Increased Intracranial Pressure (anatomy and monitoring)
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
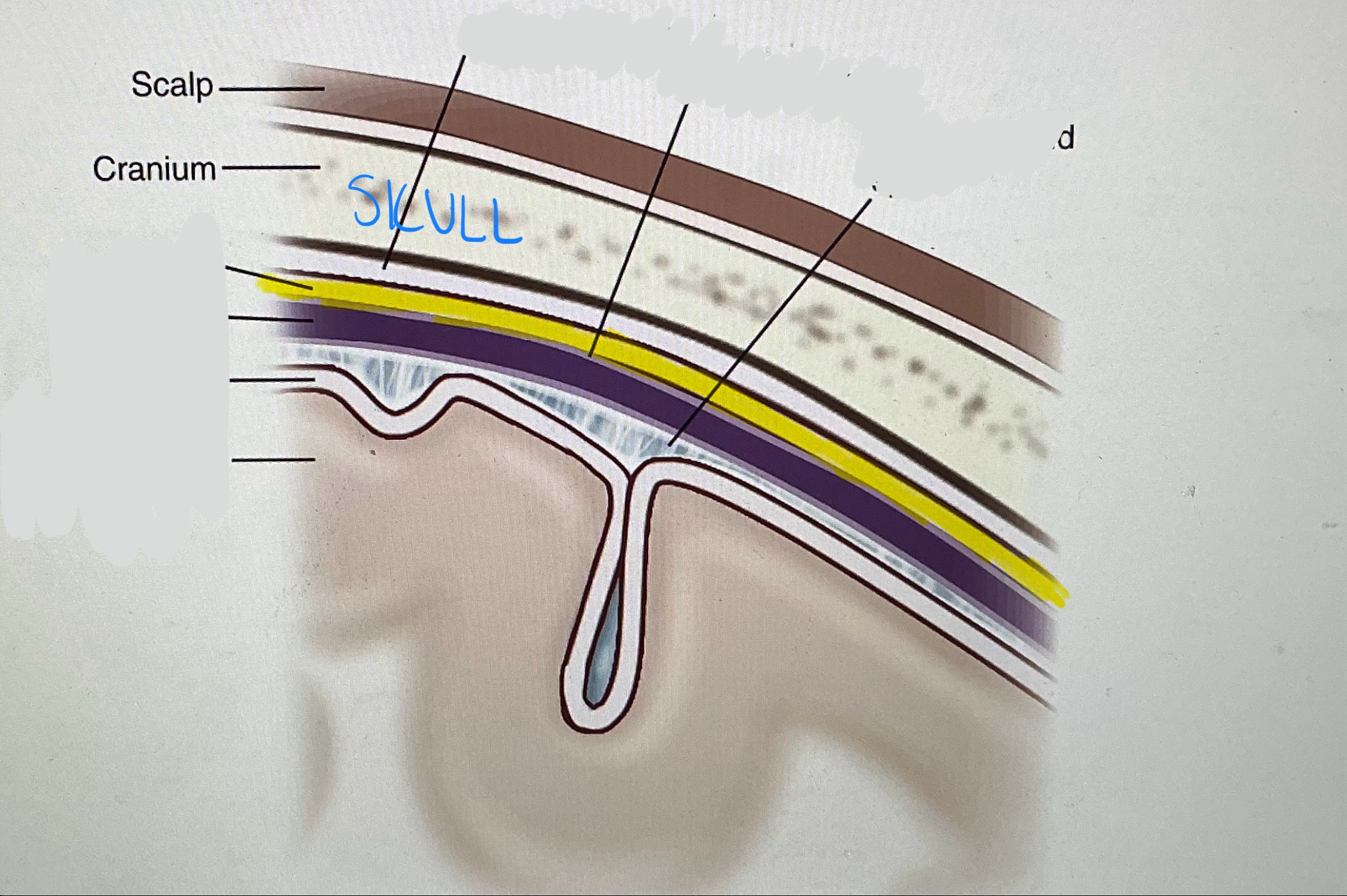
Near Skull
Dura Mater
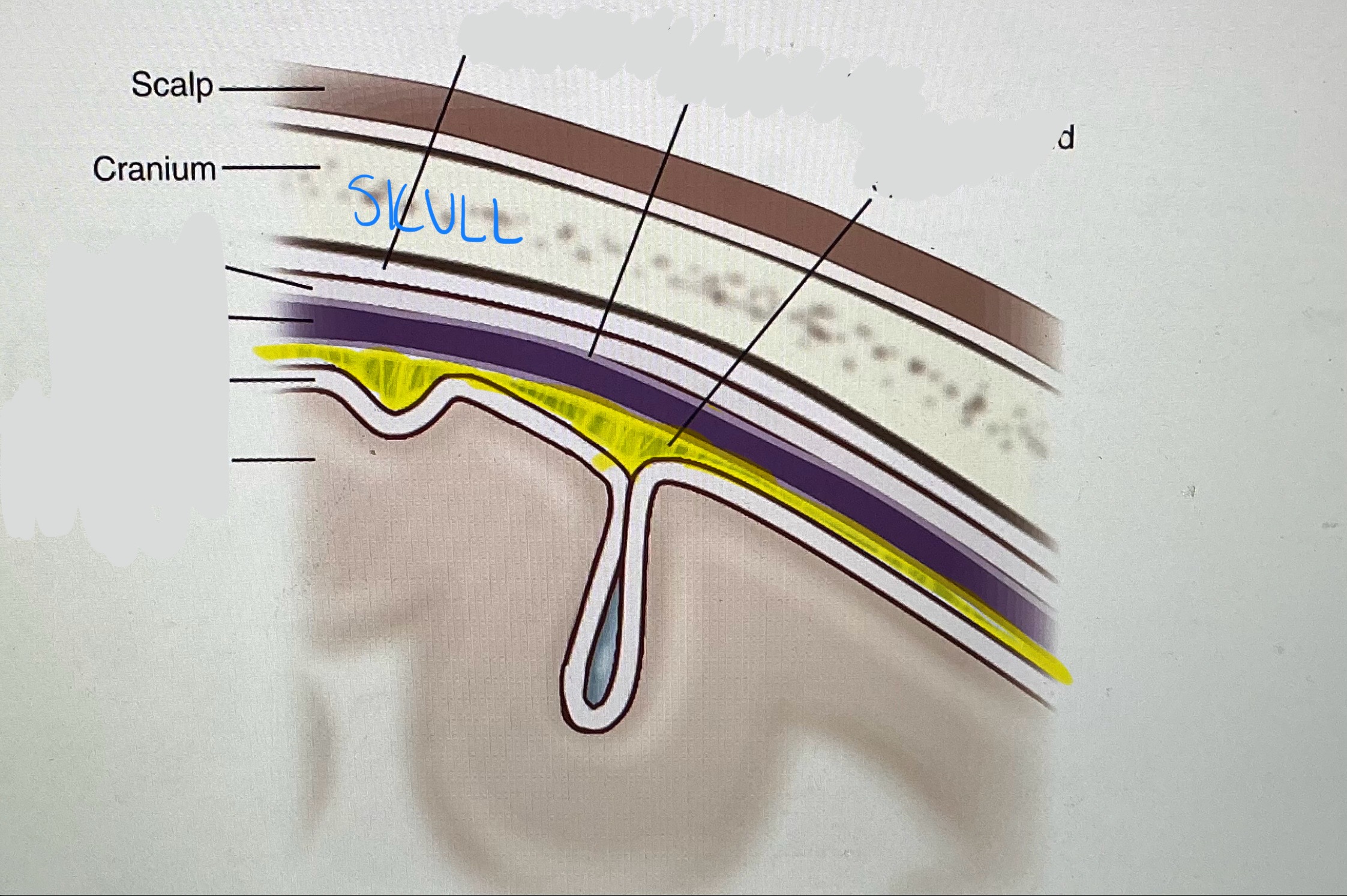
Deeper
Subarachnoid Space
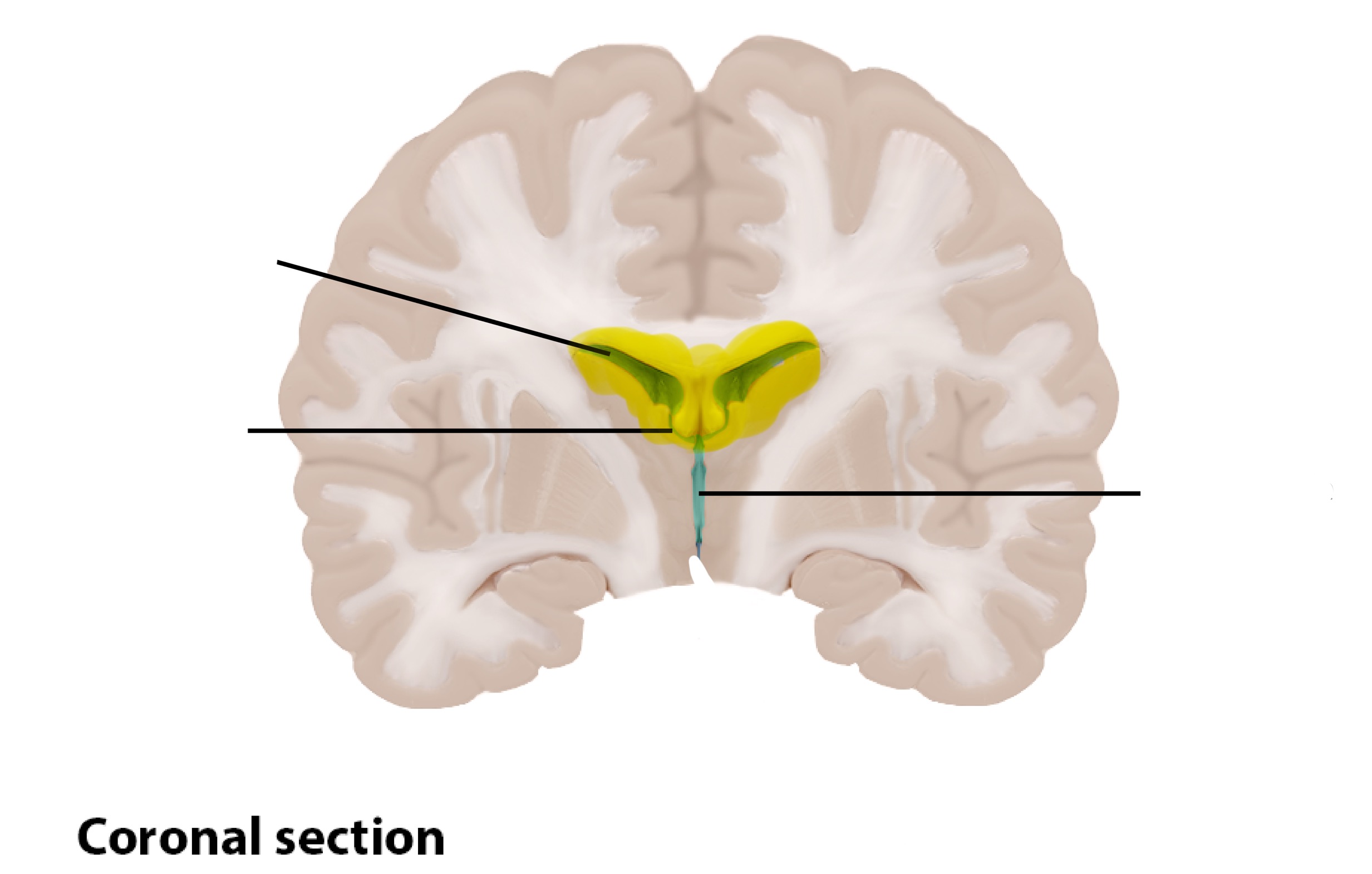
Ventricles
Three components of ICP
Brain tissue (80%)
Blood (10%)
CSF (10%)
The ability of the body to compensate by adjusting the levels of the three components
Intracranial COMPLIANCE (we want equilibrium… when others rise others must accommodate by decreasing)
Skull
Fixed Rigid Immovable “Box”
Limited Space
“Apartment”
What can occur when there is a loss of compliance?
Cerebral Herniation Sydrome
What happens during cerebral herniation syndrome
Brain tissue is displaced → brainstem compressed → BRAIN DEATH
Risk factors for ICP
Brain Bleed (Hemorrhage)
Hematoma (Above/Below Dura Mater)
Hydrocephalus (High CSF)
Encephalitis/Meningitis (Infection)
Tumor (takes up space)
TBI
What is the gold standard for ICP monitoring?
Intraventricular Catheter
Where is the intraventricular catheter placed?
In the VENTRICAL (lateral) of brain
What are the benefits of an intraventricular catheter?
It can monitor and DRAIN CSF (measure CSF output)
other methods cannot drain
A GCS score of ____ or less requires an ICP monitor to be placed
8
8 or less is indicative of SEVERE neurological issues
Normal Glasgow Coma Scale
15
Normal ICP
0-15 mmHg
Normal Cerebral Perfusion Pressure (CPP)
generally maintained above 60 mmHg
Equation for CPP
MAP - ICP = CPP
Measuring scale for external ventricular drains
mmHg
cm H2O
How can over drainage be prevented?
Maintain proper leveling of the drainage system (level at the external auditory meatus)
Proper adjustment of the drainage burette at the ordered level ABOVE the external auditory meatus
How should the patient be positioned?
Semi fowlers: 30-45 degrees
Patients head midline
Avoid sharp Hip flexion
Why should the patient’s head by midline?
Facilitate drainage of blood from JUGULAR venous system (decrease ICP)
Why should the patient avoid sharp hip flexion?
Ensures that large veins in the abdomen are not compressed → decreasing venous return
What can happen if the patient is positioned TOO HIGH?
False LOW ICP
the pressure reading will be falsely low, leading to a failure to detect and treat high ICP
What can happen if the Patient is positioned TOO LOW?
False HIGH ICP
A falsely high reading can lead to unnecessary interventions to lower ICP, such as administering medications or draining cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), which puts the patient at risk.