Chapter 2 Kepler's Laws & Heliocentric Model
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Heliocentric Model
Sun-centered solar system model proposed by Copernicus
Kepler's Third Law
Relates a planet's orbital period to its distance from the Sun
Pluto's Orbit
Takes longer due to Kepler's Third Law
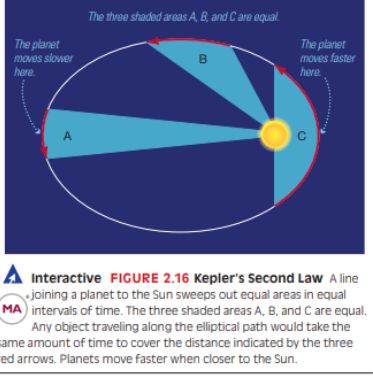
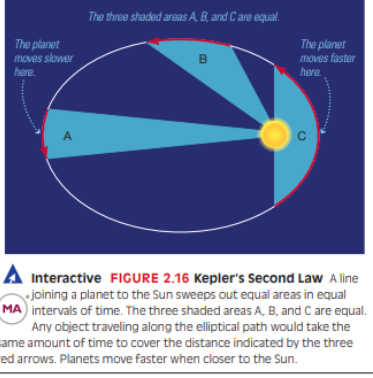
Kepler's Second Law
States equal areas are swept out in equal times
Earth's Orbit
Most similar to option A
Phases of Venus
Contradicted geocentric model observations by Galileo
Speeding Up Orbit
Occurs only during one portion of the planet's orbit
Planetary Orbits
Follow Kepler's laws; A is least like Earth's orbit
Epicycles
Used to explain planet brightness and retrograde motion in geocentric model
Ancient Astronomy
Observed skies, built structures, tracked celestial events
Geocentric Model
Earth-centered system with Ptolemy's epicycles
Telescope Invention
Around 1600; Galileo used it to support the heliocentric model
Kepler's Laws
Derived from Tycho Brahe's observations; include ellipses, equal areas, orbital periods
Aphelion
Farthest point from the Sun (A)
Perihelion
Closest point to the Sun (C)
Period
Time for a planet to orbit the Sun once
Semi-Major Axis
Measure of an ellipse's size
Astronomical Unit
Earth's orbit size around the Sun; unit of length
Eccentricity
Measure of how flattened an ellipse is
Kepler’s third law applies to
A planet around a star other than the Sun, a planet around the sun, a satellite around a planet, a comet around the sun
Pluto takes longer to orbit the sun than earth. This is due to which of Kepler's Laws?
third
Why are the phases of Venus that Galileo observed at odds with this geocentric model?
Venus would not appear ¨Full¨as the Moon does
Which of the following people used epicycles to explain the retrograde motion of the planets while maintaining a geocentric model of the solar system?
Ptolemy
Epicycles are needed in the geocentric model to explain why?
Planets seem to vary in brightness and exhibit retrograde motion.
what is retrograde motion
Motion in the eastward sense is usually referred to as direct, or prograde, motion; the backward (westward) loops are known as retrograde motion
Copernicus revolution
1) Earth is not the center of everything, 2) Center of Earth is the center of the Moon’s orbit. 3) All planets revolve around the Sun. 4) The stars are much farther away than the Sun. 5) The apparent movement of the stars around the Earth is due to the Earth’s rotation. 6) The apparent movement of the Sun around the Earth is due to the Earth’s rotation. 7) Retrograde motion of the planets is due to the Earth’s motion around the Sun
Who built their own telescope and did observations
Galileo
What was Galileo’s observations
1) Moon has mountains and valleys, 2) Sun has sunspots and rotates. 3) Jupiter has moons 4) Venus has phases.