introduction to dental anatomy
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
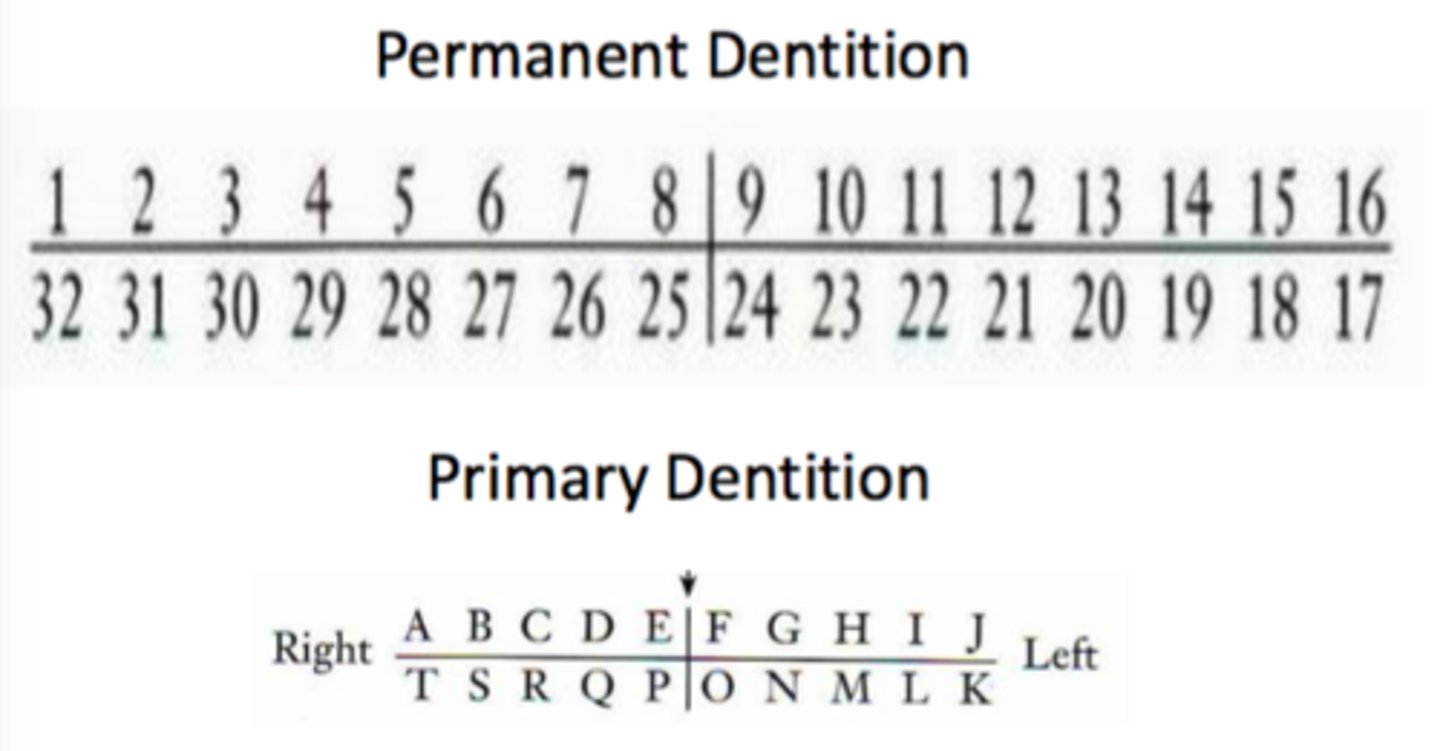
Universal Notation System
uses letters and numbers to denote tooth
clinical crown
visible part of tooth above the gum line
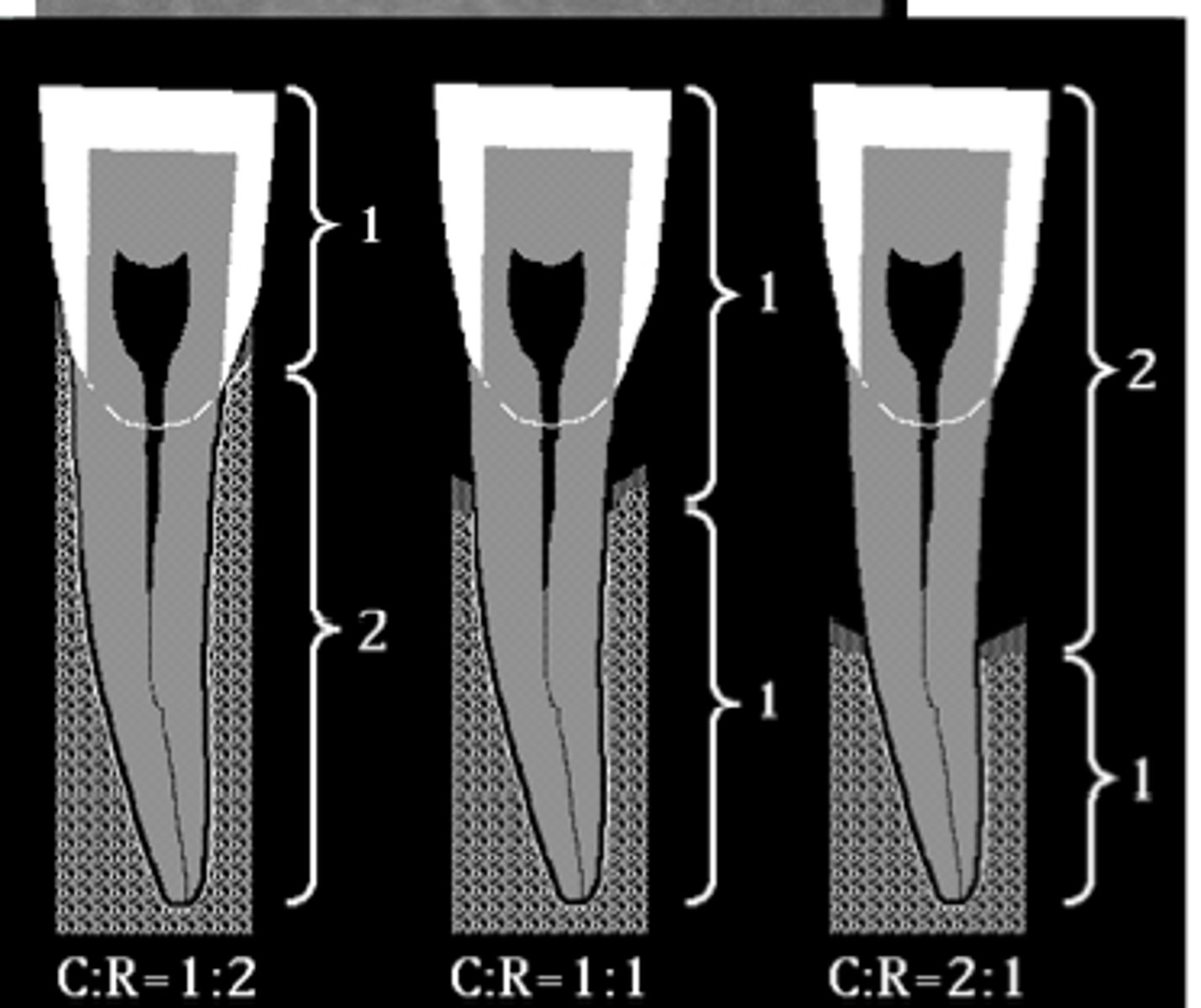
Crown to root ratio
ratio of the portion of tooth occlusal to the alveolar crest (crown) vs. the portion of tooth embedded in bone (root)
Root
Part of tooth embedded in the alveolar process and covered by cementum
Apex
tapered end of root tip
Apical Foramen
opening at the root tip
Does enamel have vitality?
No
Can enamel repair itself?
no
can pulp repair itself?
yes
Enamel
Makes up anatomic crown
Hardest material in the human body
What is enamel made of?
Hydroxyapatite enamel rods in a crystalline structure
Dentin
Makes up bulk of tooth (volume)
Covered by enamel on crown and cementum on the root
Not as hard as enamel
Exposed dentin is often sensitive to cold, hot, air, and touch (via dentinal tubules)
Cementum
Covers root of tooth
Overlies the dentin and joins the enamel at the cemento-enamel junction (CEJ)
Primary function is to anchor the tooth to the bony socket with attachment fibers
Dental pulp
Soft, non-mineralized connective tissue
contains Blood vessels, nerves
functions of dental pulp
Formative
Sensory
Nutritive
Defensive/Reparative
Surfaces of teeth
- Lingual
- Buccal/labial/facial
- Medial
- Distal
- Occlusal/incisal
Proximal
Refers to either the mesial or distal surface (surface/side of a tooth next to a neighbor tooth)
Interproximal
"between teeth, or between two proximal surfaces"
contact
the place where two teeth touch (side by side, or top and bottom)