bio 226 ch. 13 + 14 (viruses and INF)
1/125
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
126 Terms
what are some features of viruses?
intracellular parasites
no binary fission
have DNA/ RNA
protein coat (NO membrane)
why are viruses considered intracellular organisms?
they need a host to survive and multiply
uses host’s proteins and machinery (ATP) to make next gen
no ribosomes or ATP making machinery
what is the spectrum of hosts a virus can infect called?
host range
most viruses infect specific parts in a host’s cells
what is a bacteriophage? what does it do specifically?
evil larry; virus that infects bacteria
attach to phage receptors (may be on cell wall, fimbriae, or flagella)
what are the parts of a bacteriophage?
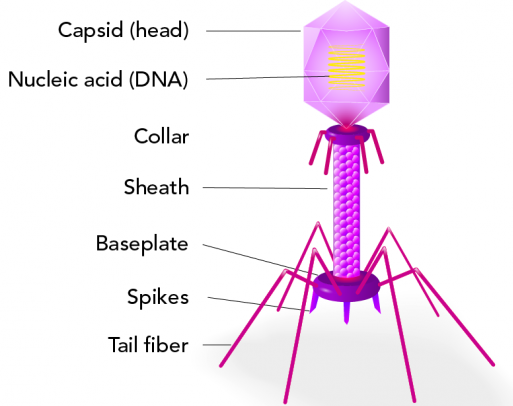
a fully developed viral particle? what is this particle made of?
virion
made of DNA/ RNA, single/ double stranded; linear/ circular/ segmented
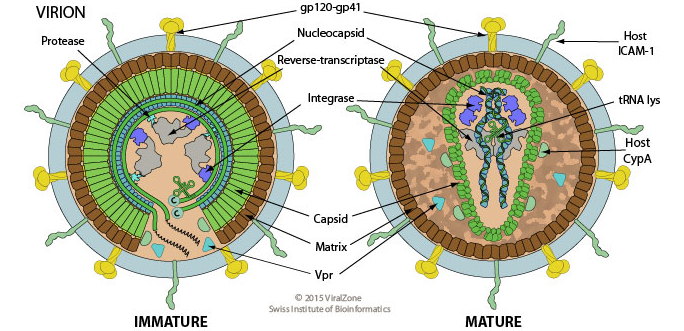
what are some parts of a virus? why are they important?
capsid - protein coat made of capsomeres (subunits)
envelope - lipid, protein, and carbohydrate coating (some)
part is formed when virus buds from host membrane
spikes - attachment/ recognition + decoration :)
can a viral genome have DNA or RNA?
one or the other; NEVER BOTH (1K - 250K nucleotides)
describe a helical virus
hollow with a cylindrical capsid
what is a virus with many sides called?
polyhedral virus
what is the main component/ part of an enveloped virus?
an outer lipid membrane (usually obtained from departure of host cell)
what is a complex virus? give one example.
viruses with complex structures
ex. evil larry
what is the naming, classification, and relation to other organisms called?
taxonomy
what is the classification system that uses nucleic acids and mRNA formation to classify viruses?
Baltimore classification system
groups of viruses are also referred to as “___"?
realms
what is the genus name ending for viruses?
“- virus”
what is the family name ending for viruses?
“- viridae”
what is the order name ending for viruses?
“ - ales”
what is the term for a group of organisms sharing the same genetic info?
species
compare plaque forming units (PFU) and colony forming units (CFU)
plaques are created from the lysis of bacteria on a plate after incubation
bacteriophages are diluted into a bacterial sample and then poured onto a plate
colonies are formed from ONE bacterial cell on a plate after incubation
bacteria are inoculated onto plate
embroynated eggs are used for viral growth. how and why?
how: viruses are injected into egg
visible changes or death of embryo = viral growth
why: this allows for the growth of viruses so vaccines can be made
in some animals, viruses can’t be grown WHILE some can grow but cannot cause disease
describe the steps of the cytopathic effect
1st - tissues treated with enzymes → separates cells
2nd - cells suspended in nutrient solution = “primary cell line”
3rd - cells adhere to container + reproduce = monolayer
visible changes/ deterioration of monolayer = viral infection
continuous source of cells needed
name some ways viruses are identified
cytopathic effect on cells/ culture
serological test - ELISA (anitbody interaction used to detect and identify viruses)
nucleic acid - PCR
what are the steps to viral multiplication?
invasion → take over key host machinery →use machinery to replicate + mature
compare the lytic and lysogenic cycle
lytic - phage causes lysis of host
attachment, penetration, biosynthesis, maturation, + release
lysogenic - phage DNA integrated into host DNA; phage conversion + specialized transduction
term for when a phage remains in a host cell but is immature/ inactive. what are some outcomes of this term?
lysogeny
lysogenic cells are immune to infection of same phage
phage conversion = cell exhibits phage’s properties
specialized transduction (specific genes transferred to bacteria via evil larry
what is a prophage?
the inserted phage DNA; replicated w/ host cell DNA
what are the steps for the multiplication of animal viruses?
attachment → entry (receptor - mediated OR fusion) → uncoating → biosynthesis → maturation → release (budding)
where are the specific parts in a cell where viruses mature?
DNA replicated in nucleus of host
capsid synthesized in cytoplasm of host via RNA - dependent RNA polymerase
capsid proteins migrate to nucleus to continue assembly
what is positive and negative ssRNA? dsRNA?
ssRNA: + sense strand → vRNA used as mRNA for protein synthesis
- sense strand → vRNA transcribed into mRNA for protein synthesis
dsRNA - double stranded RNA
what’s the significance of a provirus?
provirus - DNA made from vRNA via reverse transcriptase; integrates into host DNA
provirus DNA is protected from host’s immune system + antiviral drugs
cancer of connective tissues
sarcoma
cancer of glandular epithelial tissue
adenocarcinomas
what are genes that encode proteins that stimulate normal cell growth?
proto - oncogene
mutated proto - oncogenes make __?
oncogenes
transfer normal cells into cancerous cells
when cells acquire new properties
transformation
what do oncogenic viruses do?
integrate into host DNA → induce tumors
when cells are transformed they carry __?
TSTA = tumor - specific transplantation antigens (on surface + irregularly shaped)
viruses that infect + kill tumor cells via immune response
oncolytic viruses
organism or virus carrying a pathogen but does not exhibit symptoms of said disease
asymptomatic
what is a latent virus?
infection that is inactive inside a host cell for a long period of time
can activate bc of immunity changes
fatal infection that gradually worsens
persistent viral infection
plants get viruses through wounds or insects but are generally protected by a impermeable cell wall
short pieces of naked/ exposed RNA
viroids
viroids enclosed in a protein coat
virusoids
a proteinaceous infectious particle
prion
inherited + transmittable (ingestion, transplantation, and surgical tools)
ex. mad cow disease (prions in beef → ppl cooked or undercooked meat → ingested meat = disease)
PrPc vs. PrPsc
PrPc - normal cellular prion protein; cell surface
PrPsc - scapie protein; crowds brain cells = plaques; misfolded form (conversion of normal host glycoprotein)
study of disease
pathology
cause of disease
etiology
how a disease develops
pathogenesis
what is an infection?
invasion of pathogens in the body
when is an infection considered a disease?
when the infection changes the state of health
how early do humans establish a microbiome?
utero (in amniotic sac)
placenta provides microbiome
what microbe is present in the placenta during fetal development?
enterbacteriaceae and propionibacterium
what microbe inhabits the neonate intestine AFTER vaginal birth only?
lactobacilli
development allows for more microbial collections (food, people, pets, etc.)
importance of microbes
help and contribute to health and disease
around 4 × 1013
what is the relationship between microbial communities and the body/ human health called?
human microbiome project
microbes that are a part of the human microbiome, is permanent, and do not cause disease?
normal microbiota
microbes that are only temporary in the human microbiome?
transient microbiota
the distribution and composition of the human microbiome is important and a staple to the immune system (controlled by many factors)
compare vaginal birth and c- section birth
vaginal - gives lactobacillus and bacterioides
c- section - give only microbes that resemble human skin + staphylococcus aureus
the term for when microbes compete with each other
microbial antagonism/ competitive exclusion
normal microbiota compete w/ foreign microbes for nutrients, produce harmful substances, and affect pH and oxygen levels
give an example of a antagonistic microbe
Clostridium difficile causes intestinal infections when normal microbiota are depleted (via antibiotics)
may call for a fecal microbiota transfer (FTM) → replaces normal microbiota
symbiosis
relationship between two organisms; at least one benefits
when one organism benefits while the other does not
parasitism
when both organisms benefit
mutualism
when one organism benefits while the other isn’t effected
commensalism
microbes that exist without affecting the host but cause disease when host immune system is weakened
opportunistic microbiota
how does Koch’s postulates relate to microbiology?
Koch discovered a causitive microbe always has the same symptoms, even in different (but susceptible) hosts
what is the criteria for Koch’s postulates?
said pathogen must be present in every case of said disease
pathogen must be separated from host and grown in culture
pathogen cultured must cause same disease when inoculated into healthy host
pathogen must be isolated from inoculated organism and be proven it is the original pathogen
symptoms
subjective changes in the body; anything felt by the patient
signs
objective (observable/ measurable) changes in the body
specific group of signs and symptoms that accompany a disease
syndrome
term for a disease that spreads from host to host vs. term for a disease that is spread faster and easier (most likely a group transfer)
communicable disease vs. contagious disease
a disease that IS NOT spread
noncommunicable disease
incidence
the # of ppl who DEVELOP a disease during a specific time
prevalence
the # of ppl who HAVE a disease during a specific time
sporadic disease
disease that comes and goes
endemic disease
disease constantly present in a population
disease acquired by many ppl in a given area (short period of time)
epidemic disease
worldwide disease
pandemic
average time individuals have a disease (diagnosis →cure/ death)
duration
acute disease
symptoms develop quickly; last for a short time
symptoms develop gradually; last longer amounts of time
chronic disease
subacute disease
between acute and chronic disease
term for an agent that is inactive for some time but causes disease upon changes in immunity
latent disease
immunity in most of a population
herd immunity
the presence and extensiveness of disease in the body AND ability to cause death
severity
asymptomatic→mild→moderate→severe→critical→sepsis
infection fatality ratio (IFR)
# of deaths DIVIDED BY total # of infected in a specific time frame
case fatality ratio
proportion of individuals diagnosed w/ a disease who die within a time frame
relationship between # of diagnosis and # of deaths
infections that are limited to a small area of the body
local infection
systemic (generalized) infection
infection spreads through body via blood + lymph
systemic infection that began as a local infection
focal infection
toxic inflammatory condition from the spread of microbes
sepsis
bacteria in the blood
bacteremia
toxins in the blood
toxemia
viruses in the blood
viremia
acute infection that causes initial illness
primary infection
opportunistic infection after primary infection
secondary infection