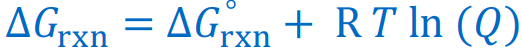
If ∆G < O, the reaction will be [...]
spontaneous

If ∆G = O, the reaction will be
at equilibrium

If ∆G > O, the reaction will be [...]
non-spontaneous
