AP Biology: Genetics
1/204
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
205 Terms
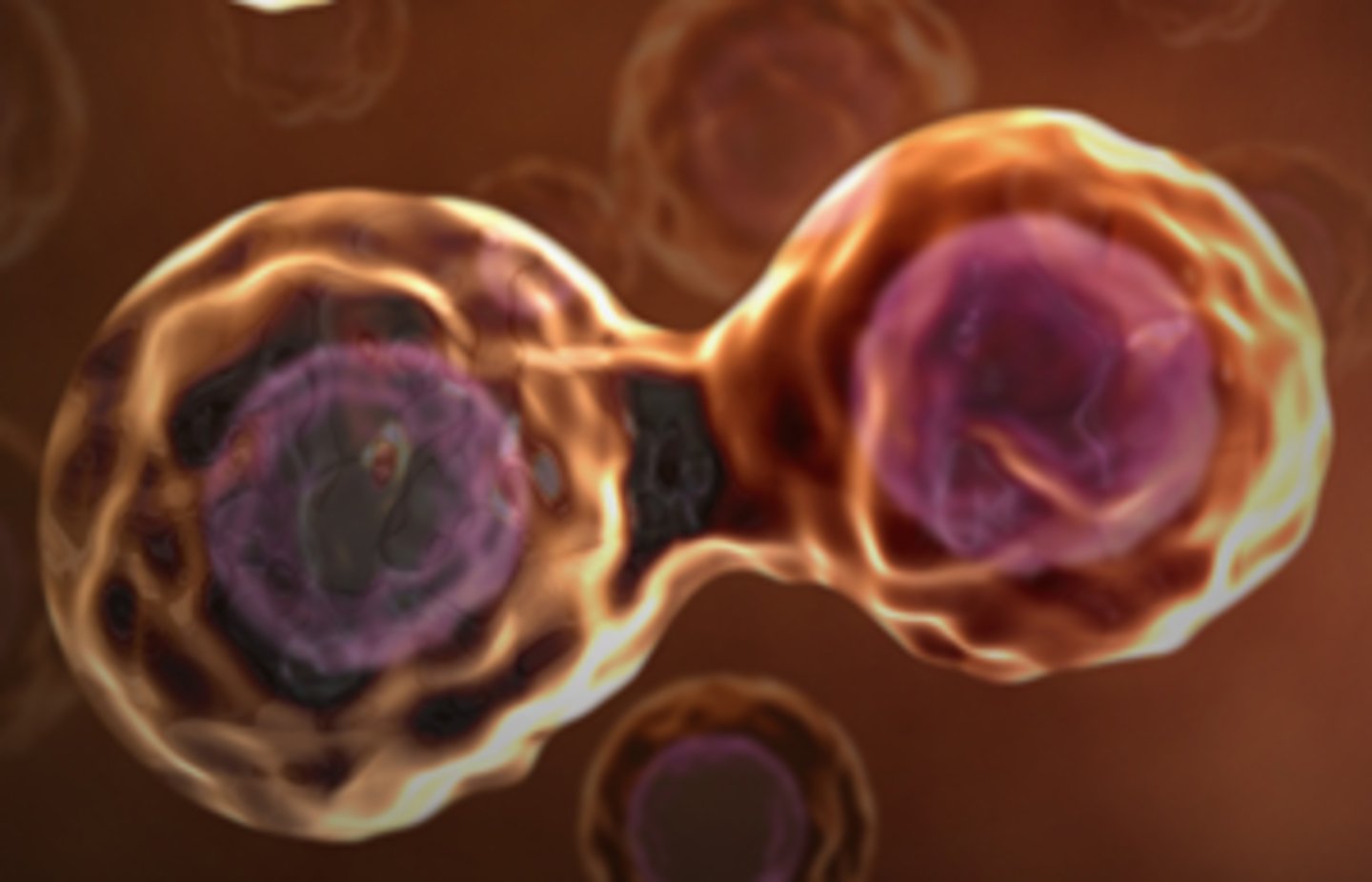
Cell Division
Process by which a cell divides into two new daughter cells
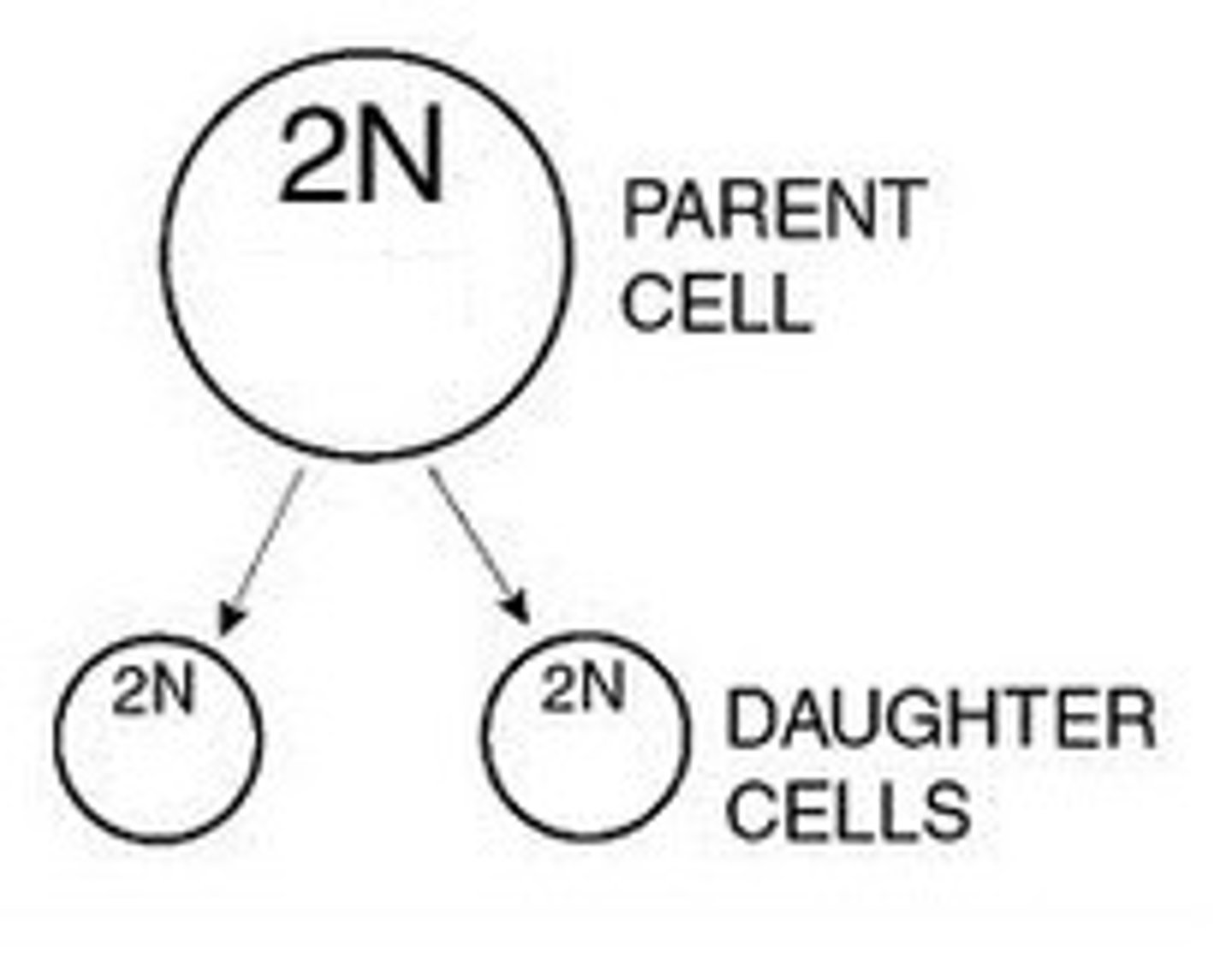
Parent Cell
original cell before cell division
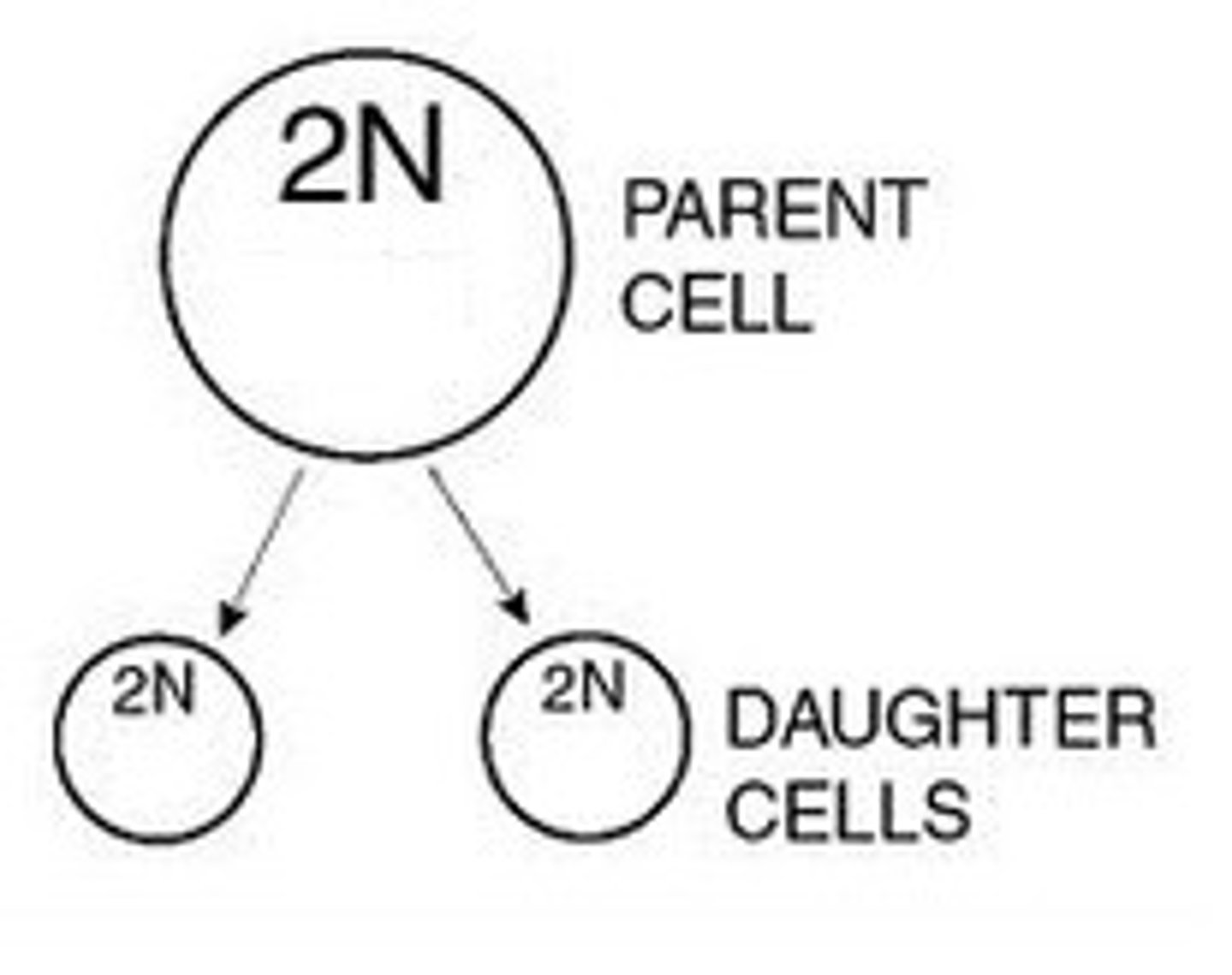
Daughter Cells
The cells that are produced as a result of mitosis. These cells are identical to each other, and also to the original parent cell.
Process of Cell Division
mitosis and meiosis
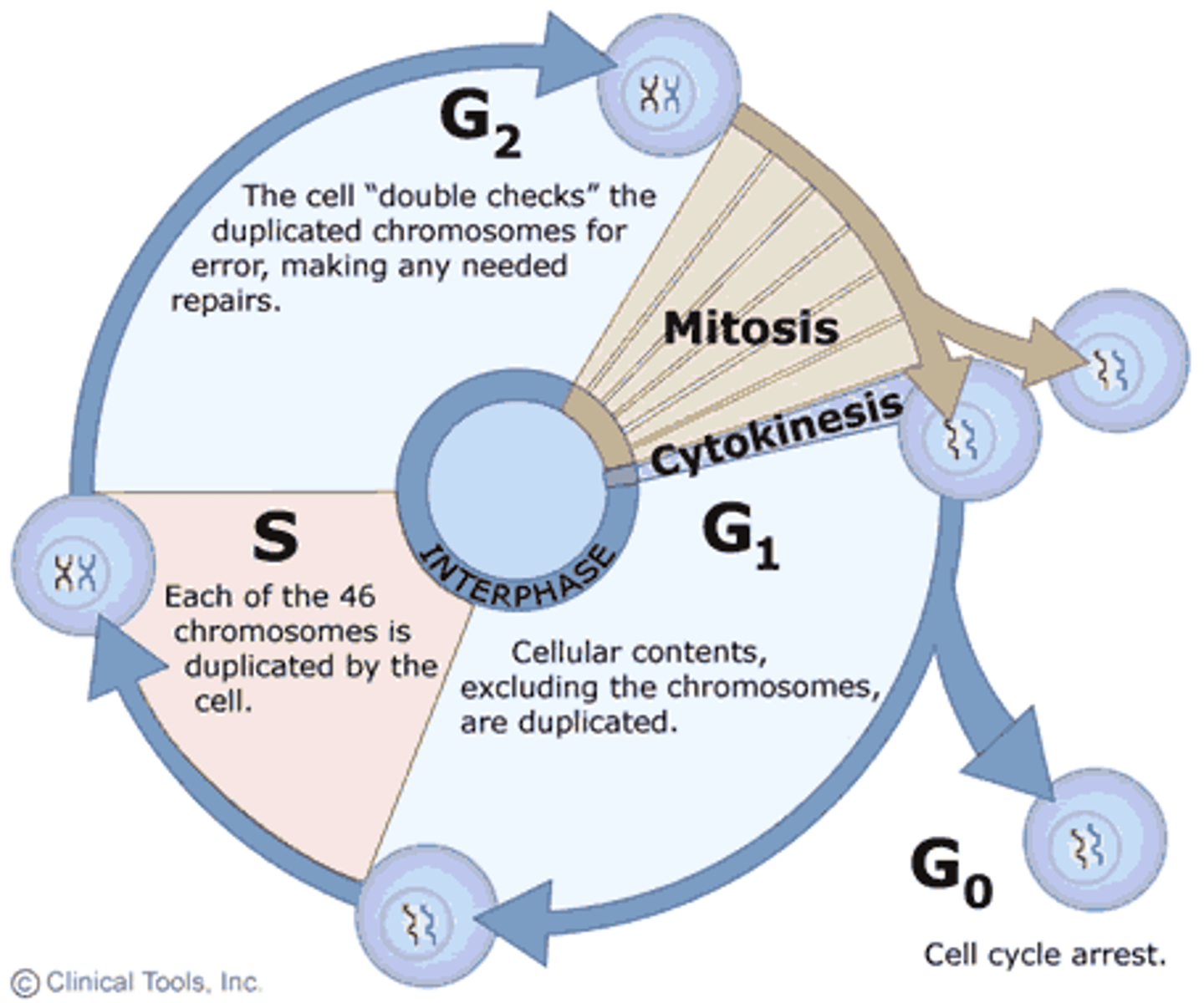
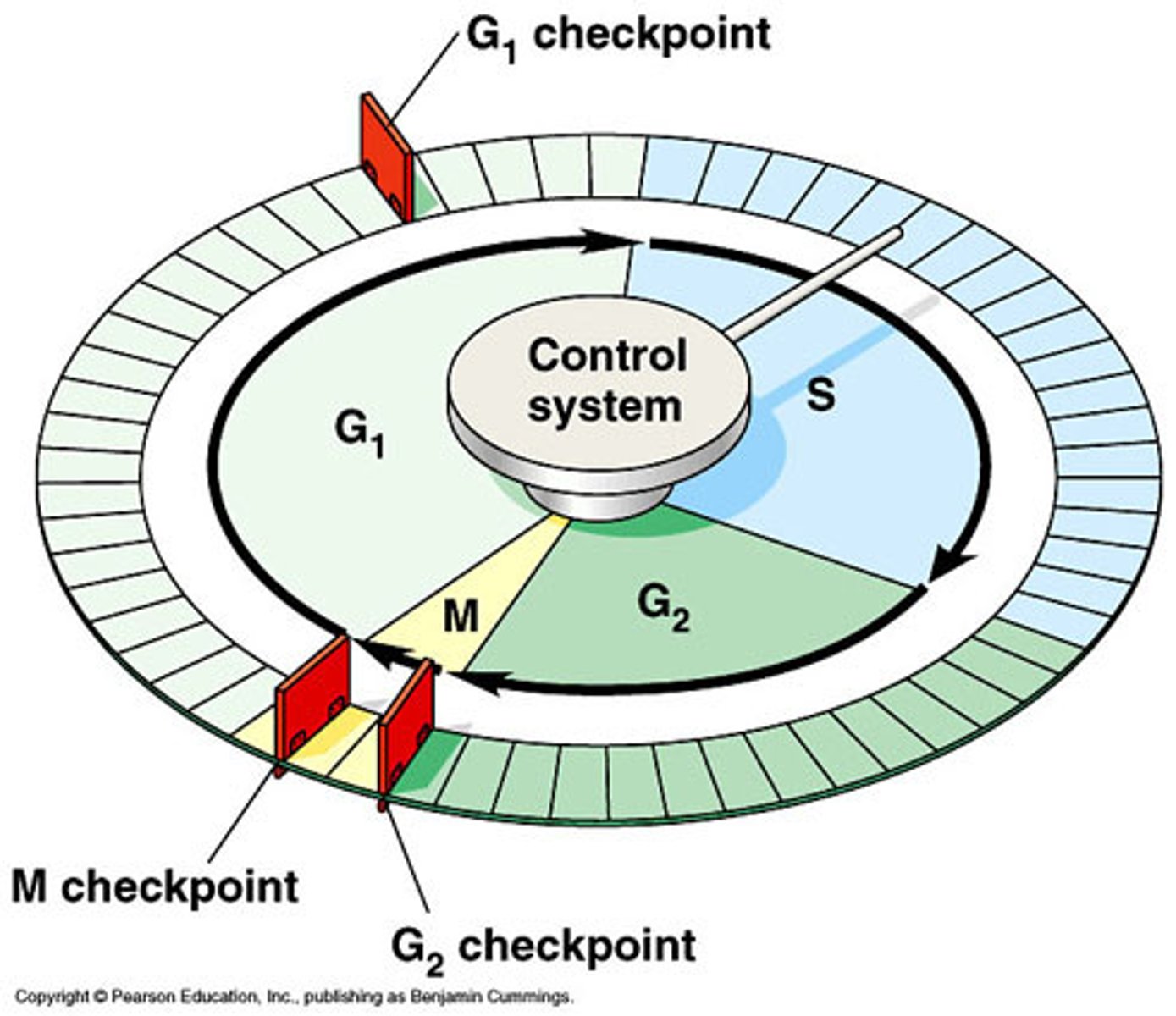
The Cell Cycle
series of events that cells go through as they grow and divide
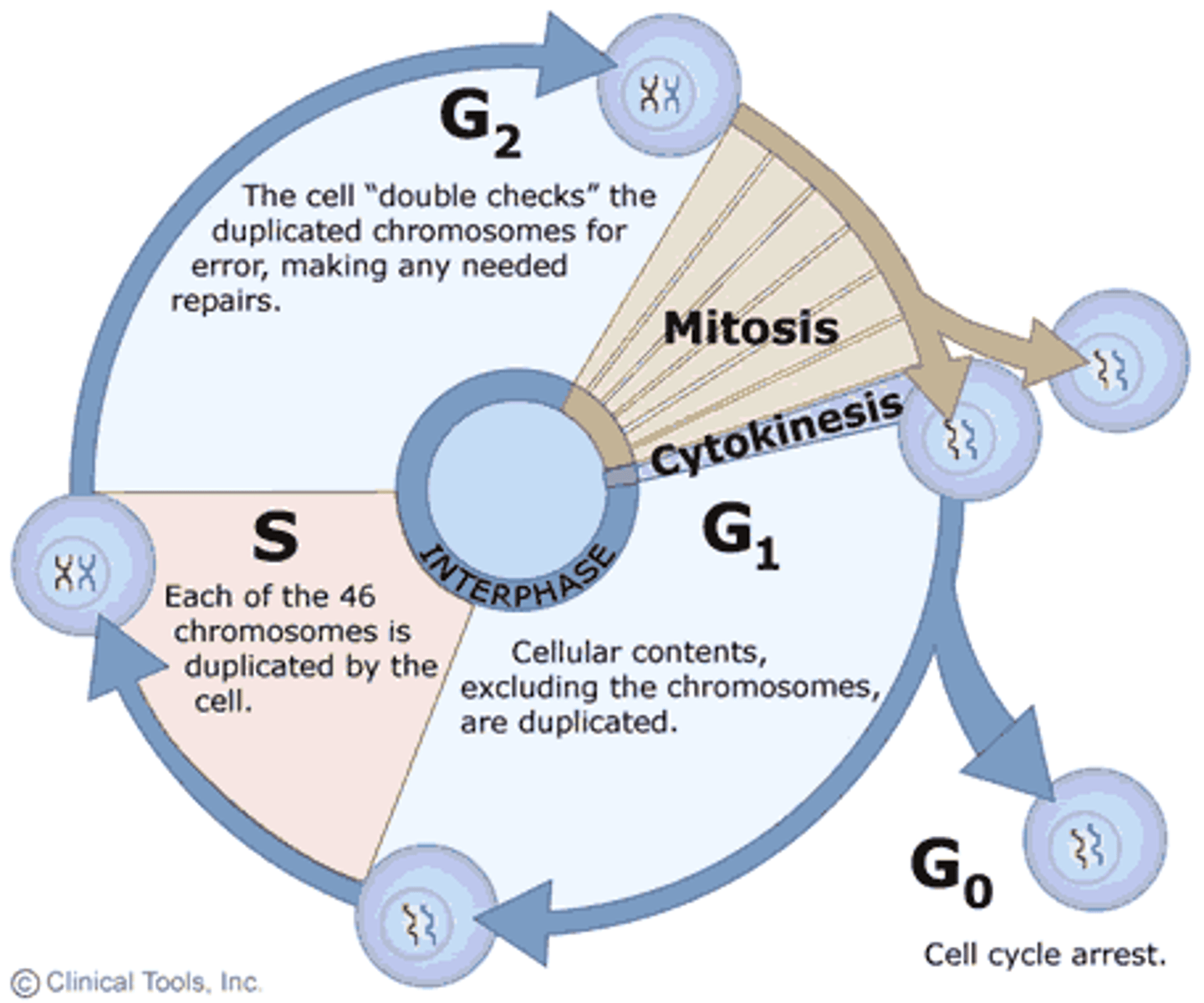
Interphase
Cell grows, performs its normal functions, and prepares for division; consists of G1, S, and G2 phases
G1 Phase
The first gap, or growth phase, of the cell cycle, consisting of the portion of interphase before DNA synthesis begins. Checkpoints: does the cell have enough energy?
Is it large enough?
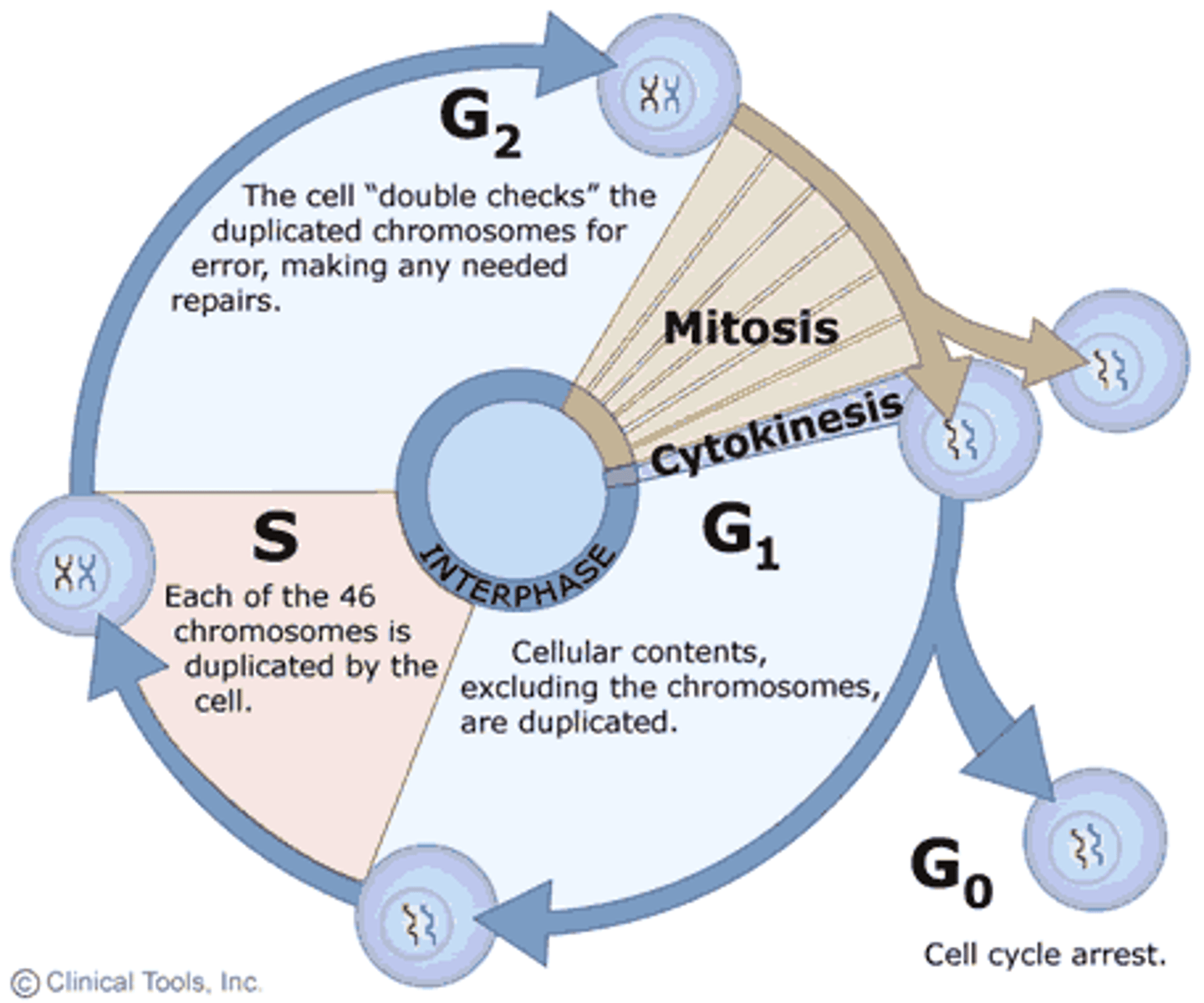
Synthesis Phase
a cell's DNA is copied during this phase. at the end of this phase, each chromosome consists of two chromatids attached at the centromere. CDKs (cyclins/cycle dependent kinase) signal the division.
cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases
The proteins that participate in the functioning of the checkpoints for cell cycle control are

G2 Phase
The second growth phase of the cell cycle, consisting of the portion of interphase after DNA synthesis occurs.
Cell size/energy reserves are assessed. More importantly: have ALL chromosomes been replicated without mistakes and or damages?
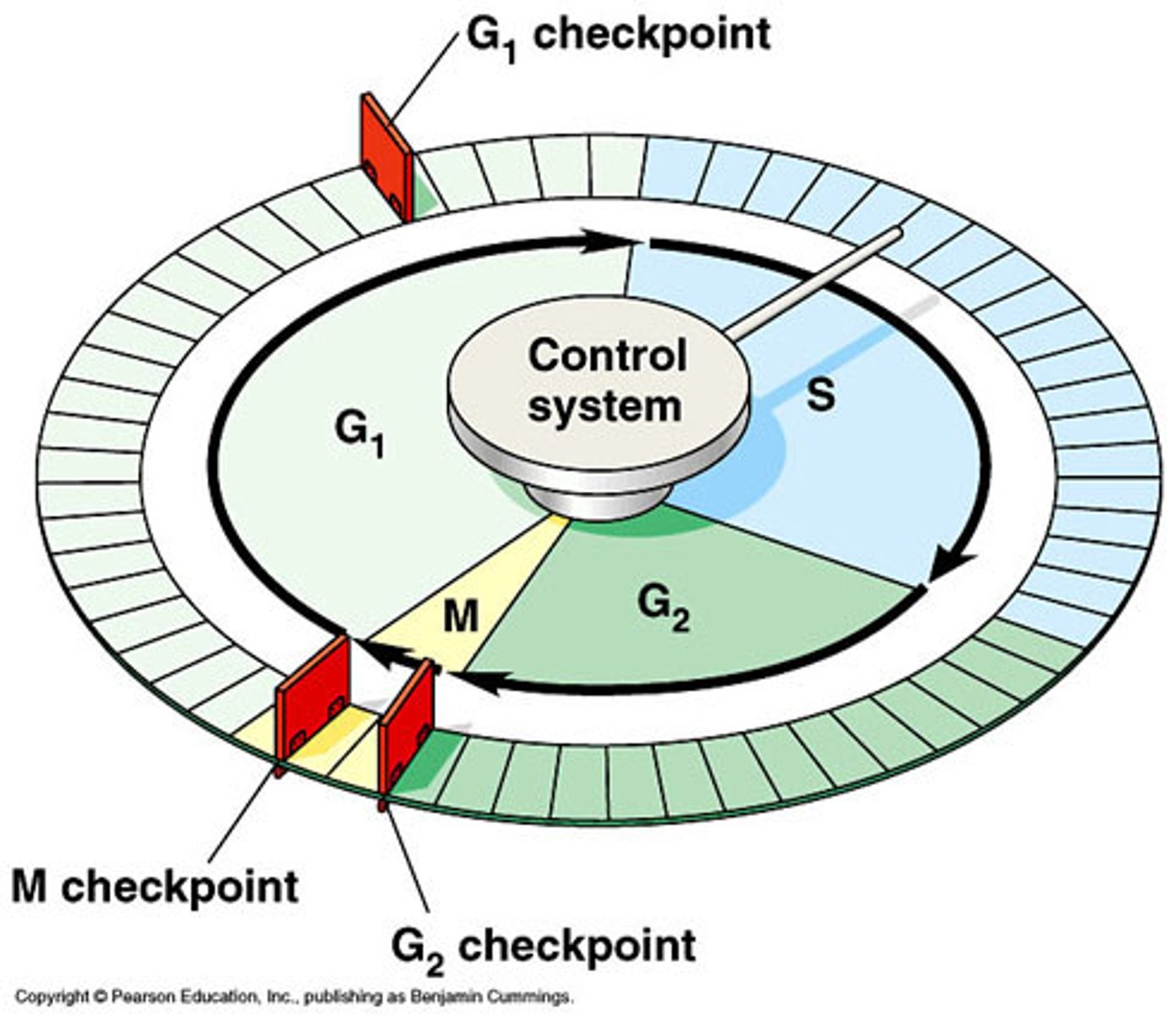
M checkpoint (metaphase)
Check for whether chromosomes properly attached to spindle fibers
Mitosis
cell division in which the nucleus divides into nuclei containing the same number of chromosomes
Meiosis
Cell division that produces reproductive cells in sexually reproducing organisms
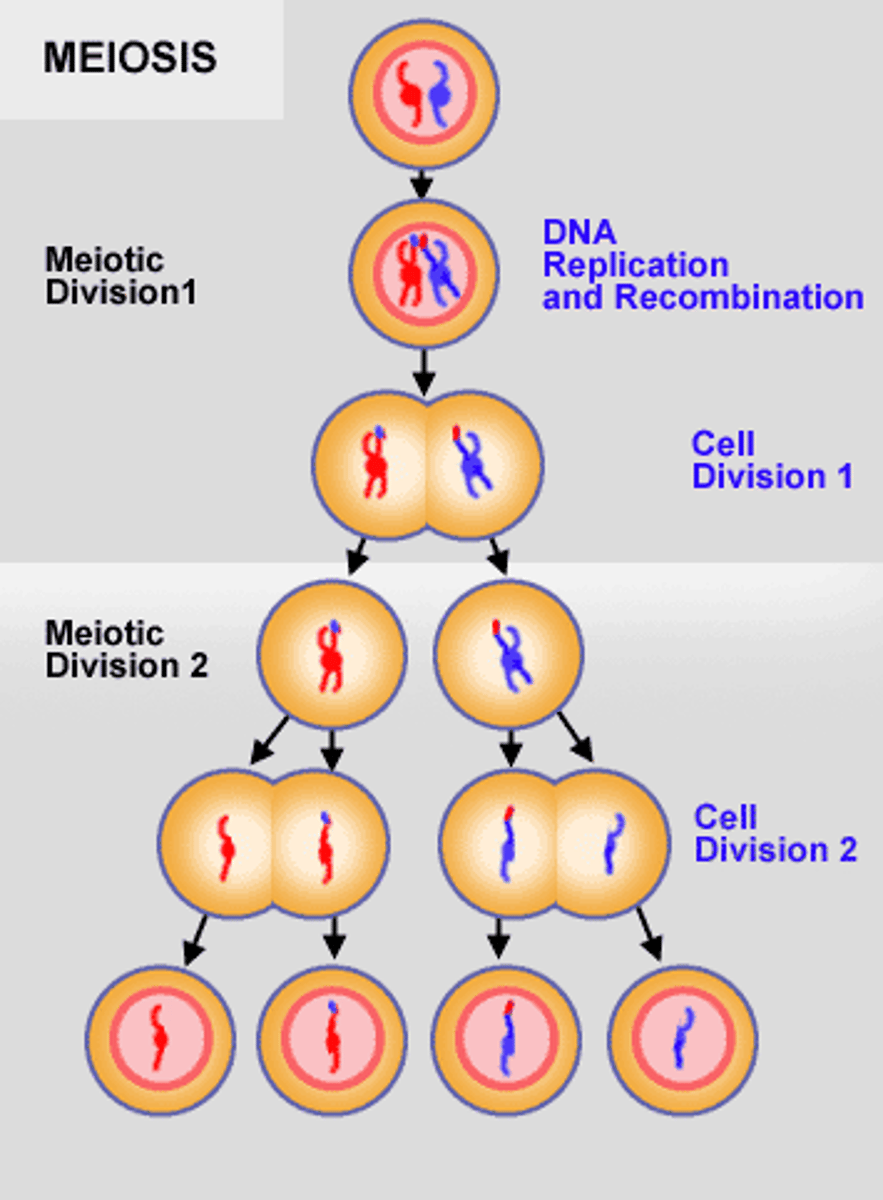
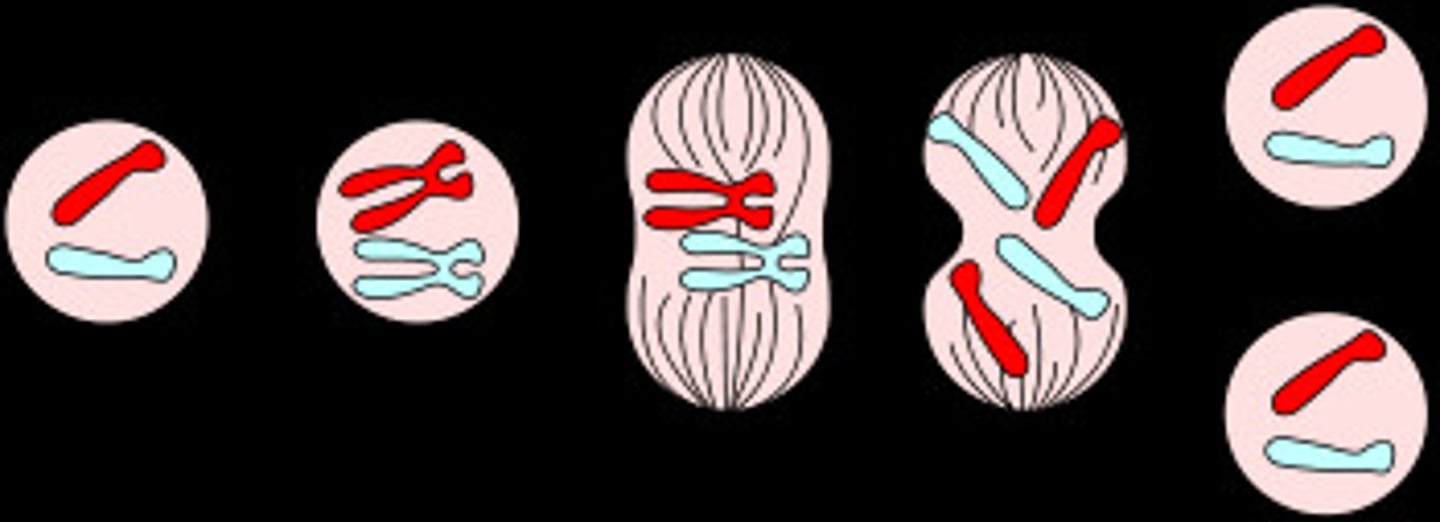
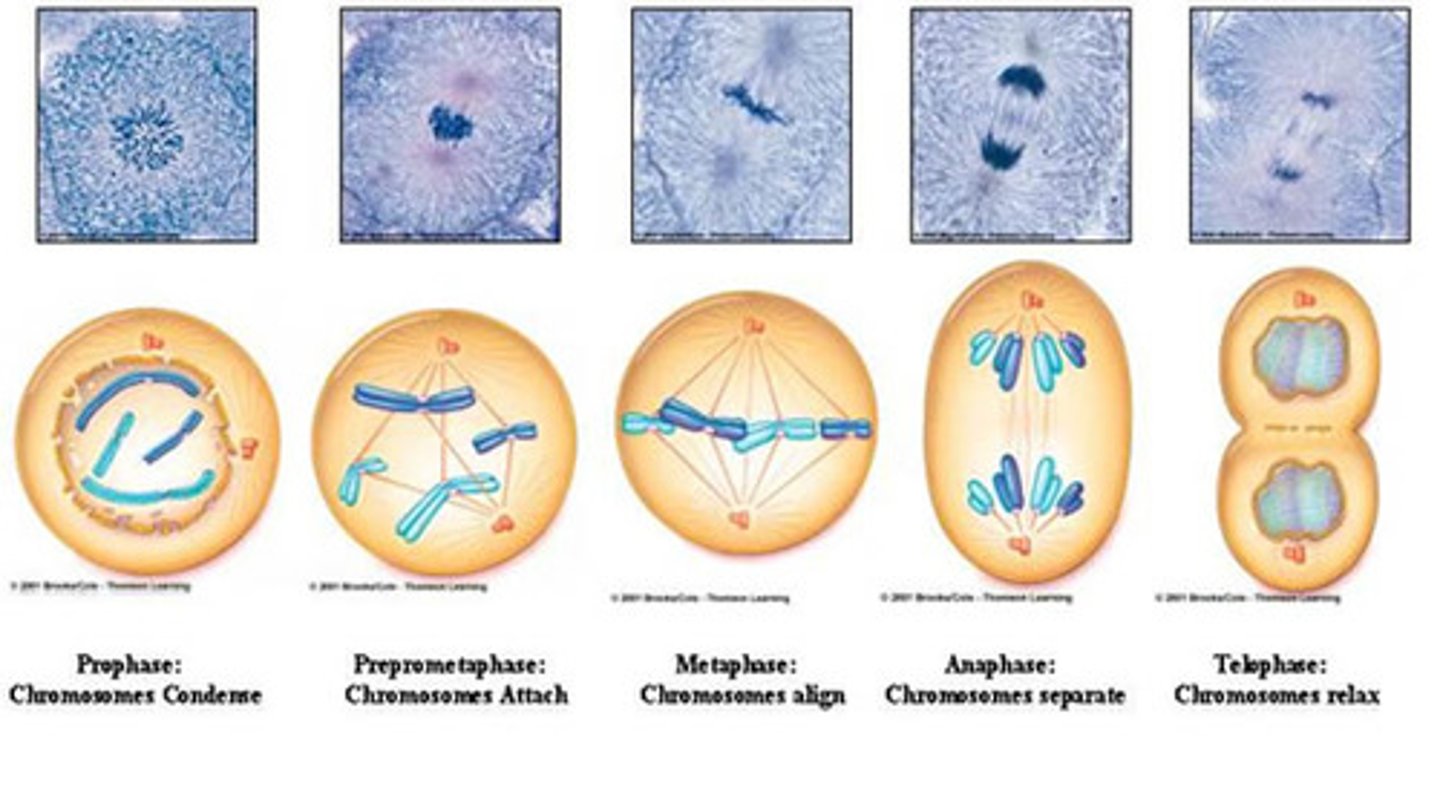
Prophase
first and longest phase of mitosis, during which the chromosomes become visible and the centrioles separate and take up positions on the opposite sides of the nucleus. Mitotic spindle forms fibers in cytoskeleton or centrioles. Kinetochores attach to the centromere. Spindle finished forming between the poles of the cell.

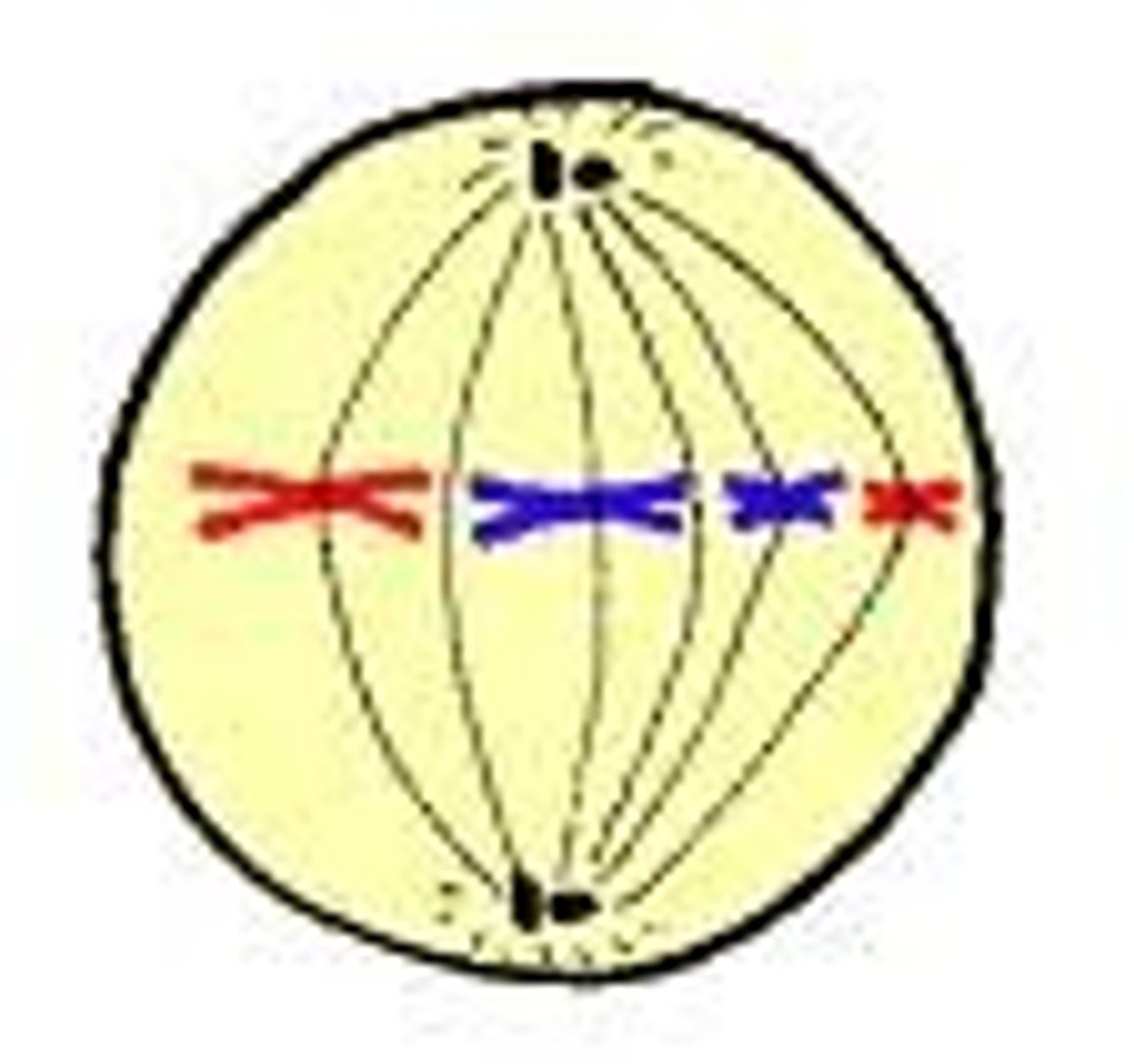
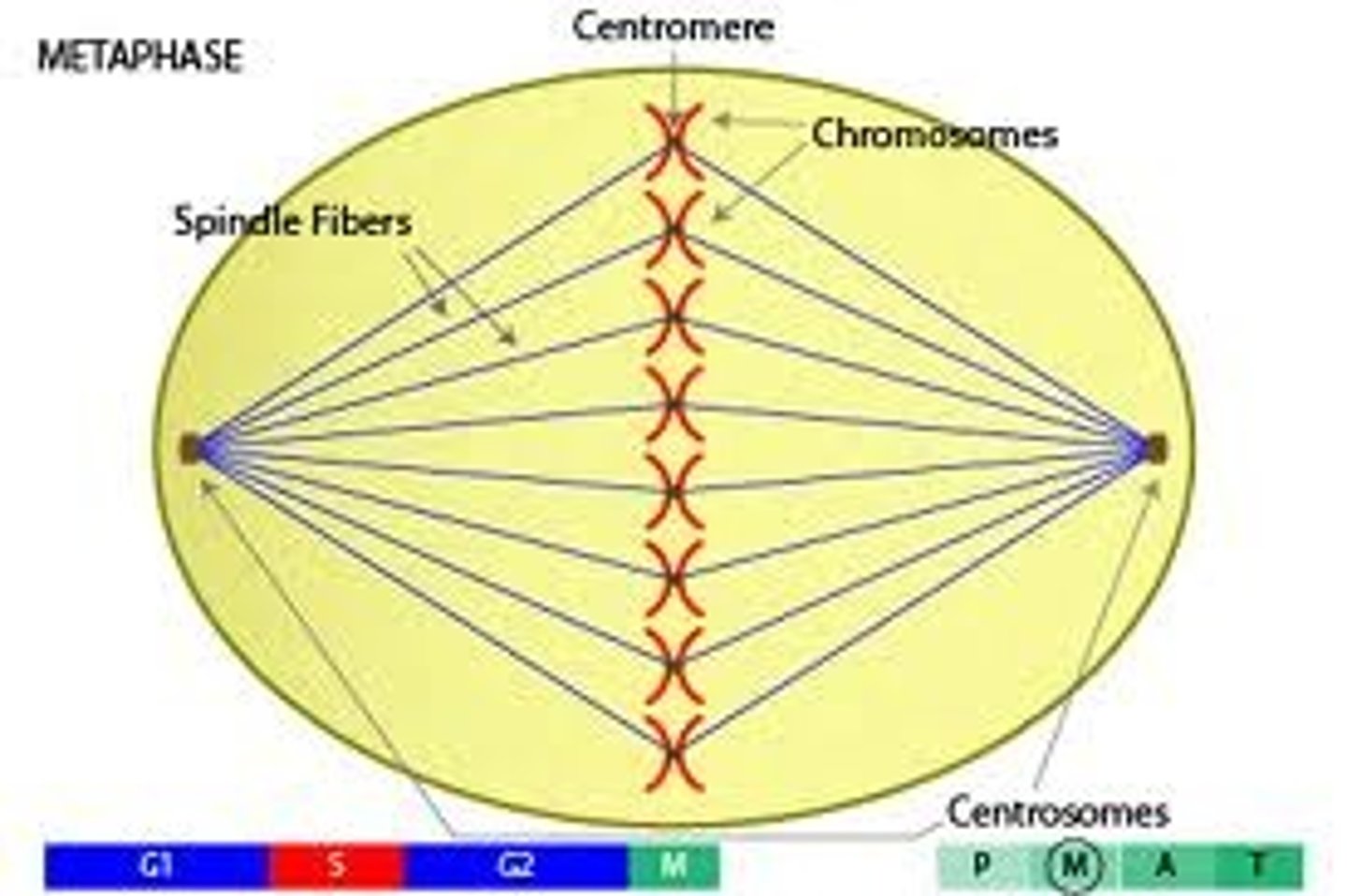
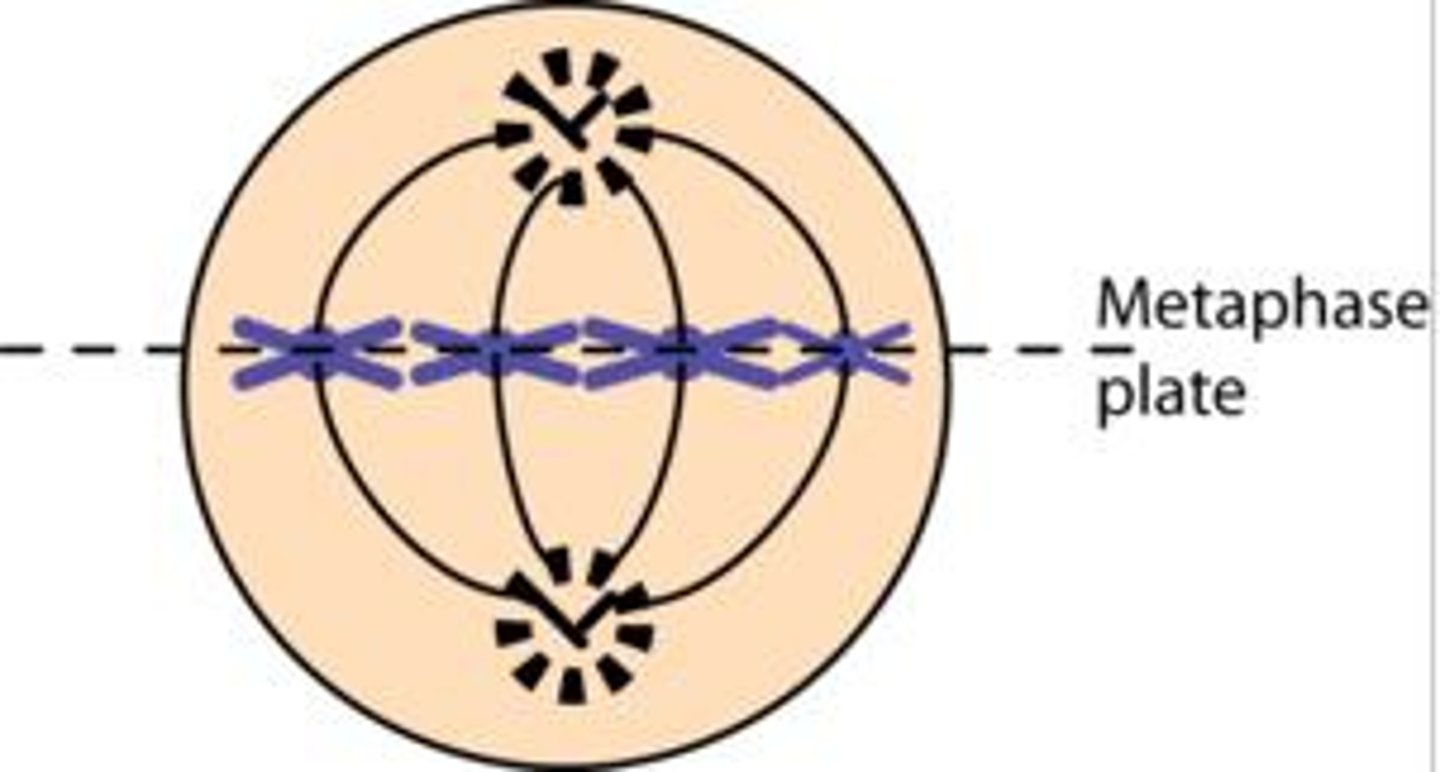
Metaphase
second phase of mitosis, during which the chromosomes line up across the center of the cell
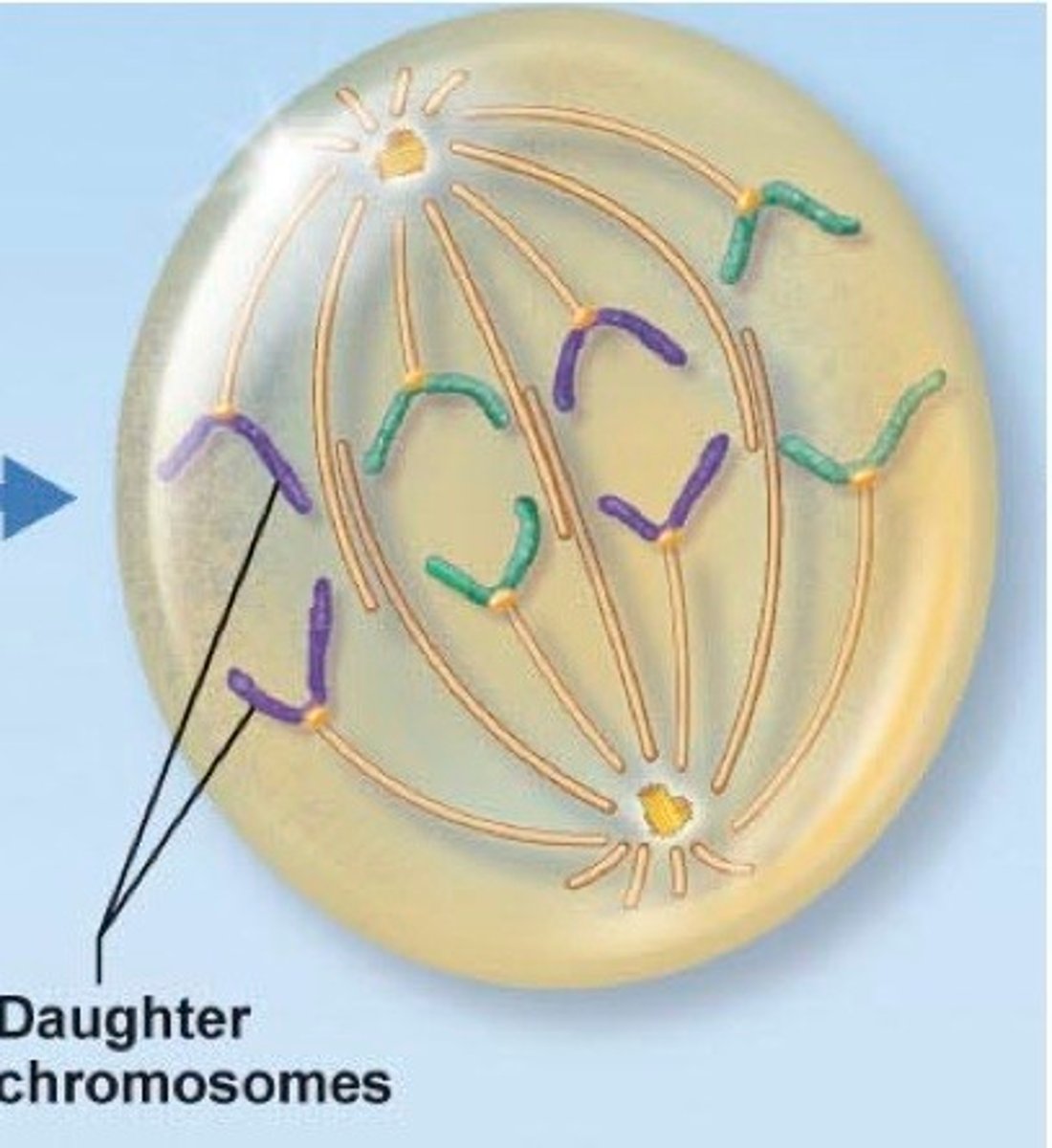
Anaphase
the third phase of mitosis, during which the chromosome pairs separate and move toward opposite poles. Occurs rapidly. Kinetochore help pull the chromosomes to opposite poles.
Telophase
the final phase of cell division, between anaphase and interphase, in which the chromatids or chromosomes move to opposite ends of the cell and two nuclei are formed. spindle disassembles. Nucleolus appears.
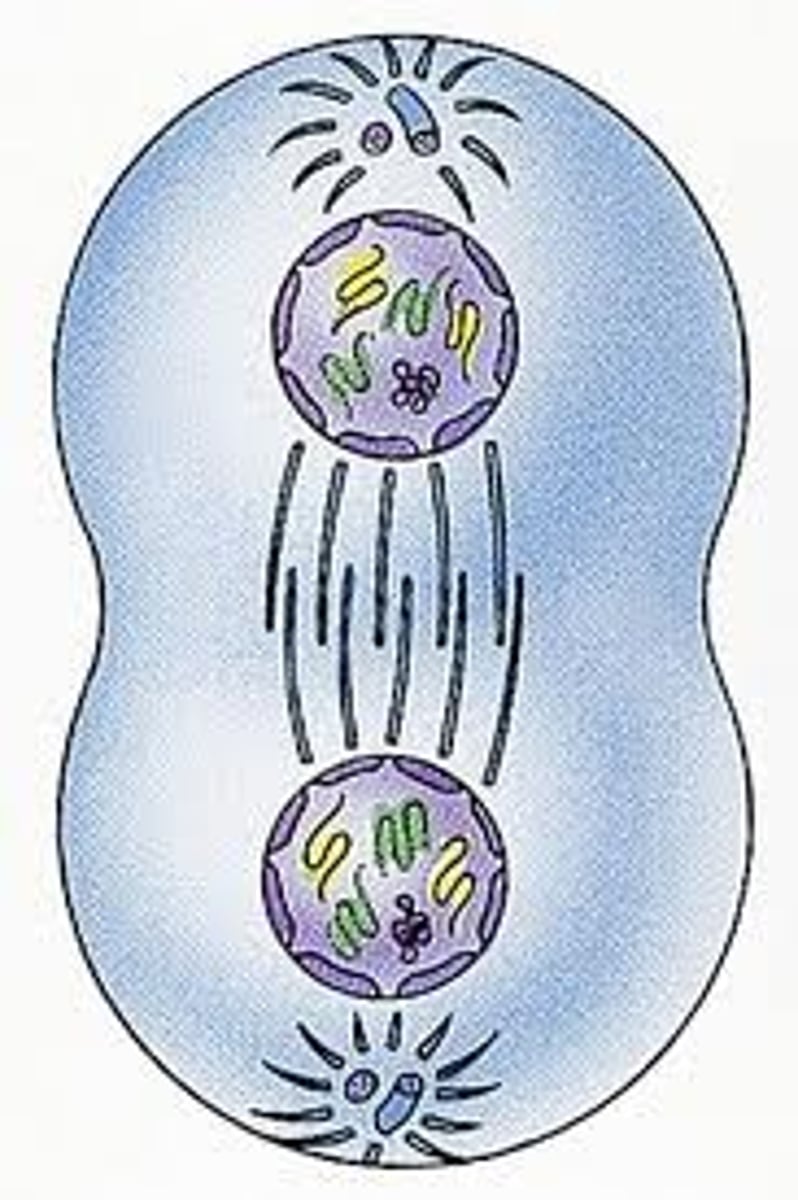
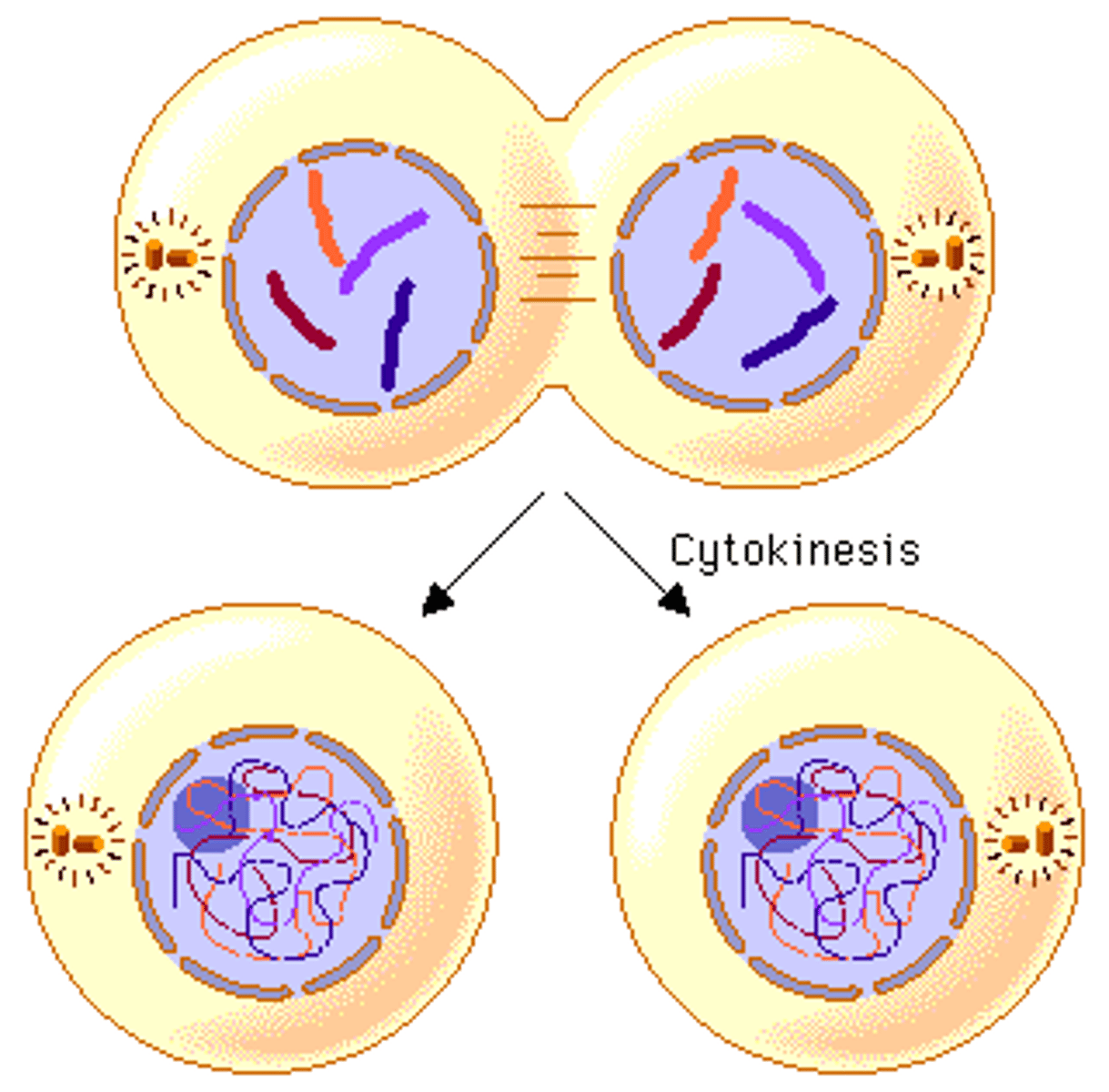
Cytokinesis
Division of the cytoplasm during cell division
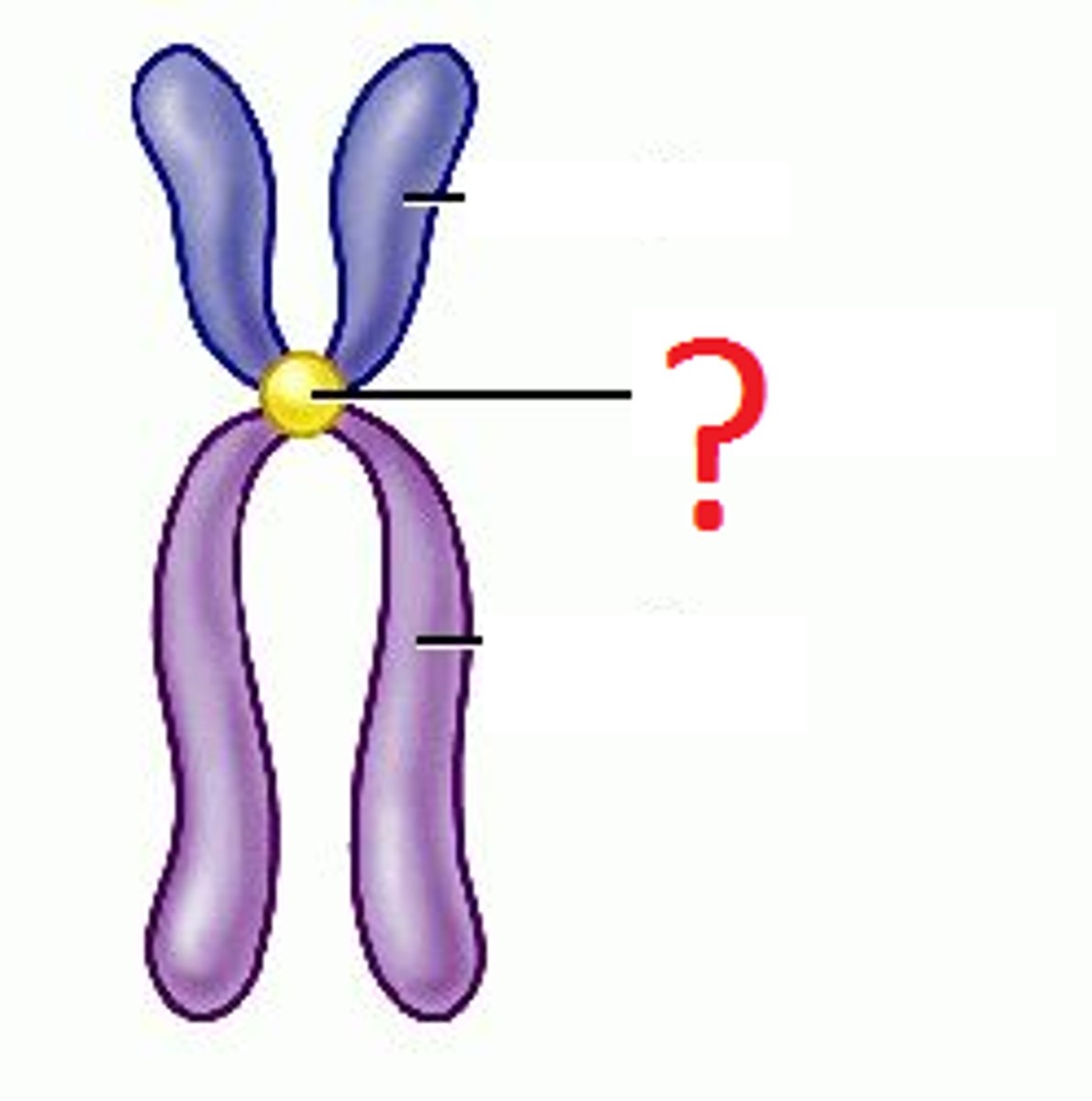
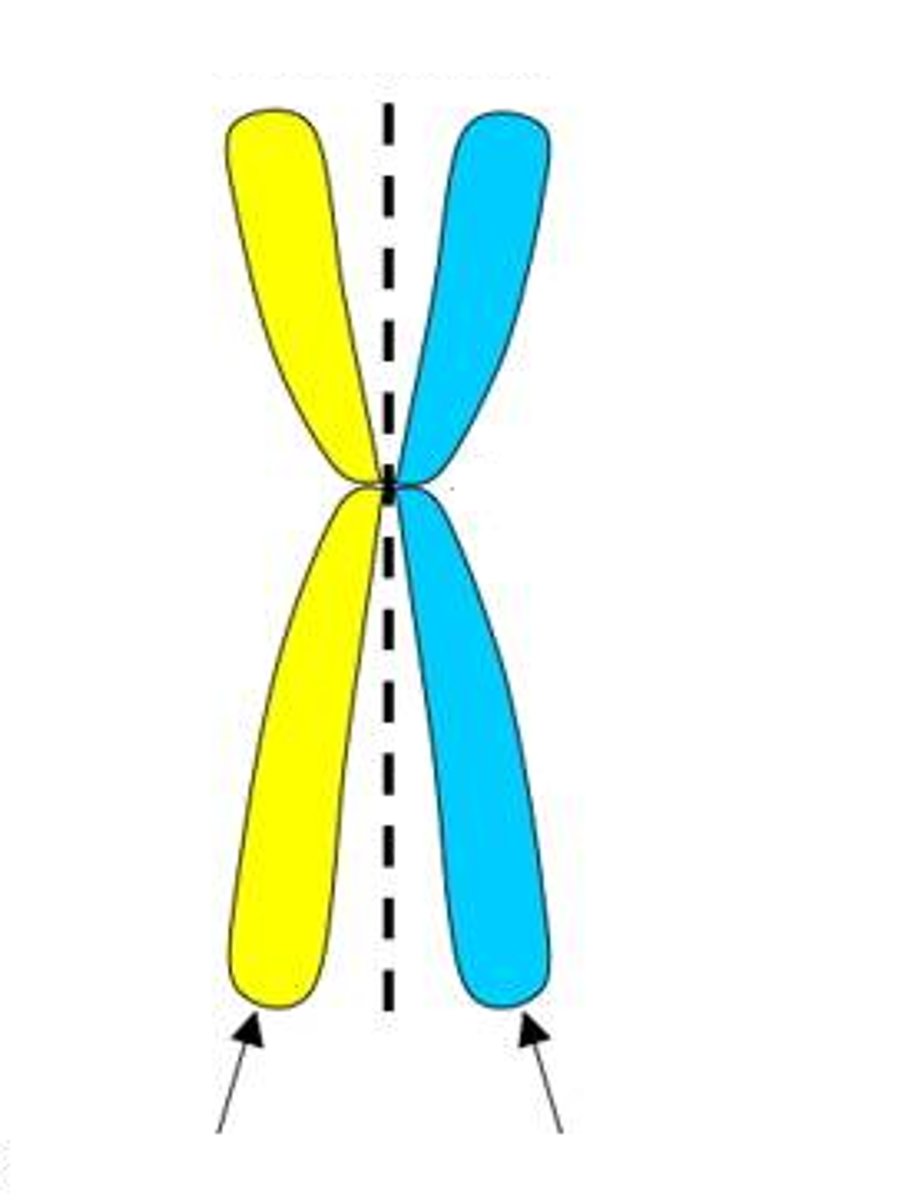
Chromatids
two identical chromosomes that split and contain the same genetic material. Must grow in size to be mature cells
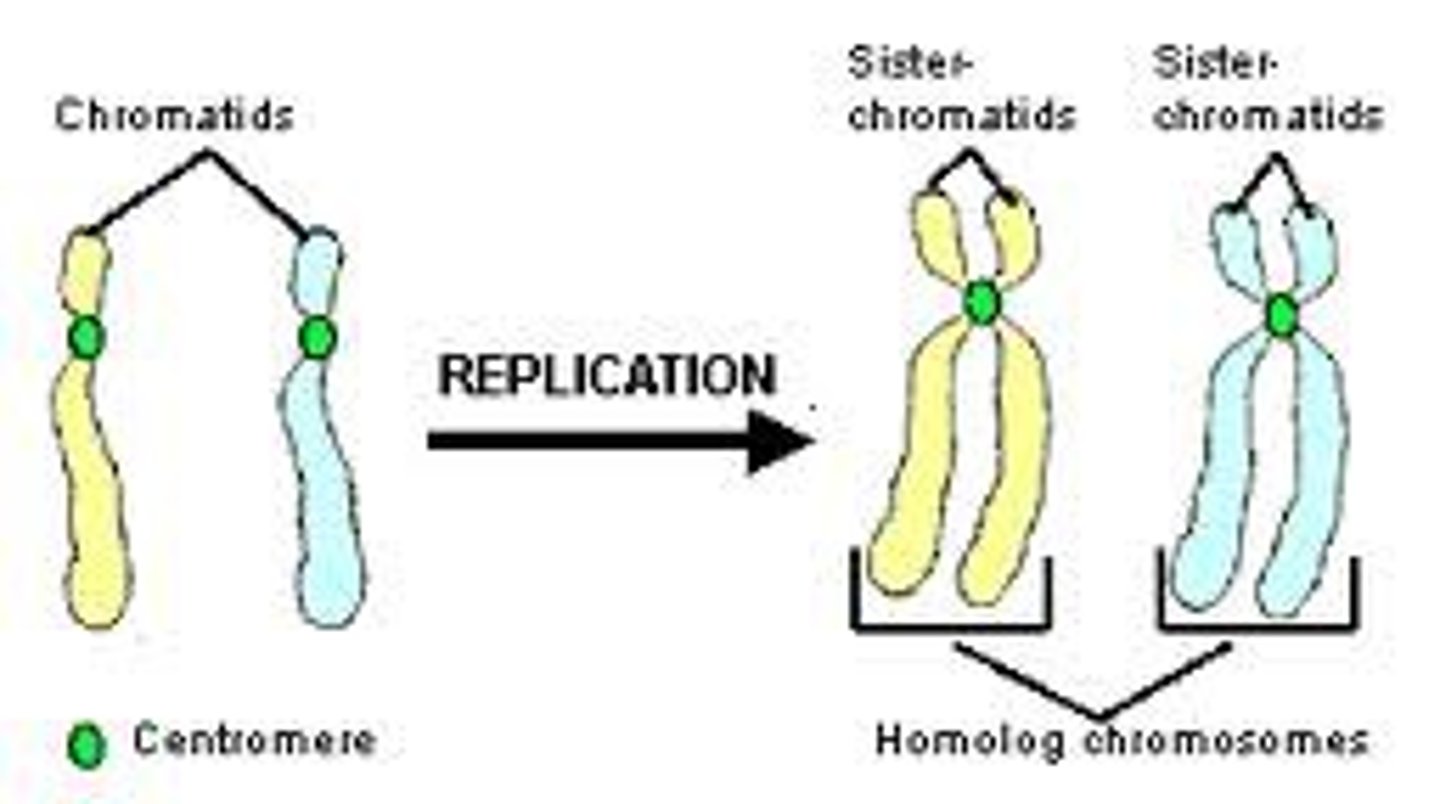
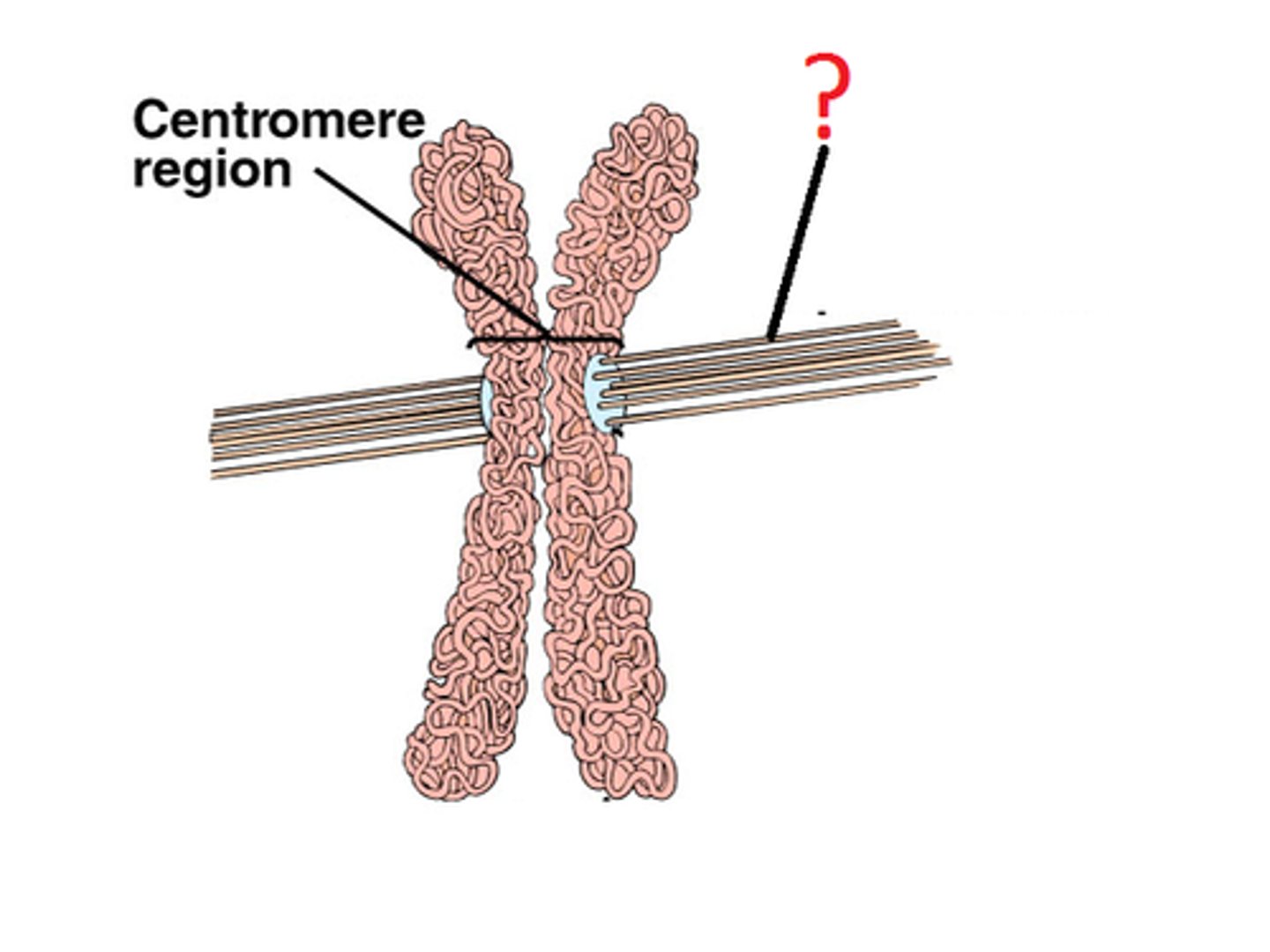
Centromeres
the point on a chromosome by which it is attached to a spindle fiber during cell division.
Spindle Fibers
Protein structures which move the chromosomes during cell division.
Cell Checkpoints
A control point where stop and go signals regulate the cell cycle; G1 checkpoint, G2 checkpoint, M-Spindle checkpoint
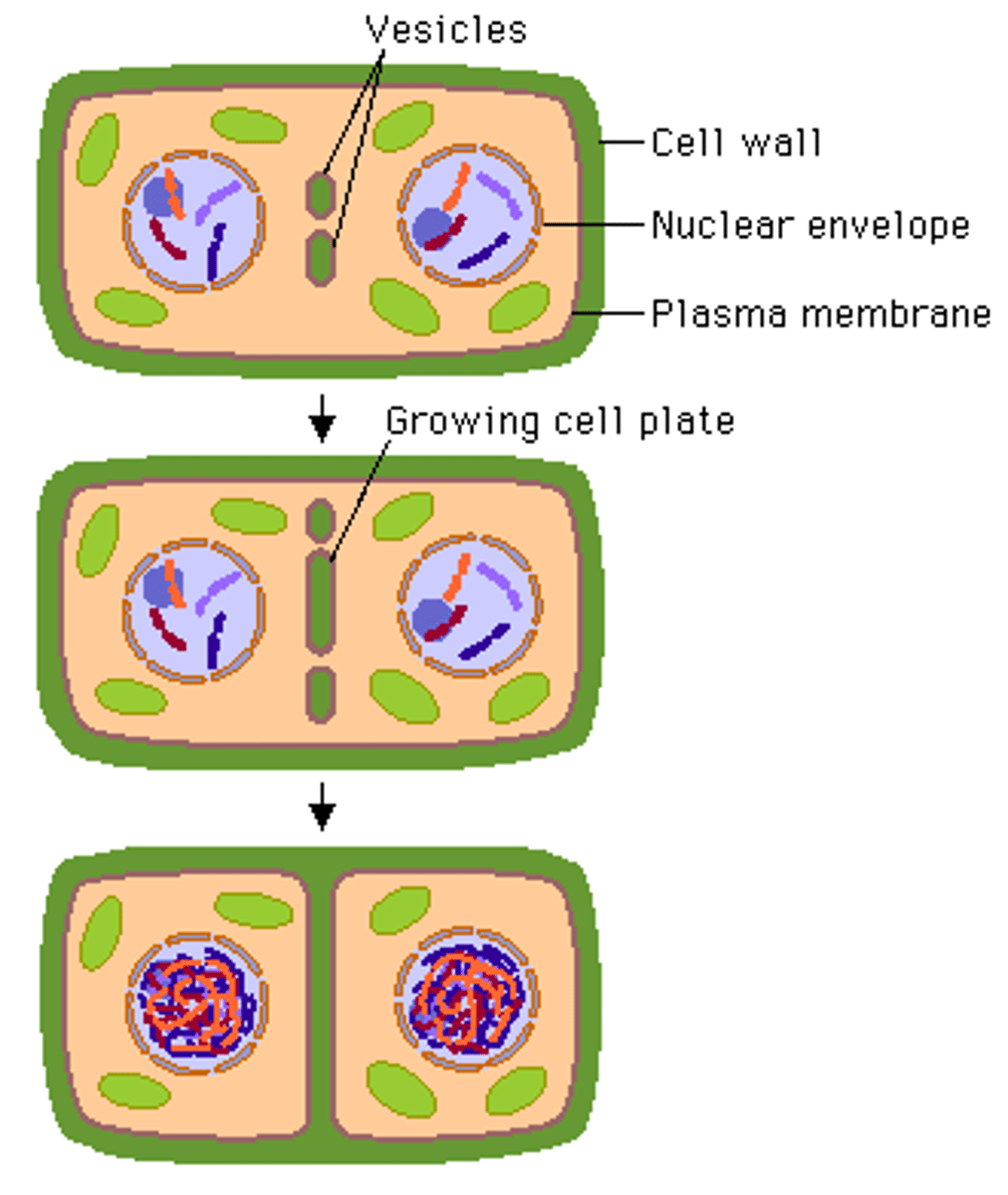
Cytokinesis in Plant Cells
divide from inside out using a cell plate in middle of cell
Cytokinesis in Animal Cells
Cell membrane is drawn inward until the cytoplasm is pinched into two nearly equal parts
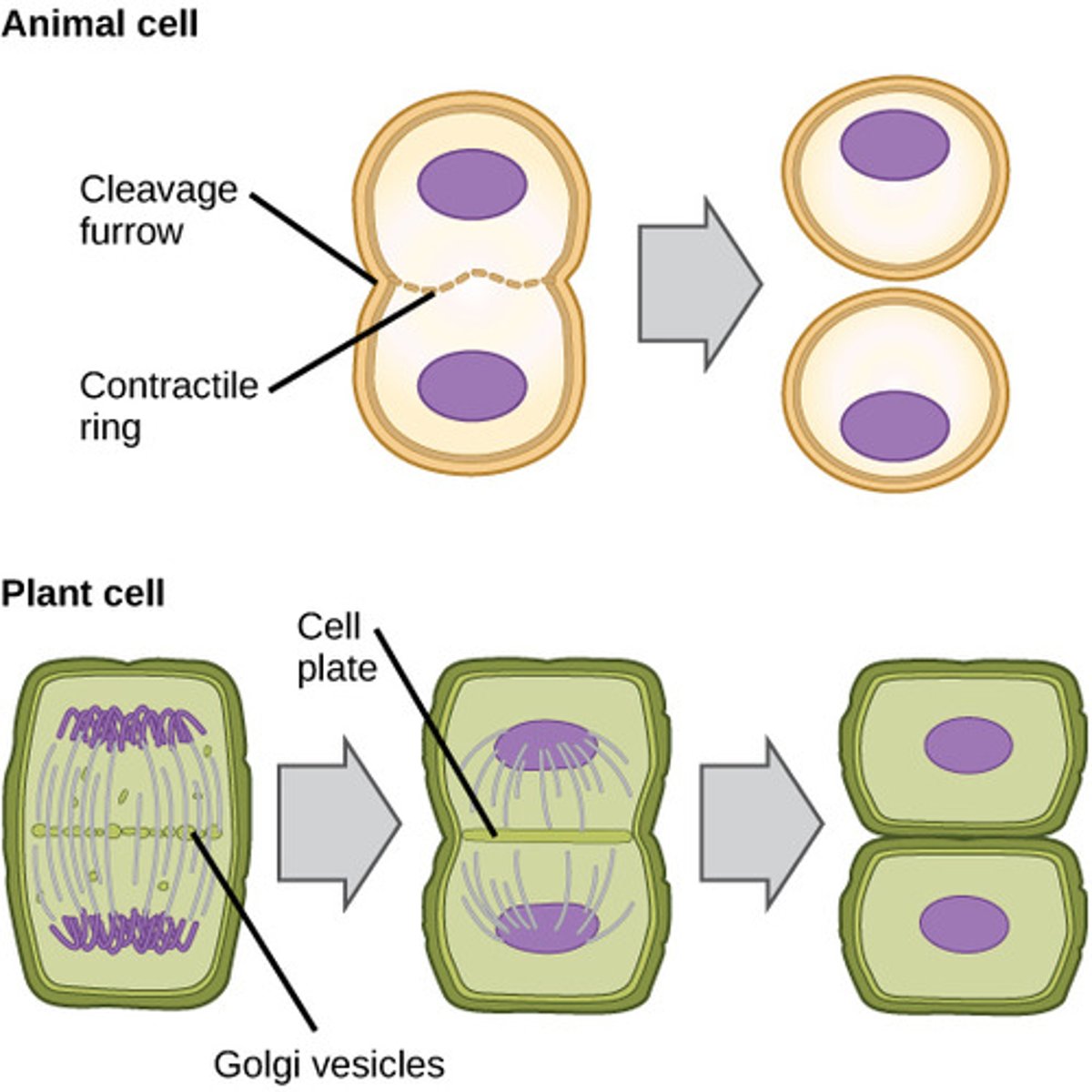
Cleavage forrow
splitting area where drawstring is pulled, breaking cell
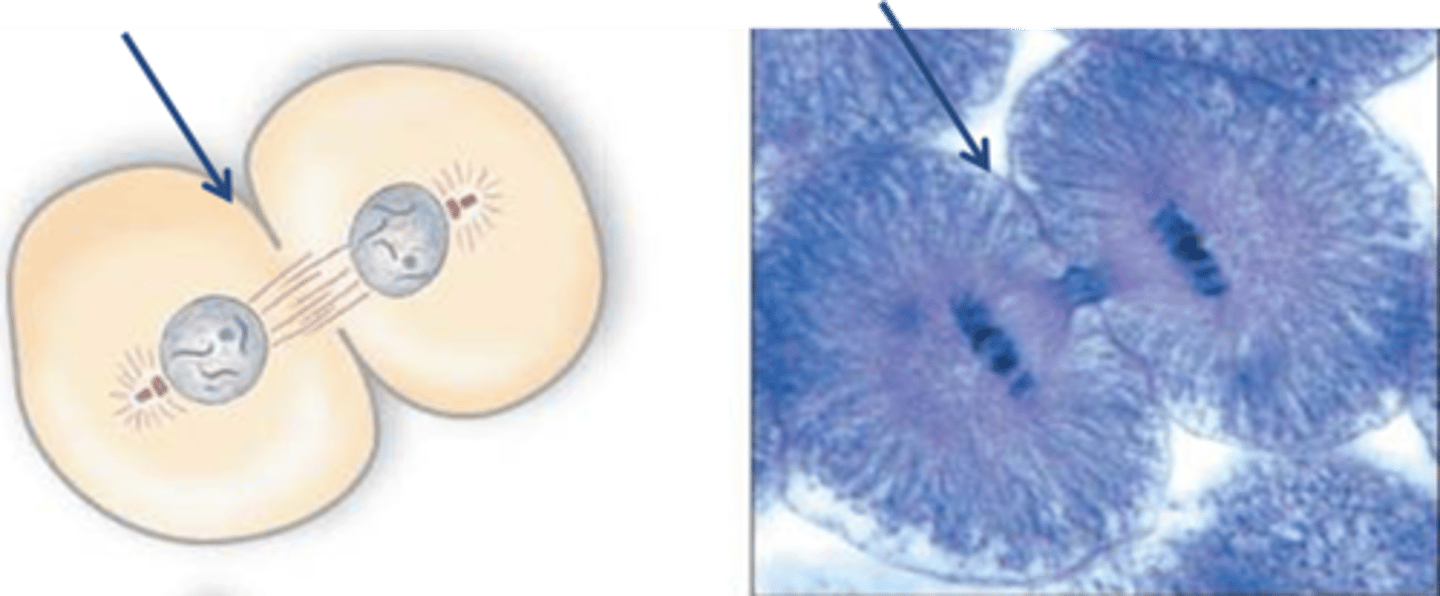
Polar Microtubules
push the poles of the cell away from each other during mitosis
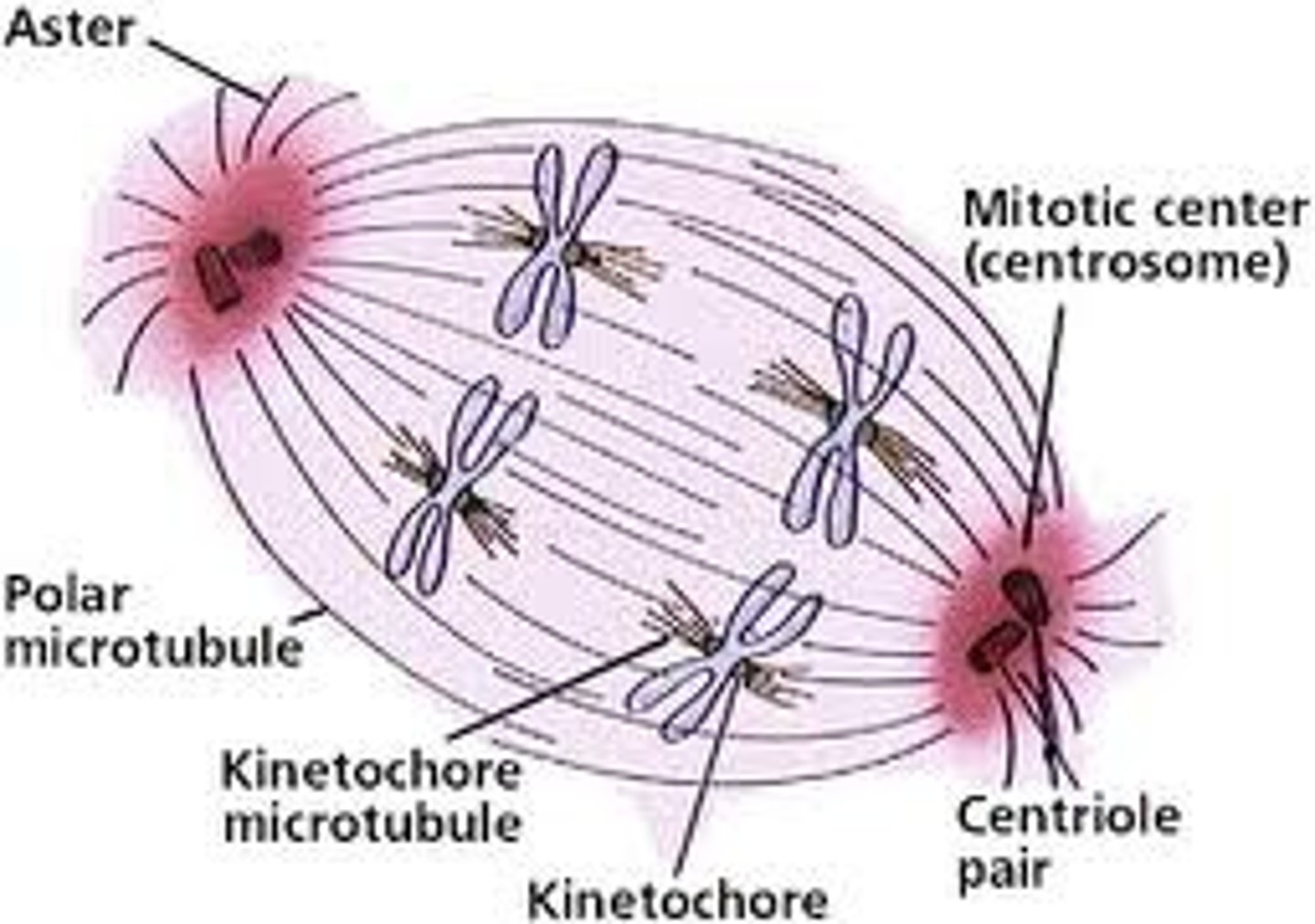
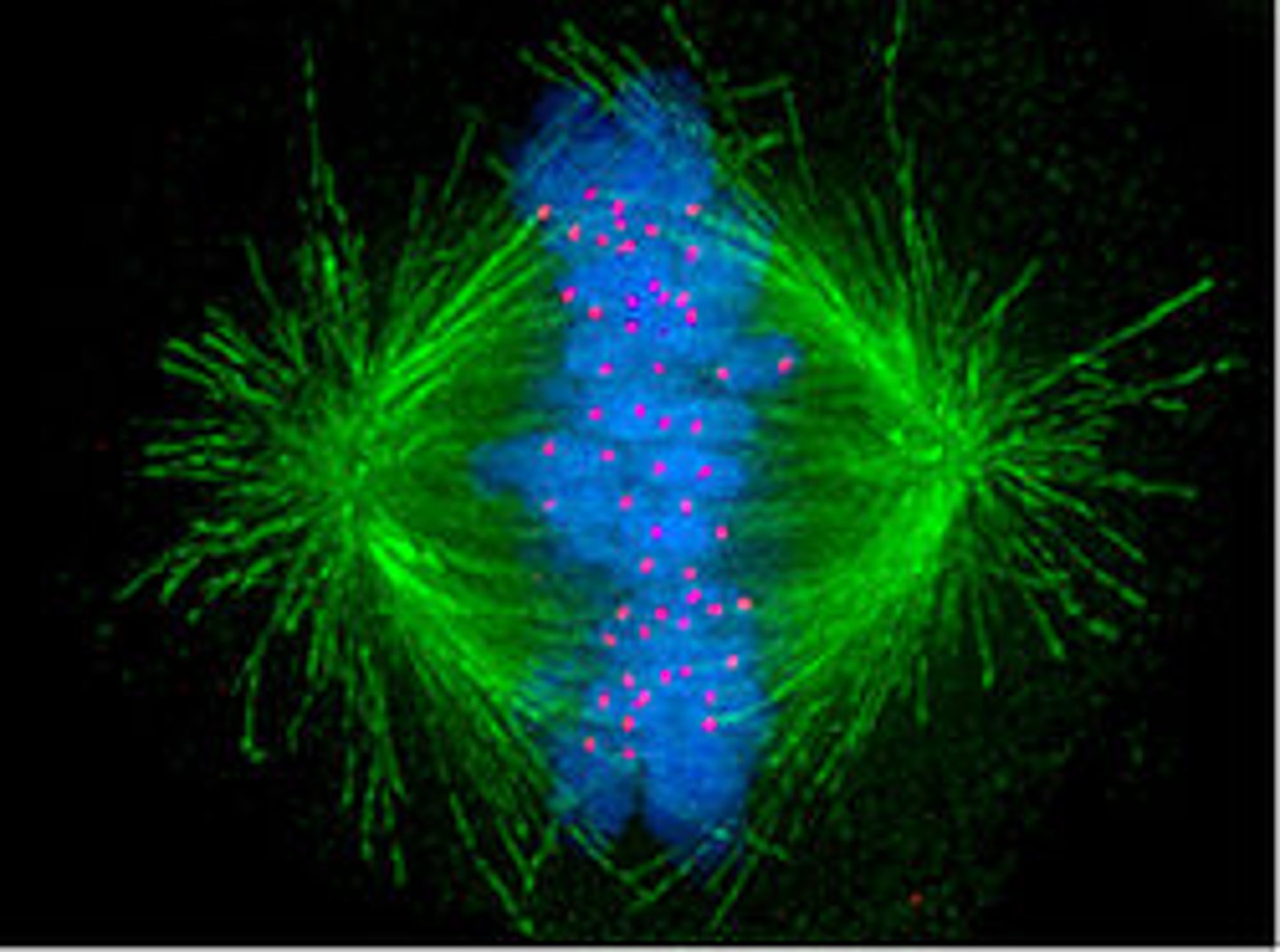
Mitotic Spindle
An assemblage of microtubules and associated proteins that is involved in the movements of chromosomes during mitosis.
Karyokinesis
division of the nucleus
eukaryotic
A cell characterized by the presence of a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. Eukaryotes can be unicellular (protists) or multicellular (fungi, plants and animals).
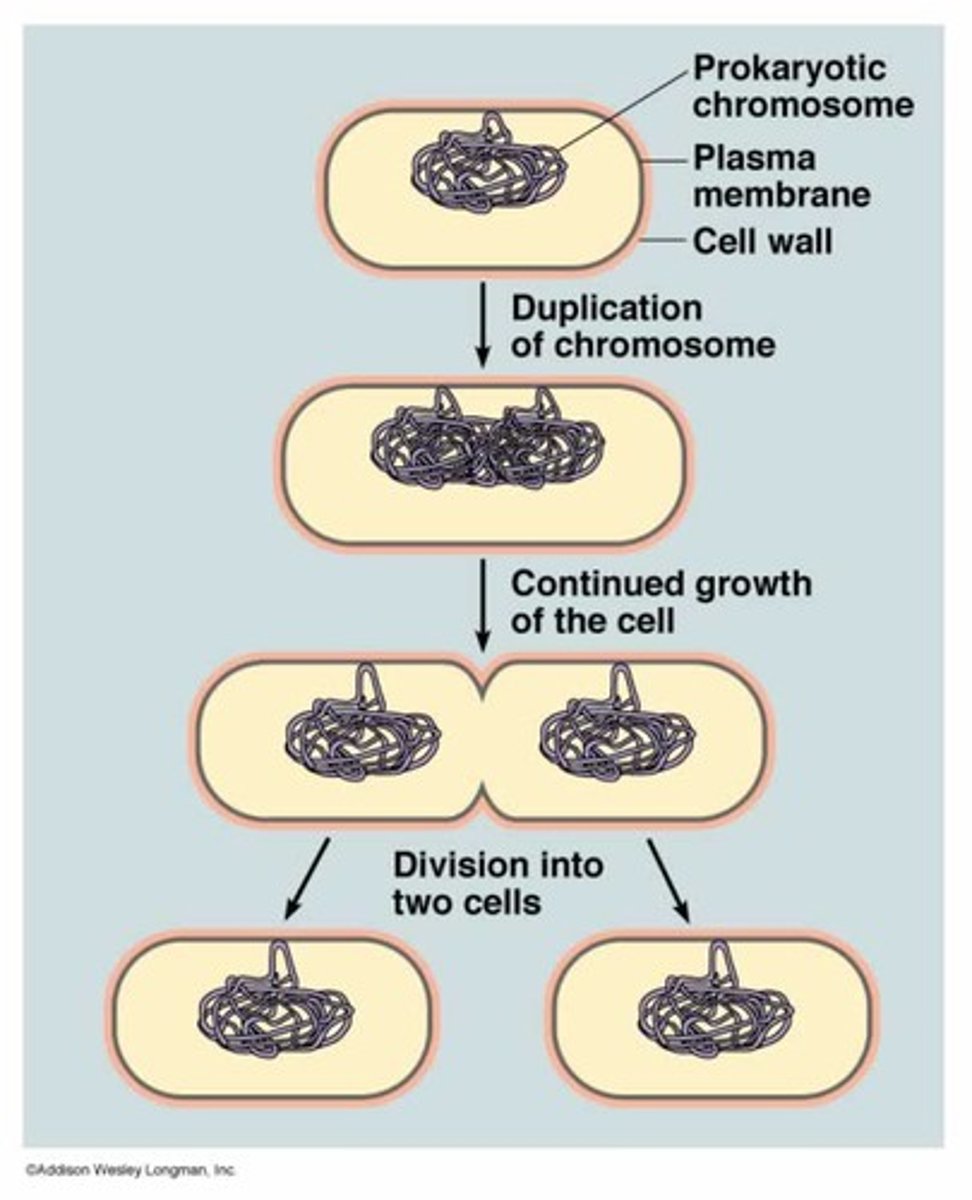
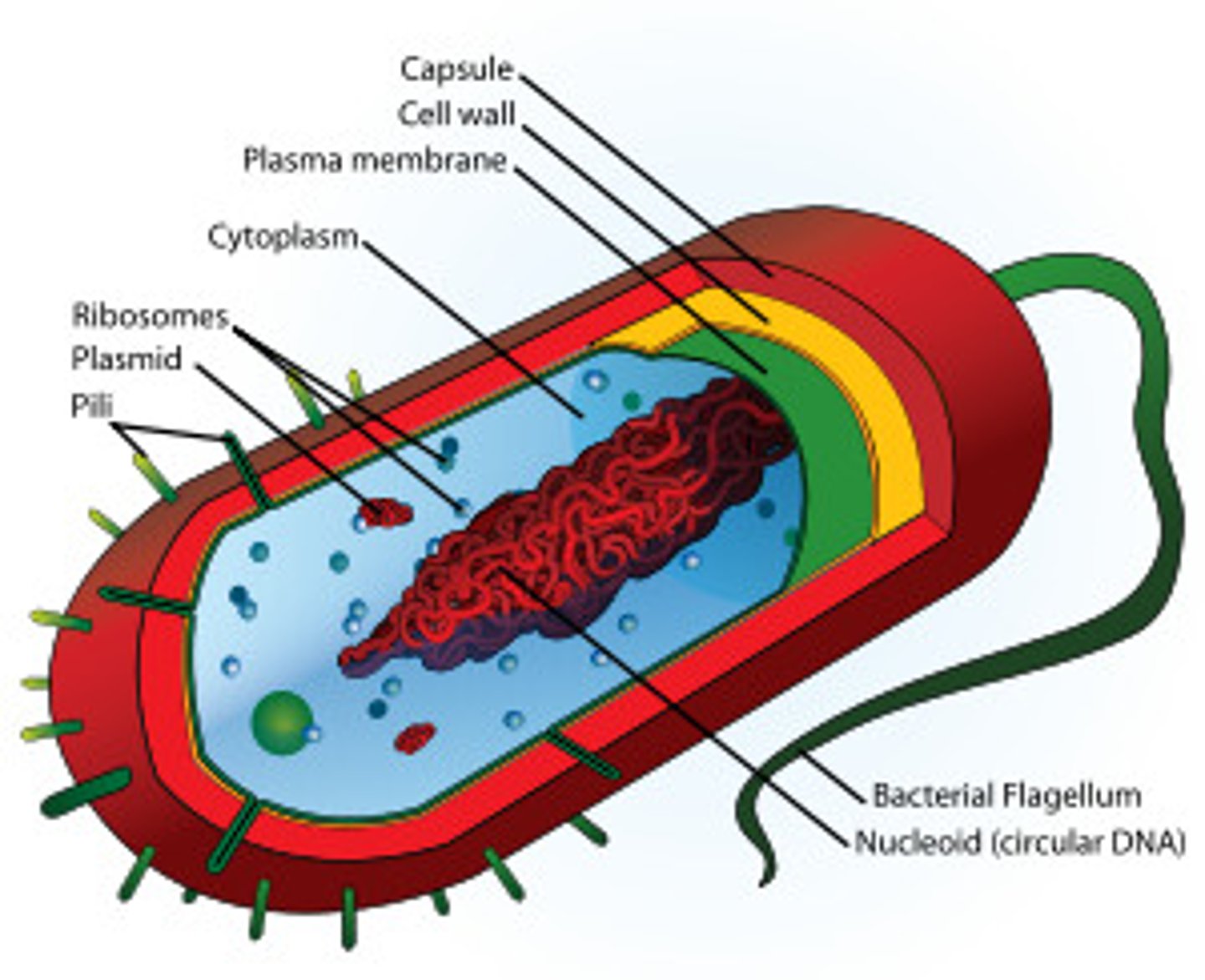
Prokaryotic Cells
do not have a nucleus or other membrane-bound organelles
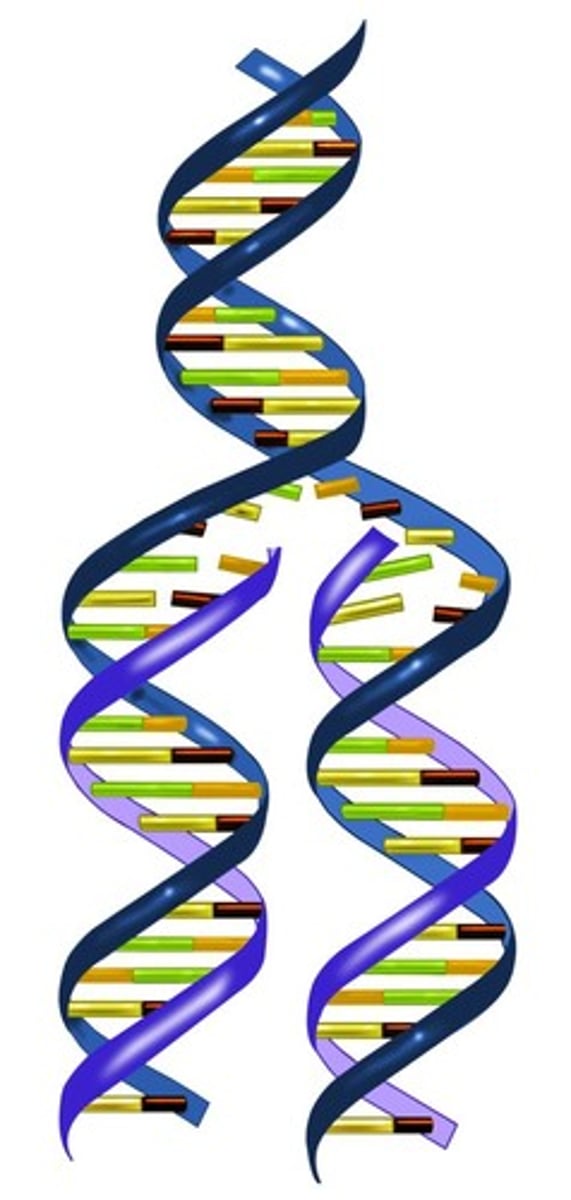
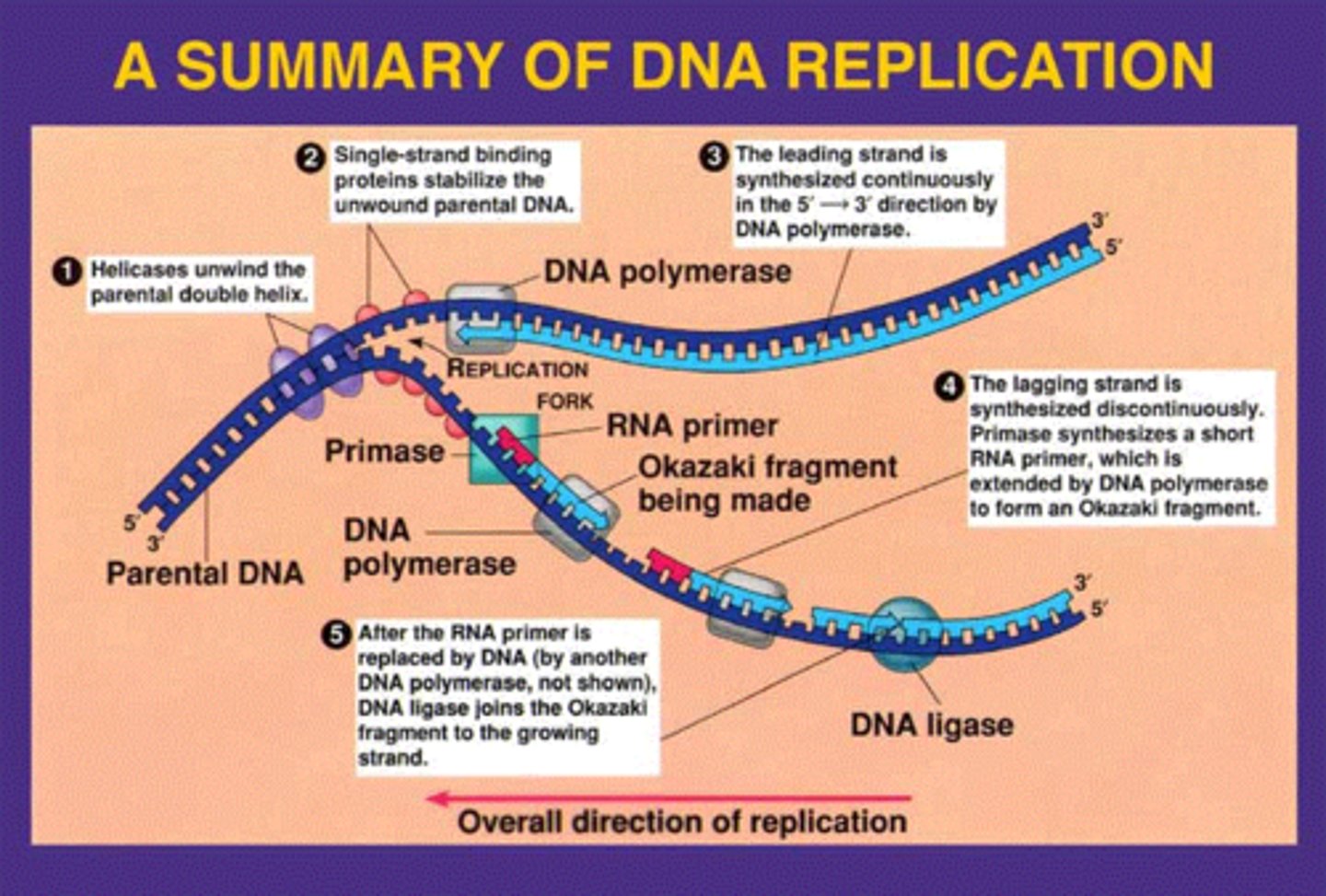
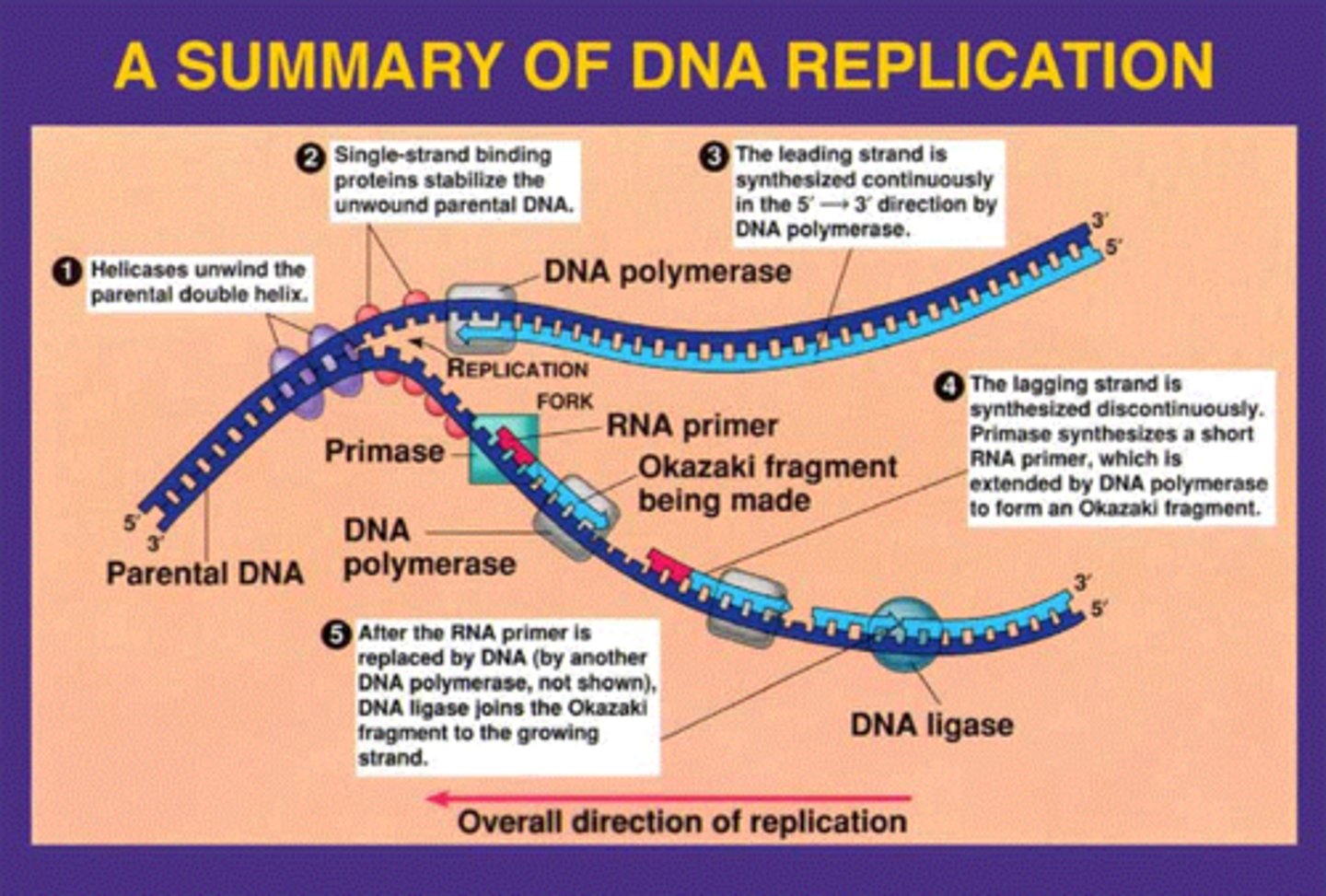
DNA Replication
DNA unzips into two parts and splits with the cell. In it's new home each side of the DNA strand attack to matching nucleotides to create 2 exact copies. It is important in puberty and other times of growth as it is the reproducing of your cells.

Process of DNA Replication
Enzymes unzip the DNA by breaking the hydrogen bonds between base pairs
The enzyme DNA polymerase joins individual nucleotides to form the complimentary strand to the existing DNA single strand
DNA polymerase also proof reads each new DNA strand to make sure each new molecule is an exact copy of the original DNA molecule
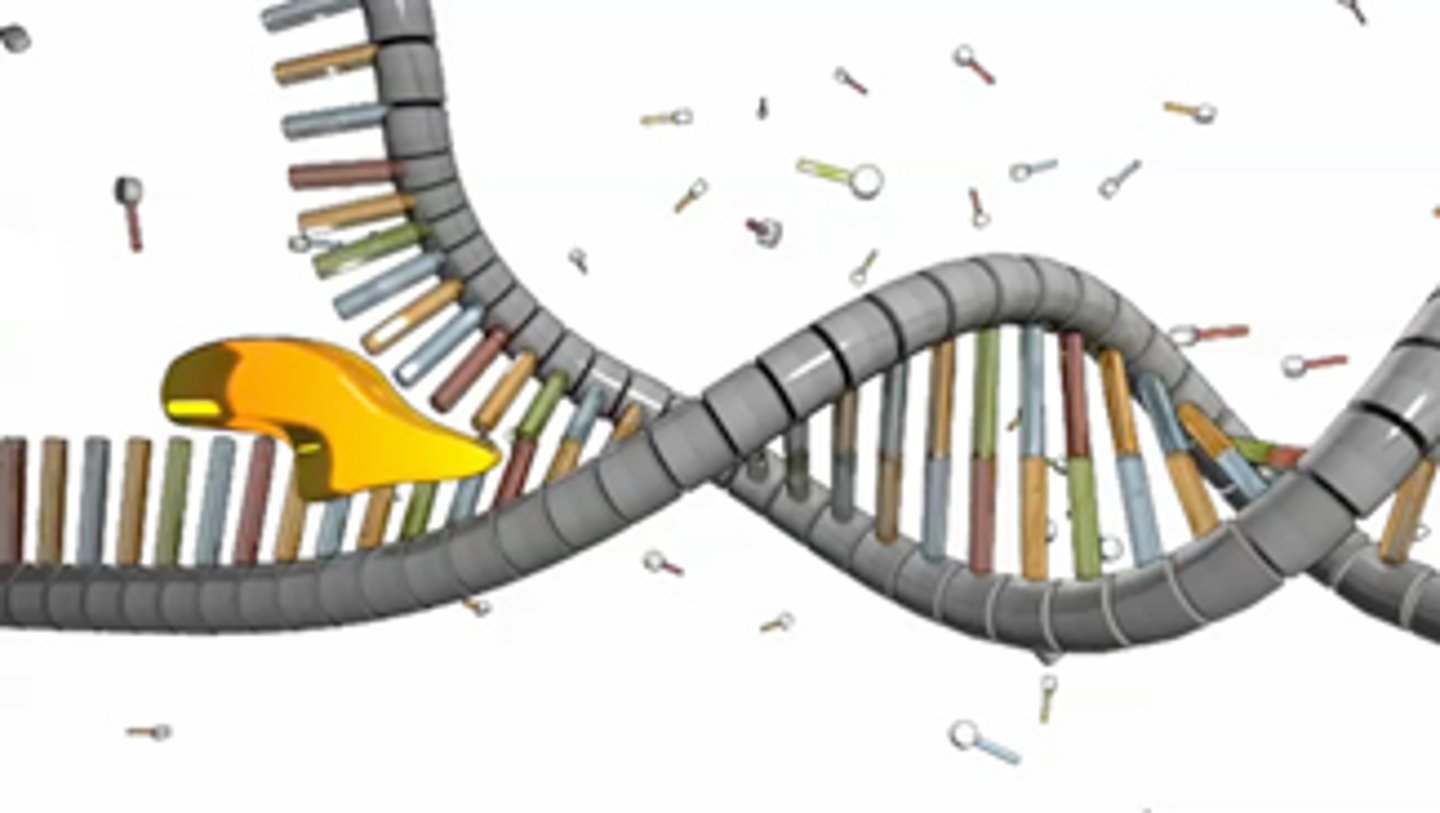
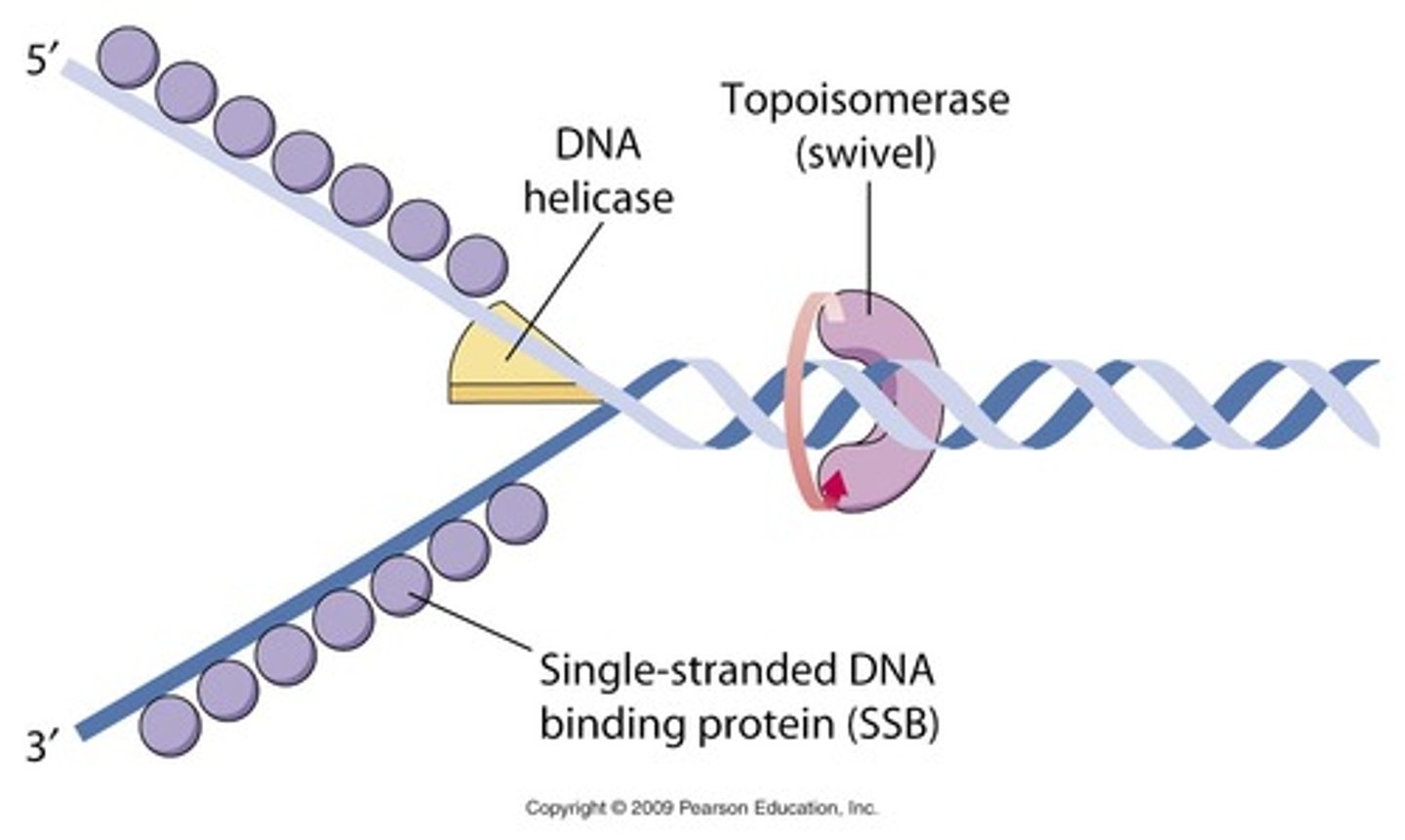
Helicase
An enzyme that untwists the double helix of DNA at the replication forks.
Primase
An enzyme that joins RNA nucleotides to make the primer using the parental DNA strand as a template.
Polymerase
DNA polymerases are enzymes that create DNA molecules by assembling nucleotides, the building blocks of DNA. These enzymes are essential to DNA replication and usually work in pairs to create two identical DNA strands from one original DNA molecule.
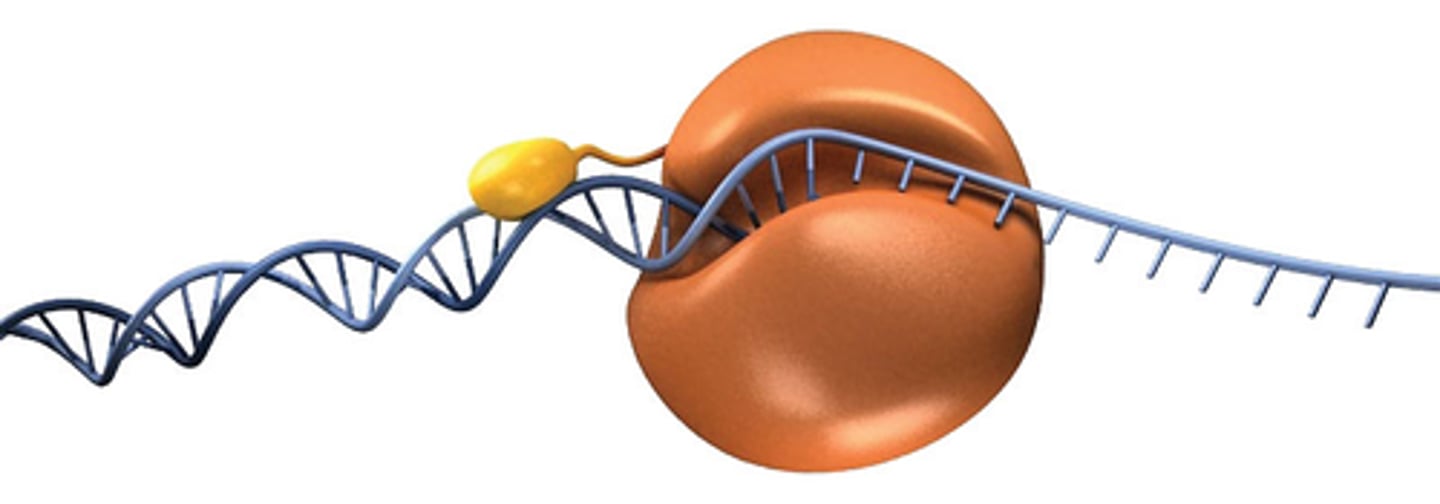
Ligase
An enzyme that connects two fragments of DNA to make a single fragment

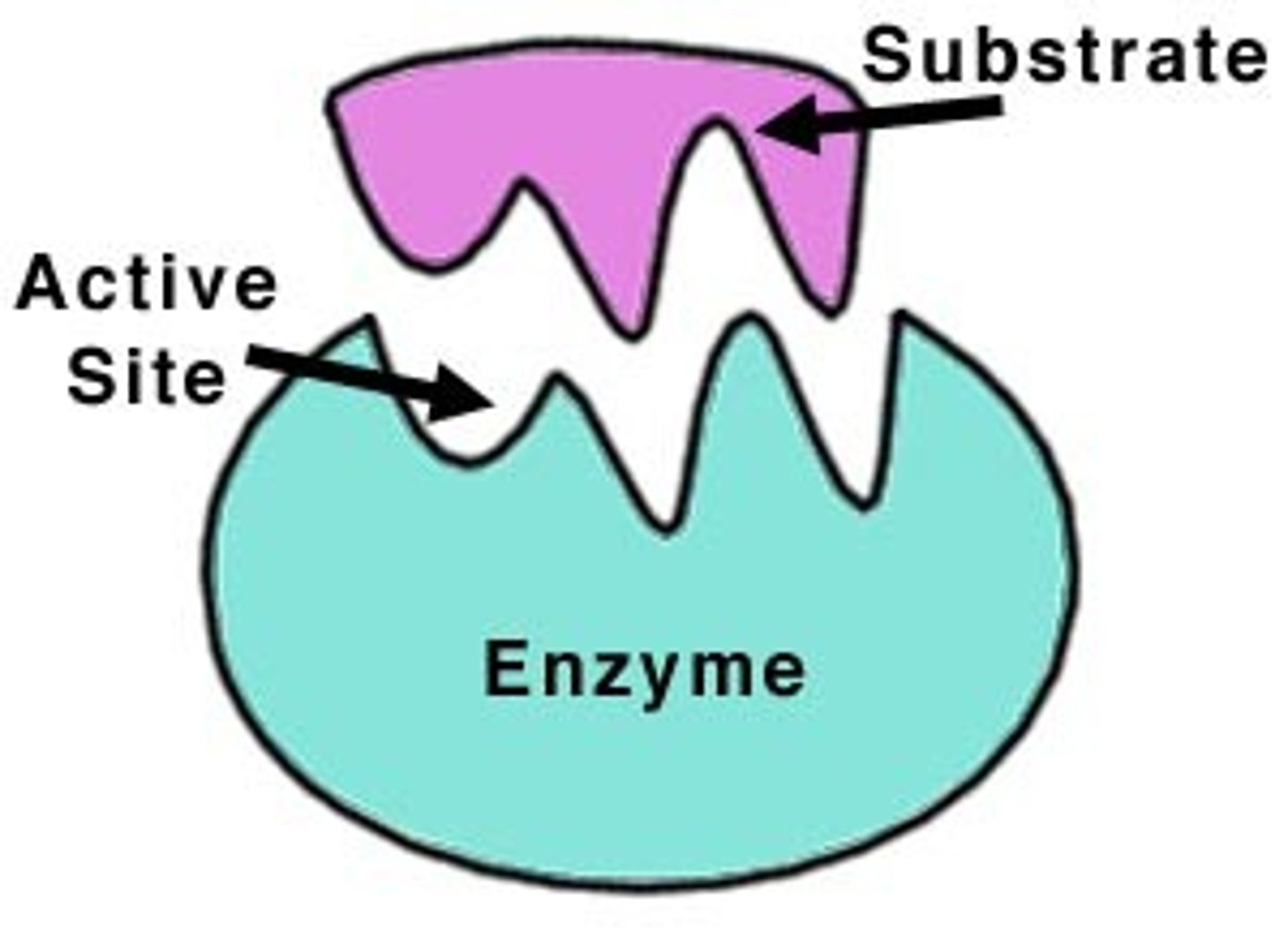
Enzymes
Catalysts for chemical reactions in living things
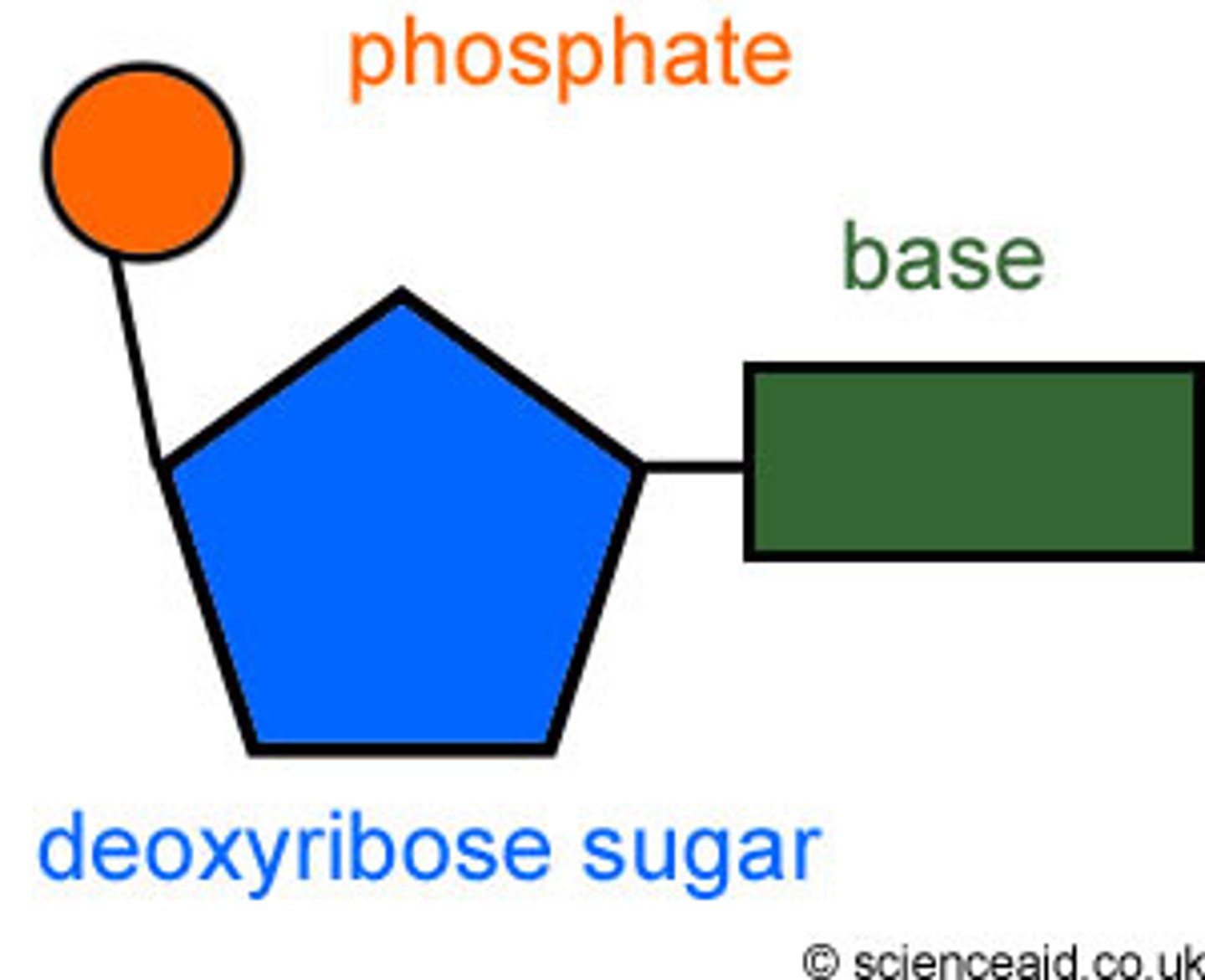
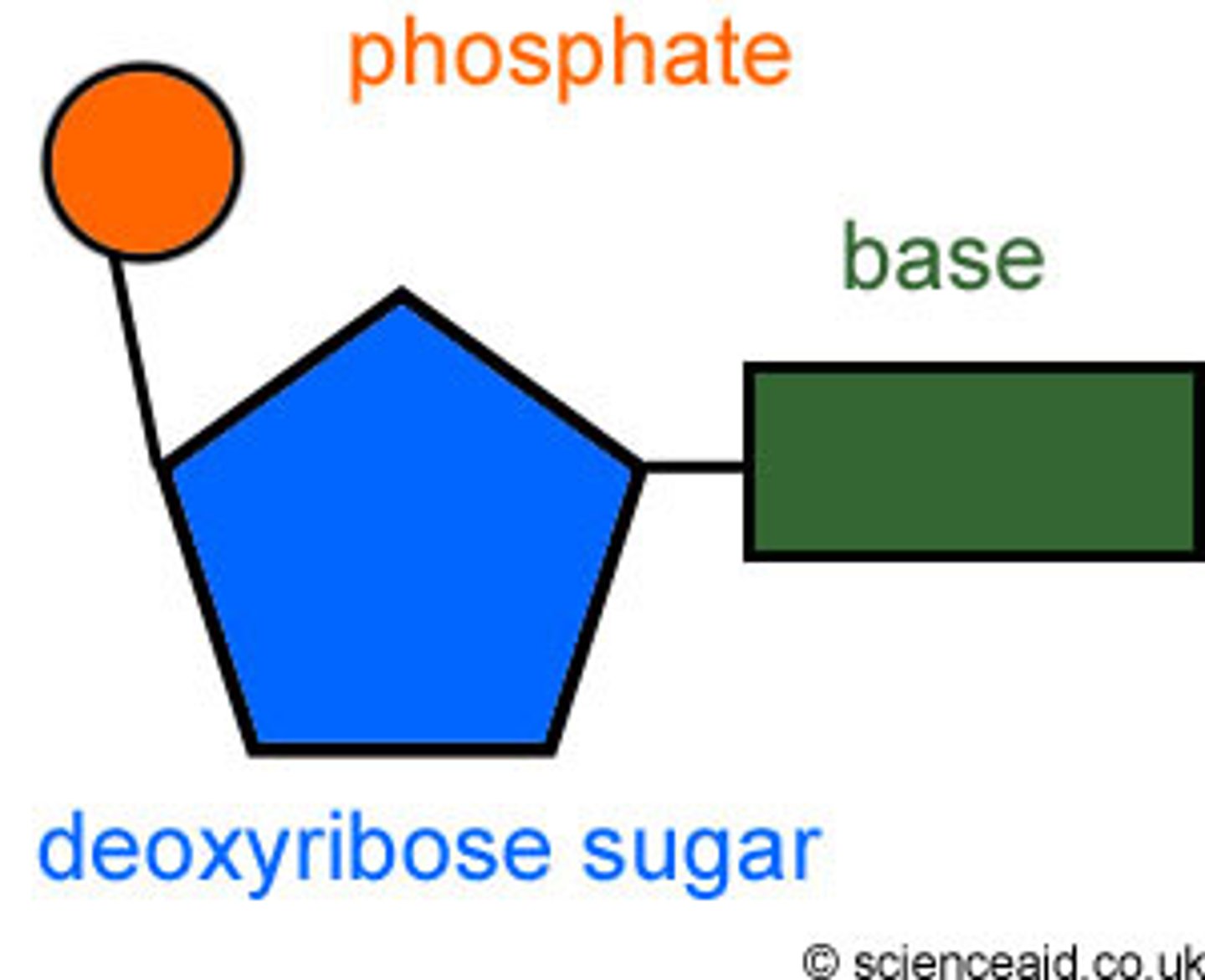
Nucleotides
Basic units of DNA molecule, composed of a sugar, a phosphate, and one of 4 DNA bases
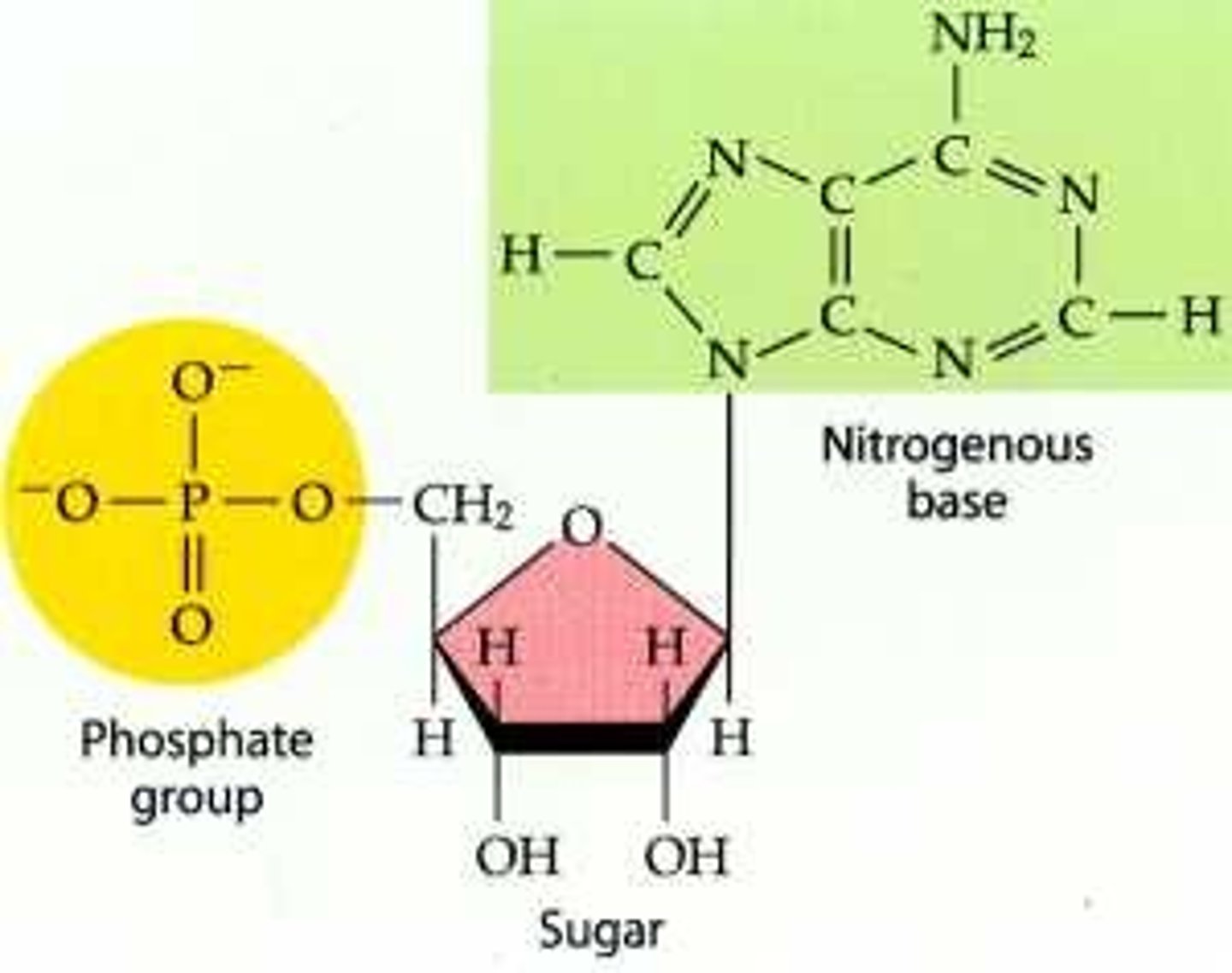
Nucleic Acid
macromolecule containing hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, carbon, and phosphorus
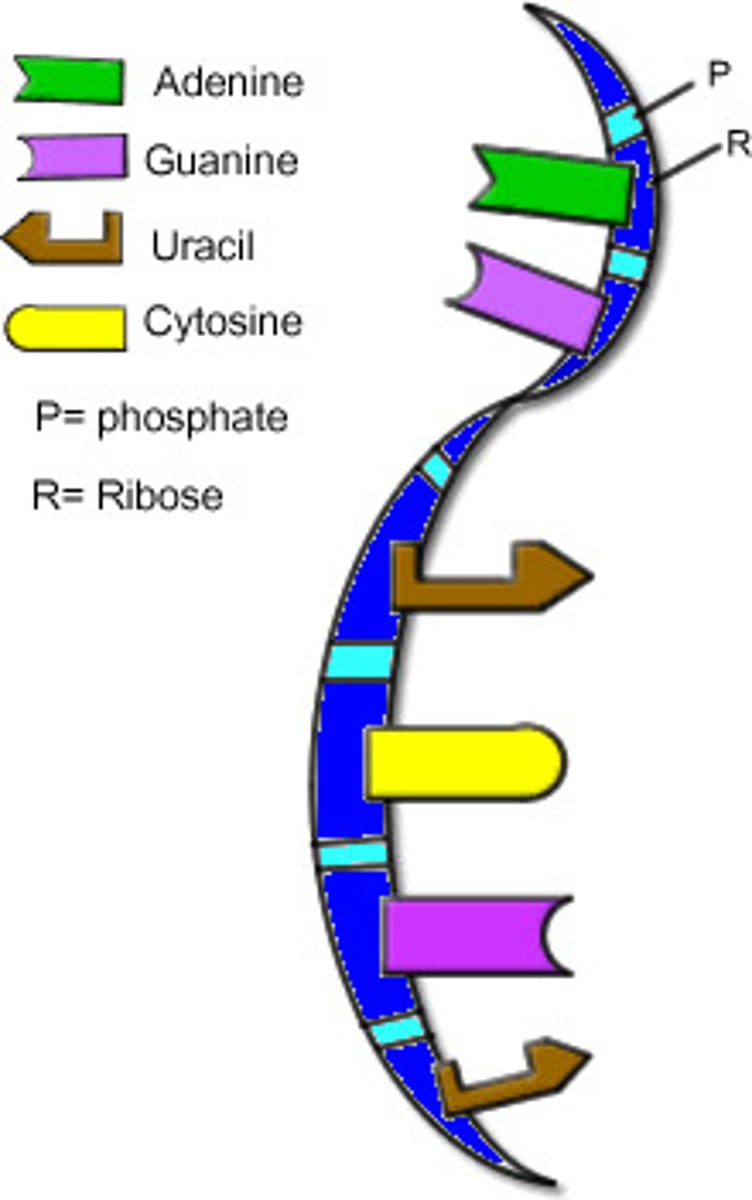
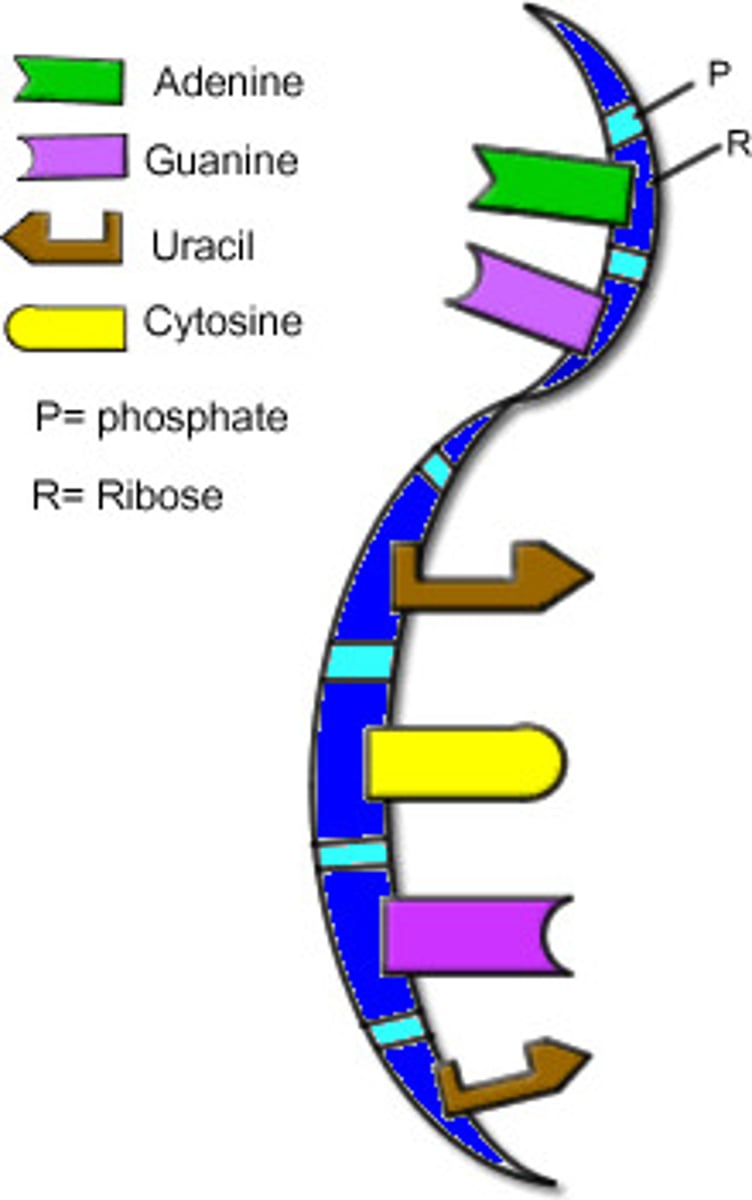
Ribonucleic Acid
(RNA) single-stranded nucleic acid that contains the sugar ribose
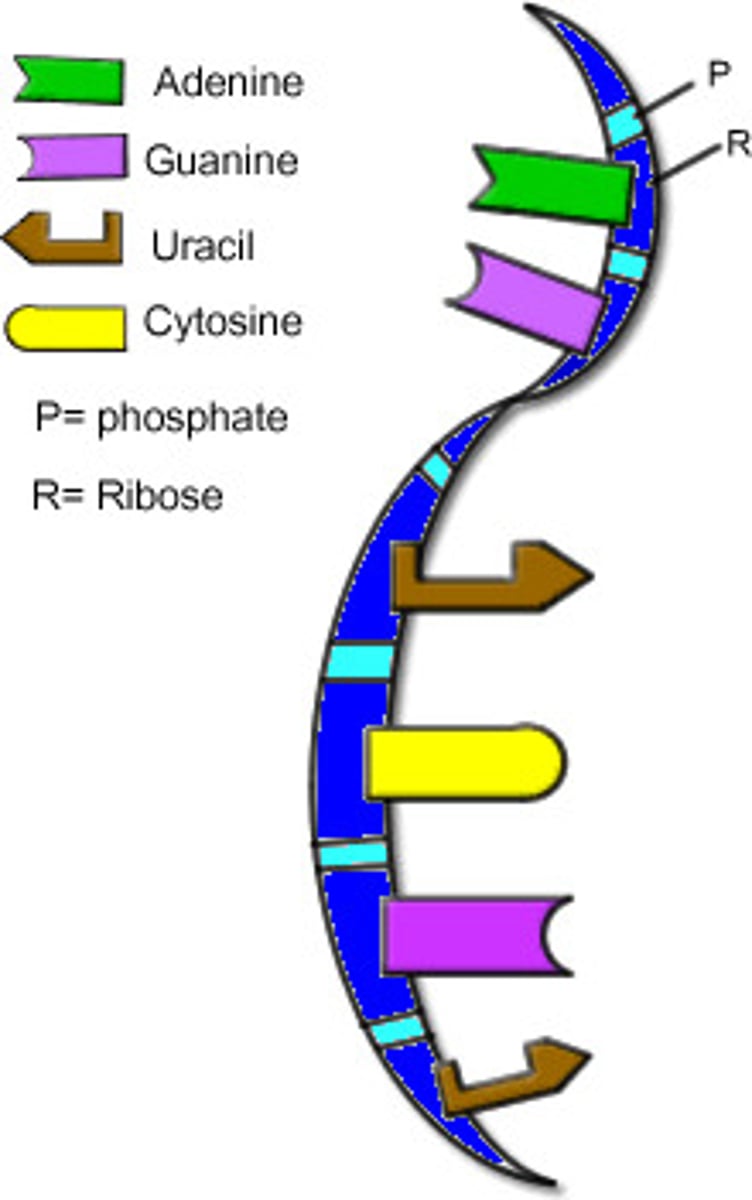
Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid
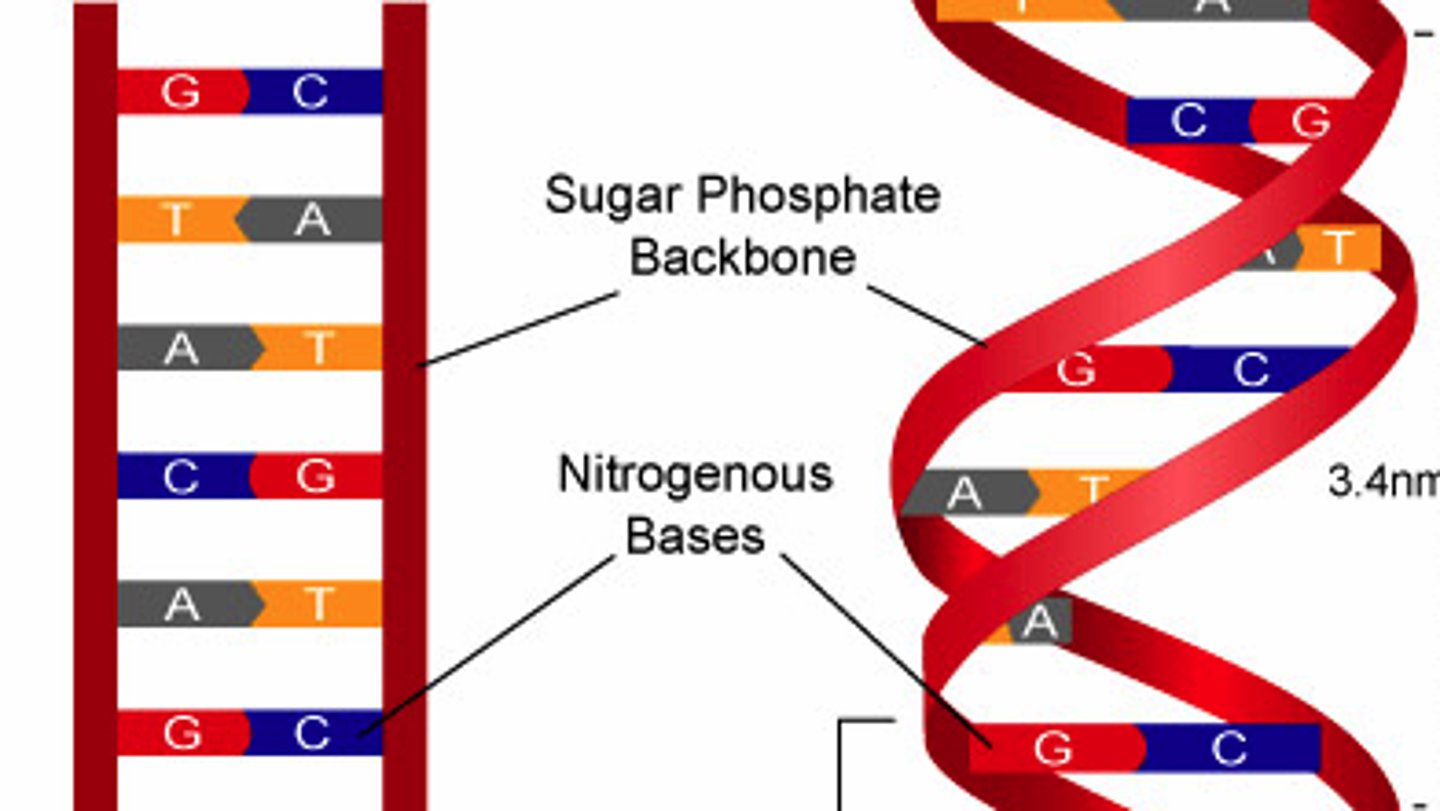
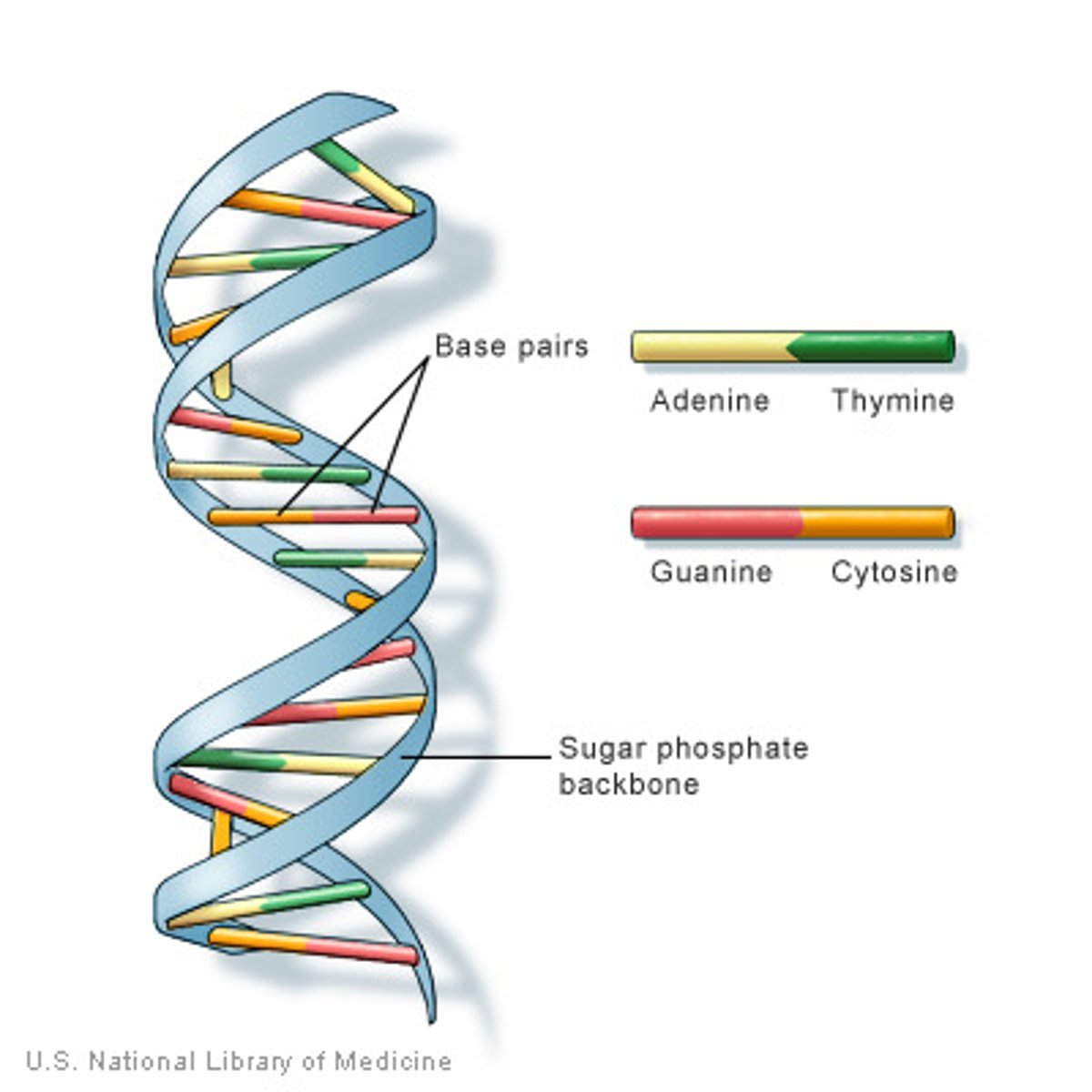
the molecule that carries genetic information for the development and functioning of an organism. DNA is made of two linked strands that wind around each other to resemble a twisted ladder — a shape known as a double helix.
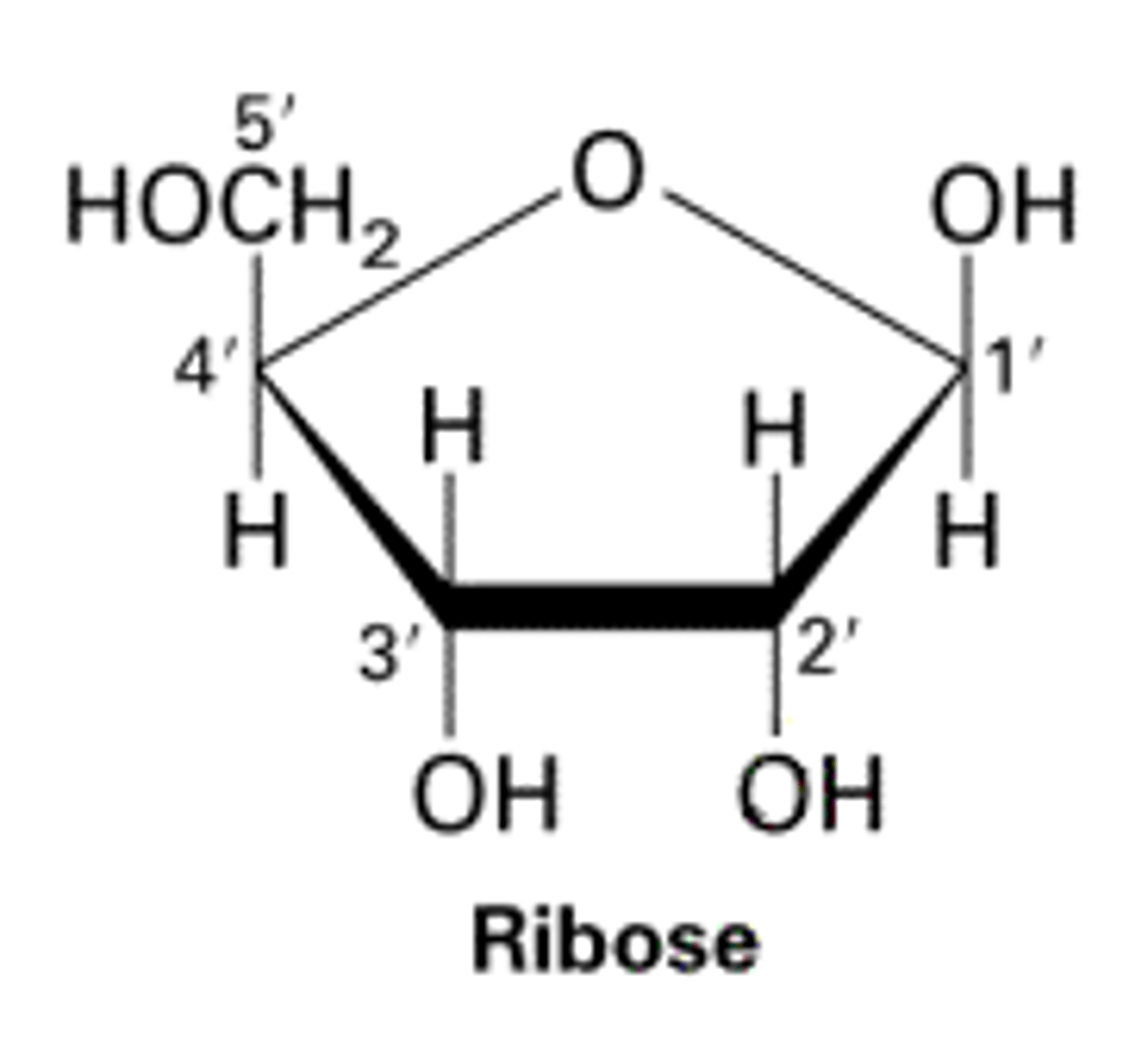
ribose sugar
sugar used in RNA to make up the "backbone"
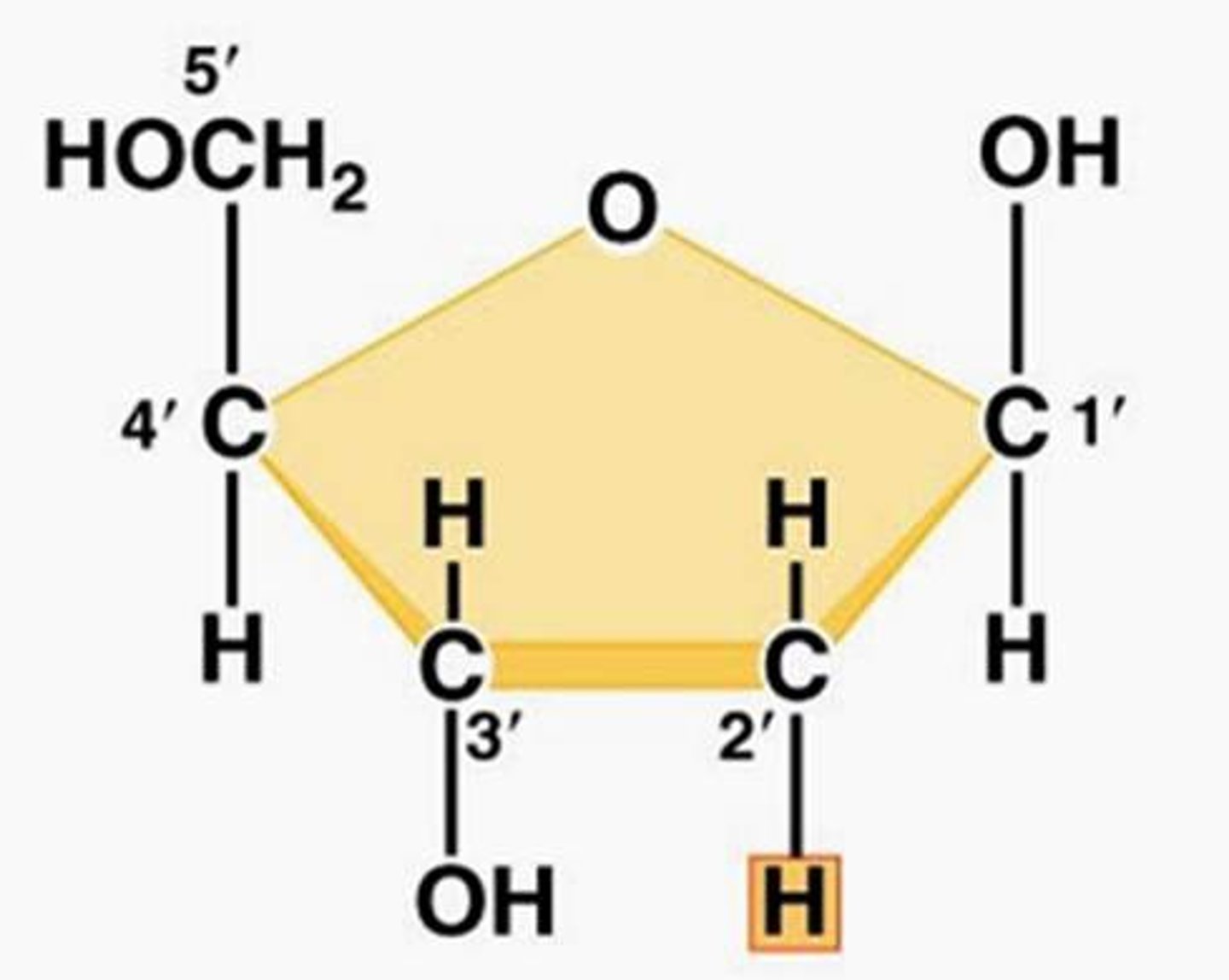
Deoxyribose
A five-carbon sugar that is a component of DNA nucleotides. Ribose sugar has a hydroxyl (OH) group at position 2, whereas deoxyribose sugar has a hydrogen (H) atom at position 2
Nitrogenous Bases in DNA
adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine
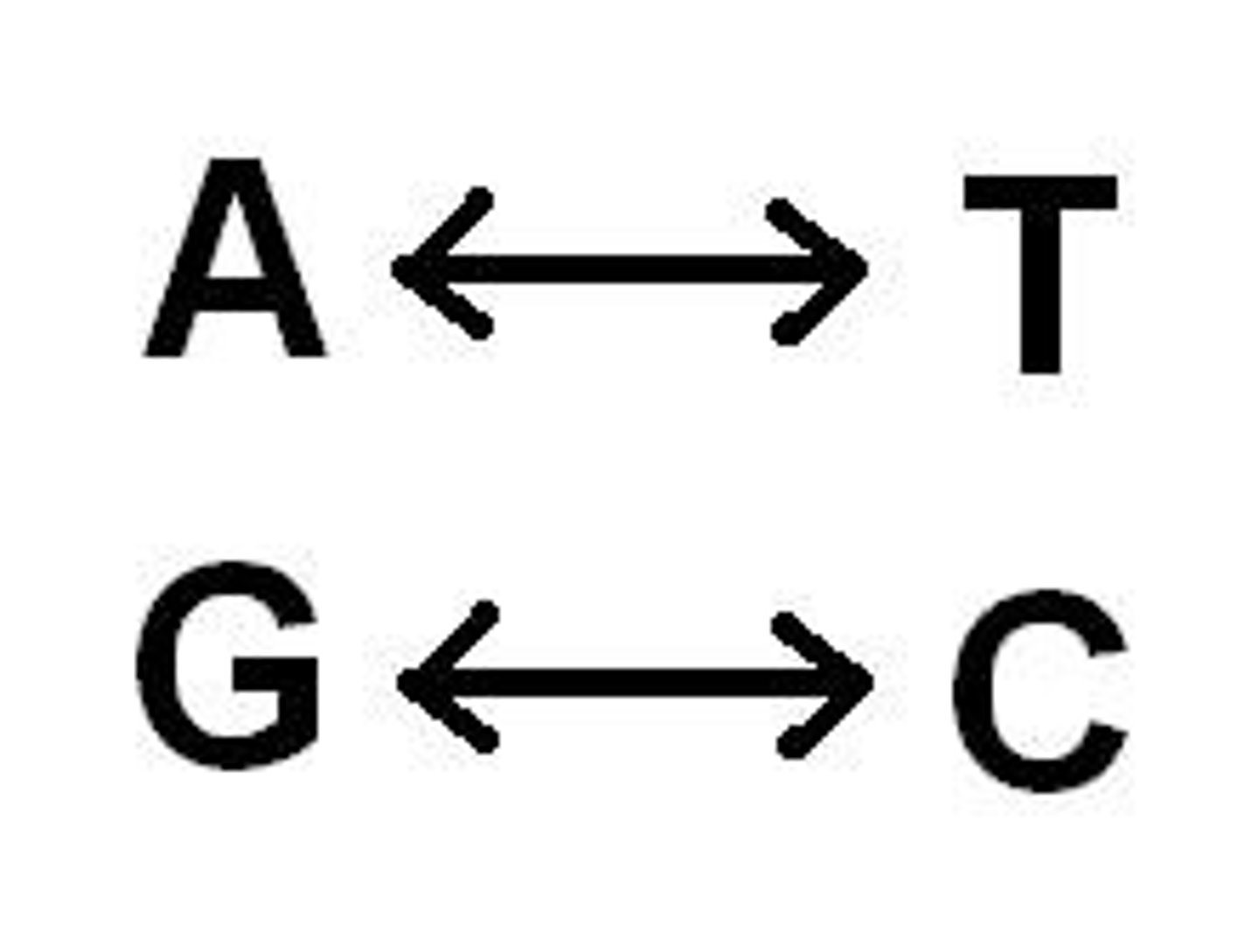
Nitrogenous Bases in RNA
Adenine, Uracil, Cytosine, Guanine
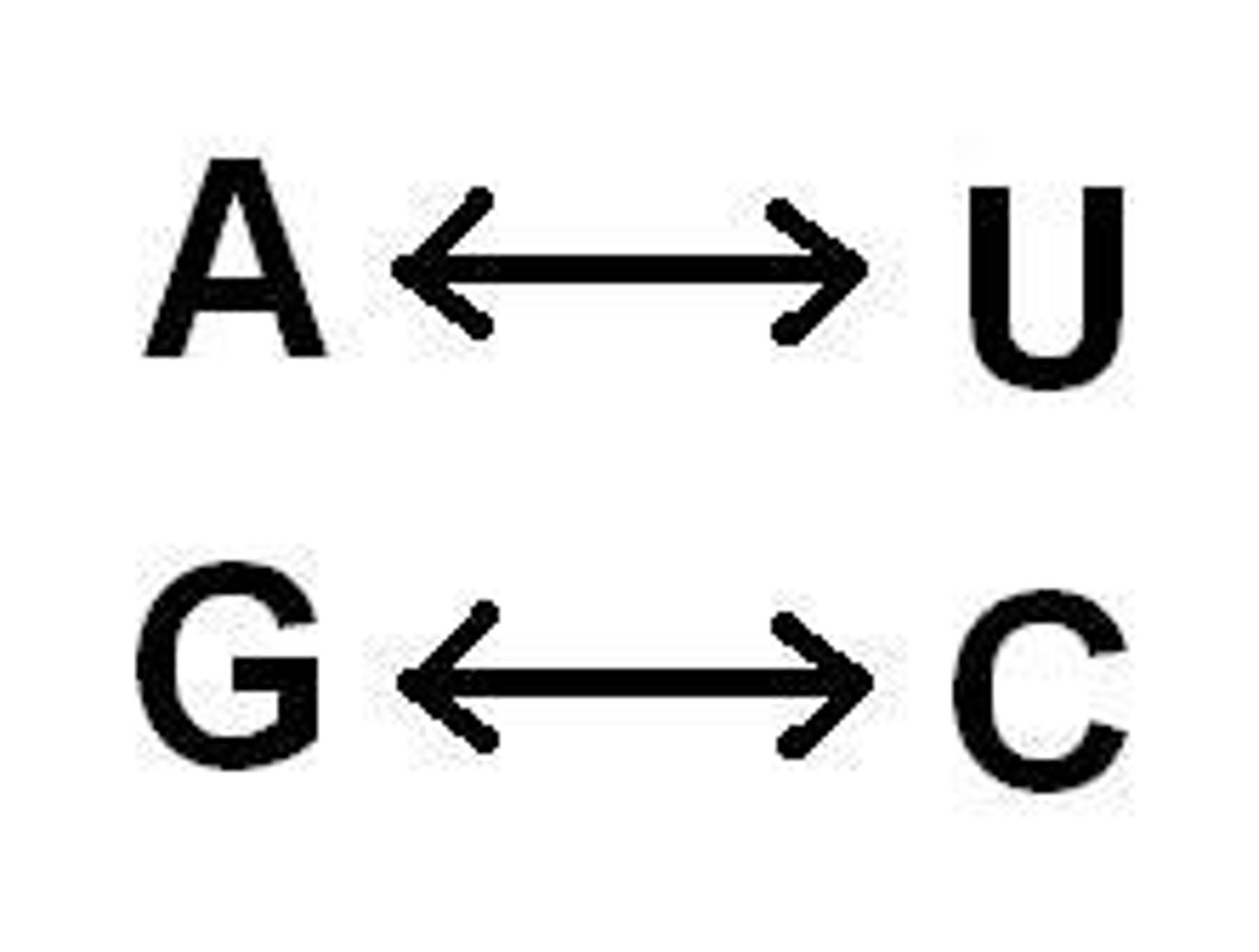
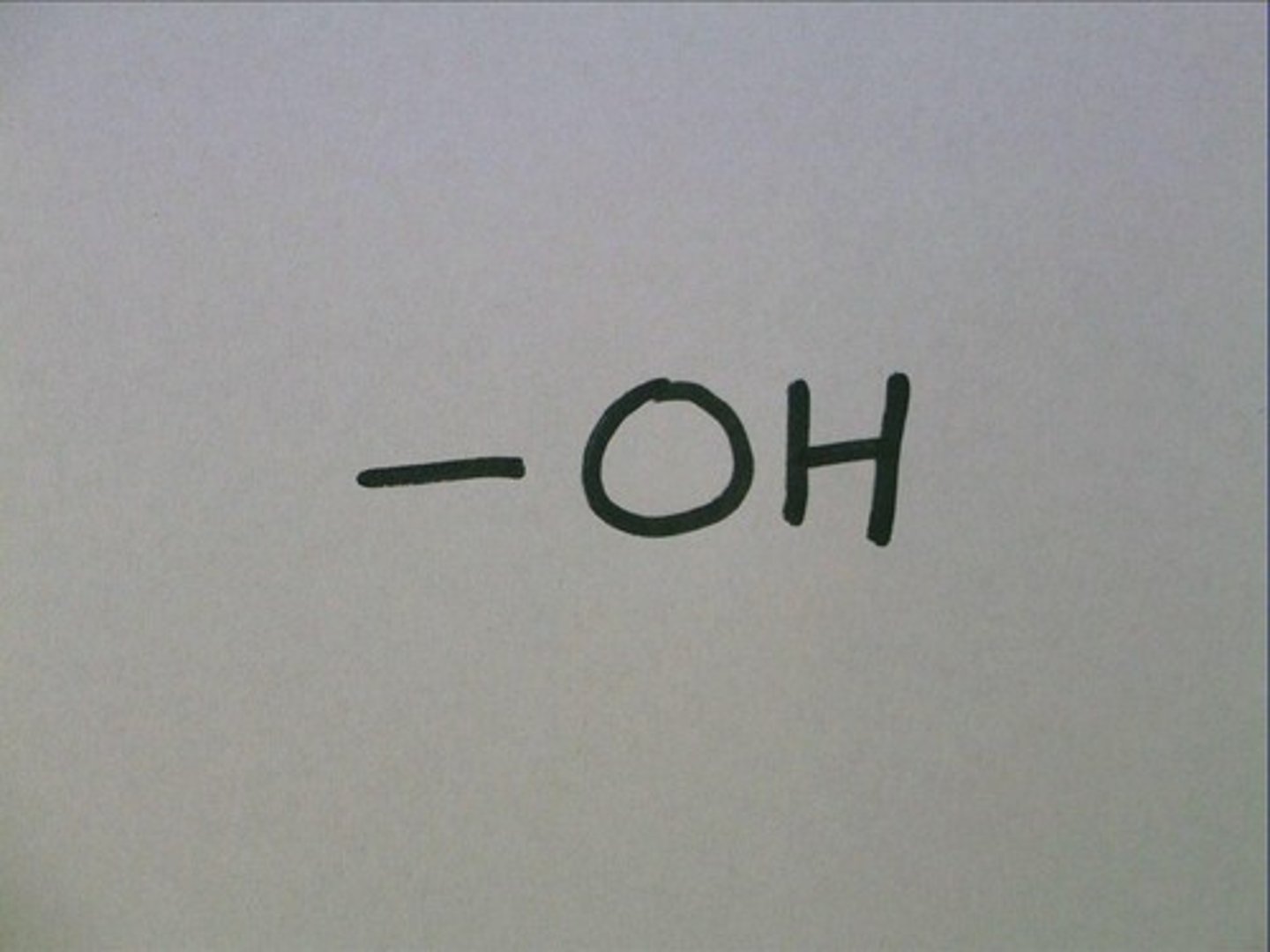
hydroxyl
OH-
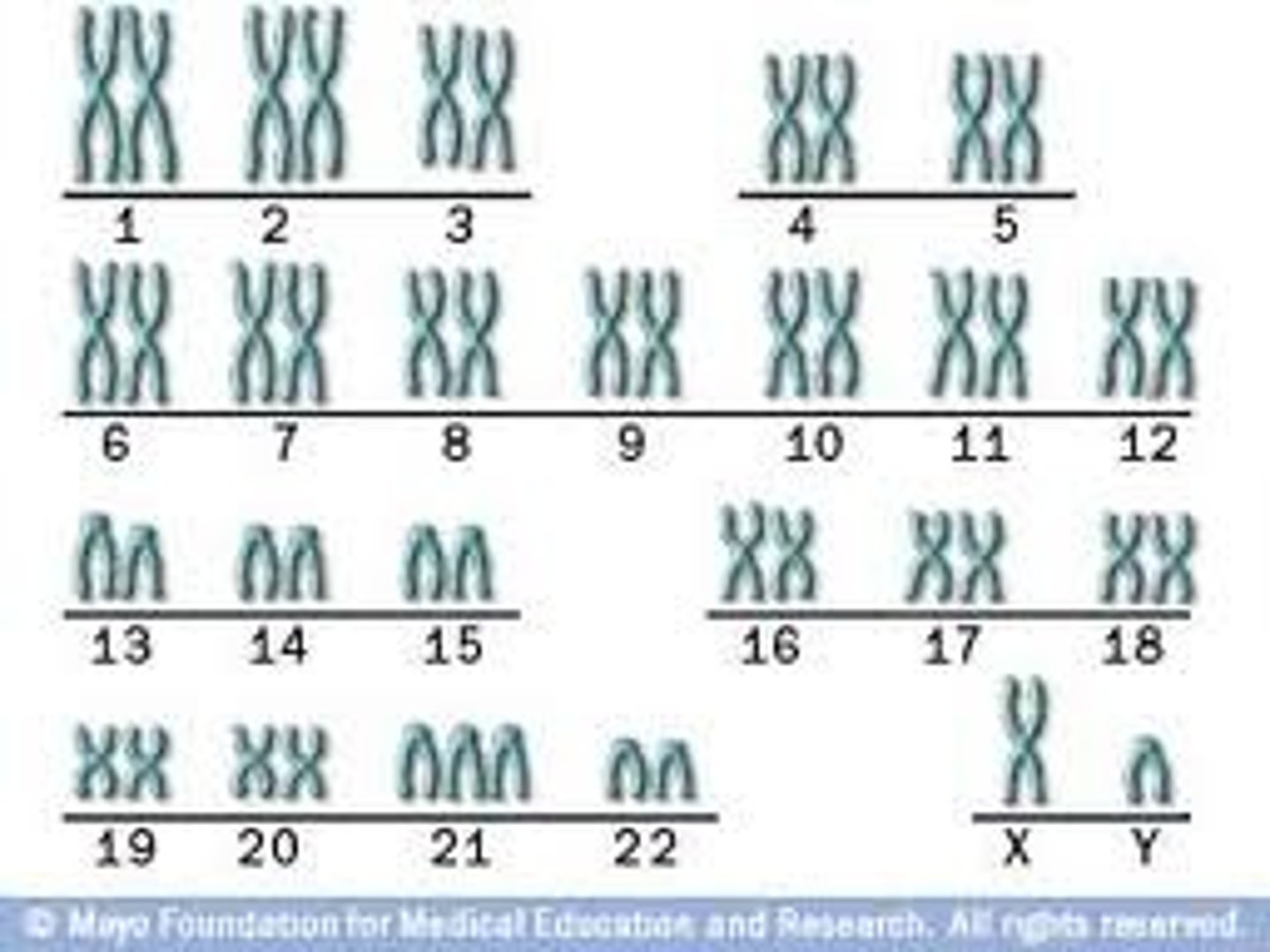
Number of chromosomes
46 (23 pairs)
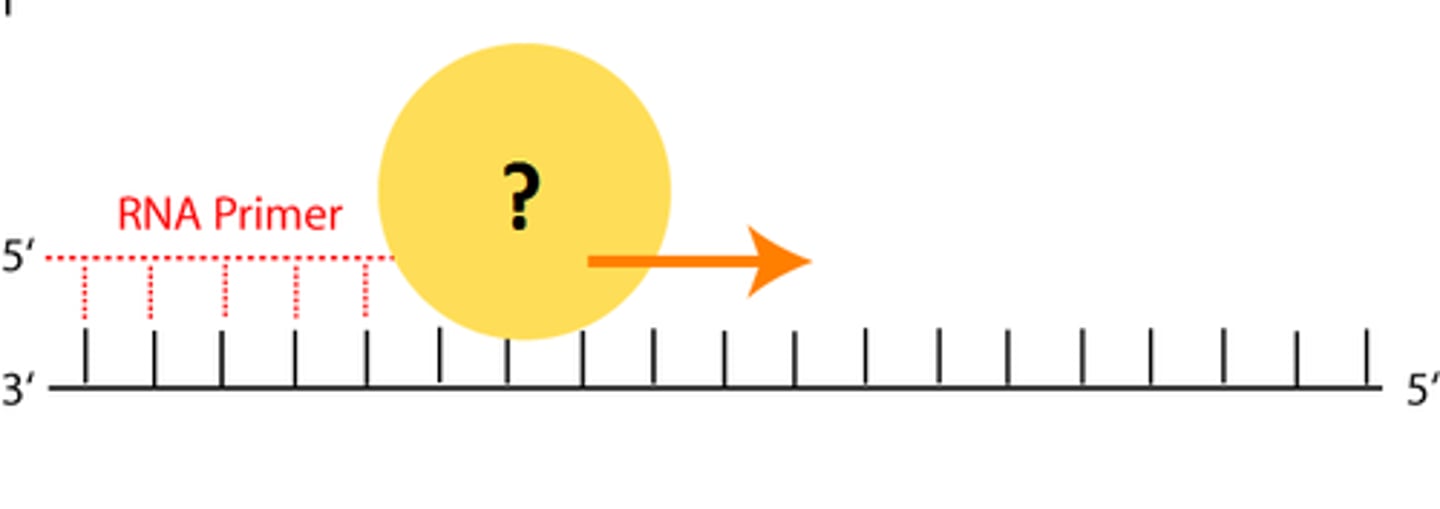
Okazaki Fragment
short segment of DNA synthesized discontinuously in small segments in the 3' to 5' direction by DNA polymerase
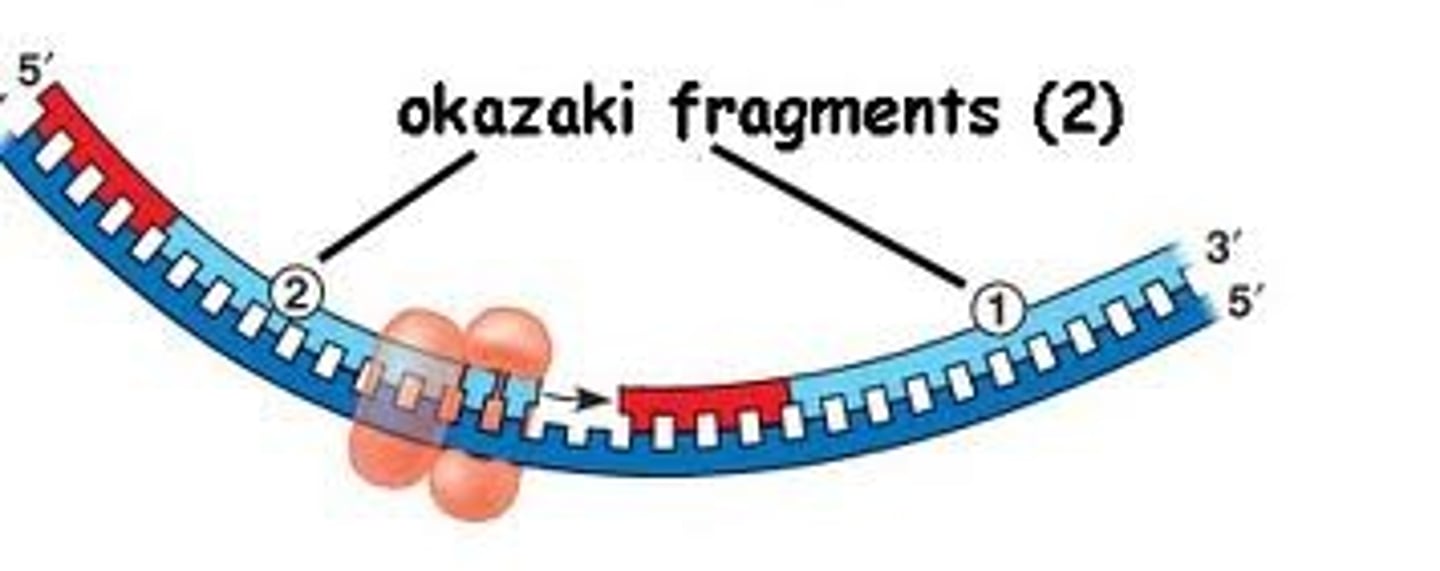
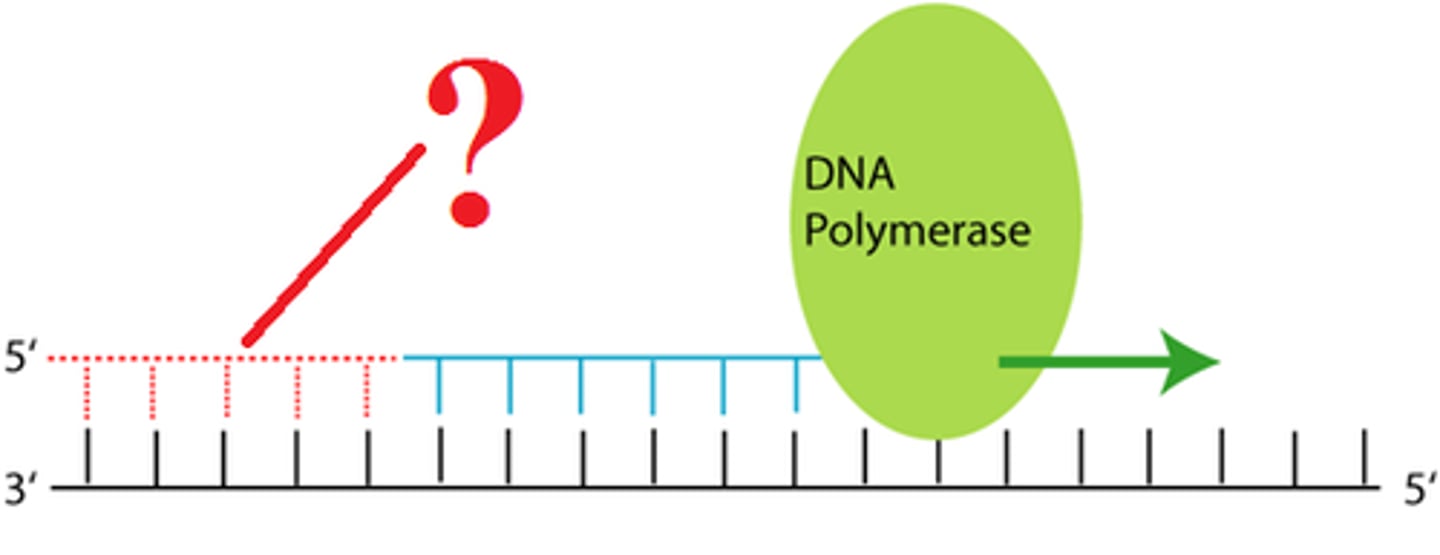
RNA Primer
short segment of RNA used to initiate synthesis of a new strand of DNA during replication
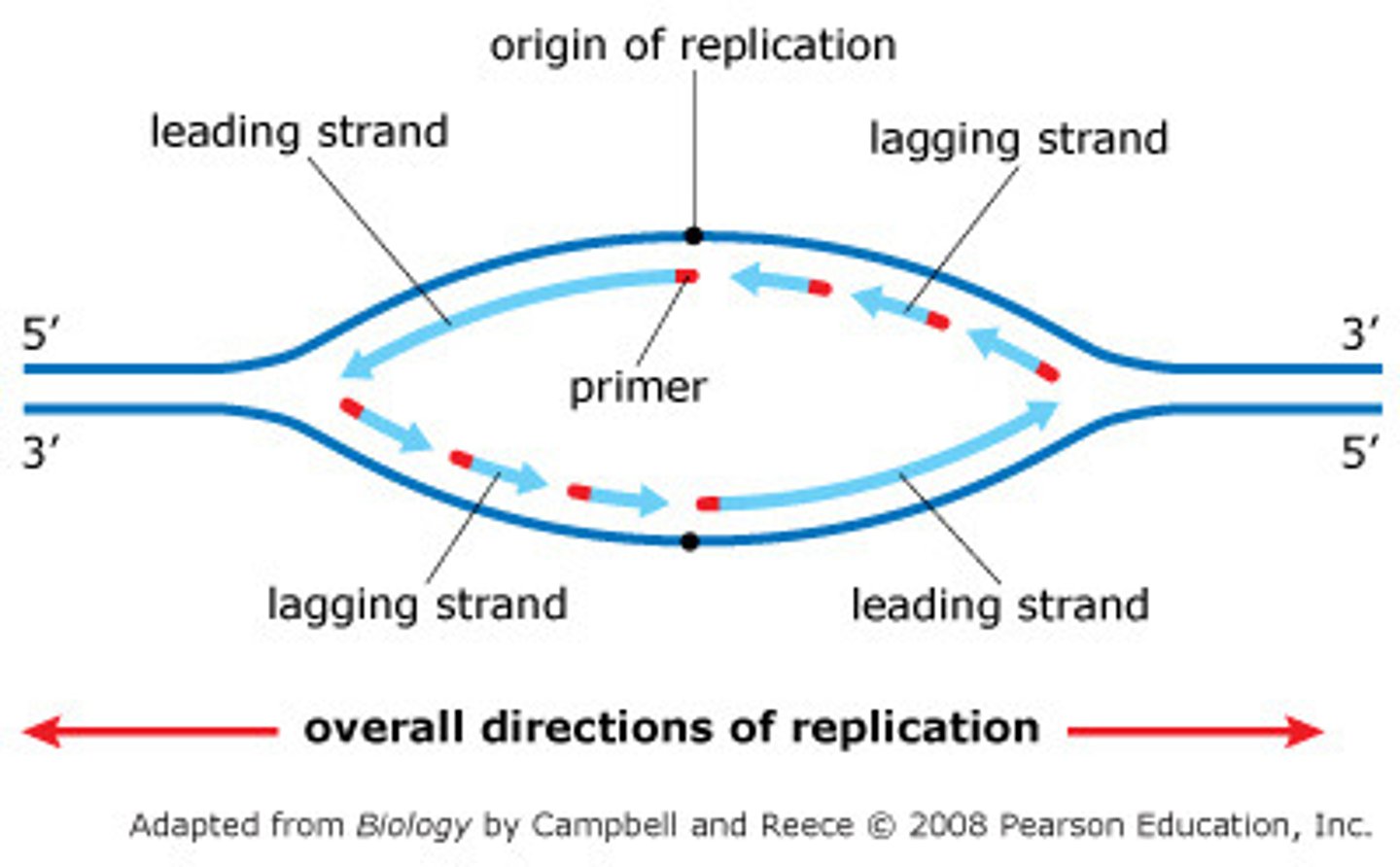
leading strand
The new continuous complementary DNA strand synthesized along the template strand in the mandatory 5' to 3' direction.
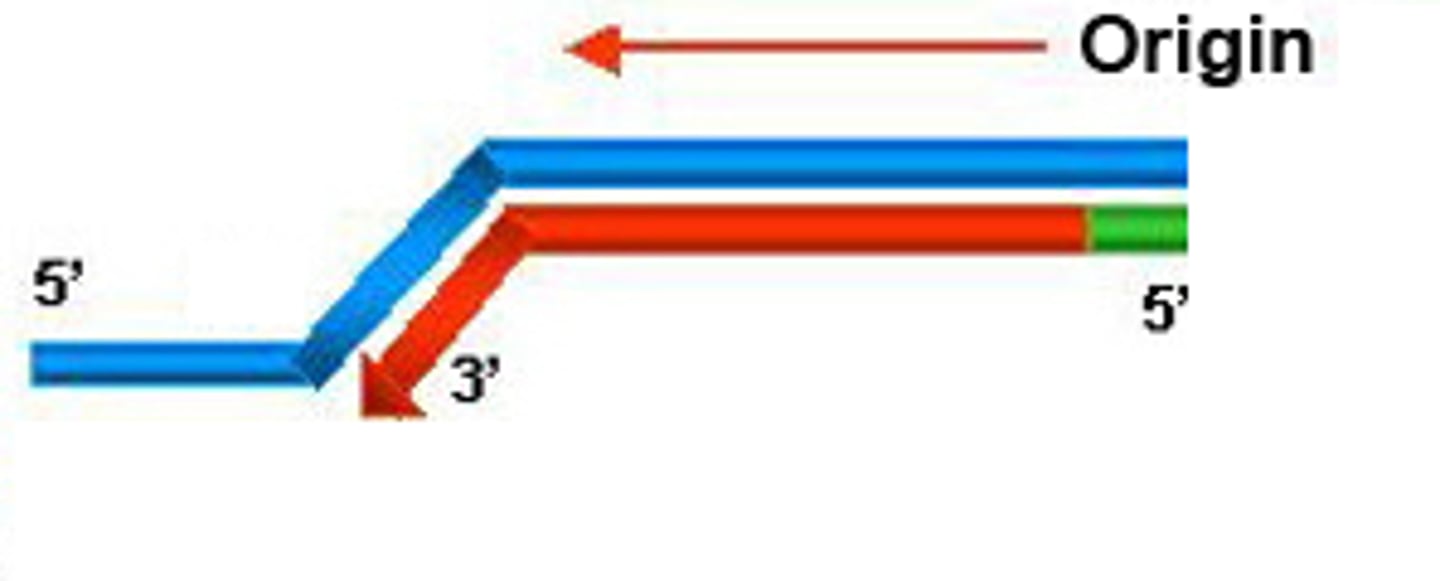
lagging strand
A discontinuously synthesized DNA strand that elongates by means of Okazaki fragments, each synthesized in a 5' to 3' direction away from the replication fork.
binding proteins
bind a specific substrate, either to sequester it in the body or hold its concentration at steady state
DNA backbone
Made of deoxyribose SUGAR and Phosphate
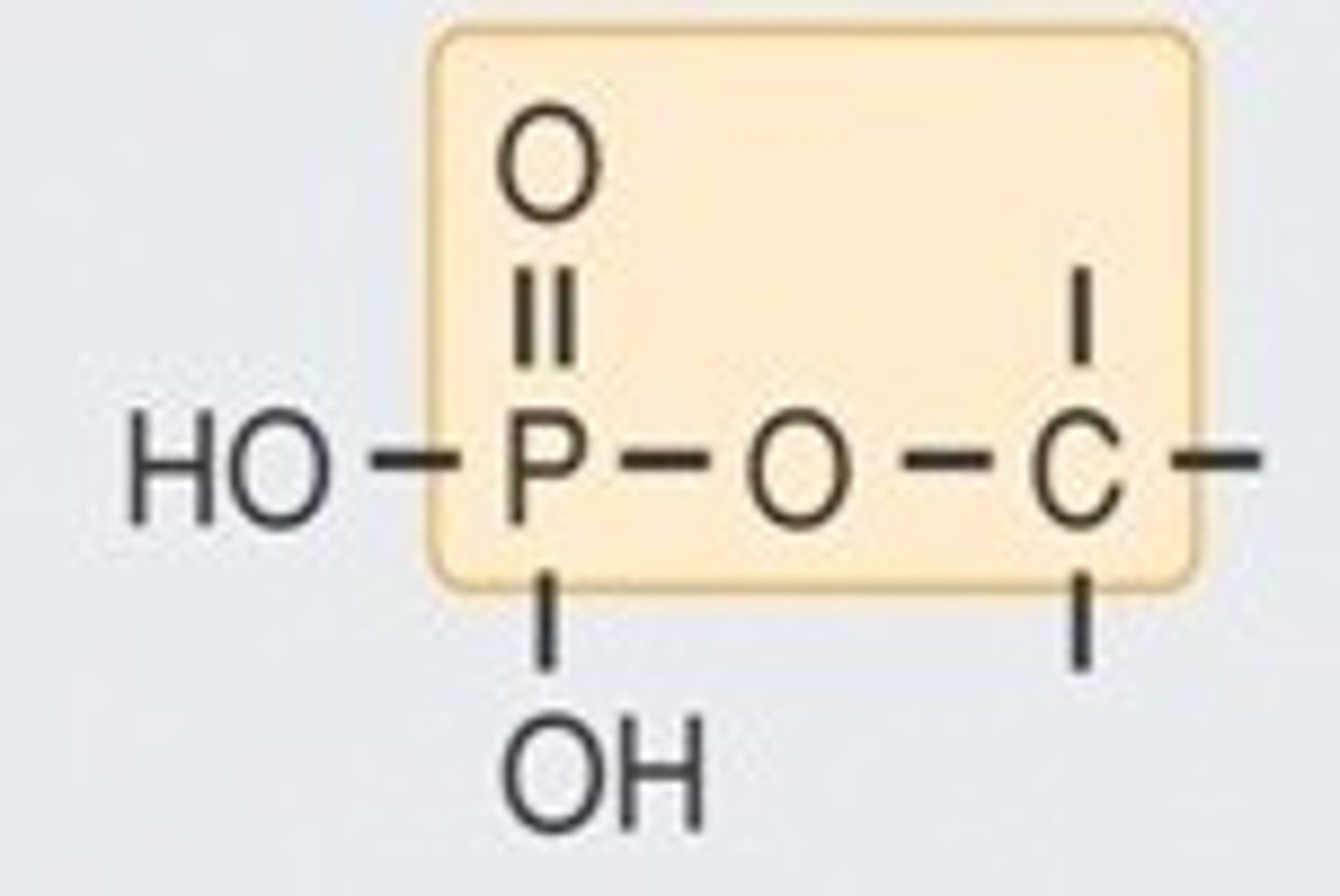
phosphoester bond
the linkage between the five prime sugar hydroxyl and a phosphate group
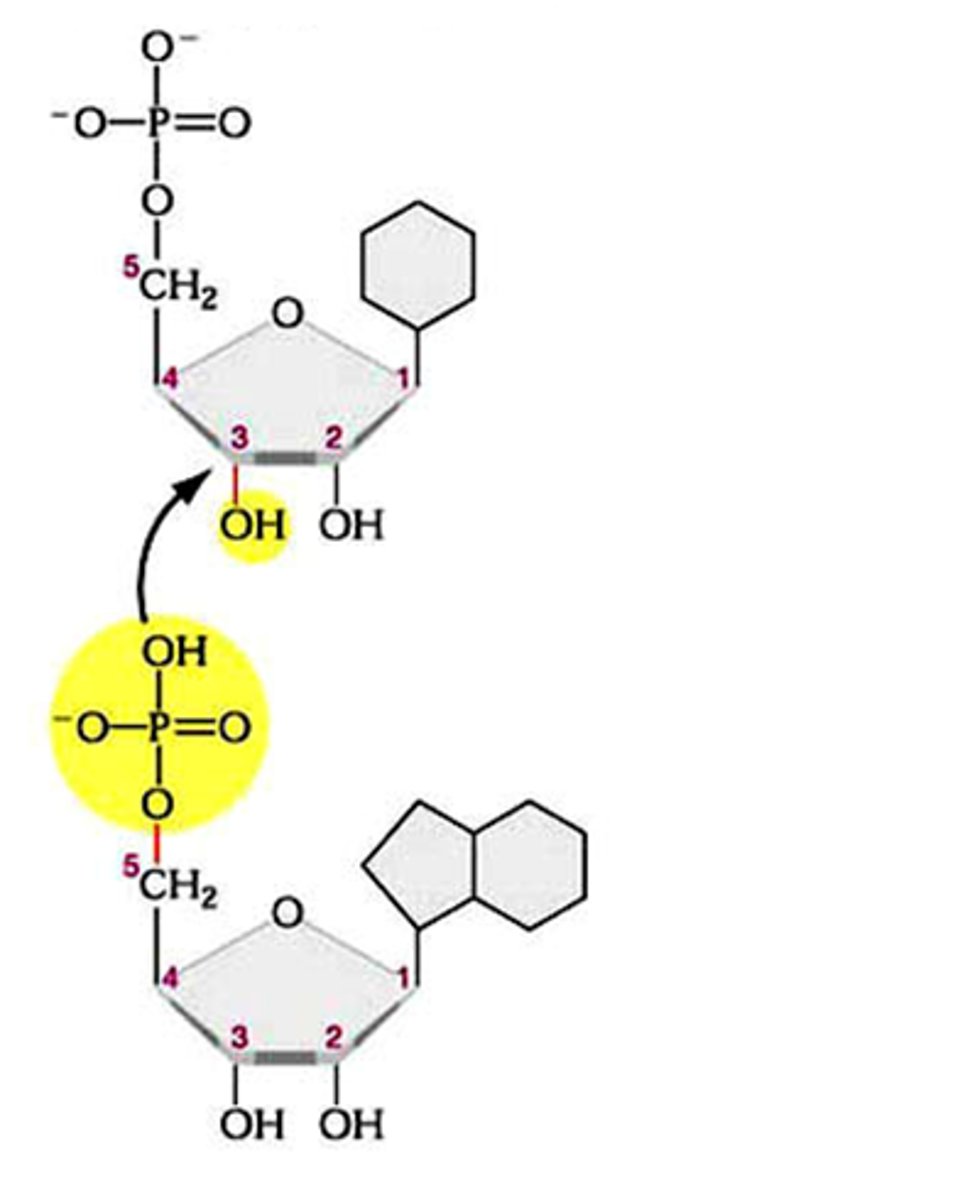
phosphodiester bond
the type of bond that links the nucleotides in DNA or RNA. joins the phosphate group of one nucleotide to the hydroxyl group on the sugar of another nucleotide
pyrimidines
cytosine, thymine, uracil
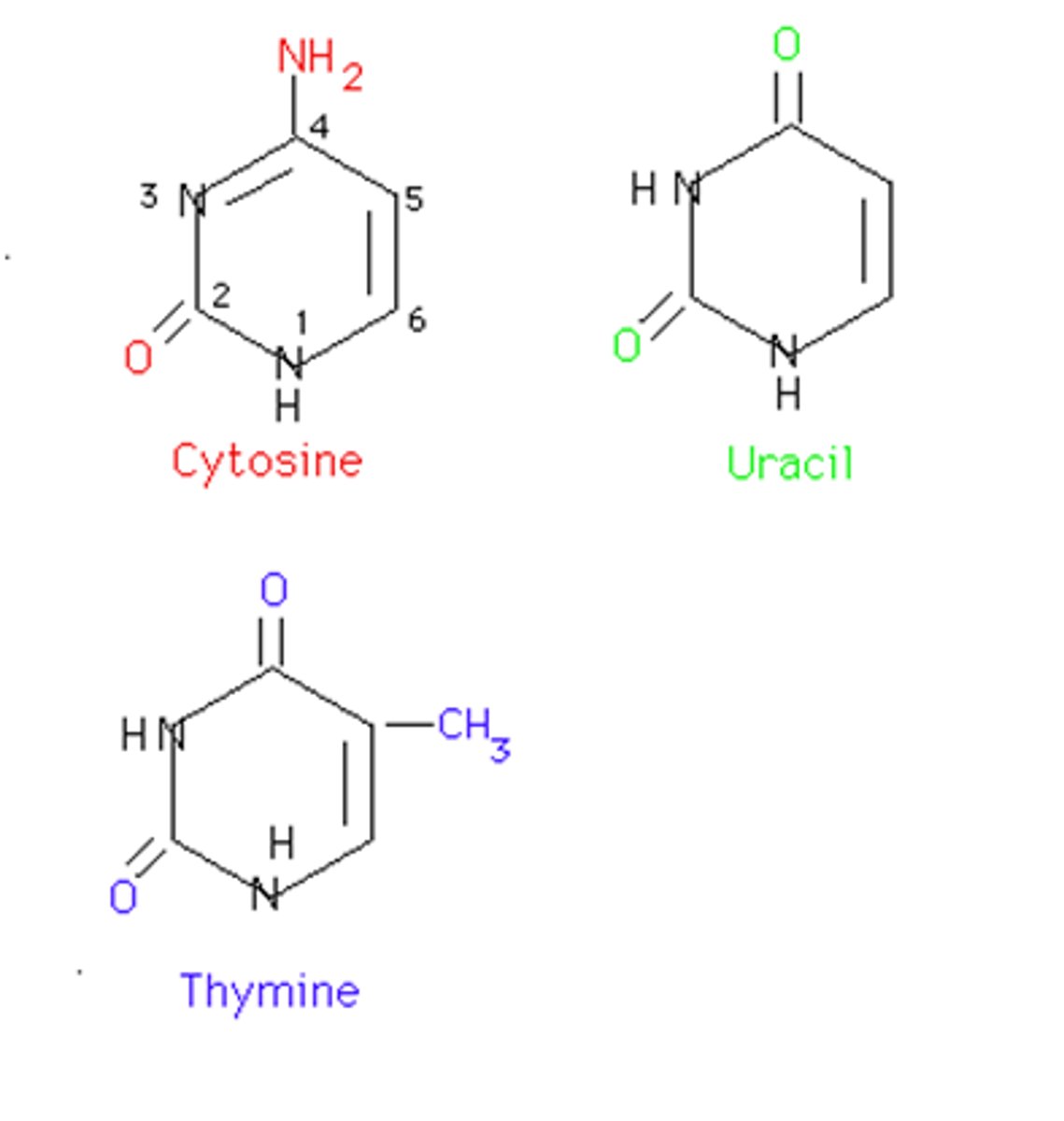
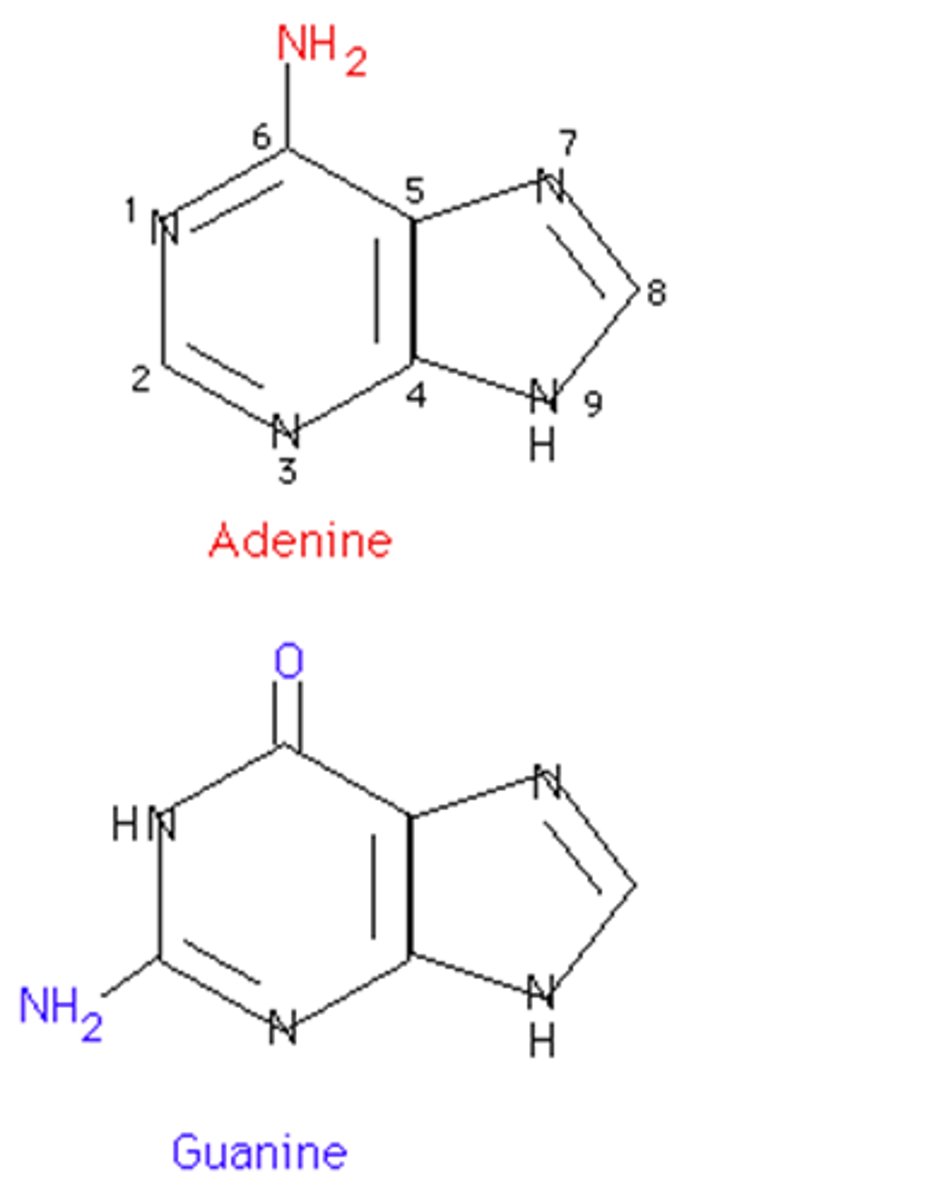
purines
Adenine and Guanine
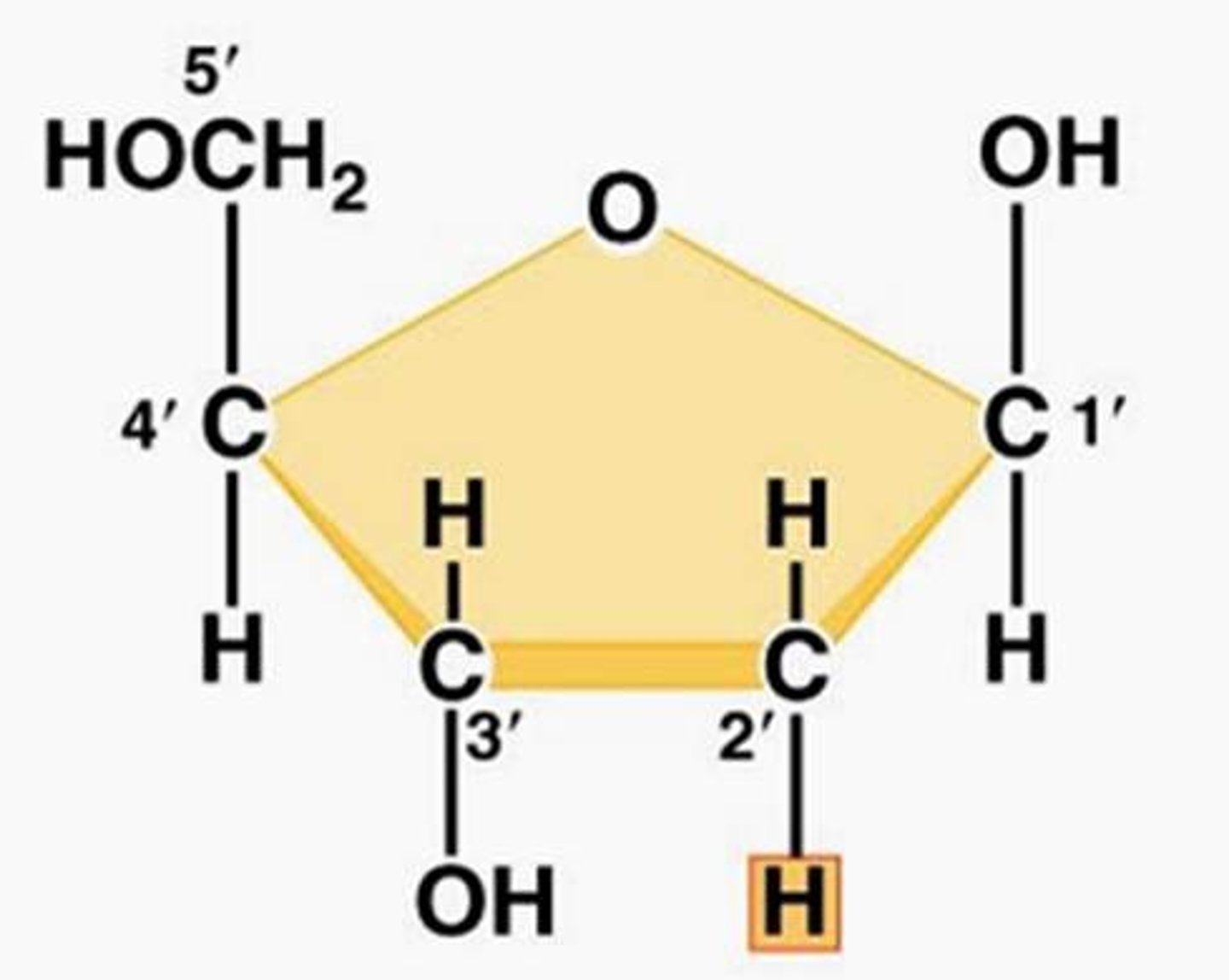
Labelling Carbons
The carbon to the clockwise direction of the oxygen held within the ring structure of glucose is identified as the 1' carbon. The carbon clockwise of the 1' carbon is the 2' carbon, and so on.
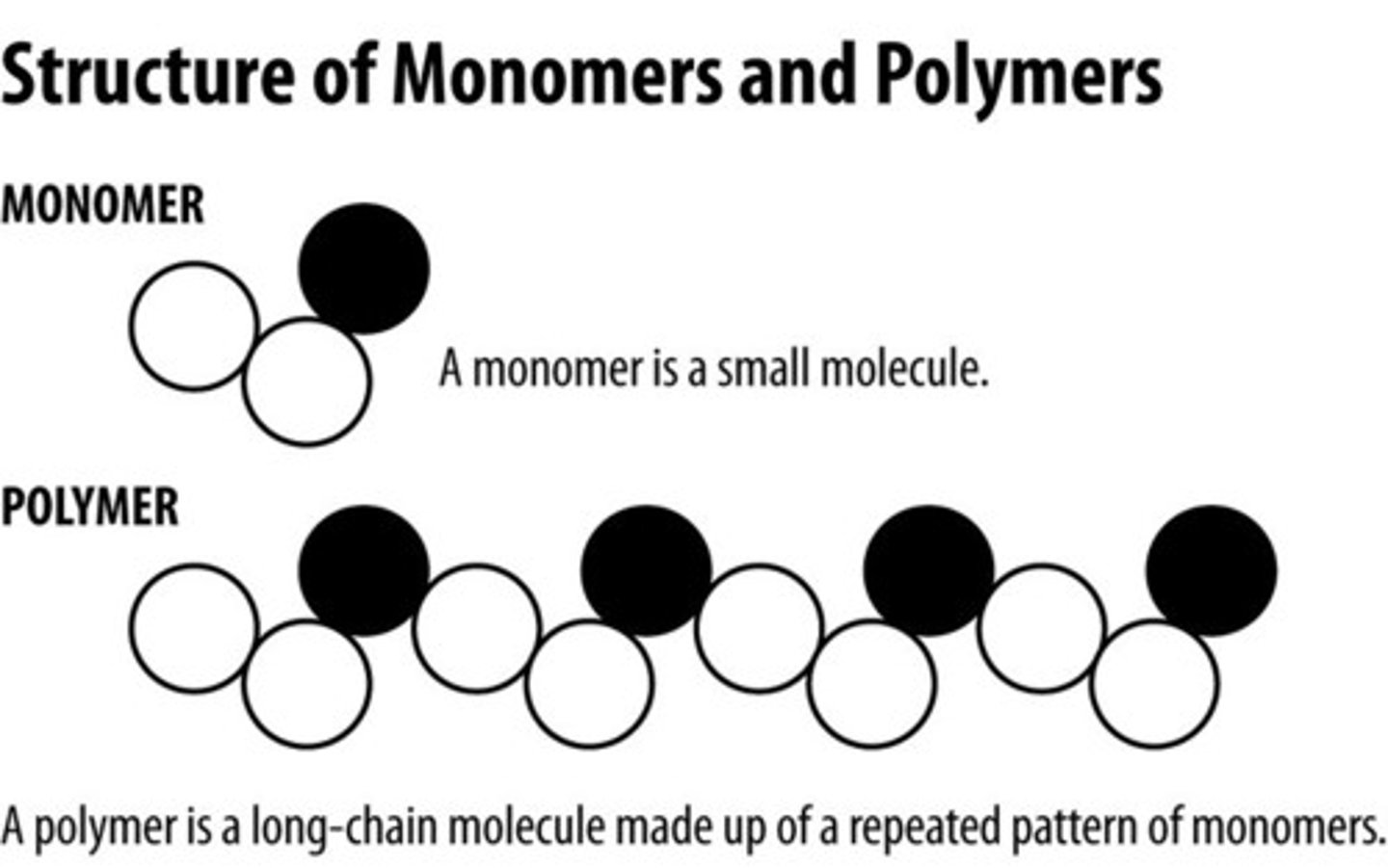
polymer
A long molecule consisting of many similar or identical monomers linked together.
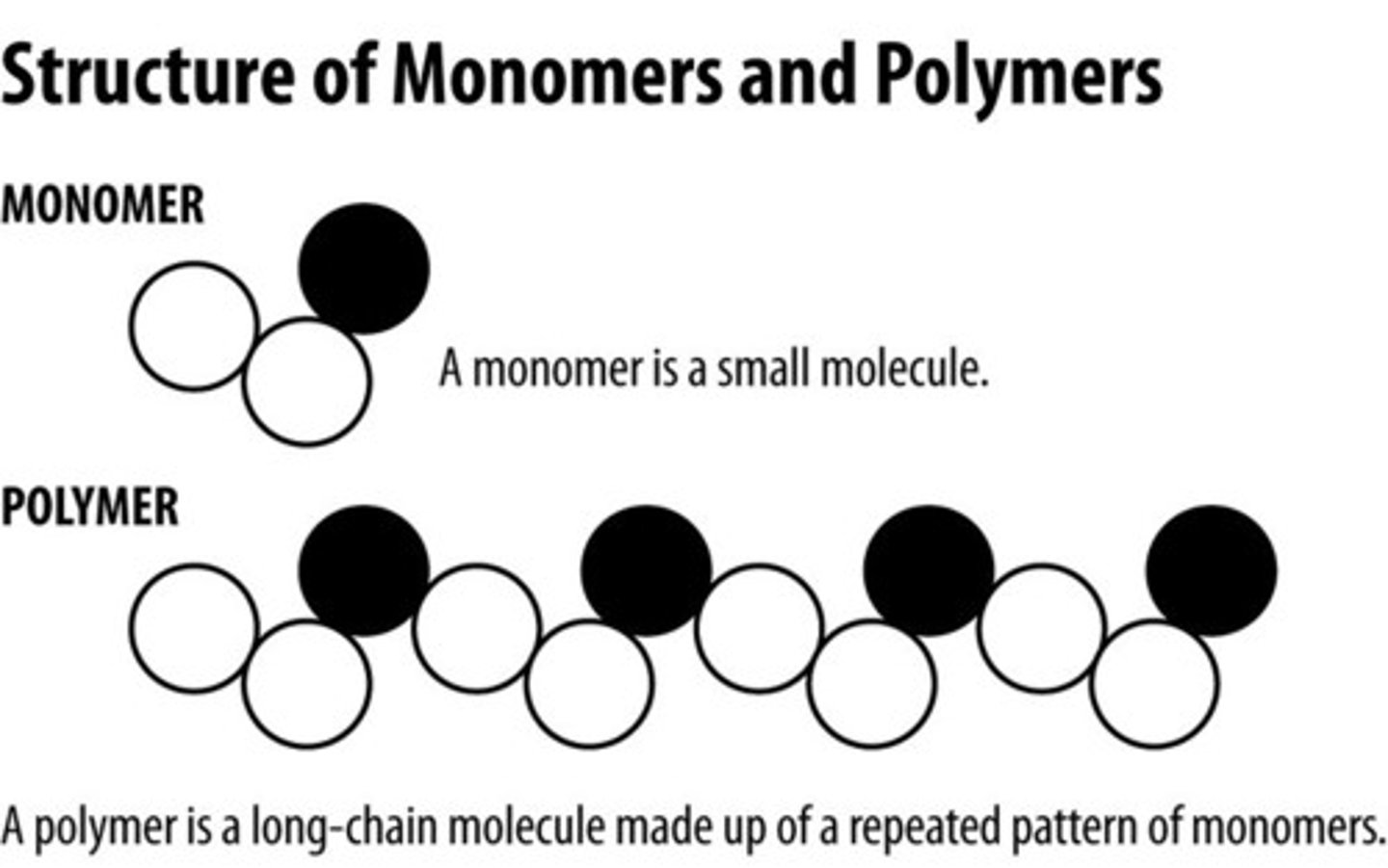
monomers
small unit that can join together with other small units to form polymers
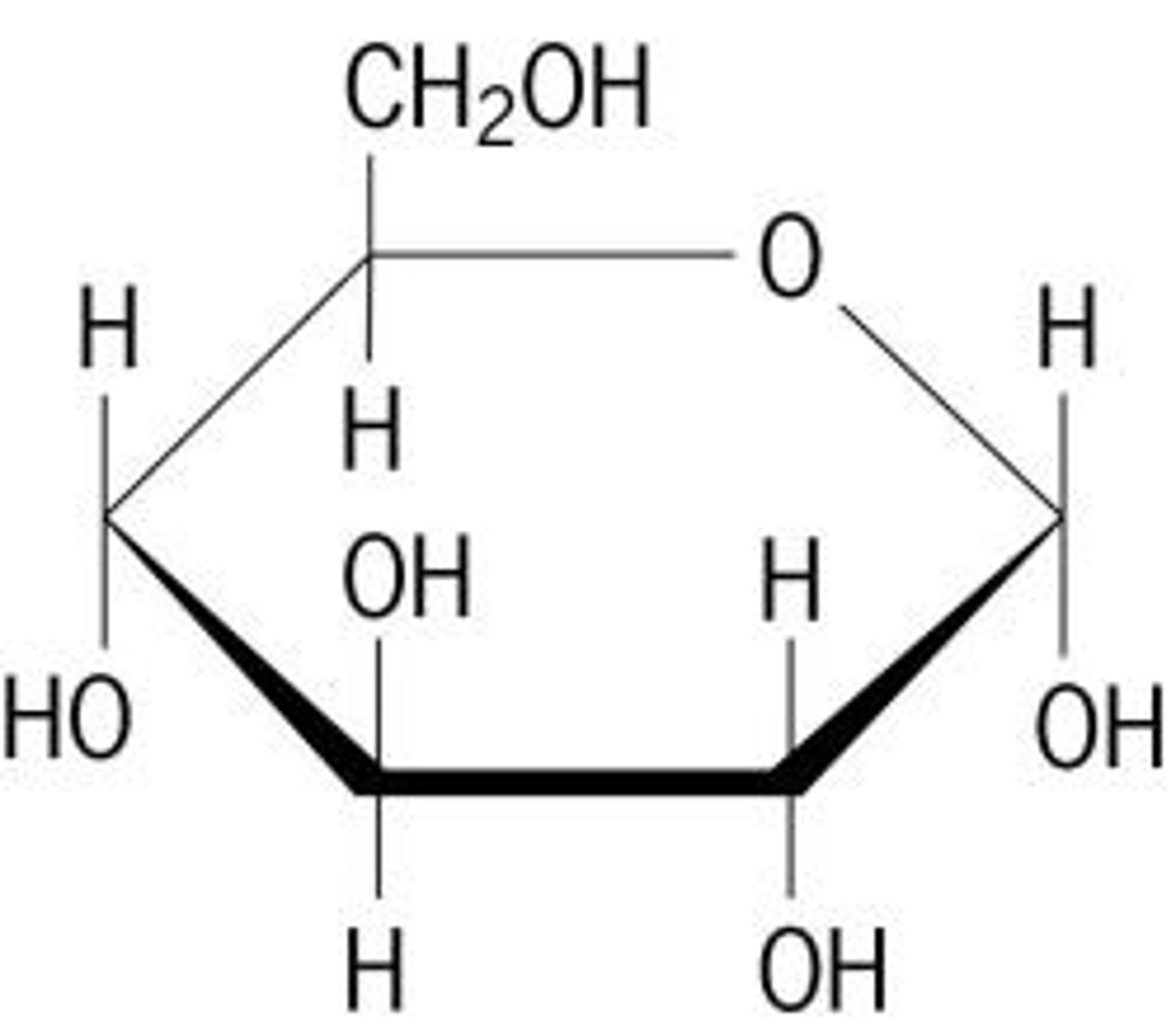
carbohydrates
the starches and sugars present in foods
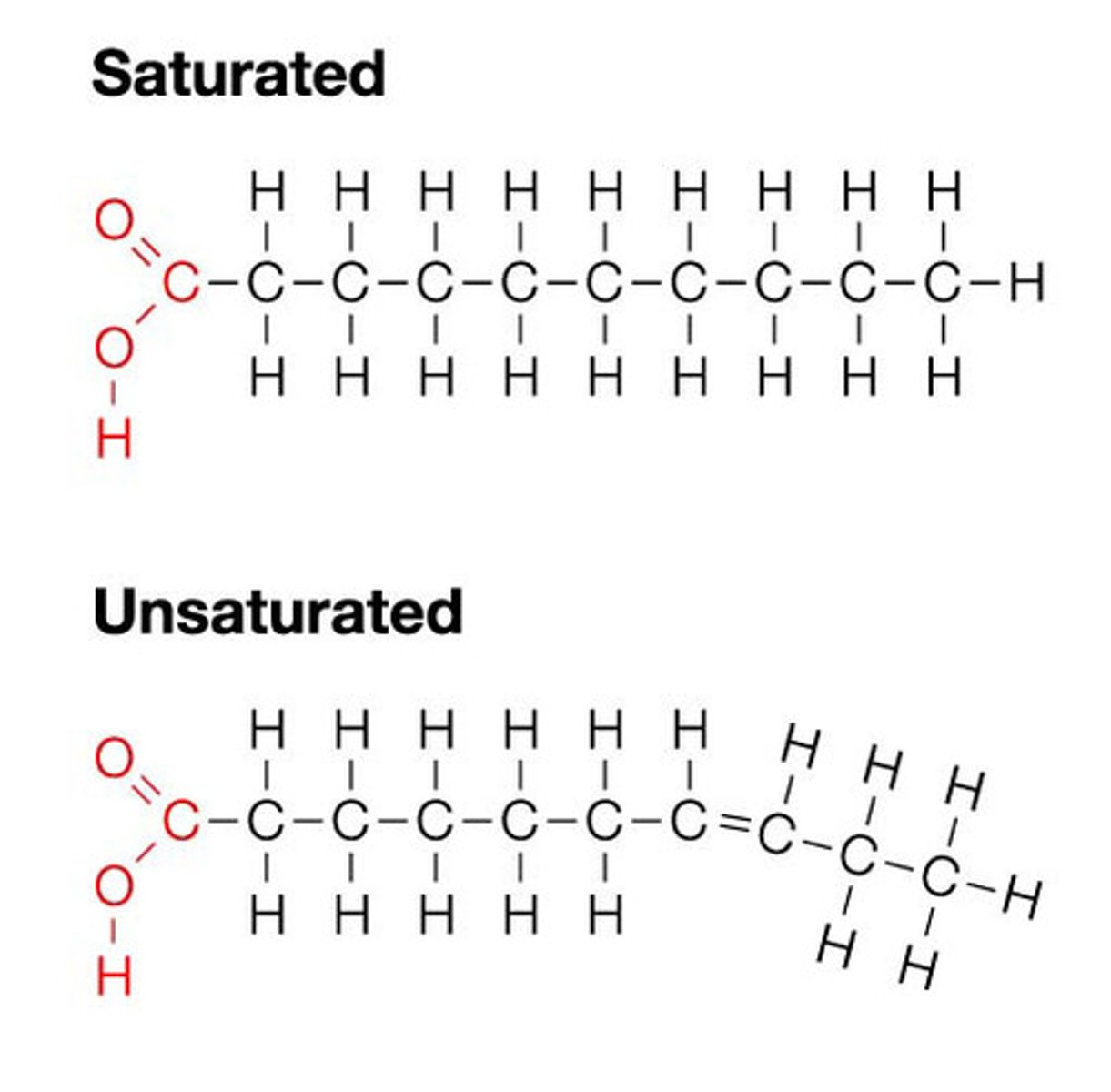
lipids
fats and oils
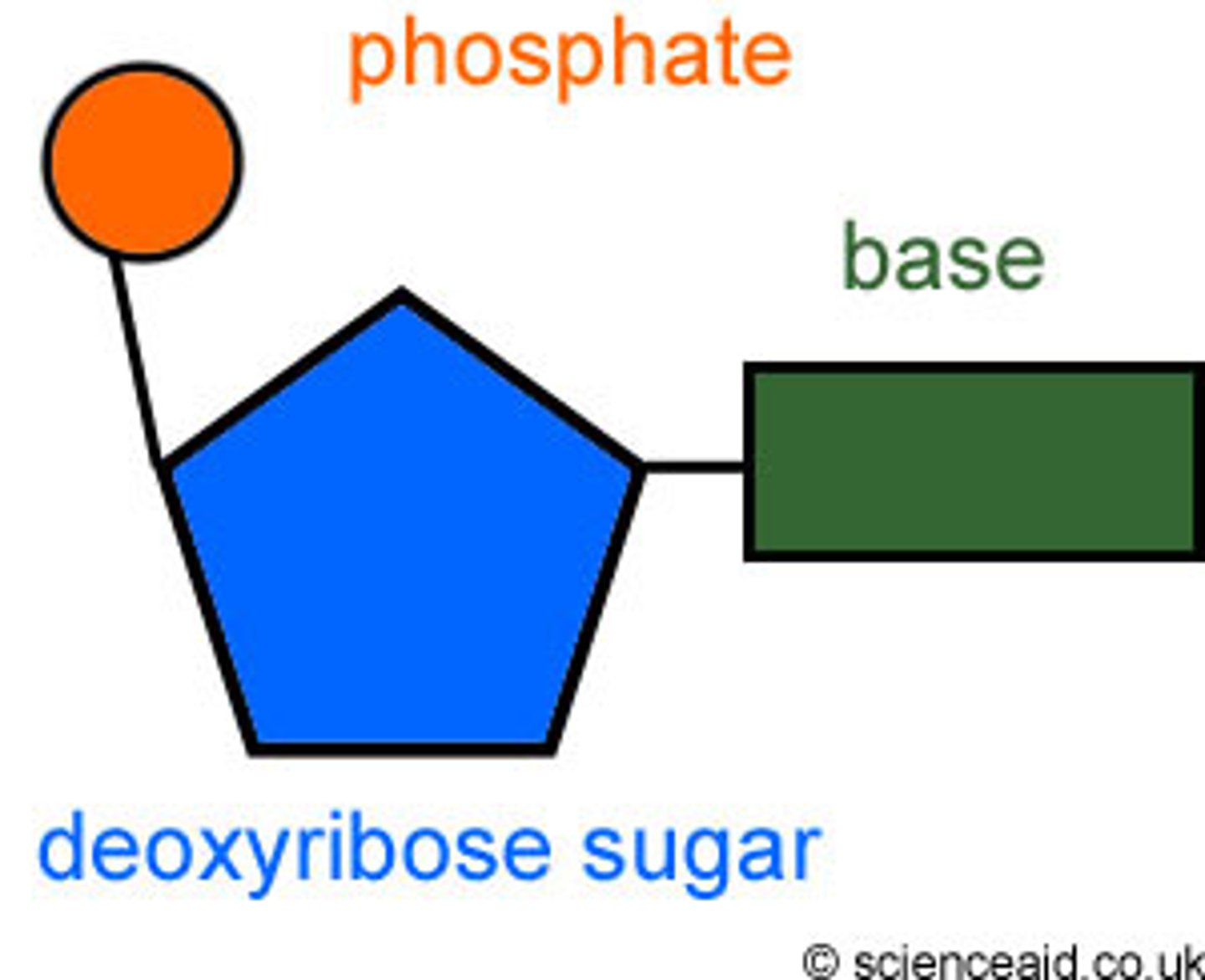
monomers in DNA
Nucleotides (sugar, phosphate, base)
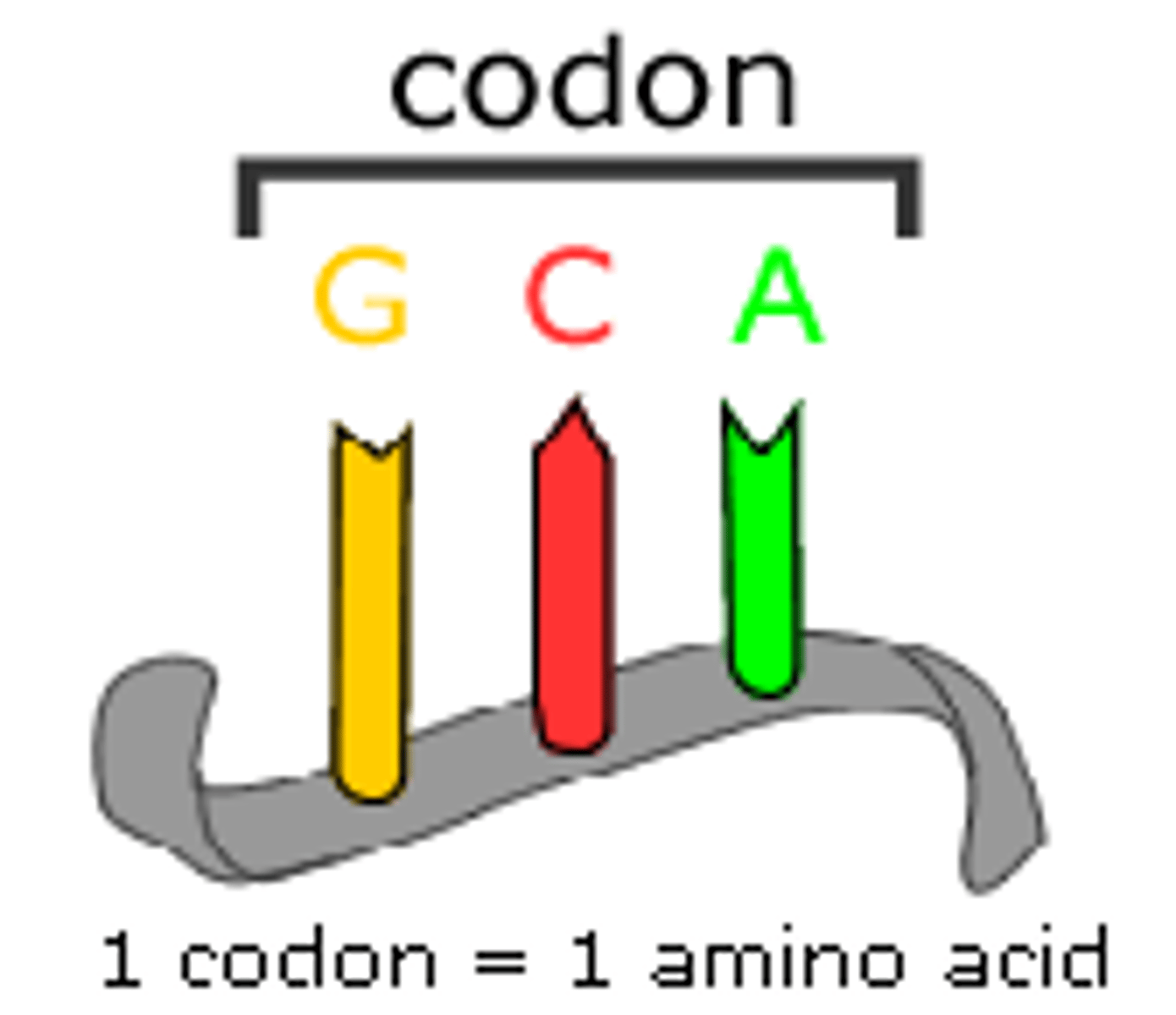
the triplet code
A set of three-nucleotide-long words that specify the amino acids for polypeptide chains.
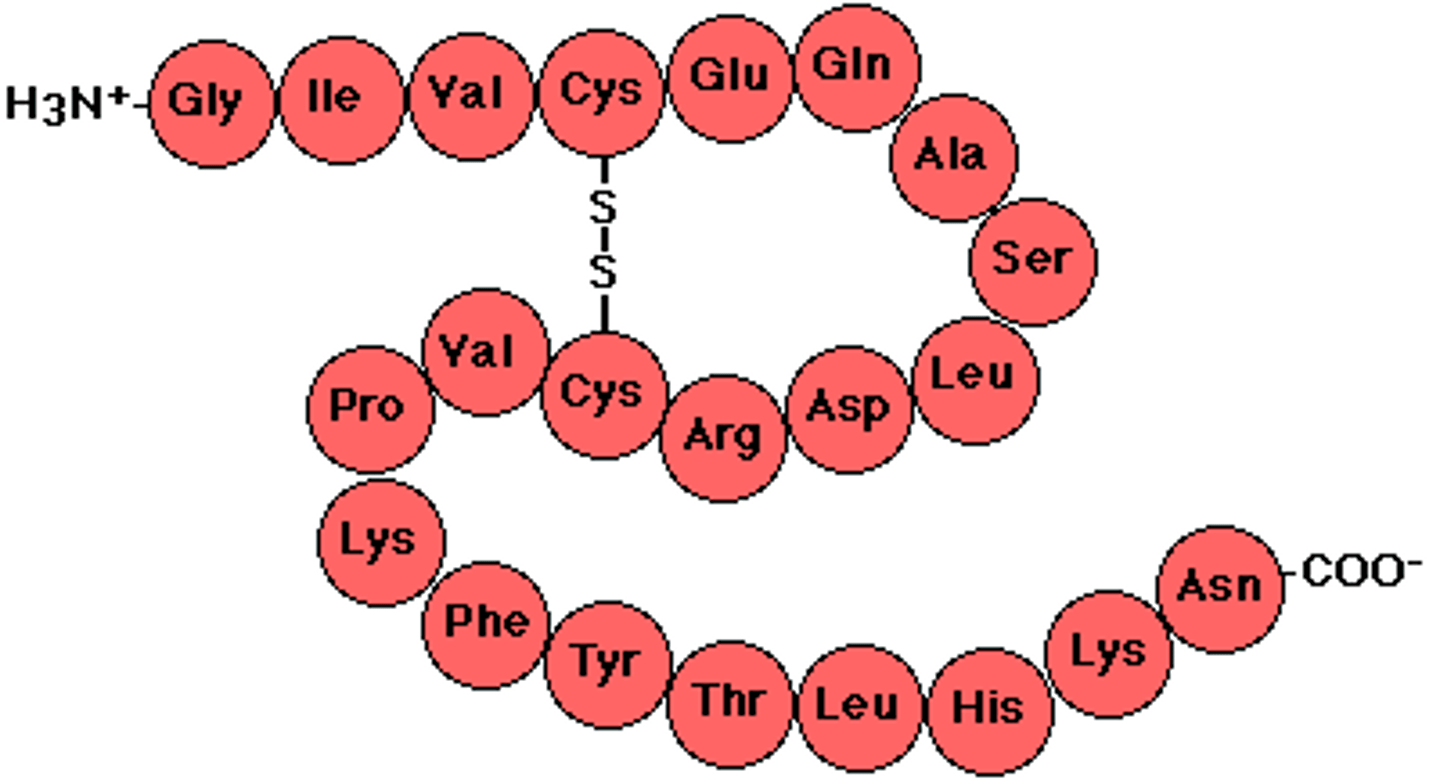
polypeptides
polymers of amino acids
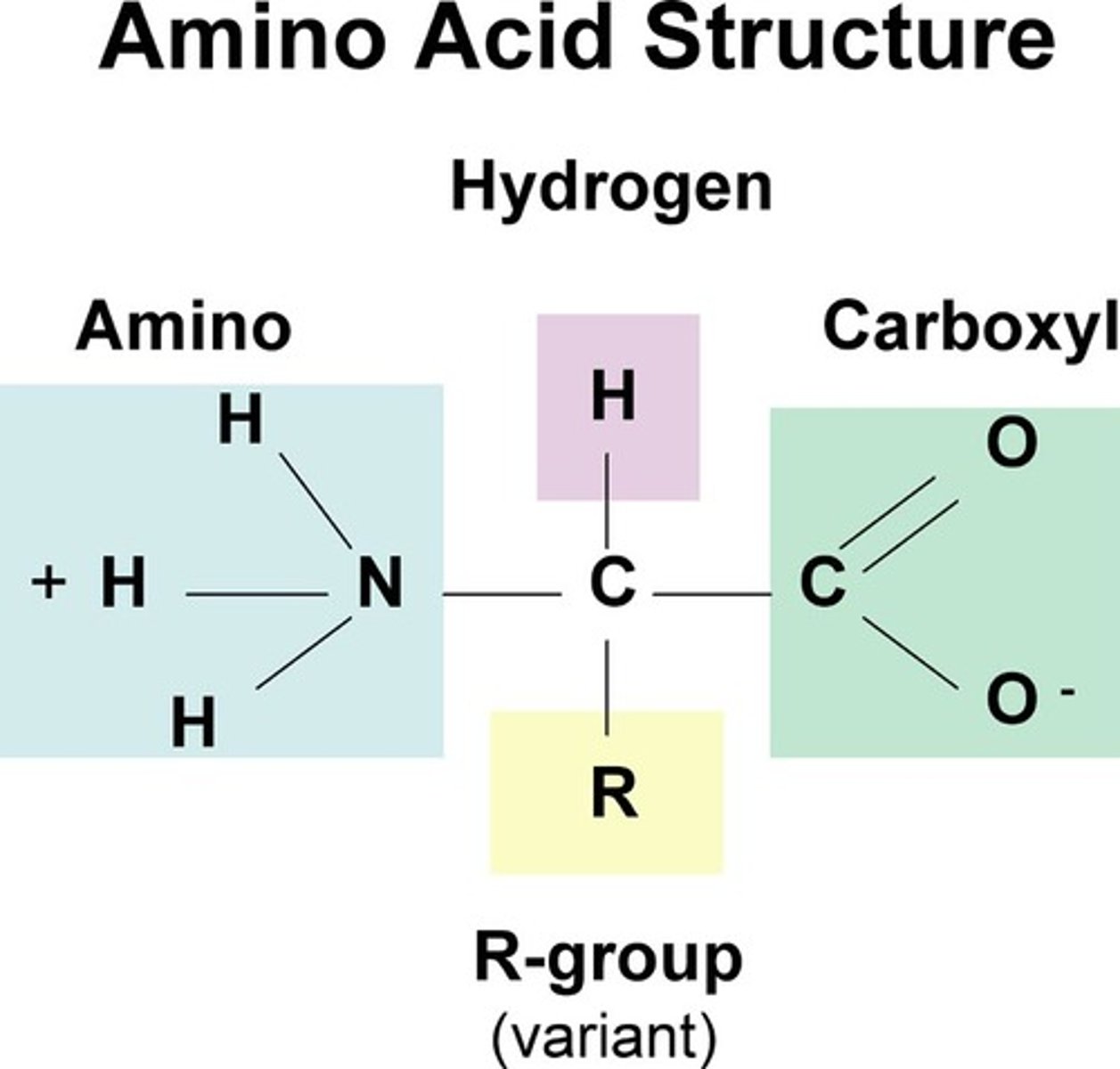
amino acid structures
have a central carbon covalently bound to four parts
1) a hydrogen atom
2) an amino group
3) a carboxyl group
4) a side chain (R)
Bonds between nitrogenous bases
hydrogen bonds
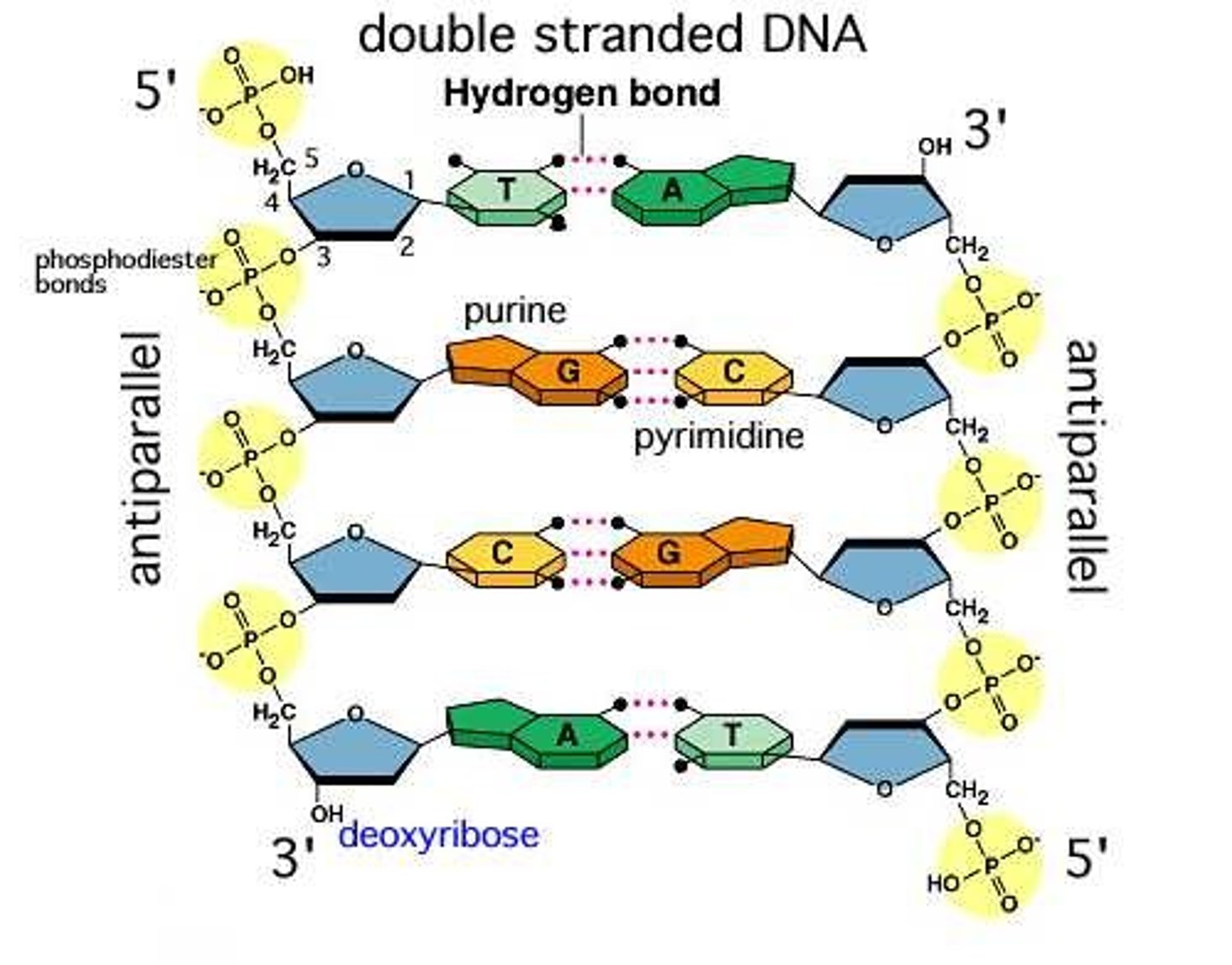
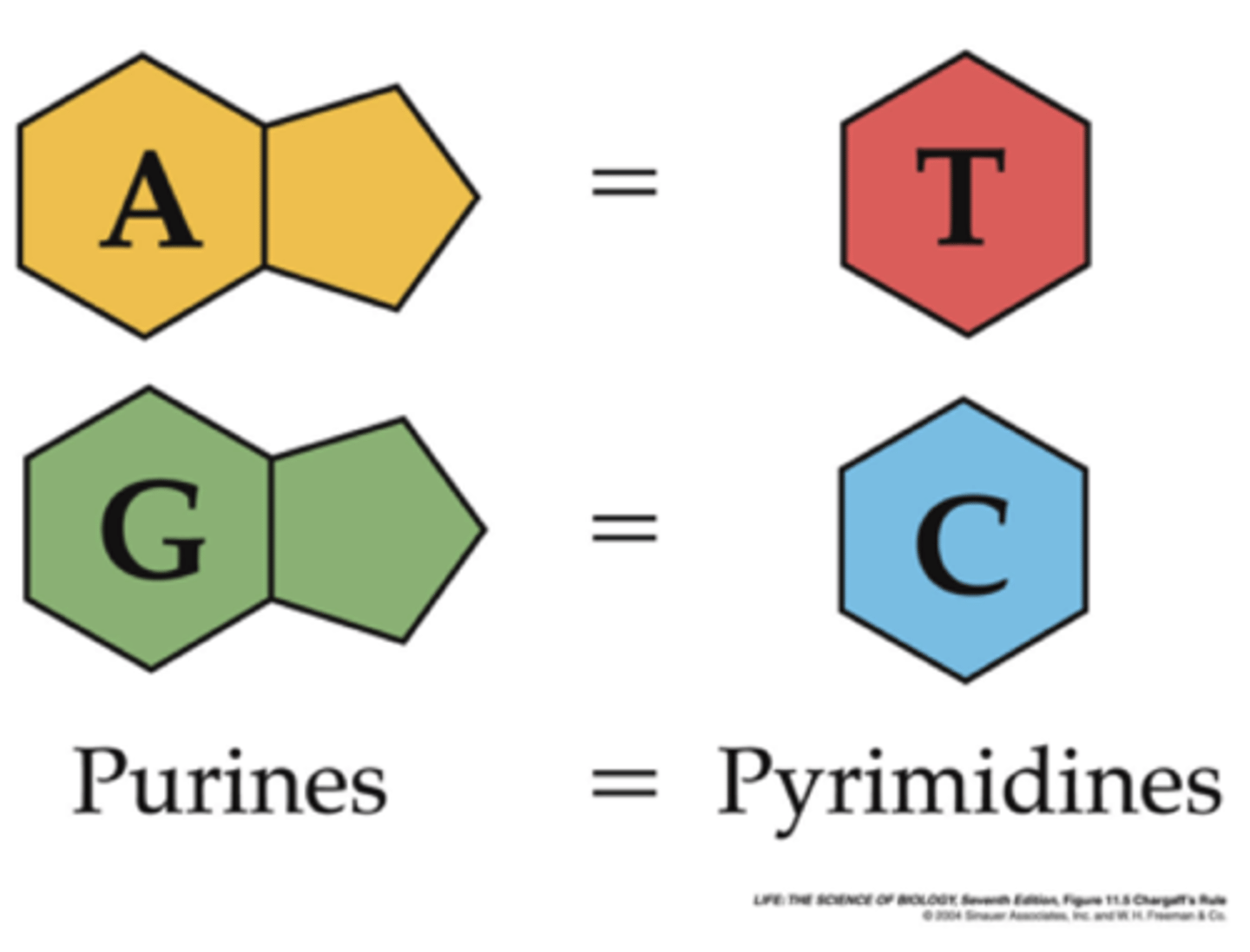
Chargaff's Rule of Base Pairing
the percentage of A is equal to the percentage of T, and the percentage of G is equal to the percentage of C
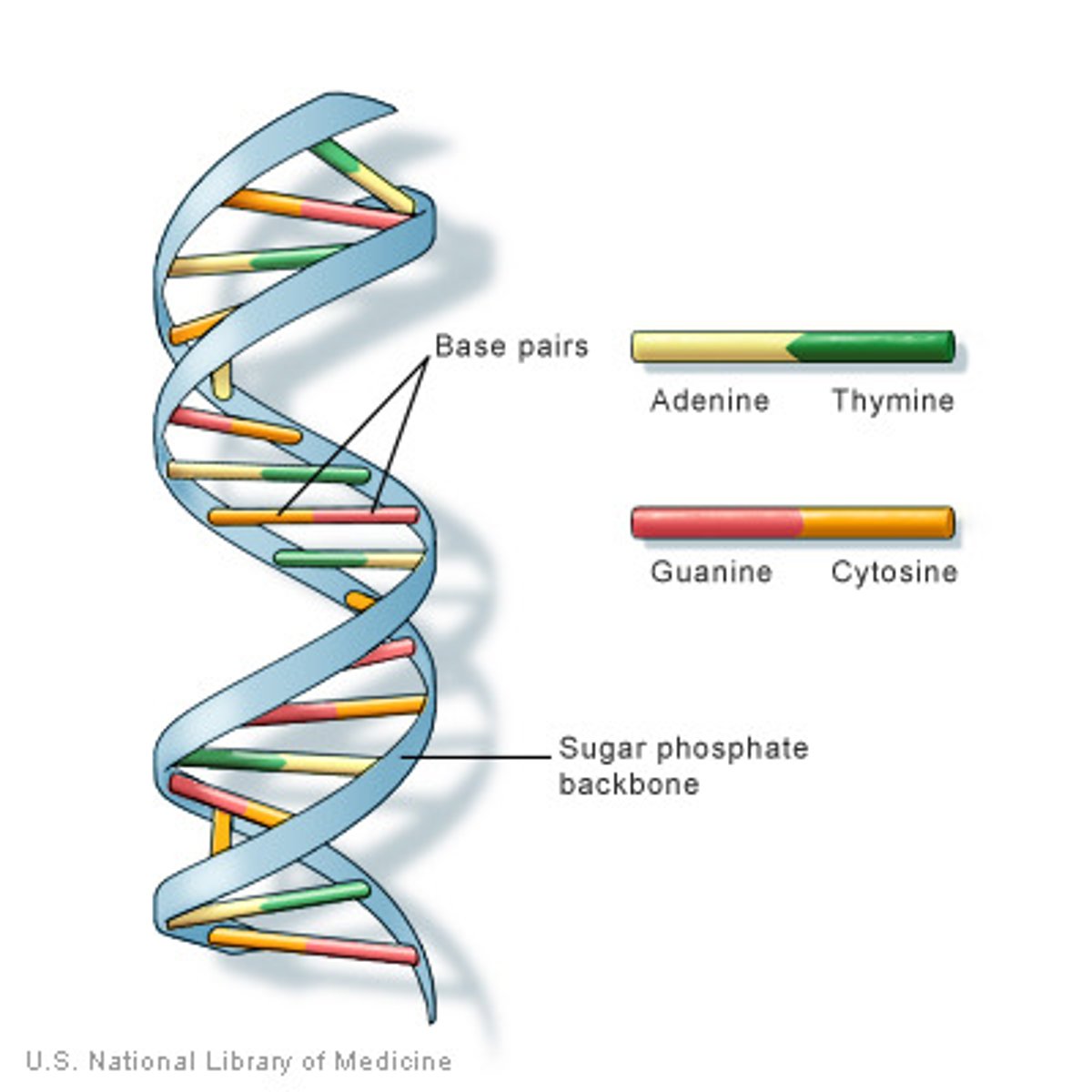
Double helix structure
antiparallel strands of RNA
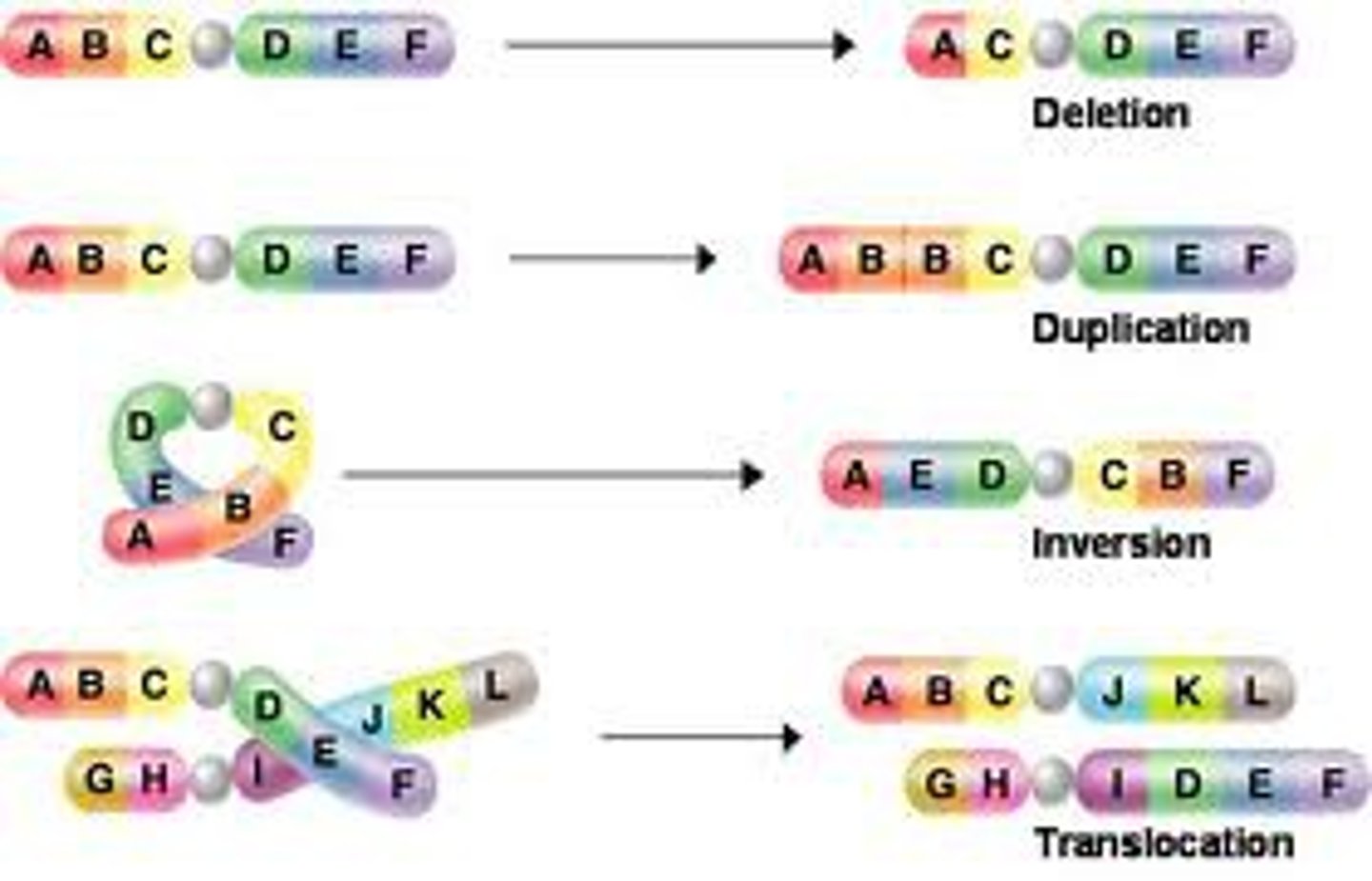
DNA mutation
When DNA changes (usually involves the bases)
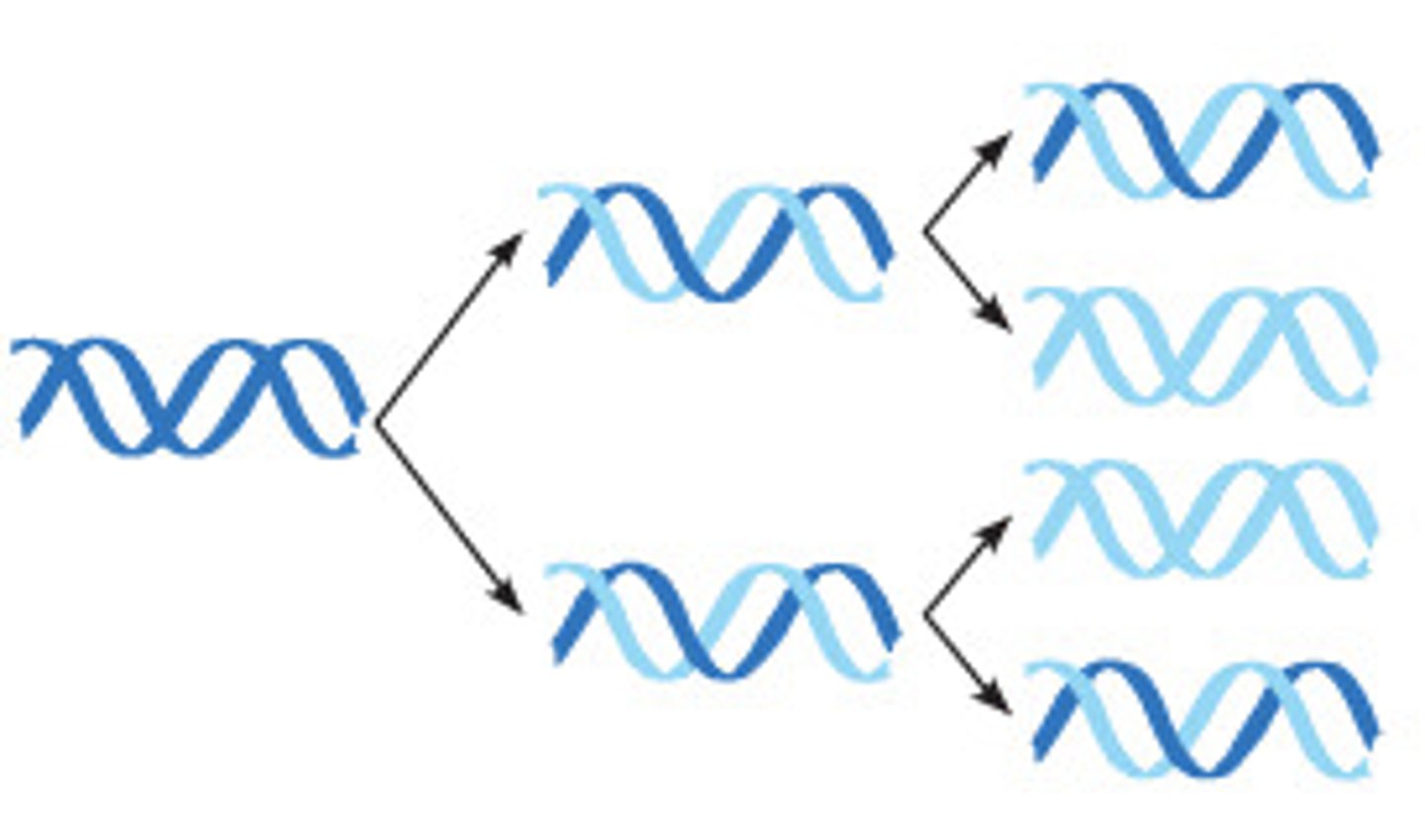
Semiconservative Model of Replication
predicts that when a double helix replicates, each daughter molecule will have one old strand (derived or "conserved" from the parent molecule) and one newly made strand
Steps for DNA Replication
1) DNA unwinds and unzips
2) polymerase binds with the DNA strands and finds nucleotides to match to the bases
3) check errors in DNA strands
4) 2 identical strands of DNA twist up
RNA function
performs protein synthesis
protein synthesis
the formation of proteins by using information contained in DNA and carried by mRNA
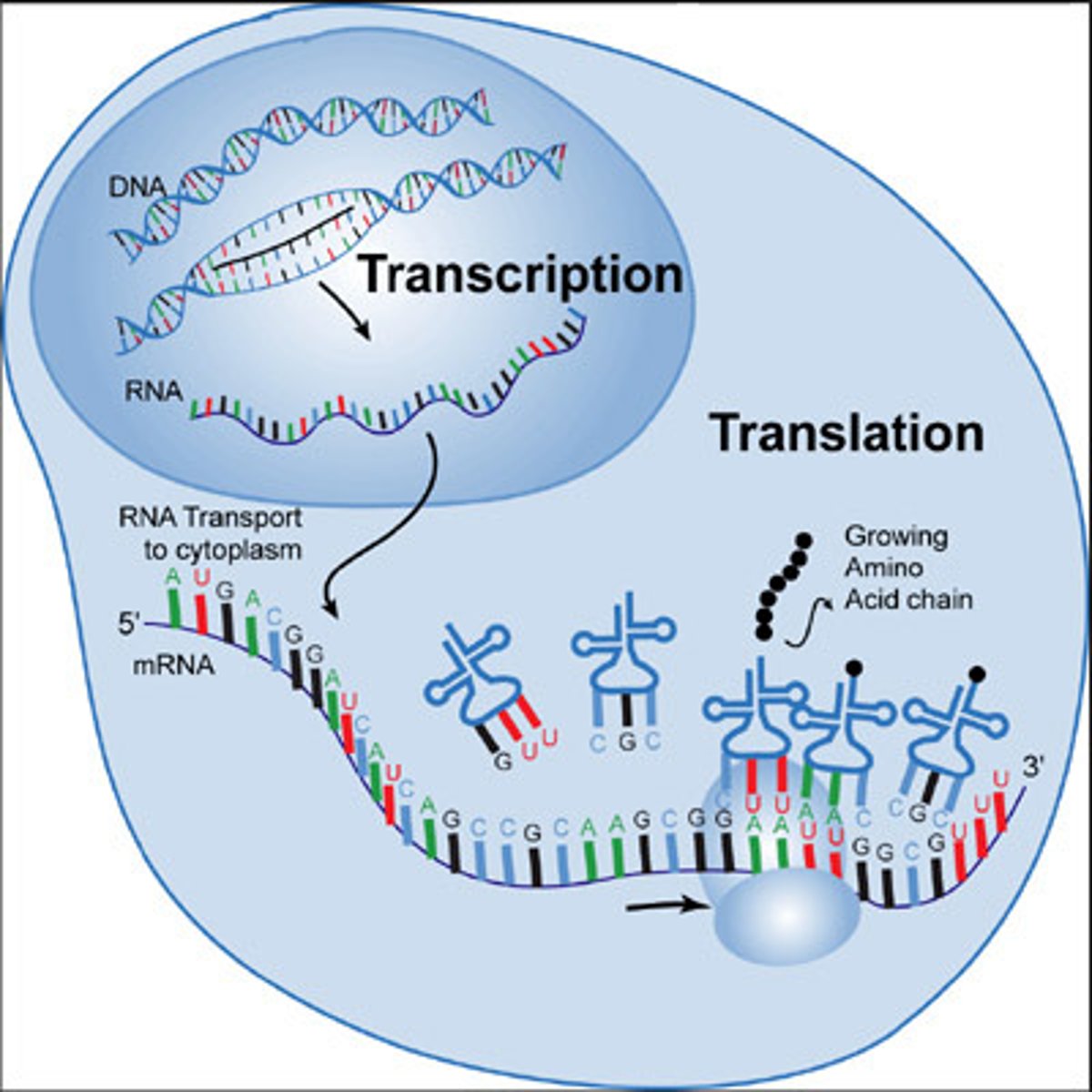
mRNA
A type of RNA, synthesized from DNA, that attaches to ribosomes in the cytoplasm and specifies the primary structure of a protein.
DNA function
DNA is the code for making proteins and stores genetic information
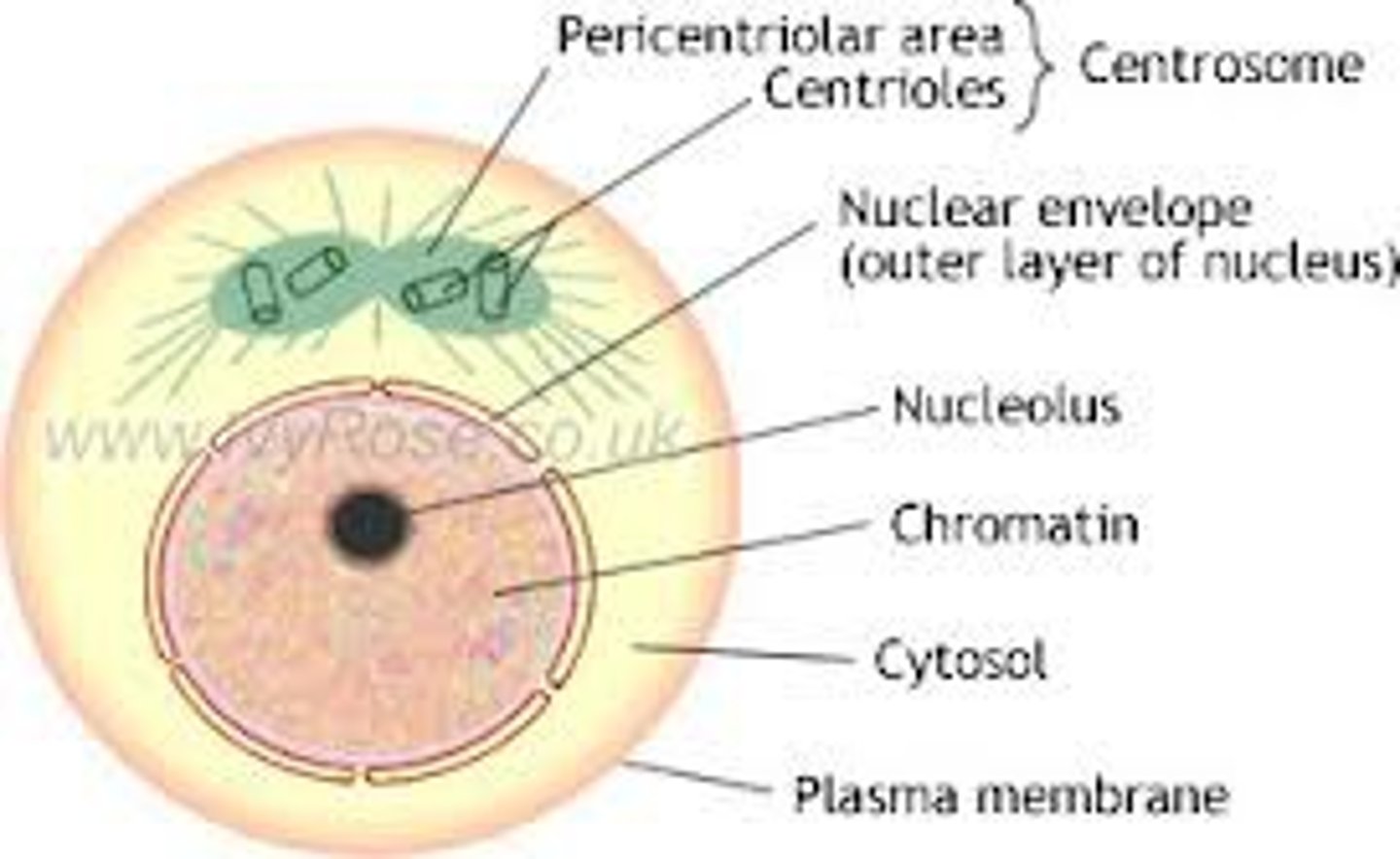
kinetochore
A specialized region on the centromere that links each sister chromatid to the mitotic spindle.
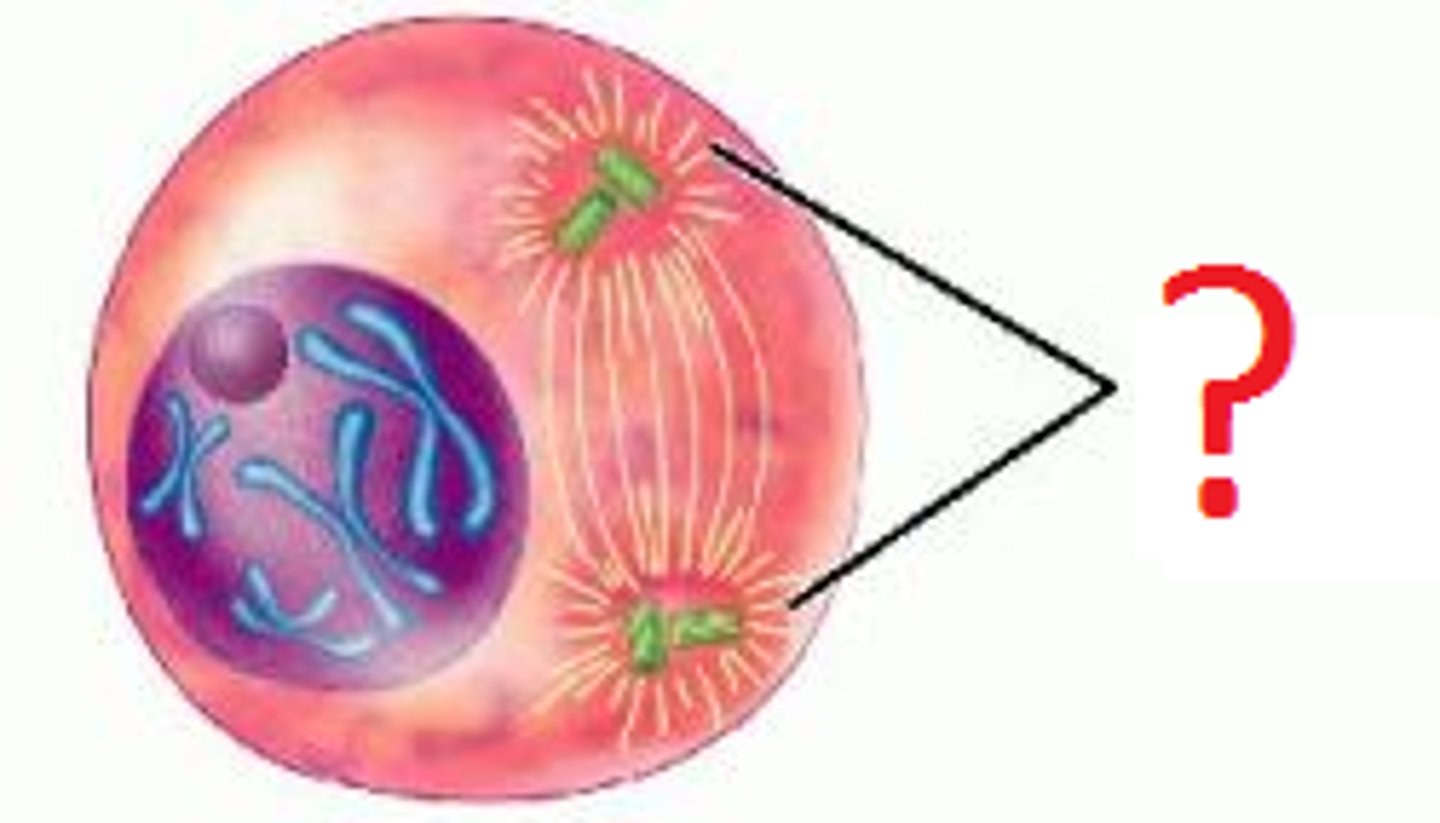
asters
Microtubules and fibers that radiate out from the centrioles.
metaphase plate/equator
the region of the spindle in the middle of the cell along which the chromatids line up
cleavage furrow
The first sign of cleavage in an animal cell; a shallow groove in the cell surface near the old metaphase plate.
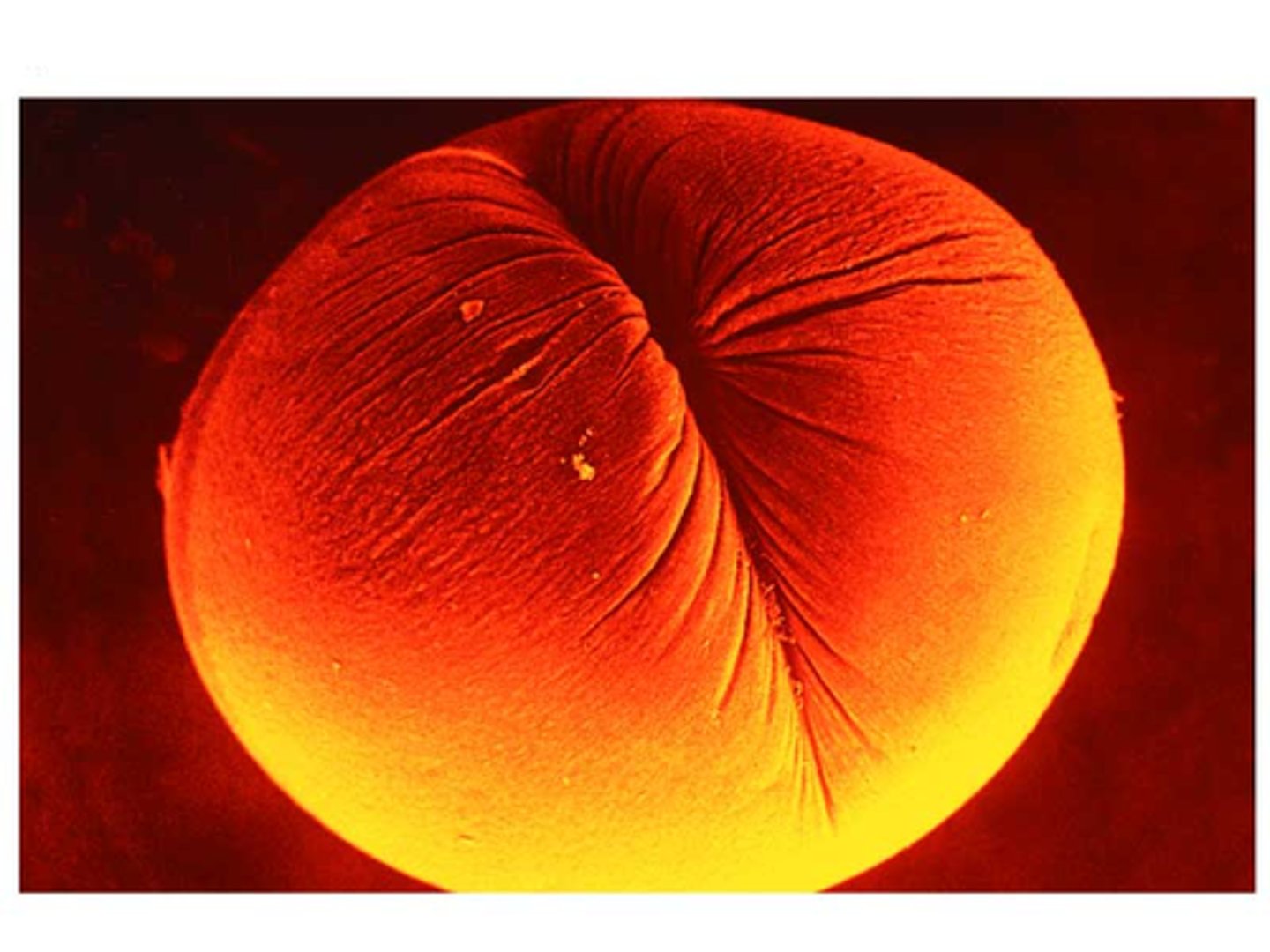
How do chromosomes form?
A single length of
DNA is wrapped many
times around lots of
proteins called
histones, to form
structures called
nucleosomes.
These nucleosomes
then coil up tightly to
create chromatin loops.
The chromatin loops
are then wrapped
around each other to
make a full
chromosome.
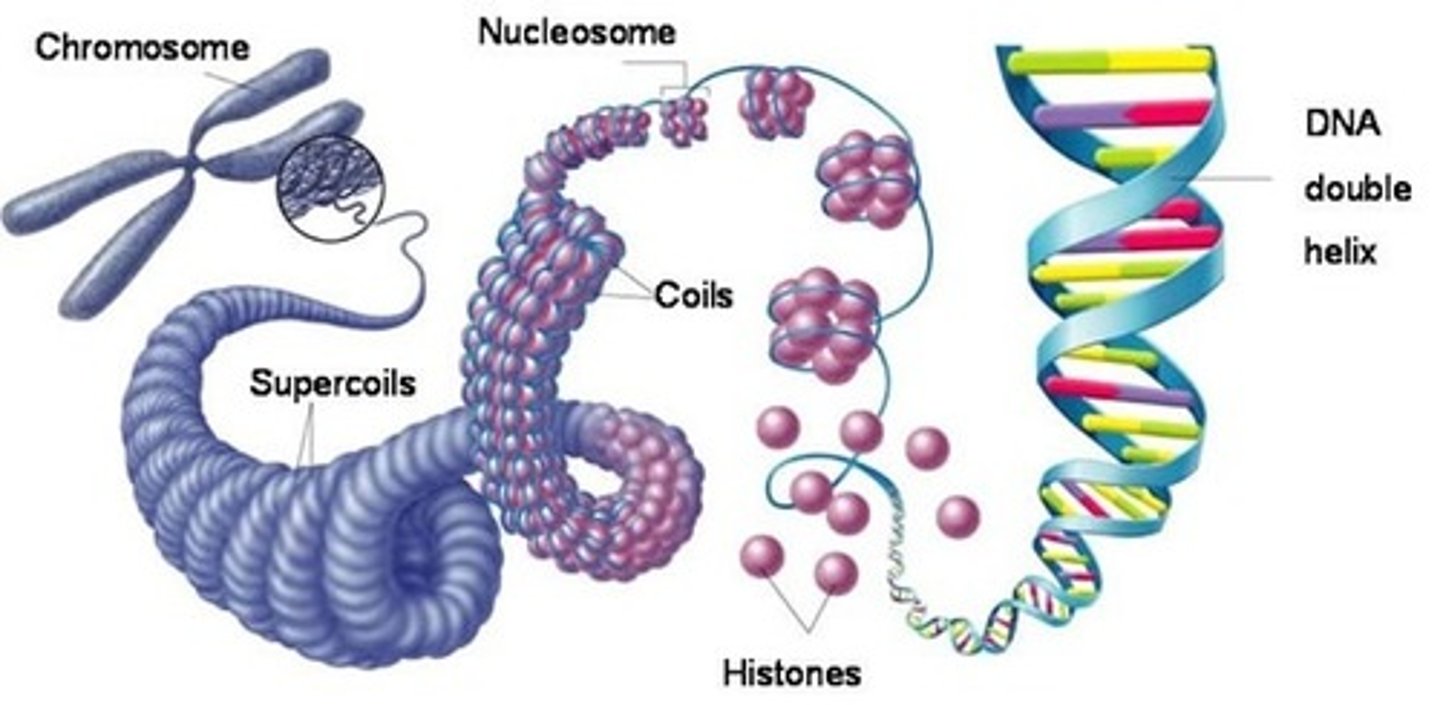
chromosome
a threadlike structure of nucleic acids and protein found in the nucleus of most living cells, carrying genetic information in the form of genes.
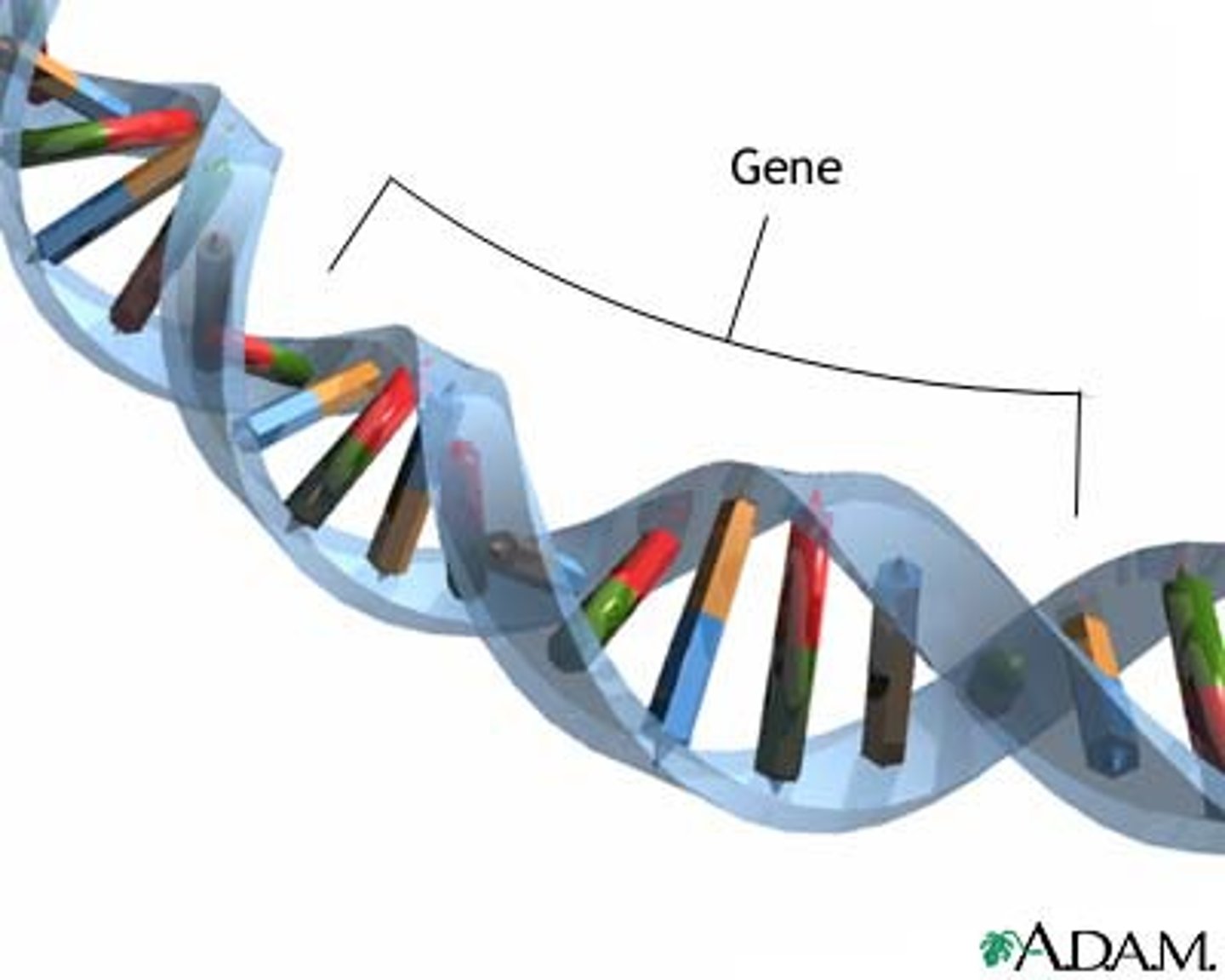
genes
basic unit of heredity in a living organism
contains the code for a single protein (enzyme)
The enzyme causes a chemical reaction that allows a
trait to be expressed (hair/eye colour, etc)
Genes hold the information to build and maintain
an organism's cells and pass genetic traits to
offspring
E.g. Gene for eye colour
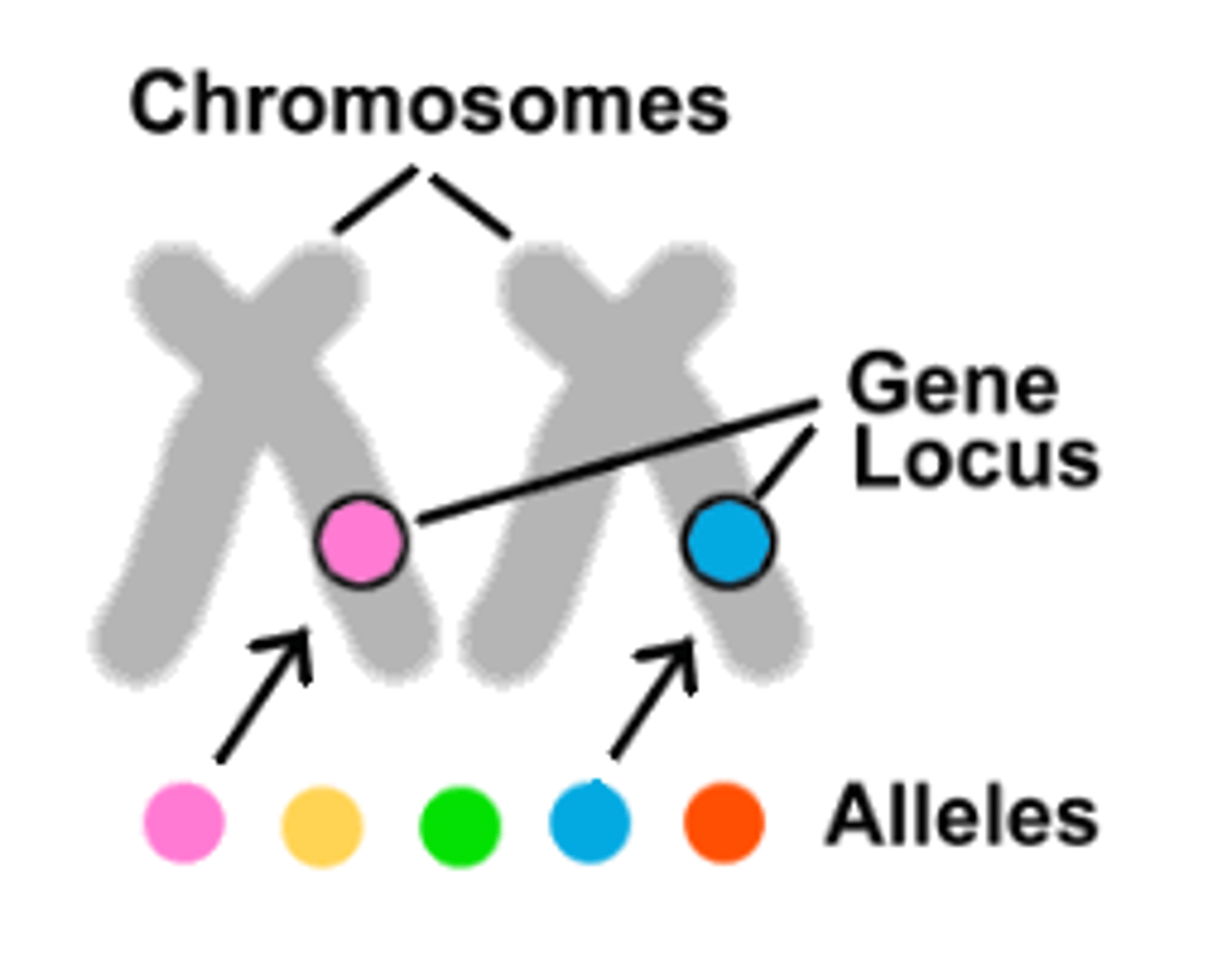
alleles
Different forms of a gene
homozygous
An organism that has two identical alleles for a trait
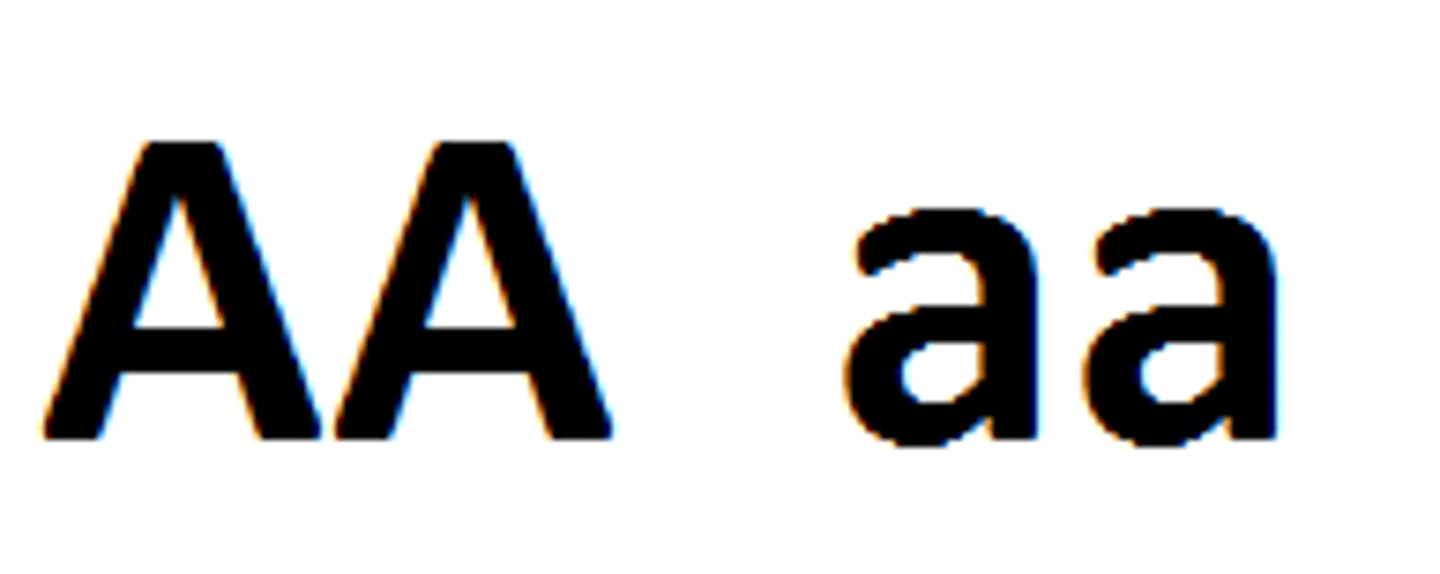
heterozygous
An organism that has two different alleles for a trait
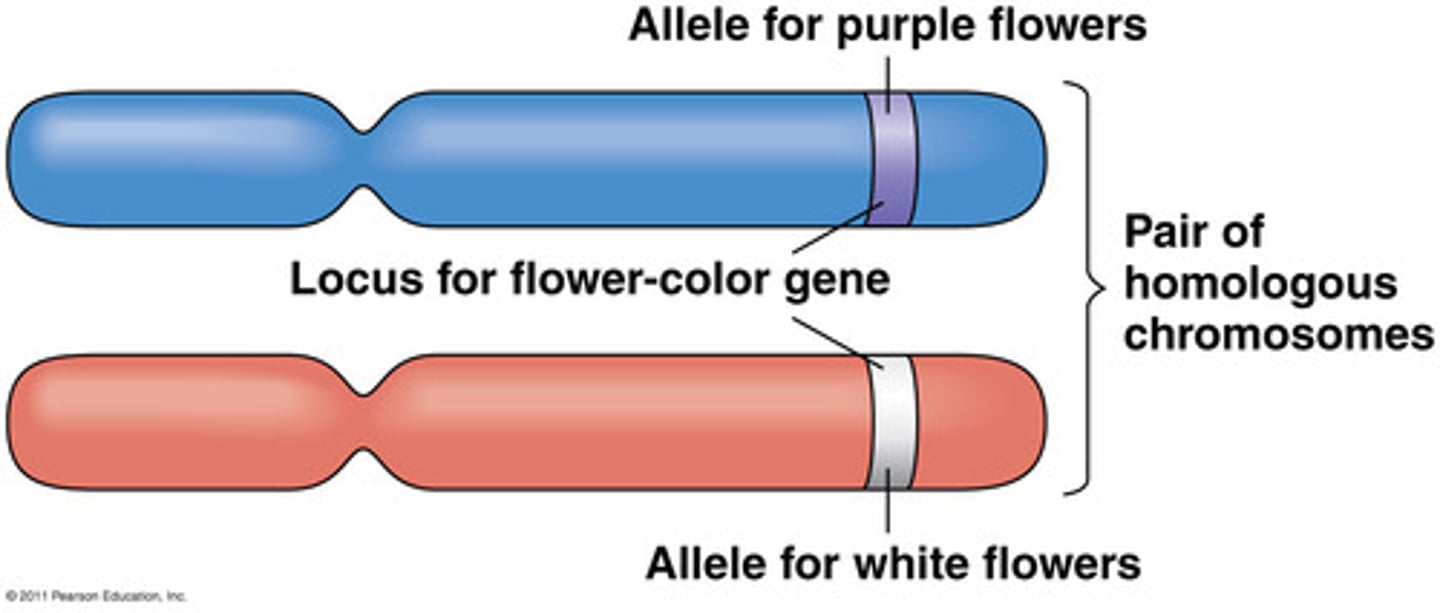
loci
Location of a gene on a chromosome
homologous chromosomes
Chromosomes that are paired - *diploid (next
slide ☺)
alike with regard to size and also position of the
centromere
also have the same genes (e.g. eye colour), but
not necessarily the same alleles (e.g. blue vs
brown), at the same locus or location
Pairs of chromosomes that are similar but NOT
identical based on:
Length
Centromere location
Banding patterns (when dyed)
Carry genes for the same trait at the same
location
tetrad
Each pair of homologous chromosomes.
Chromatids of homologous chromosomes are
aligned length wise, so that genes of one are
adjacent to corresponding genes on the other
Therefore a total of 4 chromatids
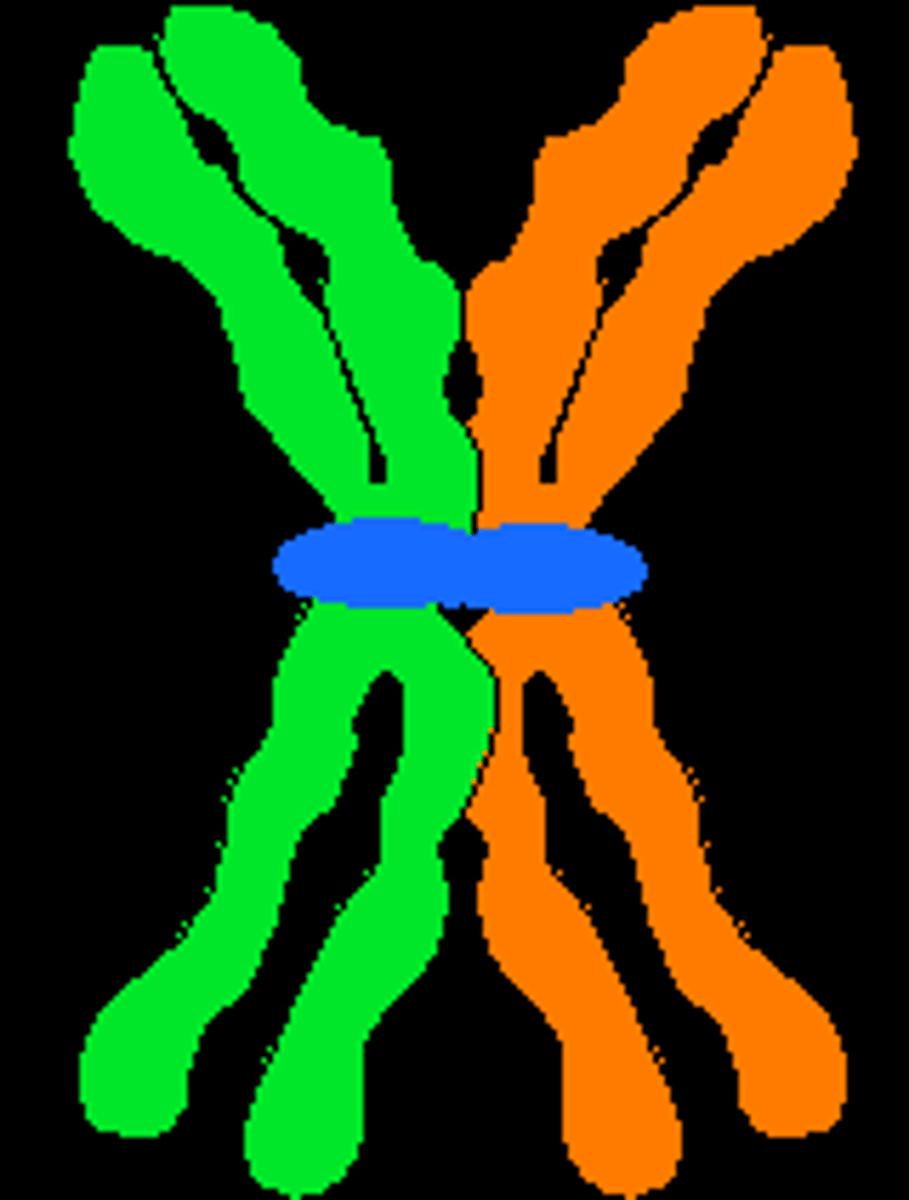
ploidy numbers
Number of sets of chromosomes in a biological cell (46 in humans)
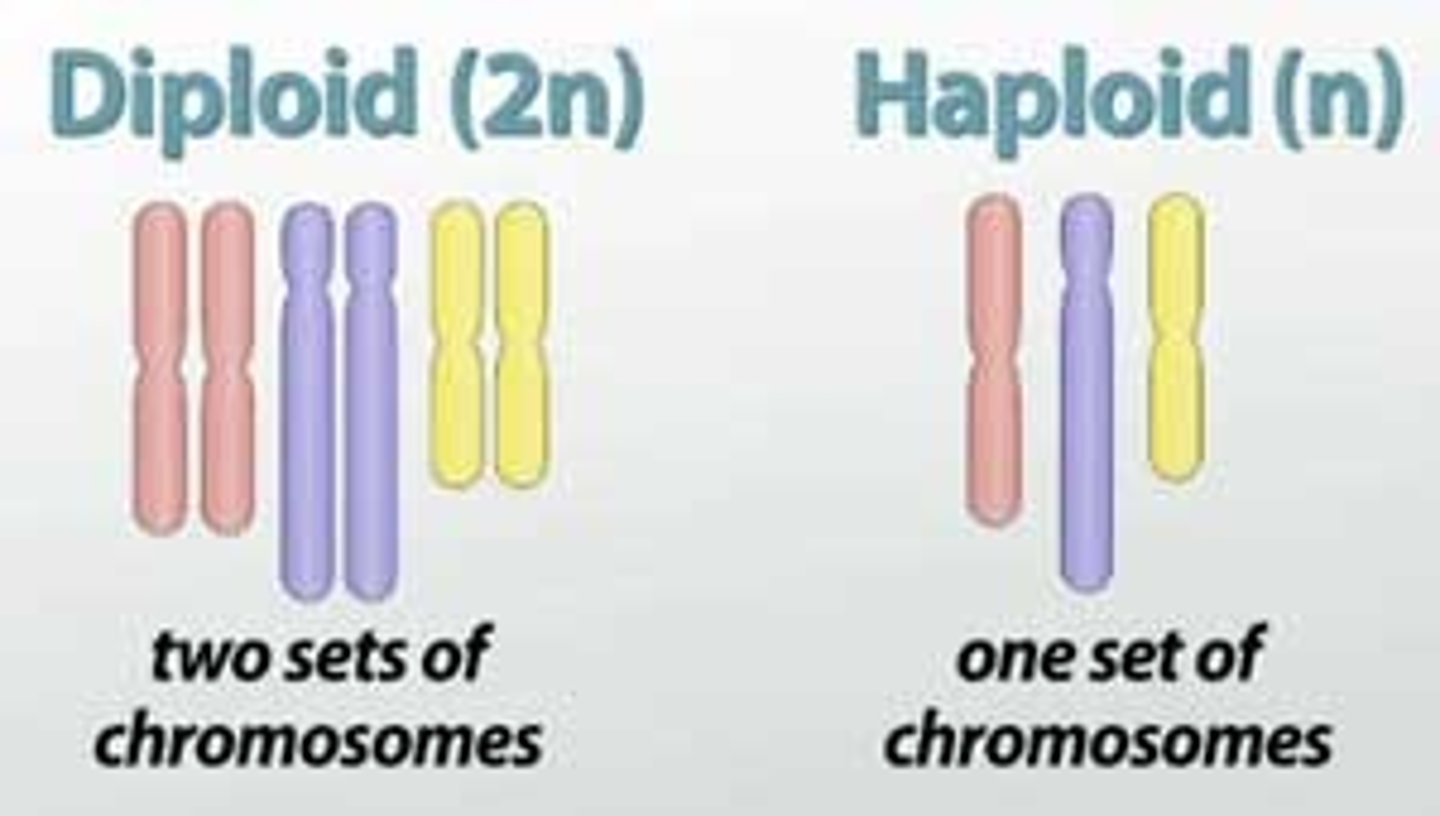
diploid
(genetics) an organism or cell having two sets of chromosomes or twice the haploid number. homologous
chromosomes
one of the pair being
derived from the ovum
and the other from the
sperm
2n = 46
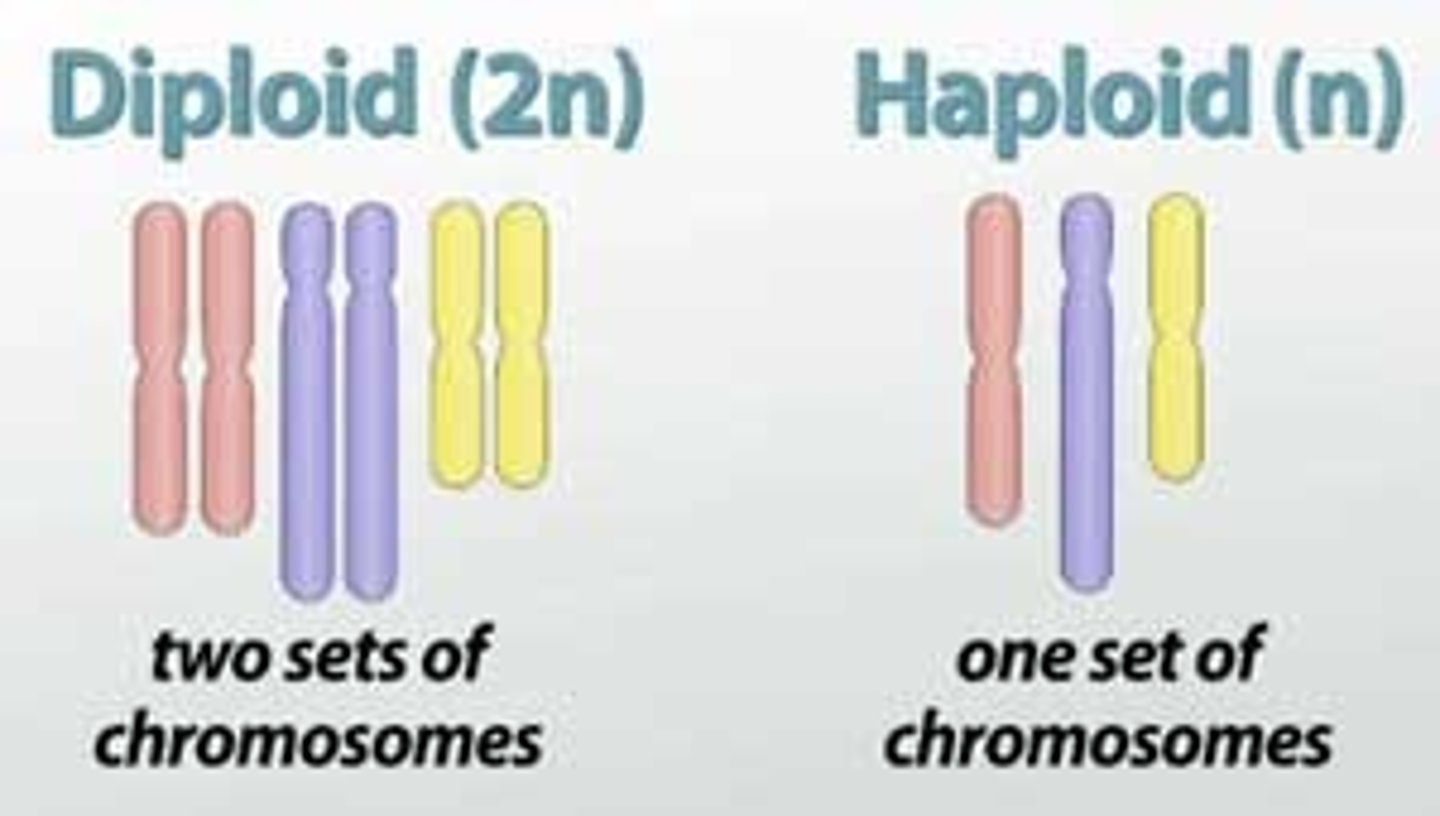
haploid
Having only one copy of
every chromosome
Example: father's X
chromosome is in one
sperm cell, and y
chromosome goes to
another sperm cell
n = 23
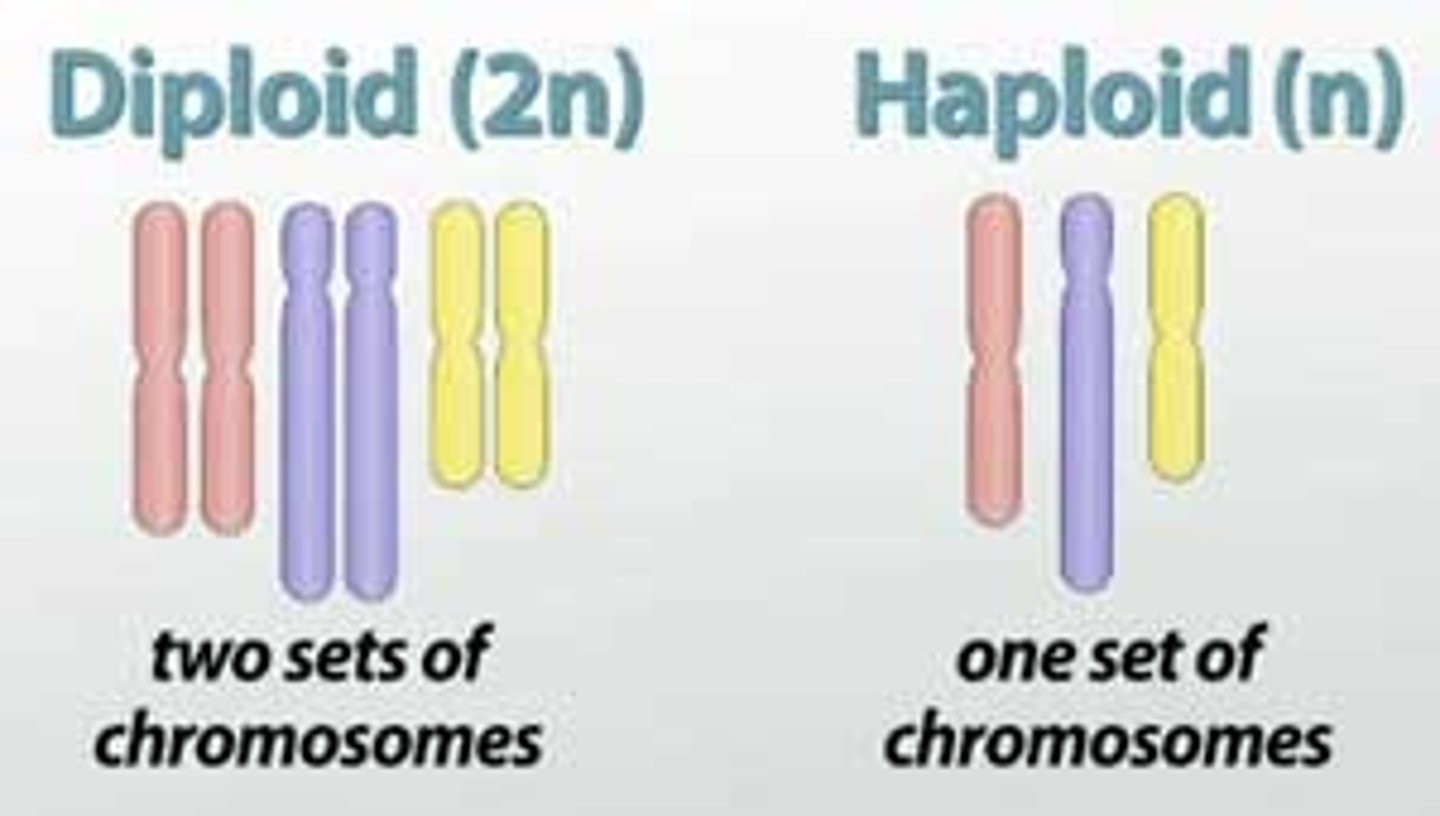
gamete
specialized sex cell such as an egg or a sperm,
which is haploid (n)
Has only half the number of chromosomes (23 in
humans)
A male gamete and a female gamete fuse and produce
a diploid zygote which develops into a new individual.
sex chromosomes
Chromosomes that determine the sex of an individual
1 pair out of 23
Called X and Y, determine individual's sex
Female XX, male XY
autosomes/somatic chromosomes
Any chromosome that is not a sex chromosome
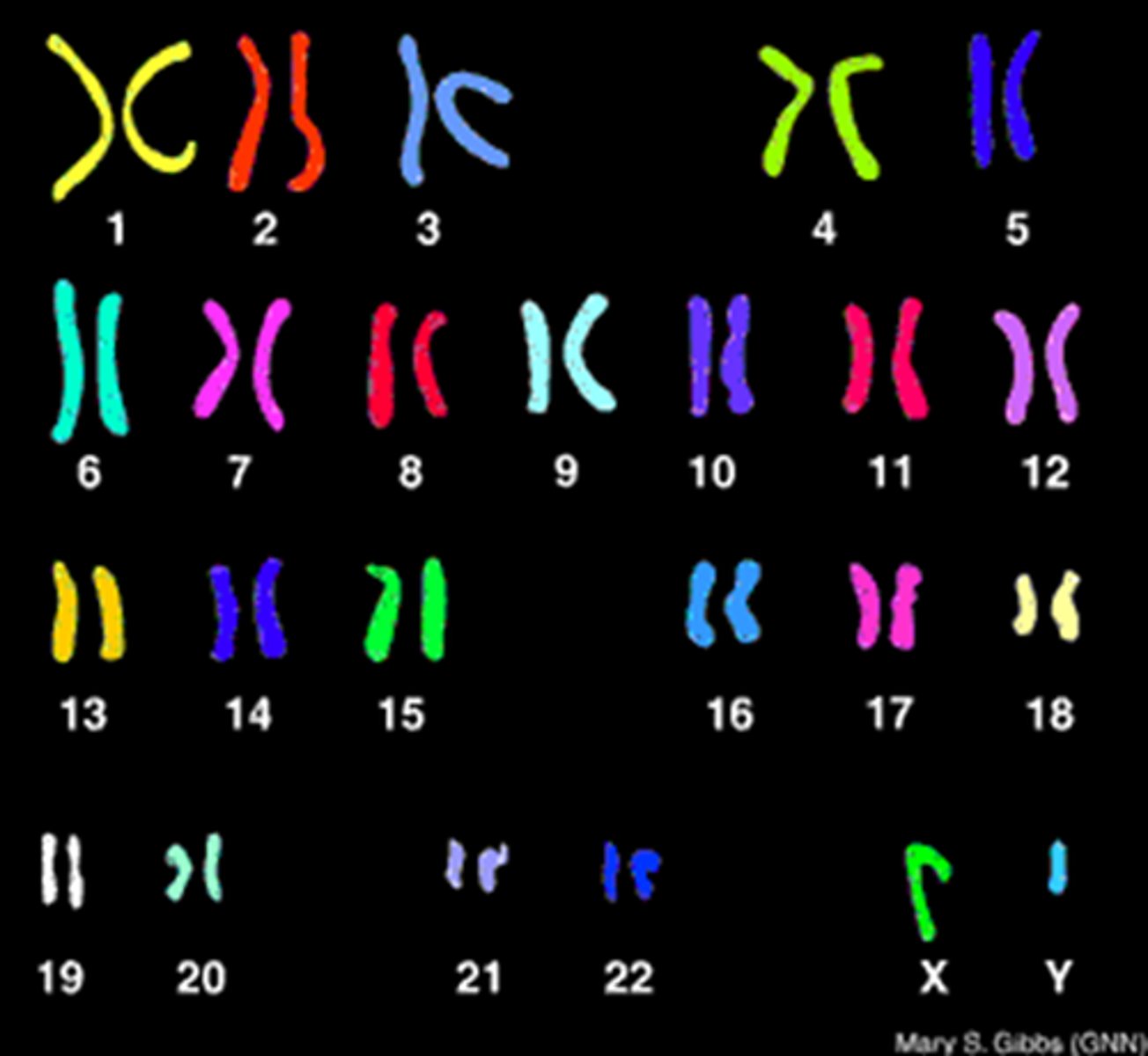
karyotype
A photograph of the chromosome pairs of a cell arranged by size and shape.
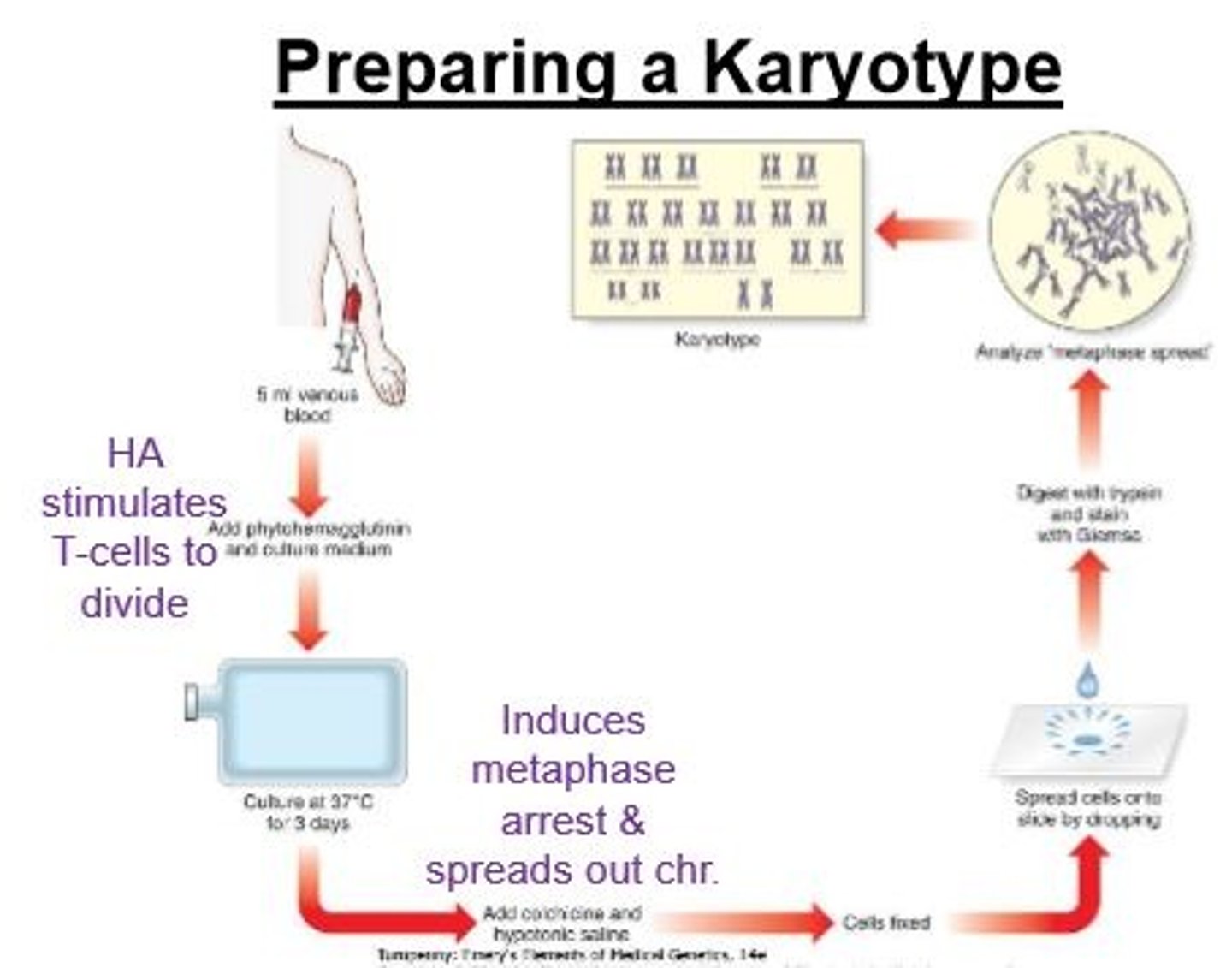
preparing a karyotype
Sample cell in metaphase, chromosomes stained,
revealing banding patterns, then sorted and paired
homologous
term used to refer to chromosomes that each have a corresponding chromosome from the opposite-sex parent
sister chromatids
Identical copies of a chromosome; full sets of these are created during the S subphase of interphase.
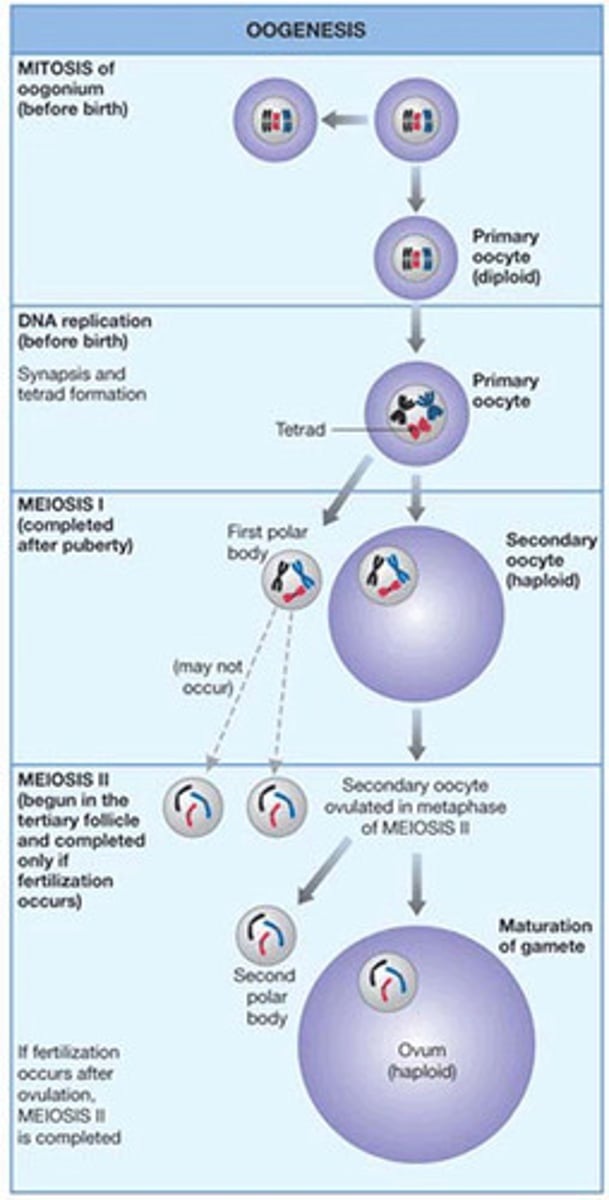
oogenesis
the production, growth, and maturation of an egg, or ovum