L42: organs and structures of abdominal and pelvic cavity pt.2
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
91 Terms
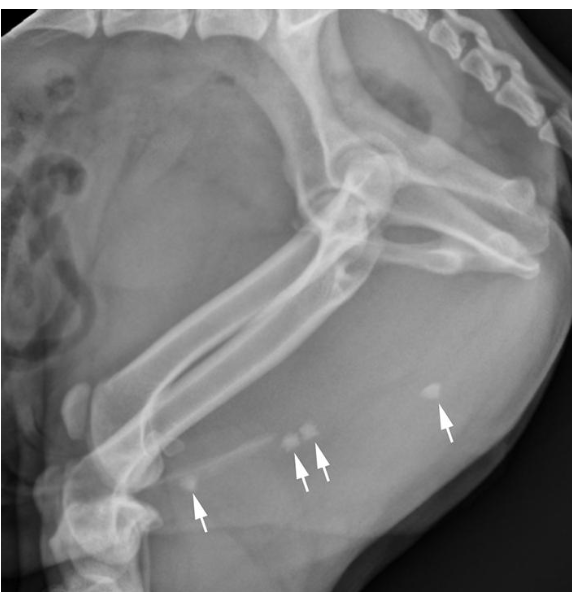
MCQ: what organ is obstructed by the calculi?
penile urethra
list the urinary organs located only within the abdominal cavity,
kidneys and renal pelvis
lis the urinary organs located only within the pelvic cavity
urethra
what urinary organs can be located in both the pelvic and abdominal cavities?
bladder and ureters
what other body system organs are closely related topographically to the urinary system?
reproductive system and sometimes rectum
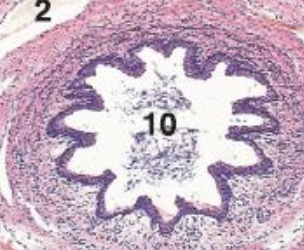
how does the lumen of the ureter appear?
star-shaped lumen created from epithelium projectiosn
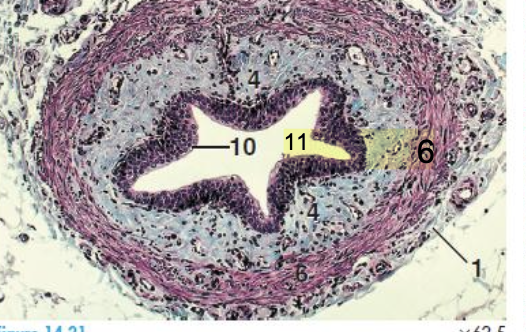
what is the histology slide showing?
ureter
what cells compose the mucosa lining the lumen of the ureter?
transitional epithelium
what within the lamina propria of the ureter is found in horses only?
tubulo-alveolar mucus glands
what layer is absent in the ureters but found in the other organs of the urinary tract?
submucosa layer
tunica muscularis
thickest layer that provides major contractile forces of the ureter against the pressure of the bladder
what is the outermost layer of the ureter?
tunica adventitia or serosa
tunica adventitia
layer of loose connective tissue, nerves, and blood vessels that surrounds the muscularis layer
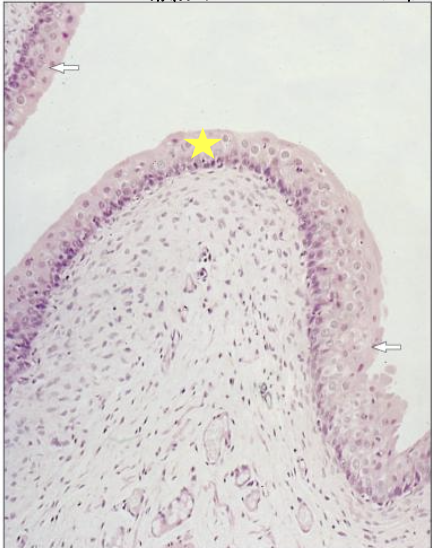
does this histological slide show a relaxed or distended bladder?
relaxed bladder; has scalloped appearance and mucosa is 5 cells thick
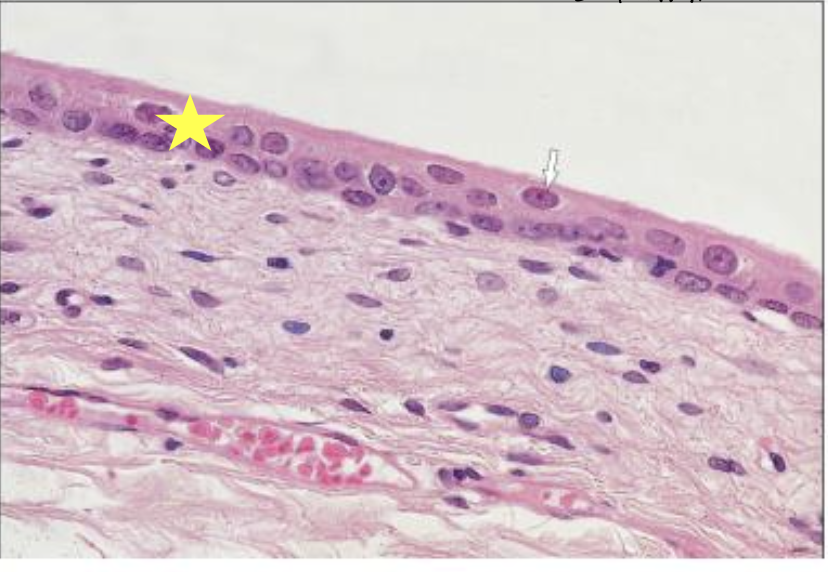
does this histological slide show a relaxed or distended bladder?
distended bladder; cells stretched and mucosa is 3-4 cells thick
tunica mucosa
epithelial lining of urinary bladder
lamina propita
composed of connective tissue that allows for bladder to have elasticity to stretch
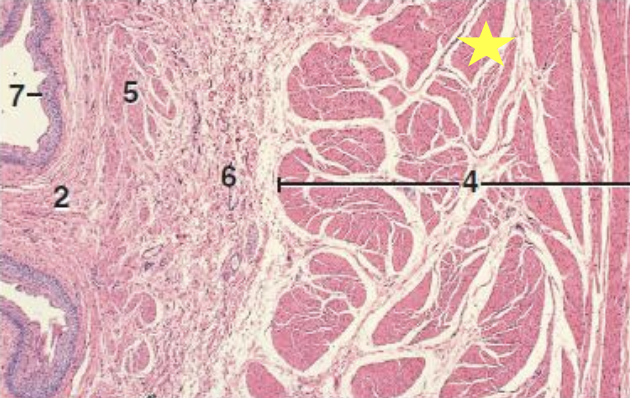
what is 4?
muscularis
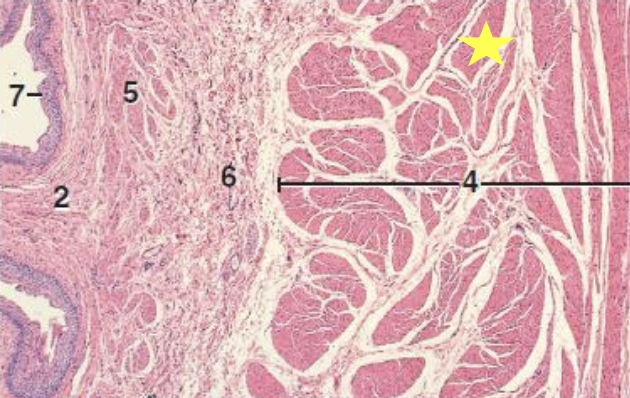
what is 6?
submucosa
what is the tunica muscularis also referred to as?
detrusor muscle of the bladder
what is present on the bladder wall surface?
parasympathetic ganglia and nerve receptors
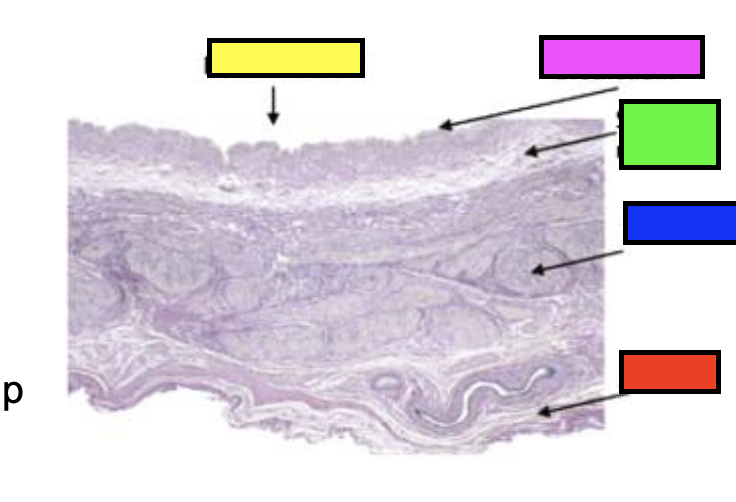
what is the red (histology showing urinary bladder)?
serosa
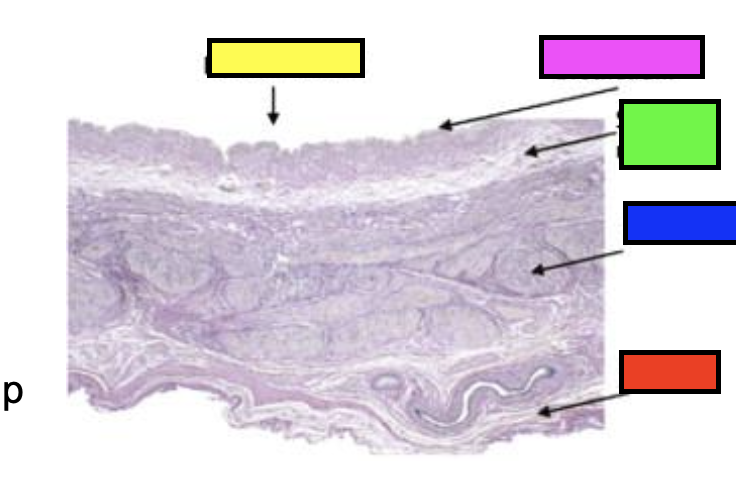
what is green (histology showing urinary bladder)?
submucosa
what is blue (histology showing urinary bladder)?
detrusor muscle
what is pink (histology showing urinary bladder)?
urothelium
what is yellow (histology showing urinary bladder)?
bladder lumen
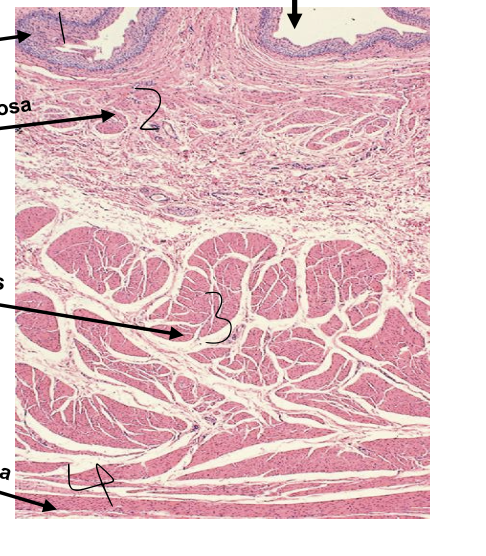
what is 1?
tunica mucosa
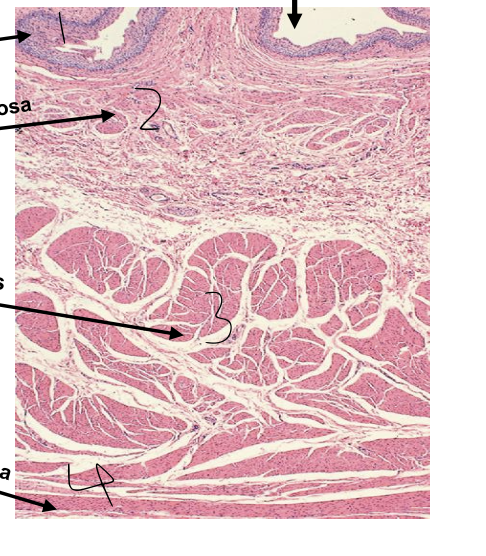
what is 2?
tunica submucosa
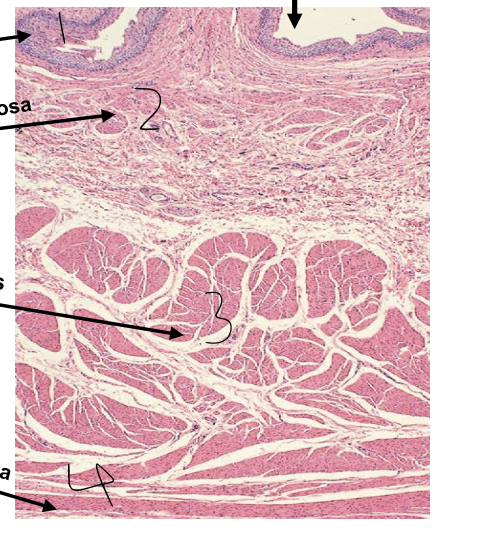
what is 3?
tunica muscularis
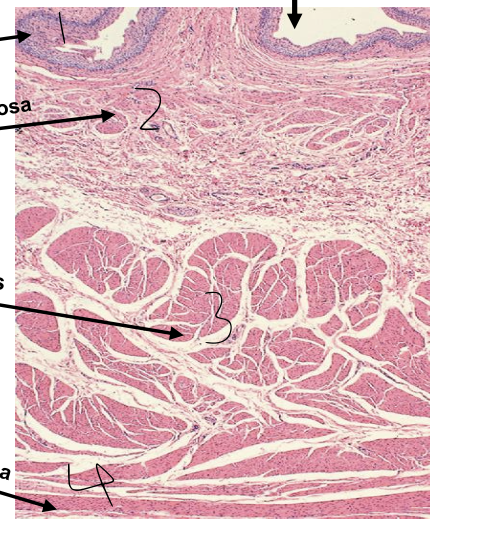
what is 4?
tunica adventitia
what histological feature of the urinary bladder is absent in feline?
lamina muscularis of the submucosa
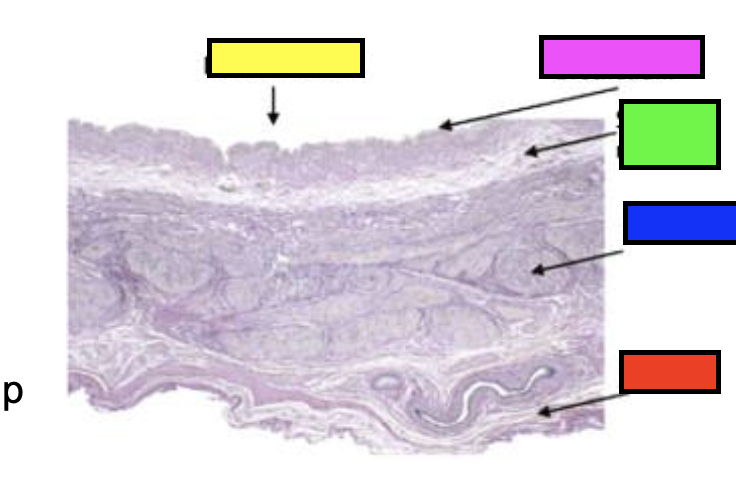
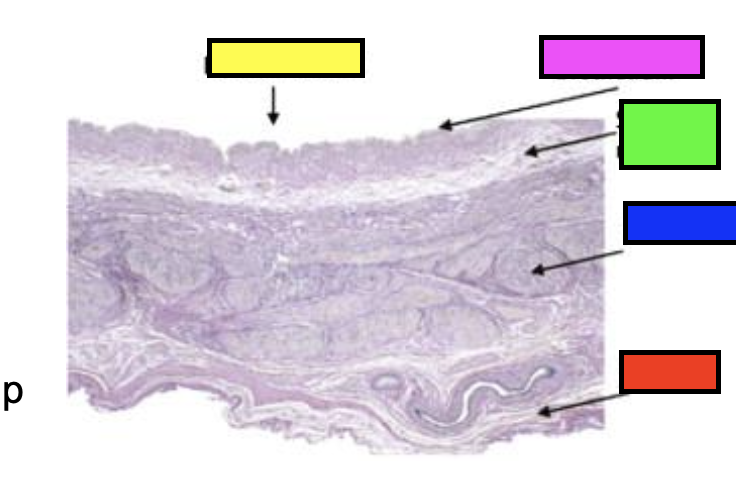
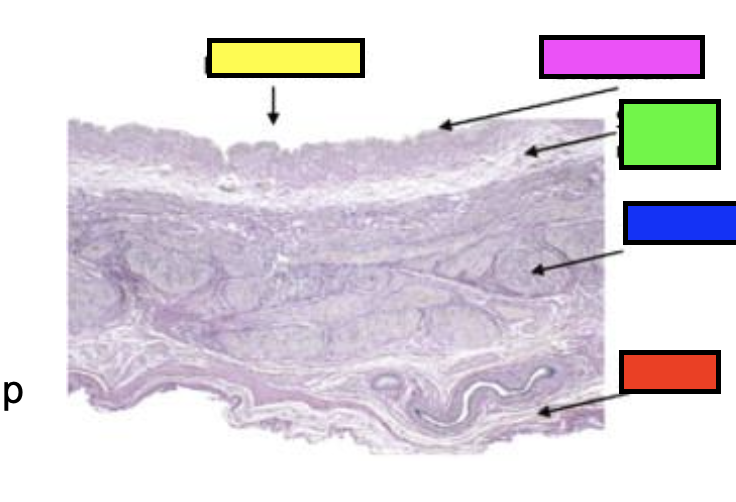
what does the slide show?
male urethra
how is the tunica mucosa folded?
longitudinally
what cells are found along the length of the penis?
stratified columnar or cuboidal
what cells are found at the urethral orifice in the tip of the penis?
stratified squamous
MCQ: during breeding, what structure is engorged with blood to provide some rigidity to the penis?
vascular cavernous spaces
MCQ: what animals have a sub-urethral divericulum?
cows and sows
MCQ: what is another name for the apex of the urinary bladder?
vertex
what are the clinical signs seen with lower
what anatomical findings will you see with LUTS?
redness and swelling of bladder
mucosal hyperplasia of bladder and uretethra
calculi/plug in bladder or urethra
why can male cats develop LUTS more than female cats?
narrow urethra predisposes to urethral obstruction, infections, and stones
what species will with see LUTS?
Main= cats; dogs as well
which sex of cat will have an increased risk if they are neutered or spayed before puberty?
ONLY FEMALES NOT MALES
what are the predispositions to LUTS?
breed and sex
what are the other causes of LUTS?
neurohormonal imbalances
stress
idiopathic (most common)
what structure is a point of obstruction when passing catheters to the bladder for ruminants (females)?
sub-urethral diverticulum
sub-urethral diverticulum
a ventral evagination formed by the urethra that opens with the urethra into the vagina
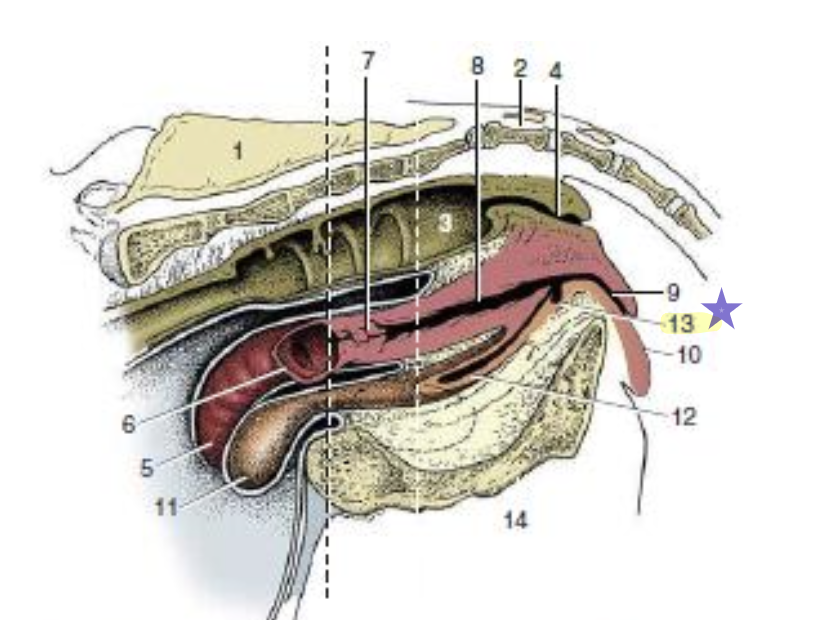
what is 13
sub-urethral diverticulum

what is the image showing?
“beans" seen in the urethral sinus of the stallion
what are “beans”?
contents of the urethral sinus that have accumulated and hardened due to the presence of smegma and other debris.
what surrounds the urethral process of the stallion?
fossa glandis
urethral sinus
a dorsal diverticulum of the fossa glandis present in stallionst hat collects secretions and debris.
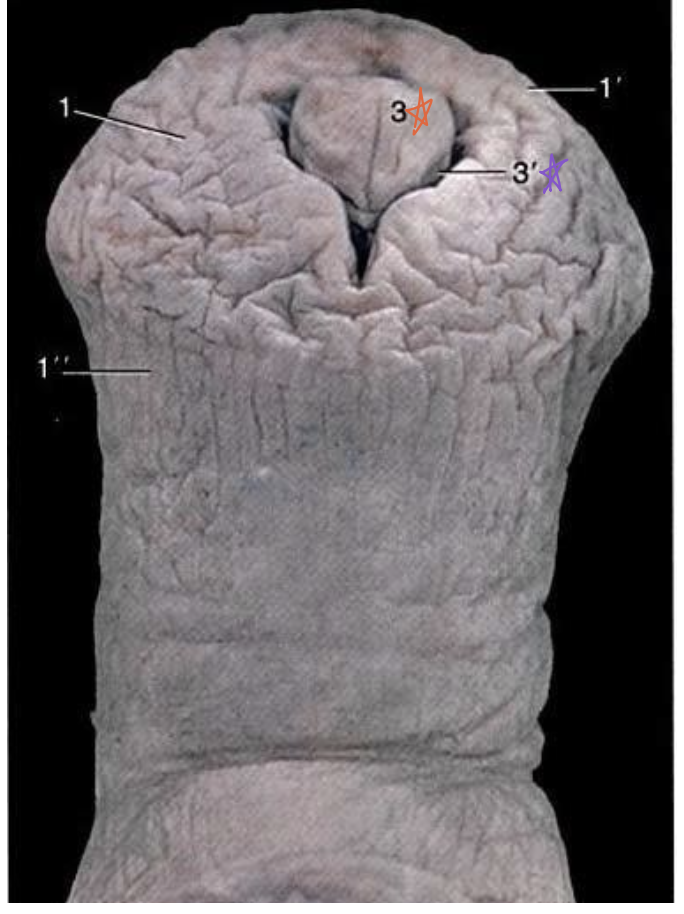
what is the orange star referring to?
fossa glandis
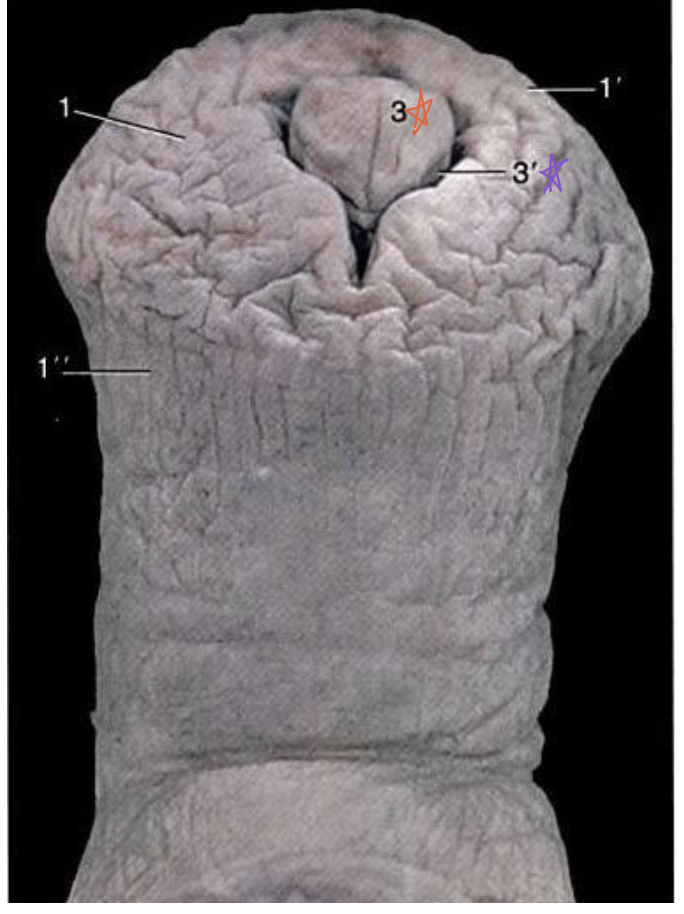
what is the purple star referring to?
urethral sinus
what species is the urethral diverticulum/recess found in?
male ruminants
location of urethral diverticulum
caudal end of the pelvic urethra forms a dorsal invagination at the ischial arch
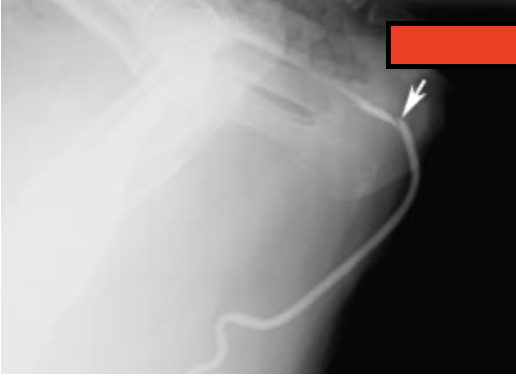
what is the arrow pointing at?
urethral diverticulum
urethral process of ruminants
short narrow tube-like structure on the tip of the penis
what is a common site for urolith entrapment in ruminants?
the urethral process or sigmoid flexure
what is the treatment of urolith entrapment in ruminants?
manually massage out urolith
amputation
what shape does the body of the penis form in ruminants and pigs and what does this allow for?
S-shaped sigmoidal flexure
extension of penis during erection
in ruminants and pigs, the urethra of which bend is more narrow: proximal or distal?
distal bend
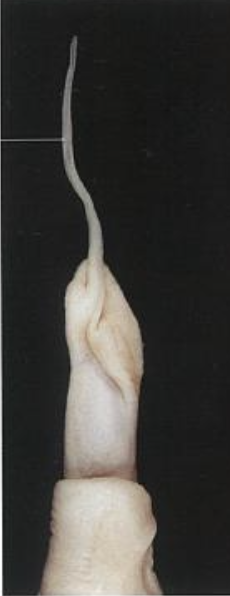
what is the arrow pointing to?
urethral process
what is the function of the urethral process in the ruminants?
guide semen in cervix of females
what are hte common sites of blockage or stones in small animals?
bladder
ureter
urethra
where is a common site in dogs for blockage/stones?
along the distal urethra where the os penis narrows the lumen diameter
what are the common reasons for urinary obstructions?
uroliths/calculi
infections (UTI)
tumors
what sex is more predisposed to urethra obstructions and why>
males due to longer and narrower urethra
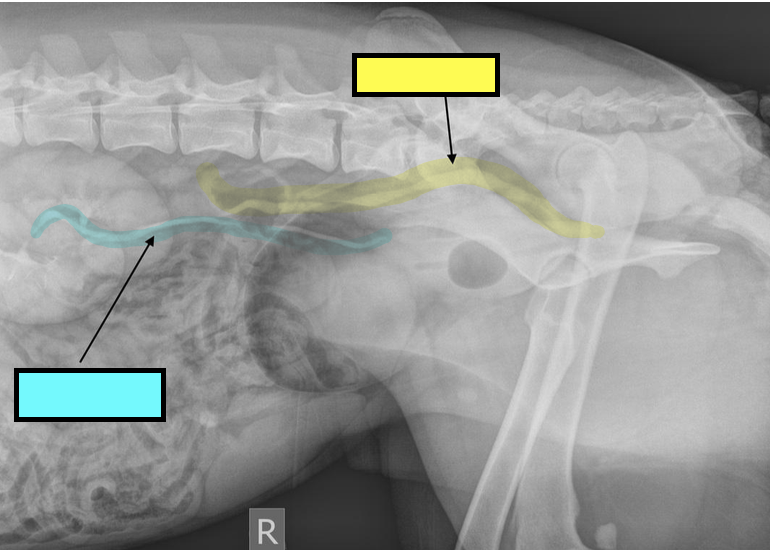
what is the yellow line showing?
ectopic ureter
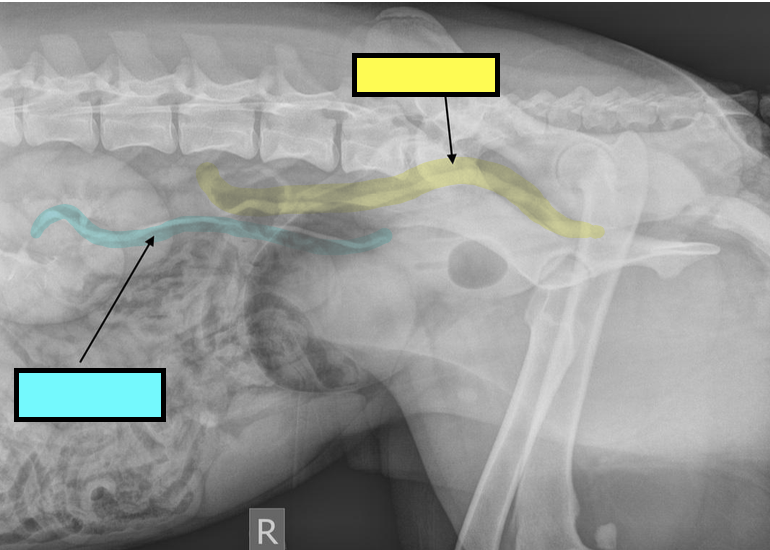
what is the blue line showing?
normal ureter
ureteral reimplatation
surgical procedure for ectopic ureters; ligate, transect, and reattach
ectopic ureters
congenital abnormality in which the ureteral orifice/s is/are located anywhere distal to the normal trigone location
what are the clinical signs seen with ectopic ureters?
urinary incontinence
stranguria
hematura
pollakiuria
pollakiuria
frequent, abnormal urination during the day
who do we typically see ectopic ureters seen in?
young female dogs about 10 months
function of genital fold
provide stability to the ductus deferens on the dorsal surface of the bladder
what is the only view you will see the genital fold?
dorsal view
movement of ductus deferens
turns caudally to get to the urethra by winding around the ureter
where are the bulbourethral sex glands located?
at the dorso-lateral caudal end of the pelvic urethra
what structures in large animals combine to form the ejaculatory duct?
ampullary gland and vesicular gland
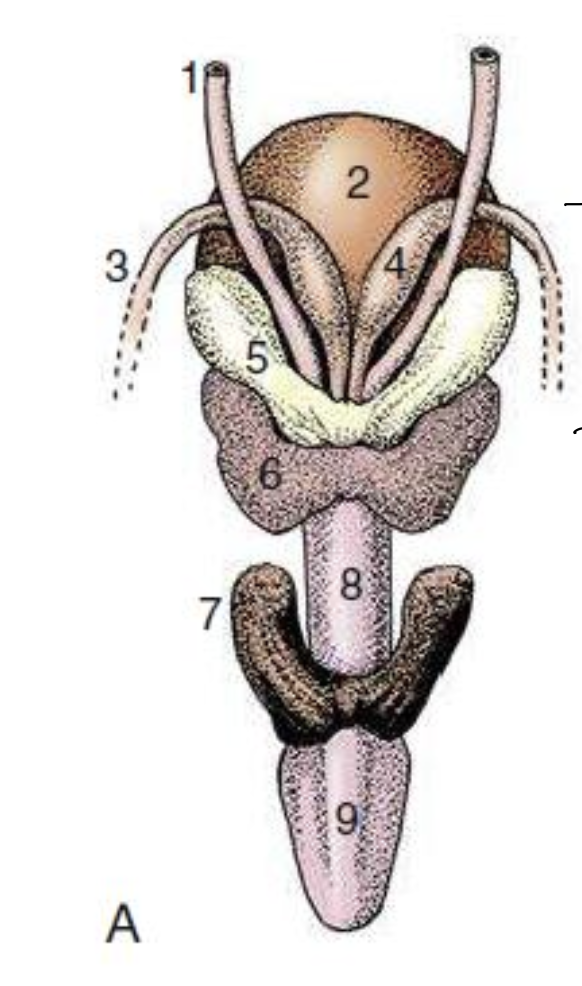
what animal is this and how do you know?
bull or stallion due to presence of ejaculatory duct
what structures are closely related to one another in the female?
broad ligaments
uterine body
ureter
vestibulovaginal junction location
between the vagina and vestibule
where does the urethra open into?
travels caudally to open into the vestibulovaginal junction
what structure is used to demarcate the vagina and vestibule of the female genital tract?
vestibulovaginal junction
why is the vestibulovaginal junction considered an incorporation of the urinary tract?
urine must pass through vestibule before exiting the vulva since urethra does not open into exterior
anatomical relation of reproductive organs to urinary organs in female
reproductive organs are dorsal
what does the urinary reproductive system share?
similar external openings,
the vulval cleft in females, and the external urethral orifice in males
endothelium-lined caverns/vascular spaces
form an erectile plexus in the lamina propria-submucosa
what is the composition of the tunica muscularis in the vicinity of the bladder?
smooth muscle
what is the composition of the tunica muscularis in the remainder of the urethra (past bladder)?
skeletal muscle