aquatic ecosystems
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
lotic ecosystems
running water, streams and rivers
properties change across river networks, needs to be considered at scales
lentic ecosystems
standing water ecosystems, ponds and lakes
wetlands ponds and lakes can have fuzzy boundaries
ab has lots of shallow lakes, catchment area important for aquatic systems
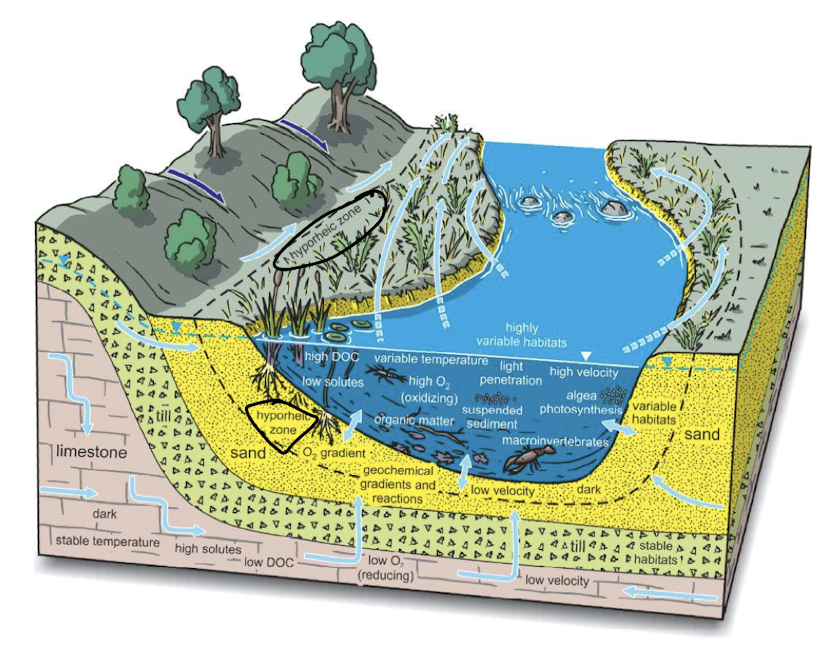
hyporheic zone
the region of sediment under or near river channel where there is mixing of groundwater (upwelling) and surface water (downwelling)
water moves slow, moderates stream temp, improves water quality (filters and denitrification)
unique habitat for biota
tectonic lake
very deep
caused by the deformation of earth’s crust
volcanic lake
formed in volcanic craters, by damming by lava, etc
small, unqiue chemistry with lots of sulfur
glacial lake
prairie potholes, kettle lakes, canadian shield
dropping ice as glaciers retreat cause depression and then melts into it
or scraping of glaciers over bedrock
fluvial lakes
formed in the course of a meandering river which is cut off
solution lakes
underground deposits are dissolved by water running through the area causing a lake to form
landslide lakes
can cause damming of a river which can be temporary or permanent
aeolian lakes
wind blown sediments act like a dam and cause a lake
shoreline lake
found near coastlines but occur due to buildup of sediment, ocean blocking an estuary, or a lake being divided
organic lake
peatlands or tropical swamps
can be up to 10 m of organics, dark water
can also be causes by beavers damming
anthropogenic lakes
reservoirs
for power generation, water supply, etc
meteortie lakes
impact crater fills with water
lake density and area
canada has 880 000 lakes > 10ha , 62% of lakes that size in the world
canadian shield, prairie potholes, etc
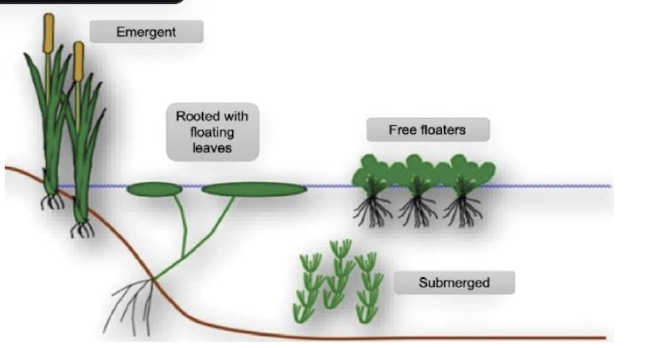
macrophytes
producers in aquatic ecosystems
flowering plants, mosses, and liverworts
no gymnosperms
slow flowing, shallow ecosystems mainly for light
includes emergent, rooted, free floaters and submerged
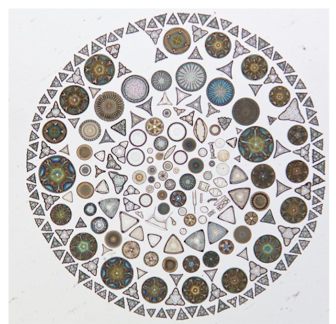
algae
attached in rivers to rocks/sediments/wood
or freefloating in lakes
can be green, yellow-brown or red
diatoms have high diversity and specific requirements
allochtonous
energy from adjacent terrestrial food webs making its way into aquatic ecosystems
autochtonous
energy from within the aquatic ecosystem
primary productivity limitations
limited by nutrients, light and temperature
water with high turbidity or DOC absorbs light and causes low productivity
consumers in aquatic ecosystems
herbivores like zooplankton, macroinvertebrates, fish
carnivores like fish, amphibians, invertebrate larvae
detrivores (allochtonous material), and parasites w high diversity
macroinvertebrates
filter feeders, collectors - FPOM, detritus and algae
grazers/scrapers, predators, shredders, parasites
meiofauna
invertebrates <0.25 mm
can be substantial component but often overlooked
aquatic food webs
interconnectedness, role of parasites, allochtonous inputs
basal, intermediate and top levels
biomass decreases with trophic levels - turns into energy
secondary production
river continuum concept
entire river system as a continuously integrating series of physical gradients and associated biotic adjustments as the river flows from headwater to mouth
aquatic invasive species
cascading effects on foodwebs
direct top down (fish) and bottom up (algal) effects
indirect affects and competitive effects, can be positive for some instances but over all poor
can also impact water quality - turbidity, light conditions and oxygen