Applied Neurophysiology
1/124
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
125 Terms
Why is the brain not capable of significant anaerobic metabolism?
It relies almost entirely on glucose metabolism for energy, which requires oxygen
What percent of total body O₂ does the brain consume?
20%
About 60% of cerebral O₂ consumption is used to
Generate ATP to support neuronal activity
What is cerebral metabolic rate (CMR) usually expressed as?
O₂ consumption (CMRO₂)
Normal CMRO₂ rate in adults:
1. Awake:
→ Per 100g/min
→ Total/min
2. Asleep/Under GA
1. Awake:
→ 3-3.8 mL/100g/min
→ 50mL/min
2. Asleep/Under GA:
→ < 1 mL/100g/min
Weight of brain in:
1. Males
2. Females
1. Males → 1300g
2. Females → 1150g
Why is the brain so vulnerable to ischemia?
→ Rapid O₂ consumption
→ Very low O₂ reserves
What happens if cerebral blood flow (CBF) is interrupted for 3-8 minutes?
ATP stores depleted → Irreversible cellular injury
What is the primary energy source for neuronal cells?
Glucose
What is the rate of brain glucose consumption? What percent is aerobic?
1. 5mg/100g/min
2. 90% aerobic
→ So lots of ATP produced
________ normally parallels glucose consumption
CMRO₂
Cerebral function is dependent on a continuous supply of what substrate?
Glucose
What effect does hypoglycemia have on the brain?
Directly injurious to brain tissue
How can hyperglycemia worsen brain injury in ischemic conditions?
Hyperglycemia accelerates cerebral acidosis (lactic acid) and cellular injury → Exacerbating global and focal brain damage
What happens to cerebral blood flow (CBF) when CMRO₂ increases?
CBF also increases to match the higher metabolic demand
Normal CBF average
50 mL/100 g brain tissue/min
→ At PaCO₂ of 40 mmHg
Gray matter CBF
80 mL/ 100 g brain tissue/min
White matter CBF
20 mL/ 100 g brain tissue/min
What is the total adult cerebral blood flow (CBF) when awake? What percent of cardiac output?
1. 750 mL/min
2. 15% of cardiac output
What CBF range is associated with irreversible brain damage?
<10 mL/ 100 g brain tissue/min
What CBF range is associated with cerebral impairment?
<20-25 mL/ 100 g brain tissue/min
Which CBF range is associated with isoelectric EEG?
<20 mL/ 100 g brain tissue/min
What is cerebral perfusion pressure dependent on?
MAP and ICP
→ MAP pushes blood in
→ ICP (or CVP) pushes against it
Cerebral perfusion pressure equation
CPP = MAP - ICP or CVP (whichever is larger)
True or False: PaCO₂ and PaO₂ affect cerebral blood flow only when acting together, not independently
False
→ Both PaCO₂ and PaO₂ independently affect CBF
What factors influence CBF?
1. CMRO₂
2. CPP
3. PaCO2
4. PaO2
5. Temperature
6. Blood viscosity
Is a significant increase in cerebral blood flow (CBF) always beneficial to the brain?
No
↑CBF → ↑CBV → ↑ICV → ↑ICP → Brain compression
1. What is normal CPP?
2. Normally ICP is below ________
1. 80-100 mmHg
2. 10 mmHg
Irreversible brain damage occurs if CPP is sustained below ______
25 mmHg
What can happen if ICP rises above 30 mmHg, with a normal MAP?
CPP and CBF can become compromised → Possible cerebral ischemia
What effect does the Trendelenburg position have on cerebral circulation?
↑Jugular venous pressure → ↓Cerebral venous drainage → ↑ICP → ↓CPP
What effect does the reverse Trendelenburg position have on cerebral circulation?
↓Jugular venous pressure → ↑Cerebral venous drainage → ↓ICP → ↑CPP
Which position decreases intracranial pressure (ICP): Trendelenburg or reverse Trendelenburg?
Reverse Trendelenburg (head up)
Which position increases intracranial pressure (ICP): Trendelenburg or reverse Trendelenburg?
Trendelenburg (head down)
What happens to ICP when CBF and CPP decrease?
ICP also decreases
↓CBF/CPP → ↓CBV → ↓ICV → ↓ICP
What happens to ICP if CBF and CPP increase?
ICP also increases
↑CBF/CPP → ↑CBV → ↑ICV → ↑ICP
1. What happens to cerebral vessels when CPP decreases?
2. What happens to cerebral vessels when CPP increases?
1. Arterial dilation (to maintain CBF)
2. Arterial constriction (to limit excess CBF)
Within what MAP range is cerebral blood flow (CBF) autoregulated and kept constant?
~60 and 160 mmHg
Outside the limits of cerebral autoregulation, what does CBF become dependent on?
Arterial pressure
What can happen when MAP rises above 150-160 mmHg?
Blood-brain barrier can be disrupted
→ Can lead to cerebral edema and hemorrhage
In patients with chronic hypertension, which way is the cerebral autoregulation curve shifted? Why?
1. To the right
2. Higher MAP is required to maintain constant CBF
What effect does long-term blood pressure control have on cerebral autoregulation limits?
It can restore the autoregulation curve closer to normal
True or false: In chronic hypertension, CBF becomes less pressure dependent
False
→ In chronic hypertension, CBF becomes more pressure dependent
What is the effect of increased intracranial venous blood pressure on the brain?
↑Intracranial venous pressure → ↓Venous drainage → ↑ICP → ↓CPP
What happens to the brain during intracranial surgery if venous drainage is impaired?
Brain becomes swollen (↑ brain bulk), making surgery more complicated
What are some causes of impaired venous drainage?
1. SVC syndrome → Obstruction of the SVC
2. Cerebral venous thrombosis → Venous clot
3. Internal jugular compression → Improper neck positioning
4. Coughing (Valsalva) → Increases CVP
How do acute changes in PaCO₂ and PaO₂ affect CBF?
PaCO₂: Acute ↑ or ↓ = Immediate proportional change in CBF
PaO₂: Minimal effect until <50 mmHg → Then CBF increases sharply
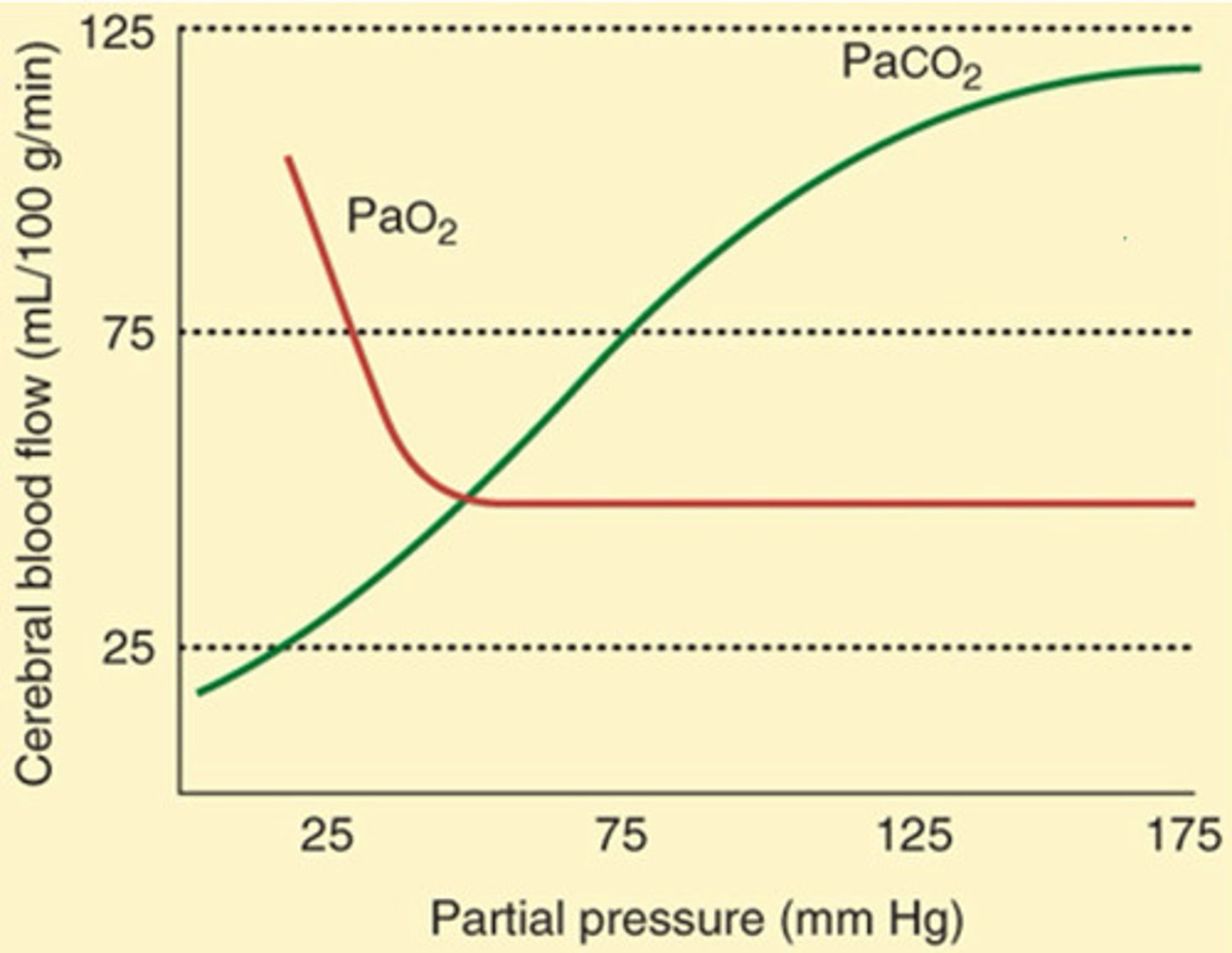
Which arterial blood gas has a linear relationship with CBF: PaCO₂ or PaO₂?
PaCO₂
Within what range is CBF directly proportional to PaCO₂?
By how much does CBF change for each 1 mmHg change in PaCO₂?
1. 20-80 mmHg
2. 1-2 mL/100 g of brain tissue/min
Why does acute metabolic acidosis have little effect on CBF?
H+ ions cannot cross BBB
What effect does severe hypoxemia (PaO₂ <50 mmHg) have on CBF?
Greatly increases CBF
How does hypothermia affect CMRO₂ and CBF?
Decreases both
By how much does CBF change for every 1°C change in body temperature?
5-7%
By how much does CMRO₂ decrease if body temperature falls by 10°C?
50%
At what temperature is the EEG isoelectric?
20°C
→ Further decreases continue to reduce the CMR of the brain
What is the most effective method of protecting the brain during focal and global ischemia?
Hypothermia
→ Reduces CMRO₂
How does hyperthermia affect brain activity, CMRO₂, and CBF?
↑Brain activity → ↑CMRO₂ → ↑CBF
How does hypothermia affect brain activity, CMRO₂, and CBF?
↓Brain activity → ↓CMRO₂ → ↓CBF
Most important determinant of blood viscosity
Hematocrit
How does a decrease in Hct affect blood viscosity and CBF?
↓Hct → ↓Viscosity → ↑CBF
How does an increase in hematocrit (Hct) affect blood viscosity and cerebral blood flow (CBF)?
↑Hct → ↑Viscosity → ↓CBF
What happens to oxygen capacity and delivery at reduced Hct?
↓Hct → ↓Oxygen-carrying capacity → Impaired oxygen delivery
At what Hct level is oxygen delivery optimal?
30%
What types of substances can pass through the BBB?
Non-ionized and lipid soluble substances
→ Also small in size
What types of substances cannot pass through the BBB?
1. Ionized molecules
2 Substances with large molecular weights
How does plasma tonicity affect water movement across the blood-brain barrier in the following cases:
1. Hypertonic plasma
2. Hypotonic plasma
1. Hypertonic plasma → Water moves out of the brain
2. Hypotonic plasma → Water moves into the brain
Which large molecule does not cross the BBB, creates plasma hypertonicity, and reduces brain volume?
Mannitol
How does autonomic innervation affect intracranial vessels and cerebral blood flow (CBF)?
SNS:
Causes vasoconstriction → ↓CBF
→ Intense activation can worsen ischemia
→ Acts as a protective mechanism to prevent sudden surges of perfusion pressure (like during systemic hypertension in “fight or flight”)
PNS:
Causes vasodilation → ↑CBF
1. What feature of cerebral capillaries creates the blood-brain barrier?
2. Why are cerebral capillaries considered a physiologic barrier?
3. What conditions can disrupt the blood-brain barrier (BBB)?
1. Endothelial cells with tightly fused junctions
2. Made of lipid bilayer that lacks pores
3. Conditions such as:
→ Hypertension
→ Hypoxia
→ Hypercapnia
→ Infection
→ Tumors
→ Trauma
→ Stroke
→ Seizure activity
Components of cranial vault
→ Rigid structure with a fixed total volume
→ 80% brain
→ 12% blood
→ 8% CSF
Monroe-Kellie Hypothesis
An increase in volume of one component must be compensated by a decrease in volume of another to prevent a rise in ICP
What are the major compensatory mechanisms that help prevent increases in intracranial pressure (ICP)?
1. Initial displacement of CSF
→ From the cranial to spinal compartment
2. Increase in CSF absorption
3. Decrease in CSF production
4. Decrease in total CBV (primarily venous)
True or false: Even small increases in the volume of one intracranial compartment are usually not well compensated
False
→ Small increases in the volume of one component are initially well compensated
Supratentorial pressure measured in the lateral ventricles or over the cerebral cortex
ICP
With ________, fairly large increases in ICV cause only a small increase in ICP, and with __________ , a further small increase in ICV causes a large increase in ICP
1. Compensation
2. Decompensation
On the intracranial elastance curve, what is happening between phase 1 → 2?
ICP does not increase because of compensatory mechanisms
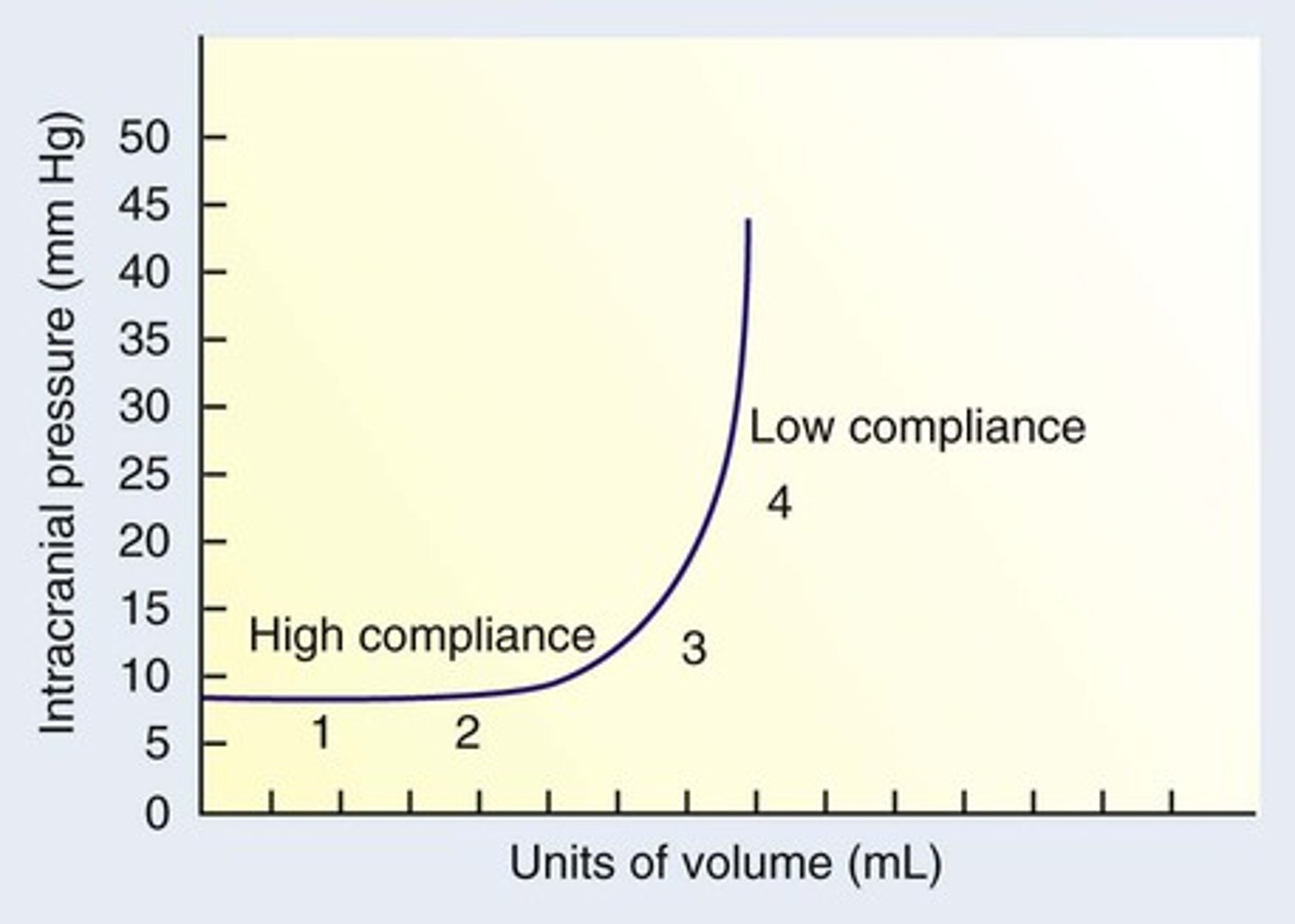
On the intracranial elastance curve, what is happening at phase 3?
1. Brain can no longer compensate for increasing ICV
2. Large ICP increases
→ Associated with clinical symptoms
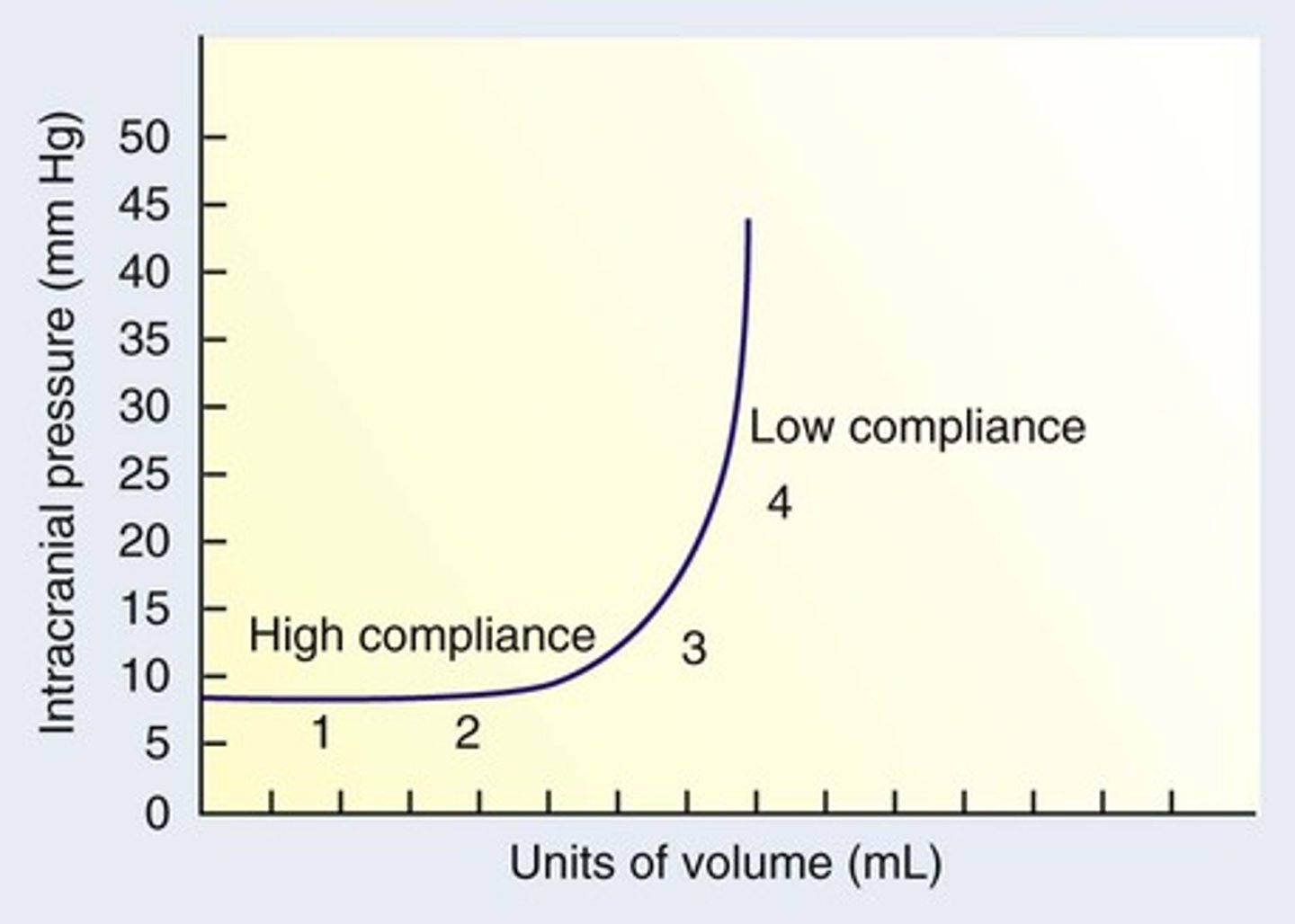
What is happening during Phase 4 of the elastance curve?
Decompensation
→ Abrupt ICP increases can happen because of anesthetics (vasodilation, increased cerebral blood volume)
Compliance equation
Compliance = ΔVolume / ΔPressure
→ High compliance = Can add a lot of volume with little pressure rise
→ Low compliance = Small volume increase causes a big rise in pressure
Elastance equation
Elastance = ΔPressure / ΔVolume
→ High elastance = Pressure shoots up with small volume changes (bad)
→ Low elastance = Pressure rises very little for a given volume (good)
With compensation, a large increase in ICV causes what change in ICP?
Small increase in ICP
What is the main goal of intracranial neuroanesthesia?
Decrease ICP by lowering ICV
→ Shifting the ICP–ICV curve downward and to the left
What are the 2 main consequences of decompensation? What is the cause?
1. Risk of cerebral ischemia
→ Due to ↓CPP
2. Risk of brain herniation
→ Due to ↑ICP
What is caused by an increase in supratentorial contents such as masses, edema, or hematoma?
Brain herniation
What are the signs and symptoms of increased intracranial pressure (ICP)?
1. Headache, nausea, vomiting, papilledema
2. ↓LOC
3. Ocular palsies
4. Cushing's response
What is the triad of Cushing's response (Cushing's reflex) to increased ICP?
HyperBradyBrady
1. Hypertension
2. Bradycardia
3. Bradypnea
How do you diagnose increased ICP?
1. Based on history and clinical symptoms
2. Imaging (CT or MRI)
→ Mass or hematoma
→ Midline shift
→ Loss of sulci
→ Ventricular enlargement (hydrocephalus)
What ICP level is considered elevated?
>15 mmHg
What is the gold standard for direct measurement of ICP?
Ventriculostomy
→ Allows measurement and removal of CSF
What instruments can directly measure ICP but do not allow CSF removal?
Transducers
→ Intraparenchymal catheter
→ Subdural catheter
→ Subdural bolt
What anatomical landmark is used as the zero reference point for ICP (EVD) monitoring?
Tragus of the ear
Which agents can decrease intracranial volume (ICV) and intracranial pressure (ICP) in the brain?
1. Mannitol
2. Hypertonic saline
3. Furosemide
4. Dexamethasone
Lowers ICP caused by localized cerebral edema because of BBB disruption
Dexamethasone
What adverse effect of corticosteroids, like Decadron, can worsen outcomes in cerebral ischemia?
↑ Blood glucose
→ When oxygen is limited, glucose is metabolized anaerobically, which produces lactic acid
→This leads to lactic acidosis
Where is CSF found?
In the cerebral ventricles and the subarachnoid space surrounding the brain and spinal cord
What produces CSF?
Choroid plexus in lateral ventricles
Total volume of CSF in adults
150 mL
How much CSF in produce per day?
500 mL/day
→ Rapid turnover
Where is CSF reabsorbed?
Arachnoid granulations (villi) in dural venous sinuses
What connects the lateral ventricles to the fourth ventricle?
Cerebral aqueduct of Sylvius