Spring Semester Exam Review and Key Concepts in Biology
1/110
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
111 Terms
Natural Selection
The process of species adapting to their environment to increase chances of survival and reproduction.
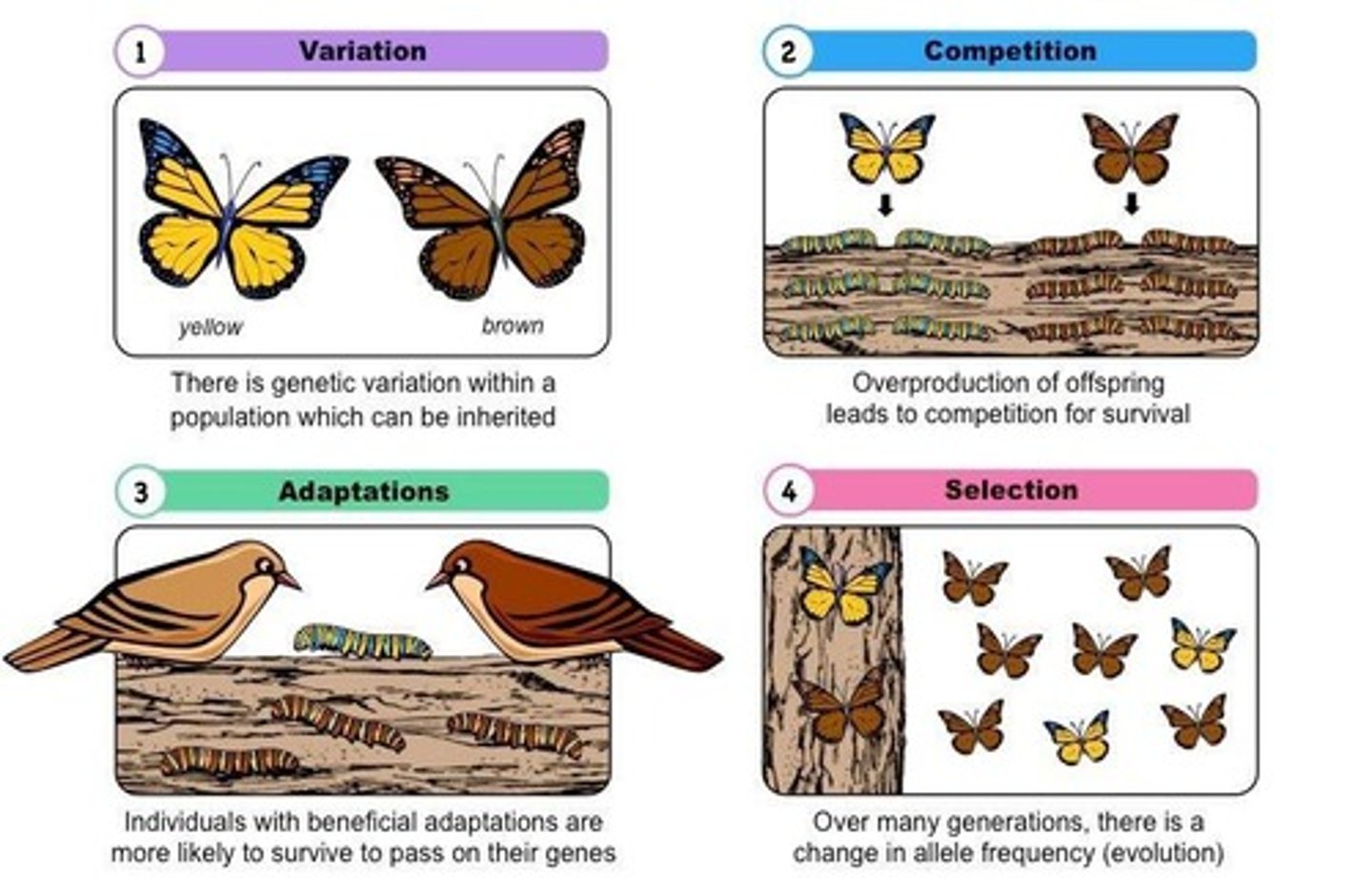
Genetic Variation
Differences in DNA among individuals that contribute to diversity within a species.
Competition
The struggle between organisms for limited resources such as food, space, and mates.
Survival of the Fittest
The concept that individuals best adapted to their environment are more likely to survive and reproduce.
Descent with Modification
The process by which species evolve over time through adaptations.
Fossil Records
Remains or traces of organisms from the past, providing evidence for evolution.

Anatomical Structures
Physical features of organisms that can provide evidence for evolutionary relationships.
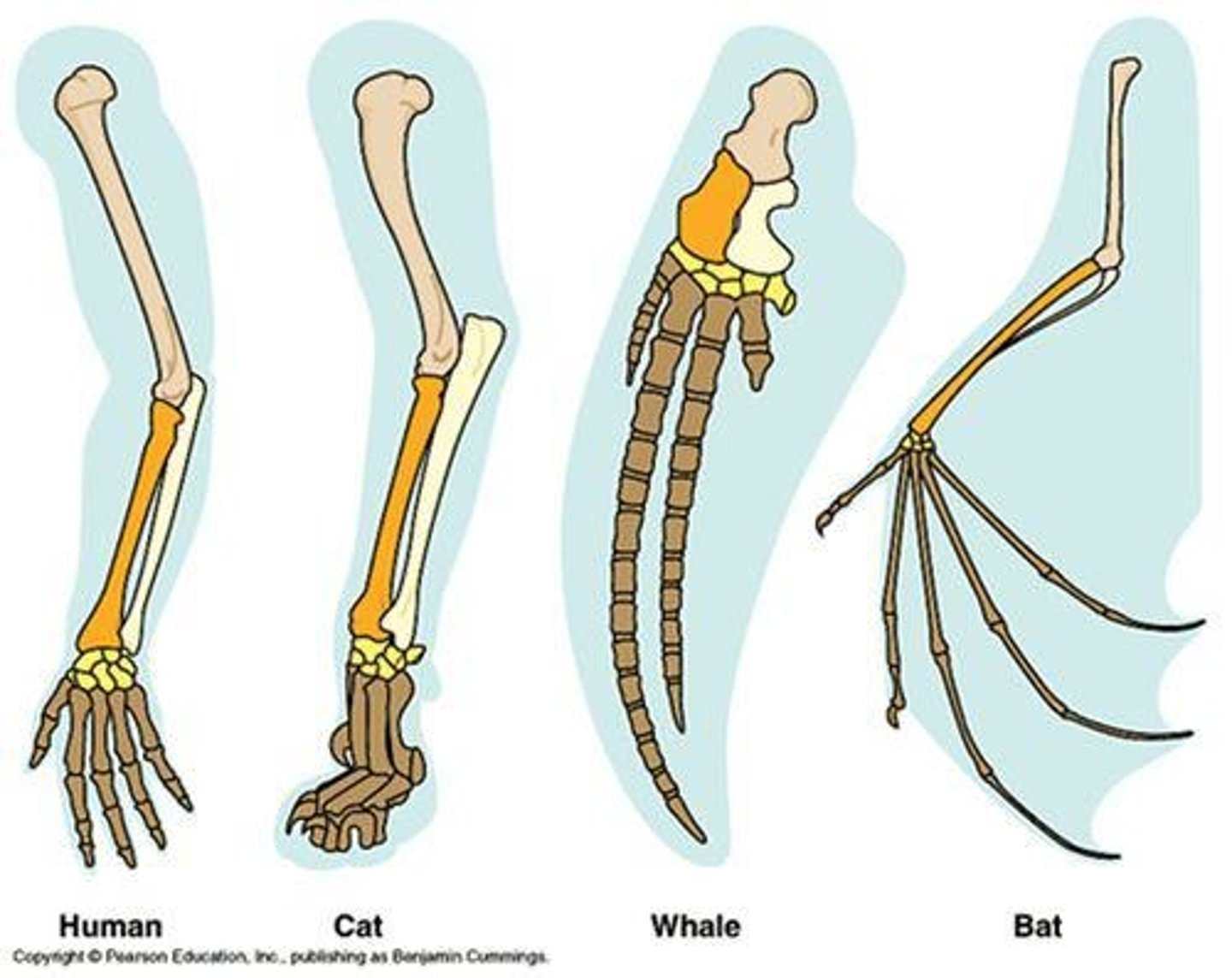
Homologous Structures
Anatomical features that are similar in different species due to shared ancestry.
Analogous Structures
Anatomical features that serve similar functions in different species but do not share a common ancestor.
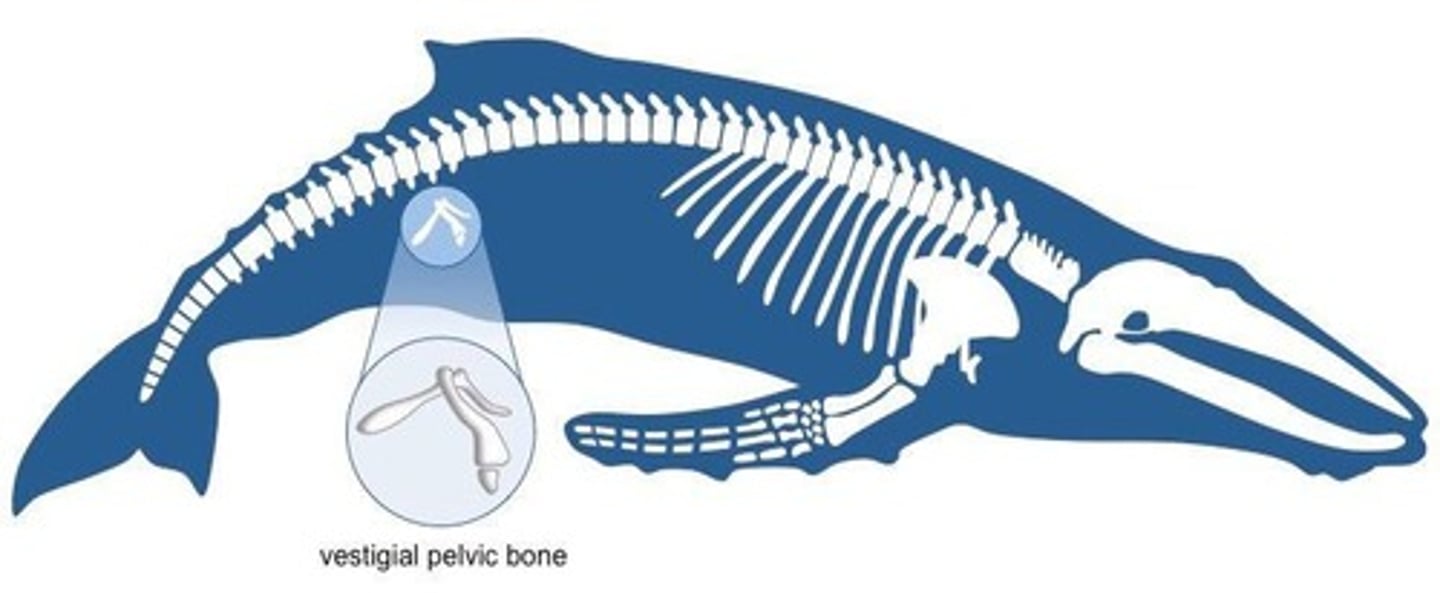
Vestigial Structures
Body parts that have lost their original function through evolution.
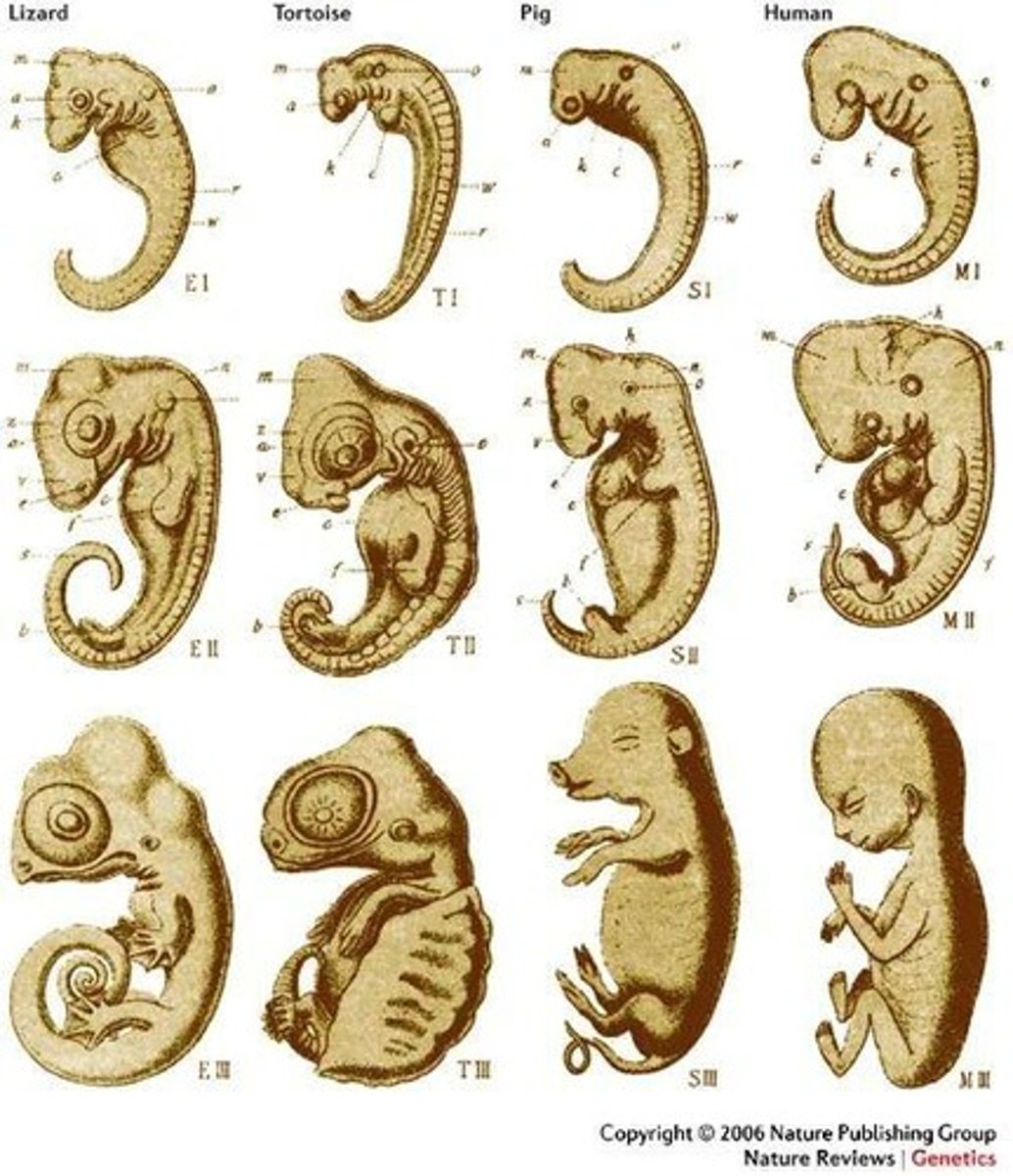
Embryology
The study of embryos, which can show similarities in development among different species.
Biogeography
The study of the geographical distribution of species, implying common ancestry.
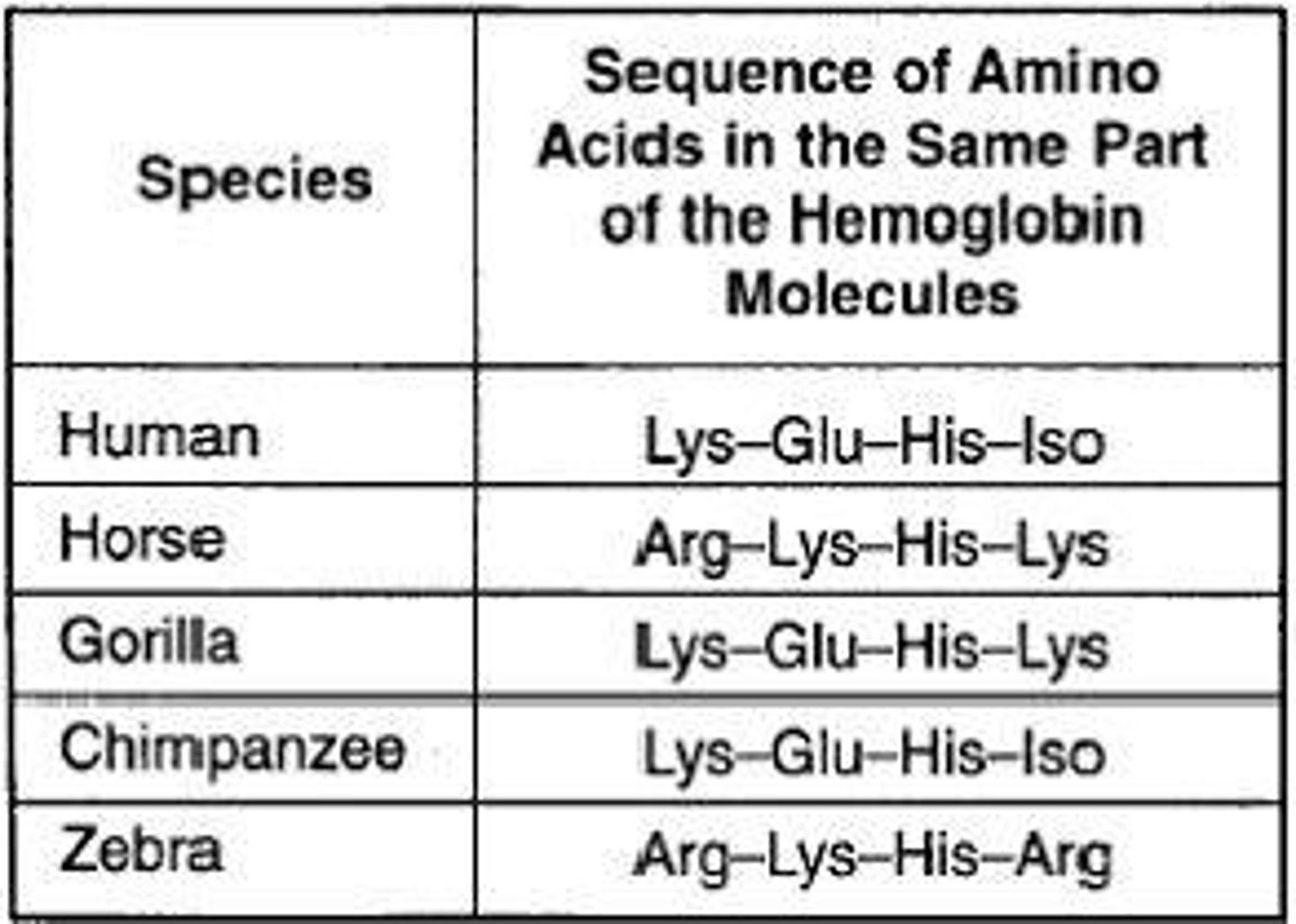
Biochemical Evidence
The comparison of DNA sequences among species to determine relatedness.
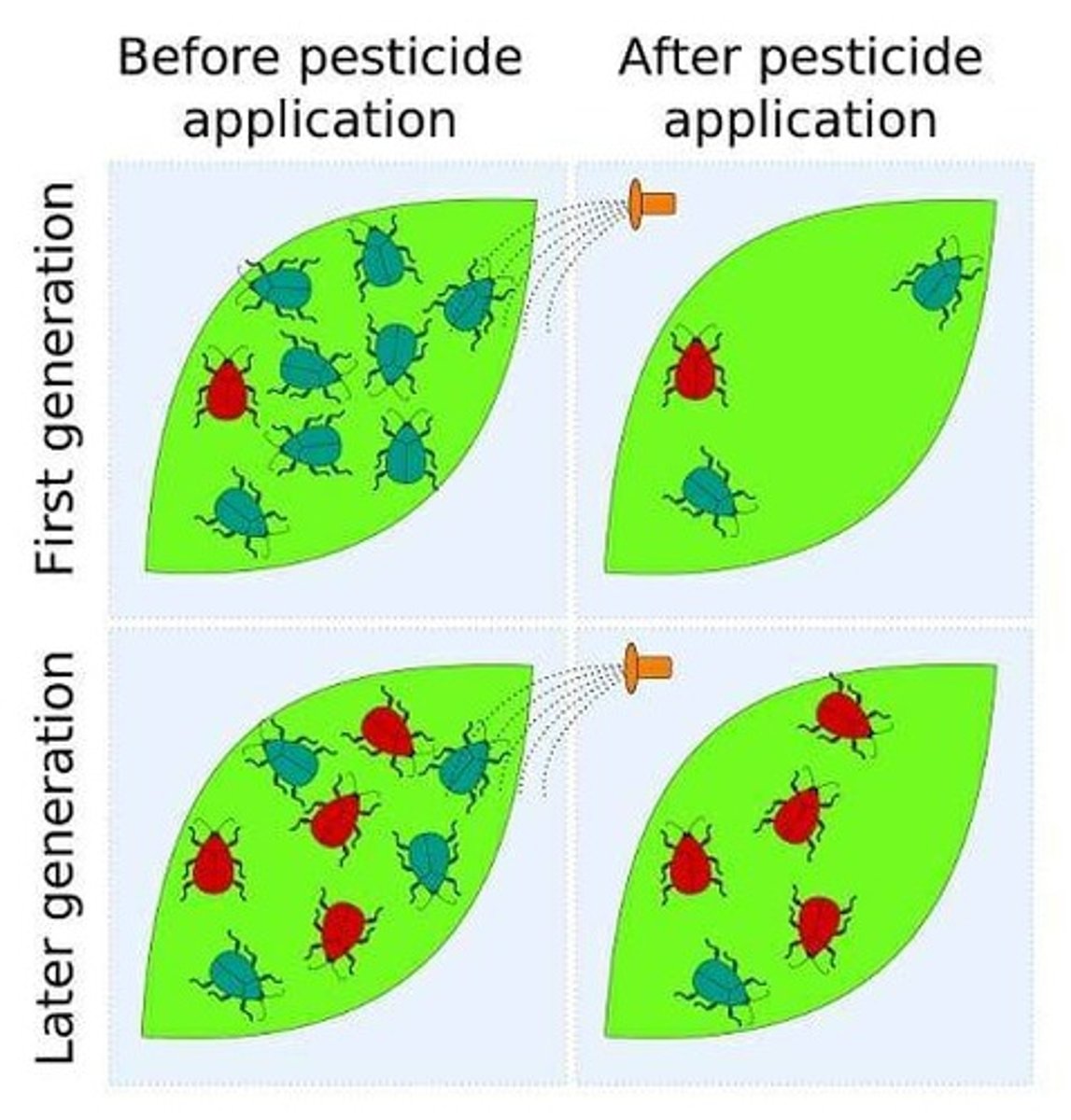
Observable Events
Rapid evolution that can be witnessed, such as changes in pathogens or pests.
Gradualism
The theory that evolution occurs slowly and steadily over time.
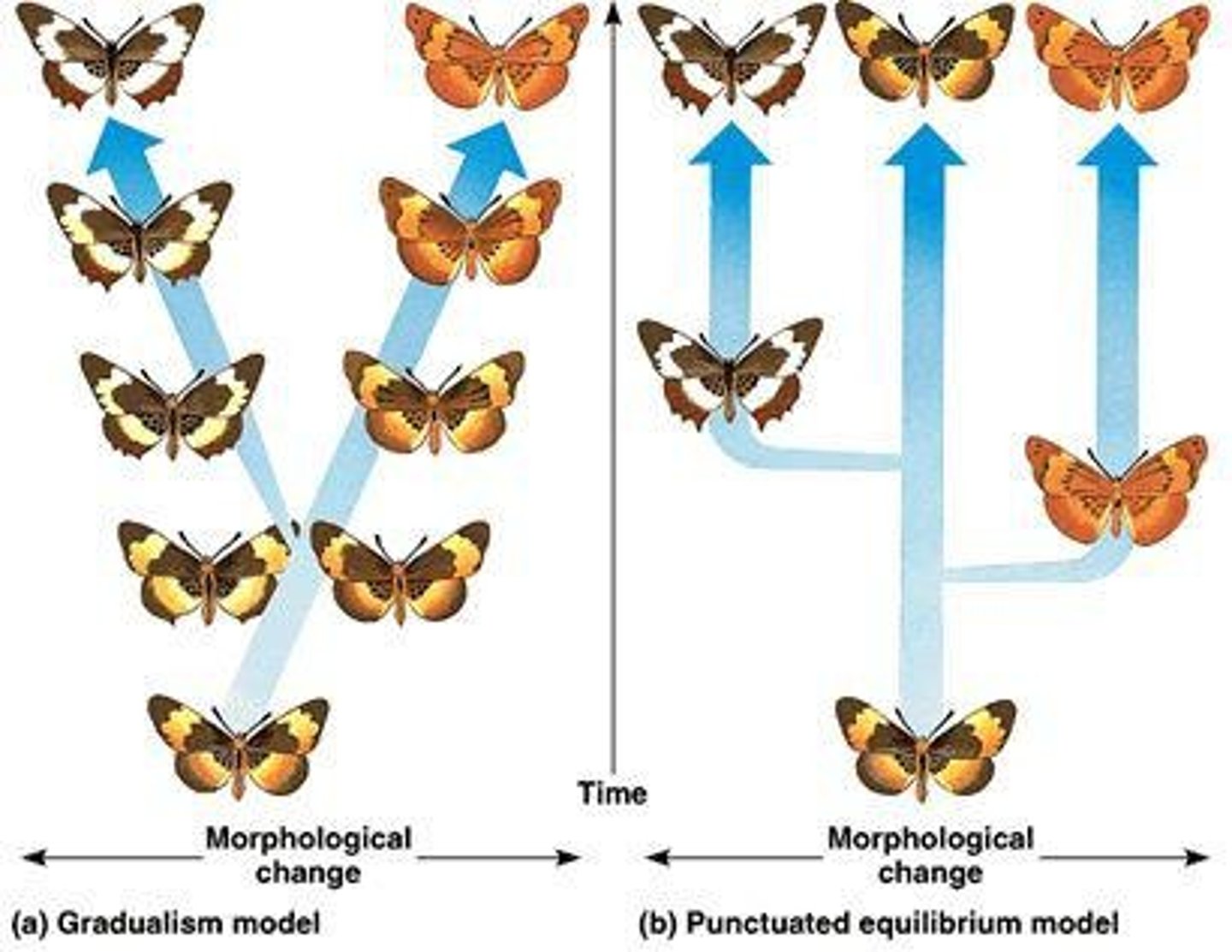
Stasis
A period in which a species remains unchanged for a long time.
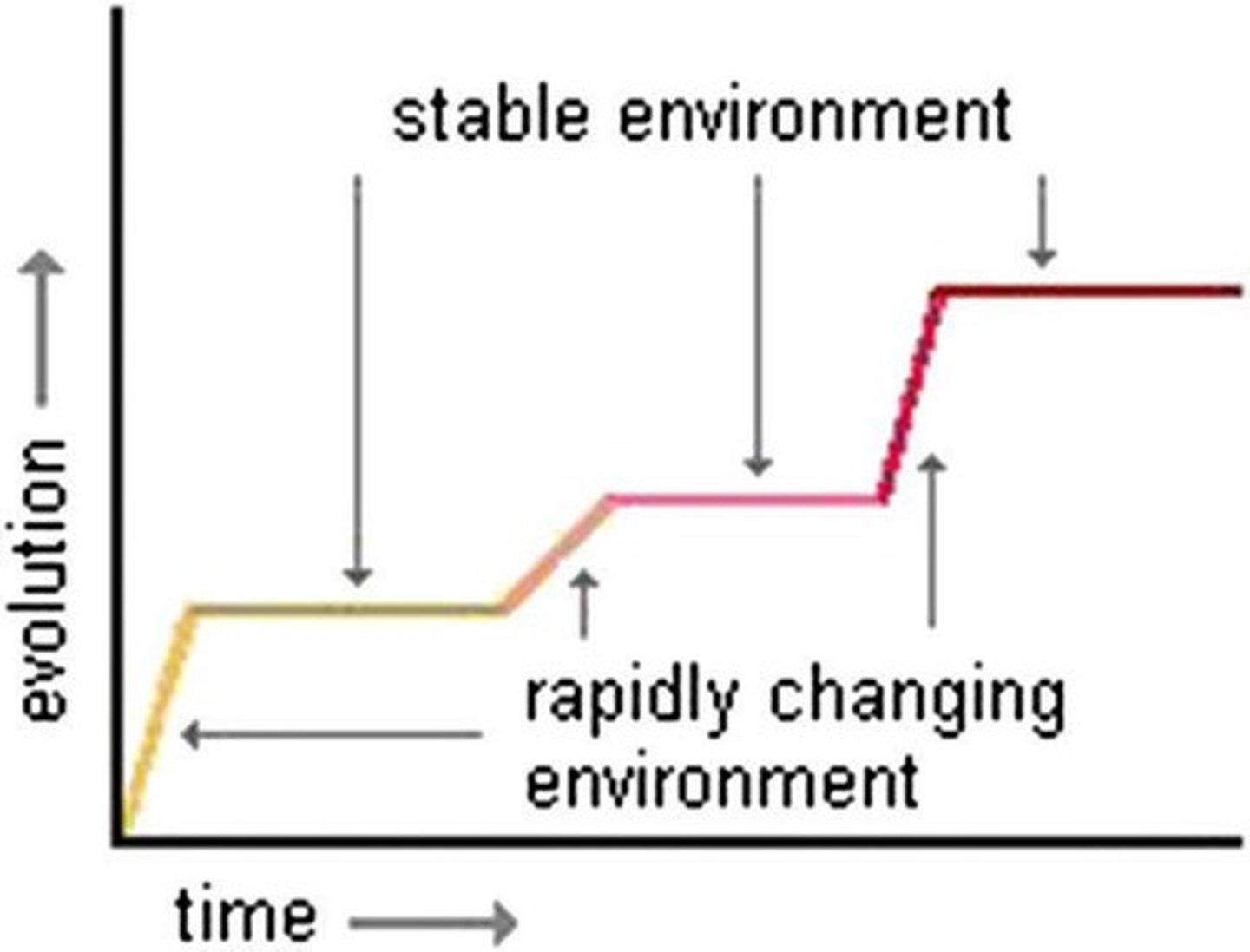
Punctuated Equilibrium
The theory that evolution occurs in rapid bursts followed by long periods of stability.
Directional Selection
A type of natural selection that favors one extreme phenotype over others.
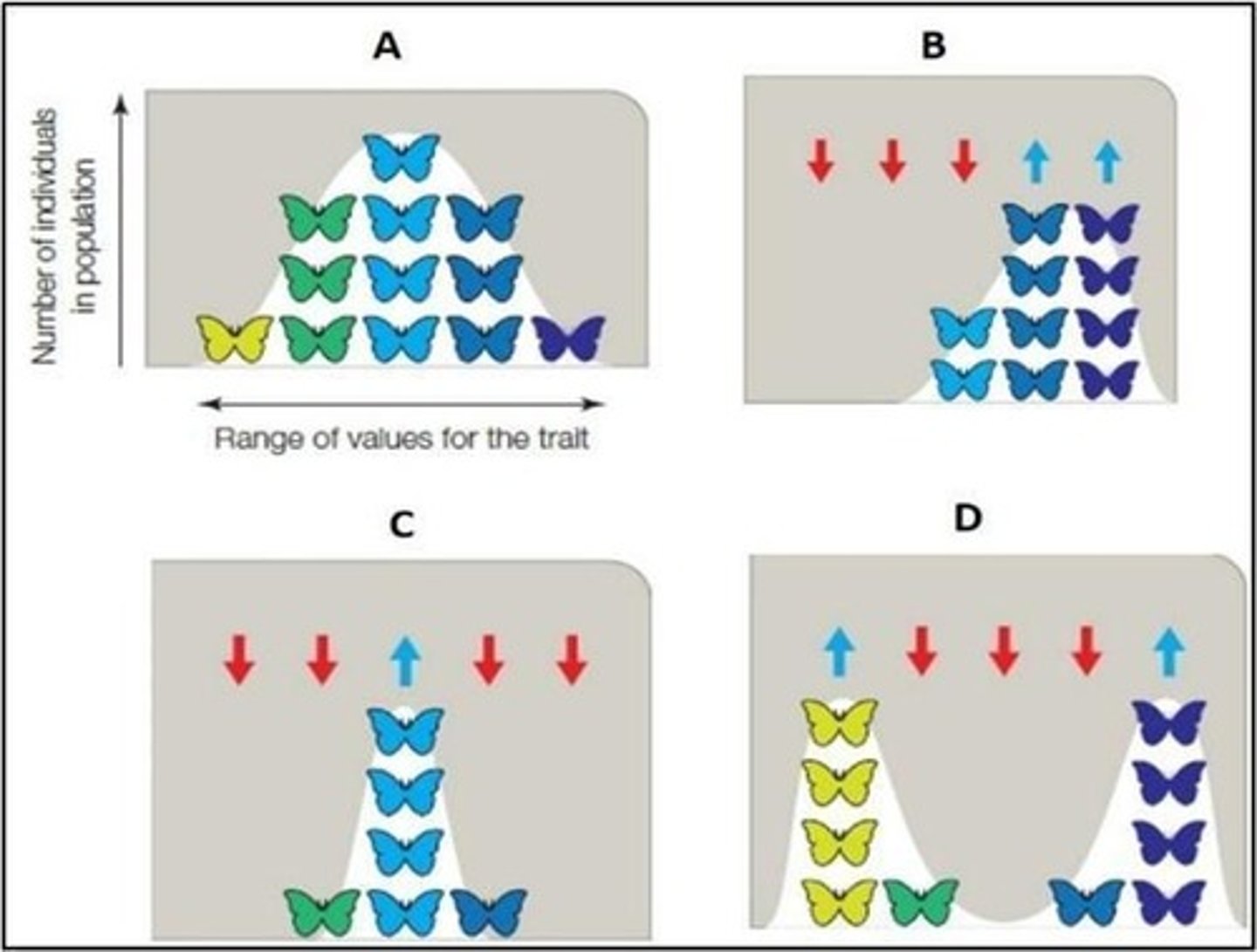
Stabilizing Selection
A type of natural selection that favors average phenotypes and reduces variation.
Disruptive Selection
A type of natural selection that favors extreme phenotypes at both ends of the spectrum.
Gene Flow
The transfer of genetic material between populations, increasing genetic diversity.
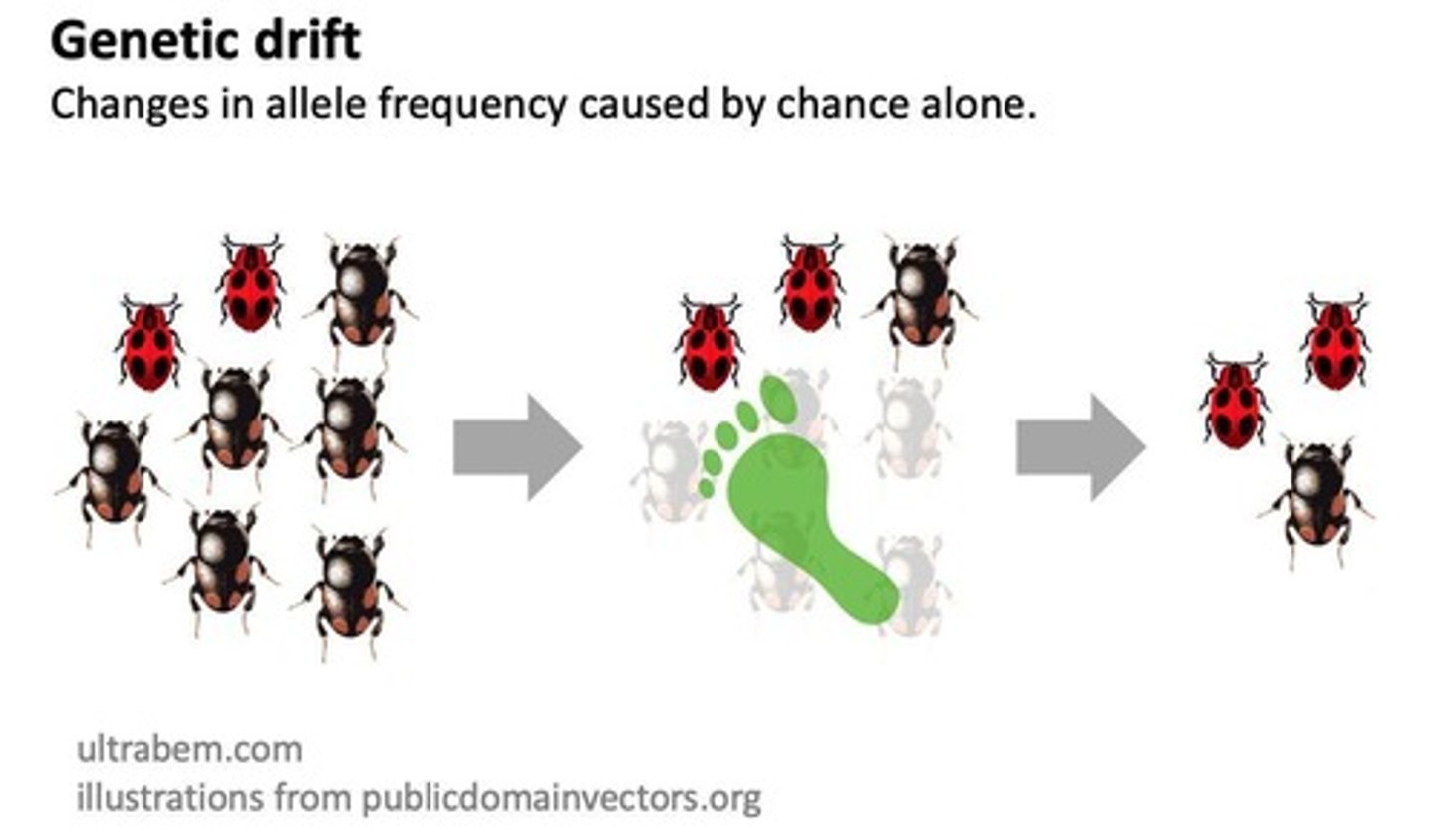
Genetic Drift
Random changes in allele frequencies in a population, often due to chance events.
Hardy-Weinberg Principle
A principle that describes the genetic equilibrium in a population under certain conditions.
SPECIATION
When one species diverges into two species.
GEOGRAPHIC ISOLATION
Physical isolation between two populations.
REPRODUCTIVE ISOLATION
Can no longer interbreed.
CLADOGRAMS
A diagram that shows the evolutionary relationships among various biological species.
DERIVED CHARACTERISTICS
Gained traits.
GENETIC DIVERSITY
Is important because it allows for better survival (adapting to changing environments).
HOMEOSTASIS
Maintaining internal balance; essential for survival.
SKELETAL SYSTEM
Provides support and structure.
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
Produces hormones.
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
Transports substances.
MUSCULAR SYSTEM
Facilitates movement.
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
Produces gametes.
IMMUNE SYSTEM
Defends against illness.
EXCRETORY SYSTEM
Removes waste.
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
Breaks down food for energy.
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
Facilitates the exchange of O2 and CO2.
INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM
Acts as a barrier.
NERVOUS SYSTEM
Sends and receives signals.
NEGATIVE FEEDBACK
Used to maintain balance.
POSITIVE FEEDBACK
Used to complete a job.
VIRUSES
Are not considered living, need a host cell to do anything.
GLYCOPROTEINS
Genetic material for infecting specific cells.
ENVELOPE
For protection (not all viruses have this).
CAPSID
Made of protein for protection.
LYTIC REPRODUCTION
Quicker reproduction.
LYSOGENIC REPRODUCTION
Slower reproduction.
LINES OF DEFENSE
1st line: Physical barrier; 2nd line: Inflammatory response; 3rd line: Targets specific antigens.
SECONDARY IMMUNE RESPONSE
Response is FASTER and STRONGER upon exposure to a pathogen.
PRIMARY IMMUNE RESPONSE
Response is WEAK and SLOW upon initial exposure to a pathogen.
PLANT CELLS
Cells that have chloroplasts, a large central vacuole, and a cell wall.
PLANT TISSUES
Types of tissues in plants including vascular, ground, and dermal.
VASCULAR TISSUE
Transports materials in plants.
GROUND TISSUE
Stores materials in plants.
DERMAL TISSUE
Outer covering of plants.
XYLEM
Vascular tissue that transports water and minerals.
PHLOEM
Vascular tissue that transports sugars.
ROOTS
Organs that absorb water and anchor the plant.
STEMS
Organs that support the plant and transport materials.
LEAVES
Site of photosynthesis in plants.
TRANSPIRATION
Process of movement and evaporation of water in plants through a guard cell.
BRYOPHYTES
Non-vascular plants that reproduce with spores.
PTERIDOPHYTES
Vascular plants that reproduce with spores.
GYMNOSPERMS
Vascular plants with naked seeds and no flowers.
ANGIOSPERMS
Vascular plants with covered seeds, flowers, and fruits.
STIGMA
Part of the flower that collects pollen.
PETAL
Part of the flower that attracts pollinators.
ANTHER
Produces pollen in the flower.
STYLE
Pollen tubes travel through this part of the flower.
OVARY
Protects plant zygotes and helps develop pollen.
SEPAL
Protects budding flowers.
SEED DISPERSAL
Increases chance of survival by reducing competition.
AUXINS
Hormones that promote lengthening in plants.
CYTOKININS
Hormones that help with cell division.
GIBBERELLINS
Hormones that cause dramatic increases in size.
ETHYLENE
Hormone involved in the ripening of fruit.
PHOTOTROPISM
Response of plants to a light source.
GRAVITROPISM
Response of plants to gravity.
THIGMOTROPISM
Response of plants to touch.
PHOTOSYNTHESIS
Process where plants convert light energy into chemical energy, represented by the equation 6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2.
CELLULAR RESPIRATION
Process where cells convert glucose and oxygen into carbon dioxide and water, represented by the equation C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O.
BIOSPHERE
The global sum of all ecosystems.
BIOME
Large ecological areas on the earth's surface with distinct plant and animal groups.
ECOSYSTEM
A community of living organisms and their physical environment interacting as a system.
COMMUNITY
A group of different species living together in one area.
POPULATION
A group of individuals of the same species living in a specific area.
INDIVIDUAL
A single organism.
AUTOTROPH
Organisms that make their own food.
HETEROTROPH
Organisms that consume others for food.
FOOD CHAIN
A linear sequence that shows the flow of energy from one organism to another.
FOOD WEB
A complex network that shows the flow of energy from multiple organisms.
DECOMPOSER
Organisms that break down dead organic matter.
QUATERNARY CONSUMER
An organism that is at the top of the food chain, feeding on tertiary consumers.
TERTIARY CONSUMER
An organism that feeds on secondary consumers.
SECONDARY CONSUMER
An organism that feeds on primary consumers.
PRIMARY CONSUMER
An organism that feeds on producers.
PRODUCER
Organisms that produce energy through photosynthesis.
PREDATOR-PREY
A relationship where one organism captures and feeds on another.