3.8 - taxes as policies to reduce income and wealth inequalities, direct and indirect, recessive progressive and proportional
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
effect of taxation
income redistribution
types of taxes
direct taxes
indirect taxes
direct taxes
paid directly to the government tax authorities
types of direct taxes
personal income taxes
corporate income tax
wealth tax
social insurance contributions/ pay roll taxes
personal income taxes
PROGRESSIVE
taxes paid by households/ individuals on their income (what earned → tax → disposable income)
most important source of government tax revenues
paid on income
wages
rent
interest
profit
corporate income tax
PROGRESSIVE
taxes on the profits of the corporations, assessed on their net income after expenses and allowable deductions.
wealth taxes
PROGRESSIVE
taxes on the net wealth of individuals or households, targeting accumulated assets and property
property tax
inheritance tax
social insurance contributions/ pay roll taxes
PROPORTIONAL
taxes paid by employees and employers to fund social insurance programs such as Social Security and Medicare
tax revenues are not paid into government’s budget
indirect taxes
ALL REGRESSIVE
taxes that are not directly paid by individuals but are instead included in the price of goods and services
sales taxes
excise taxes
tariffs/ customs duties
sales taxes/ general expenditure taxes (VAT → value added tax)
taxes on spending/ selling on goods and services
fixed % of retail price of goods and service
may exclude/ offer different rate for some goods and services on ground of equity
excise tax
tax paid on specific goods or services (usually demerit)
eg. on cigarettes, alcohol etc
tariffs/ customs duties
taxes imposed on imported or exported goods
aimed at regulating trade and generating revenue for the government.
why are all indirect taxes regressive
! indirect taxes account for a bigger proportion of income of low-income households compared to high-income households
example:
car price = 10 000
sales tax = 10%
income A = 20 000
income B = 100 000
*both pay 1 000 $ od tax
but
A = 1 000/ 20 000 = 5%
B = 1 000/ 100 000 = 1%
tax rate
tax as % of income
the 3 natures of taxes
proportional taxation
progressive taxation
regressive taxation
proportional taxation
tax rate remains constant regardless of income level
progressive taxation
tax rate increases as income increases,
reduces income inequality
the more progressive taxation the more equal after-tax distribution of income
regressive taxation
tax rate decreases as income increases
places higher burden on low-income households
calculation of taxes
marginal tax rate
the amount of tax paid on an additional dollar of income
average tax rate
the total tax paid divided by total income
marginal tax rate and average tax
tax brackets
applying a different marginal tax rate to each bracket
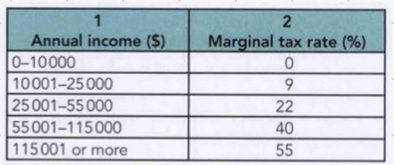
example calculation based on the photo:
calculate the amount of income tax paid on an annual income of $59 000
(0 × 10 000) + (0.09 × 15 000) + (0.22 × 30 000) + (0.40 × 4 000) = 0 + 1350 + 6600 + 1600 = 9550$
average tax: 9550$/ 59000$ = 16.2% or 0.162
calculating indirect taxes
a = value after indirect tax (disposable income)
x = indirect tax
in = income after income tax
s = amount of spending on indirect tax/ value of indirect tax
a+ax = in
eg.
60 000 = total income
15 000 = value of income tax
60 000 - 15 000 = 45 000 = income after income tax
12.5% = indirect tax
so:
a + 0.125a = 45 000
0.125a = 45 000
a = 40 000
s = 45 000 - 40 000 = 5 000
average rate of indirect tax
arit = indirect tax value/ total income
total average indirect tax rate
tatr = (vale of income tax + value of indirect tax)/ total income
percentage of redistribution that occurs through tax system
25%
downsides of progressive taxes
(in theory more progressive taxes = more equal distribution of income)
disincentive effects
income tax reduces after-tax income, acting as a disincentive to work
lower quality of labour offered in the market
lower quantity of savings
lower investment
lower production of new capital goods
lower economic growth rate
lower income taxes may not lead to more work
lower corporate taxes may not to lead to greater investment