Radiation Biology, Safety and Protection
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
Biological effects of radiation exposure can be classified as either
Stochastic
Deterministic
What is the significance of different biological effects in dental imaging?
The radiation dose; there are varieties of radiation effects in the body
What are deterministic radiation effects?
A radiation dose threshold is required for the radiation damage. After the threshold is met, the severity of the damage is proportional to the radiation dose
What are stochastic radiation effects?
There is no radiation threshold and the probability of the effect is directly proportional to the radiation dose. Even one single x-ray can induce a cancerous effect. The chance of this effect increases with higher radiation dose
Tissue reaction characteristics
Lethal DNA damage
Occurs when radiation exceeds a threshold level
Does not occur below threshold level
Above dose threshold, the severity of the effect is proportional to dose
Cell death
Decreased tissue and organ function
Stochastic characteristics
Sub lethal
No minimum threshold for causation
Probability, not severity of occurrence increases as dose increases
Gene mutation
Replication of mutated cells
What are some examples of tissue reactions effects
Xerostomia
Osteoradionecrosis
Cataracts
Fetal development
What are some examples of stochastic effects
Leukemia
Thyroid cancer
Salivary gland tumors
What is radio-sensitivity and how does it translate to patient imaging?
Sensitivity of cells to radiation varies between cells and tissue
Cells that are more rapidly dividing (immature/non-specialized) are more sensitive
The radiation effect varies depending on the area that is imaged
What are some areas that are radiosensitive (H&N)?
Thyroid (most sensitive)
Salivary glands (2nd most sensitive)
Bone marrow
Esophagus
Skin
Bone surface
Brain
How are age and radiosensitivity correlated?
Children are up to 5x more prone to carcinogenic effects of radiation
This is d/t higher cell and tissue sensitivity to radiation & longer expected life span
Radiosensitivity to various organs
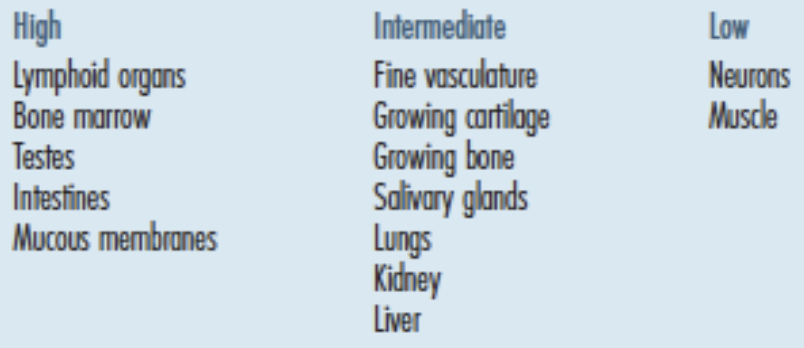
High radiosensitive organs
Lymphoid organs
Bone marrow
Testes
Intestines
Mucus membranes
Intermediate radiosensitive organs
Fine vasculature
Growing cartilage
Growing bone
Salivary glands
Lungs
Kidney
Liver
Low radiosensitive organs
Neurons
Muscle
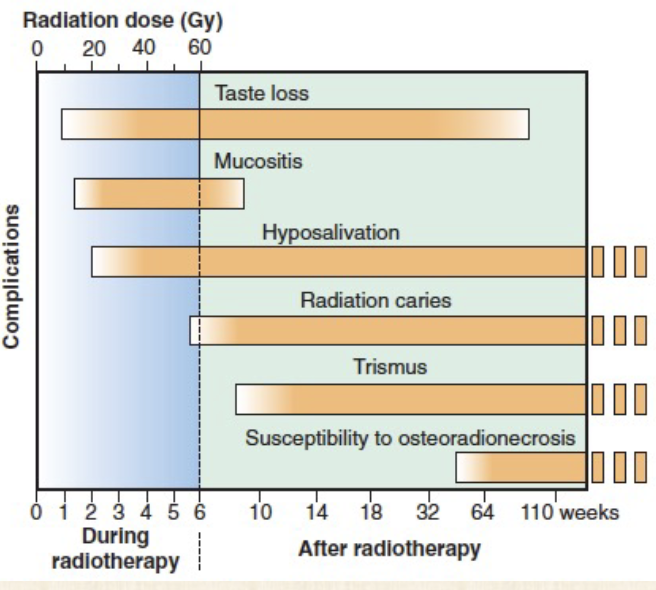
Results of radiotherapy- deterministic effects after radiotherapy
Taste loss
Mucositis
Hyposalivation
Radiation caries
Trismus
Susceptibility to osteoradionecrosis
What is the model currently used in the Radiation Protection Guideline?
Linear non-threshold model (explains stochastic effect of ionizing radiation)
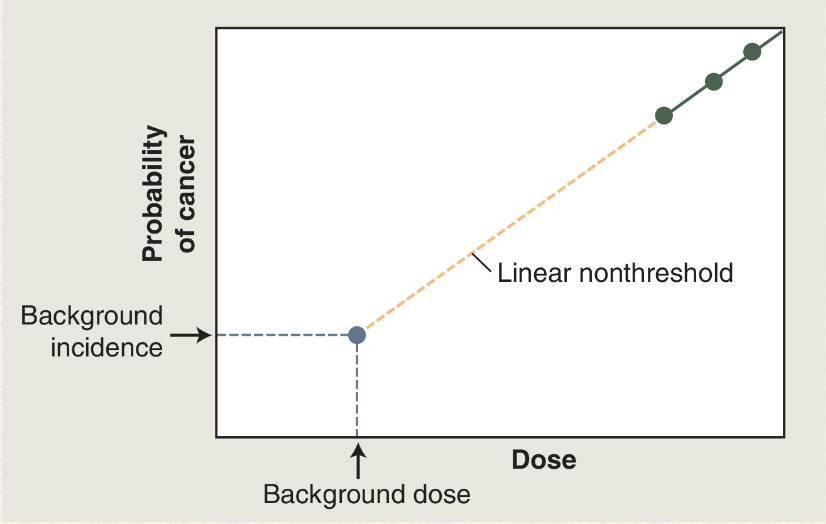
What is the linear non-threshold hypothesis?
At doses less than 100 mSv there is a linear relationship between dose and risk AND there is no threshold dose below where there is no additional rise
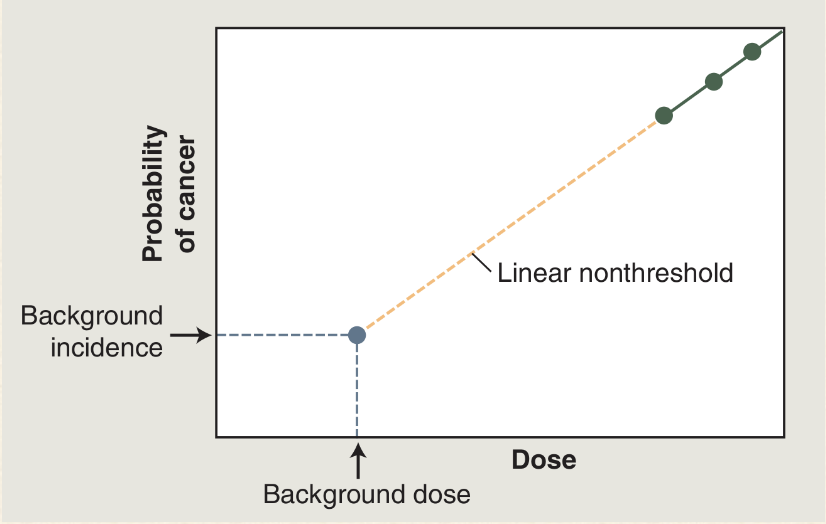
How does the linear non-threshold model explain stochastic effect
The probability of occurrence due to radiation effect increases as dose increase
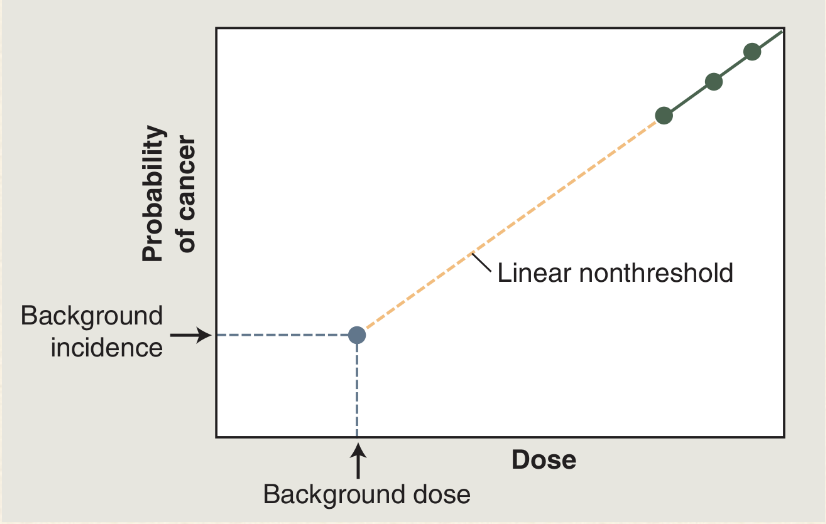
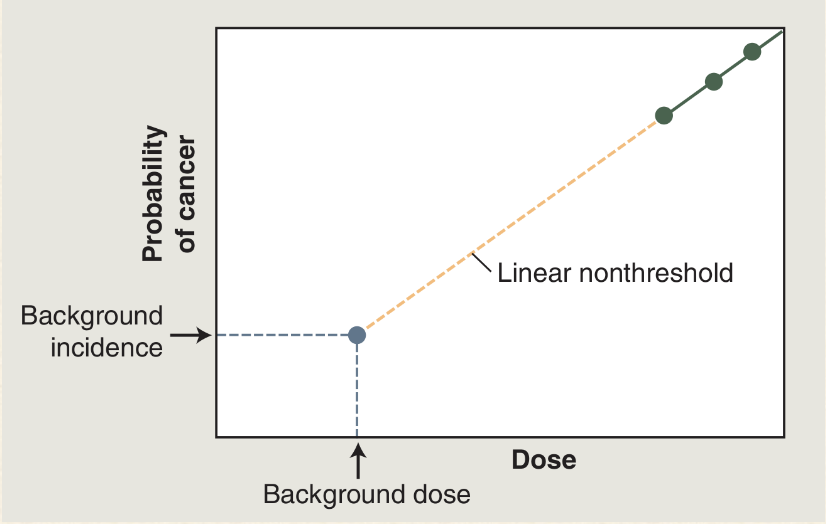
What does this mean?
The gray-blue dot: there is a certain natural prevalence of cancer and a certain natural background radiation exposure
Green dots: doses of radiation greater than 100mSv results in a dose-dependant increase in the cancer rate
How would you compare radiation dose of different types of radiographs?
They are reported in Sieverts (Sv). The effective dose is measured with consideration of the type of tissue and degree of radiation sensitivity of the tissue that was exposed during a certain radiograph
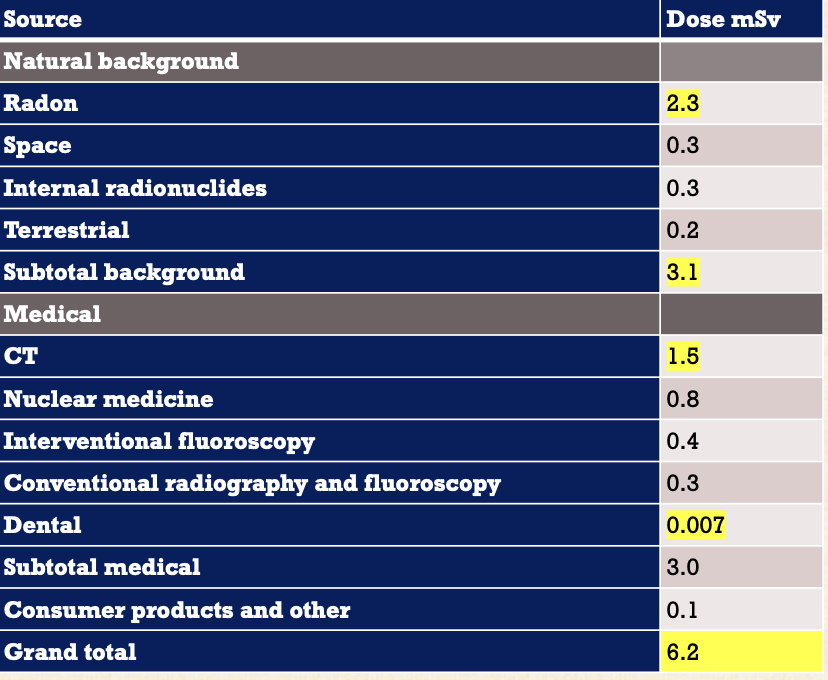
Average annual effective dose of ionizing radiation
Natural
Total - 3.1
Radon- 2.3
Medical
Total -6.2
CT- 1.5
Dental- 0.007
Compare the different effective dose between a full mouth PSP film and CCD sensor
PSP is 35Sv, CCD sensor is 17. It is a 2:1 ratio
Compare the different effective dose between round collimation and rectangular
Round is 5: Rectangular is 1
Compare the effective dose of pan/FMX
There is less especially compared to round collimation FMX
Compare the effective dose of CBCT and FMX
They both are less compared to round collimation FMX
The largest field of view CBCT view is still higher than
Pano + Ceph
CCD FMX is similar to
One chest x- ray
Congenital malformations can occur with
0.1 Gy Threshold
Estimate dose from a FMX
0.17 mSv (approx. 0.1-0.2mGy)
Natural background dose to embryo and fetus
2250 microGy = 8 microGy/day
Compare a dental FMX to natural background dose and pregnancy
FMX is 20 days of natural background dose, and will not cause congenital malformation
Can you take dental x-rays on pregnant people?
Yes, it is allowed any time during pregnancy if there is a special indication. But in principle, defer optional imaging to the end of pregnancy like screening bitewings
What is the primary risk from dental radiography
Cancer
What is the primary concern from dental radiographs according to the linear non-threshold theory?
The stochastic effect of ionizing radiation and the primary risk is cancer
Cancer is a common disease. What are some stats regarding it?
It affects 40% of all people and
Accounts for 20% of all deaths
What is the risk from exposure in your childhood vs adulthood
The risk from exposure during childhood is 2-3x as great as the risk during adulthood
What is the evidence around cancer and radiation?
There is tons that links large radiation exposure to cancer risk (100 mGy), but the data is more uncertain regarding cancer risk from low-dose exposure
Define justification in radiation protection principles
Identify situations where benefit exceeds risk
Define optimization in radiation protection principles
Use every reasonable means to reduce exposure to patients, staff, and yourself. Follow ALARA
Define dose limitation in radiation protection principles
Legal limitations are placed on occupational and public exposures. No limitations on patient exposure but justification ensures benefit outweighs risk
What is the ALARA principle?
The goal is to remain below the dose limits and keep doses to patients and workers As Low As Reasonably Achievable. It is required by regulations
What does the ALARA Principle imply?
Any radiation dose that can be reduced without major difficulty, great expense, or inconvenience should be reduced or eliminated
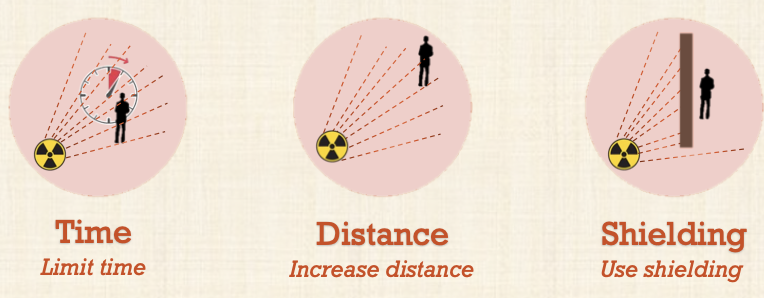
What are the 3 principles of reduction of radiation exposure?
Limit time
Increase distance
Use sheilding
Time - ALARA Principle
Decreasing time spent in unshielded area while the x-ray beam is on
No one else should be in the room during exposure
Avoid retakes
Avoid present intervals
Distance - ALARA principle
Apply the inverse square law - radiation dose is inversely proportional to the square of the distance from the source
Doubling your distance (x) from a radiation source decreases your dose by a factor of 4
Stand at least 6 feet away from the x-ray tube
Source to skin distance
Use of long source-to-skin distances of 40cm rather than short distances of 20cm to decrease exposure.
Distances between 20-40cm are appropriate but the longer distances are optimal
Use of the long cone results in
A reduction in exposed tissue volume because the x-ray beam is less divergent, and results in a smaller apparent focal spot size increasing the resolution of the radiograph
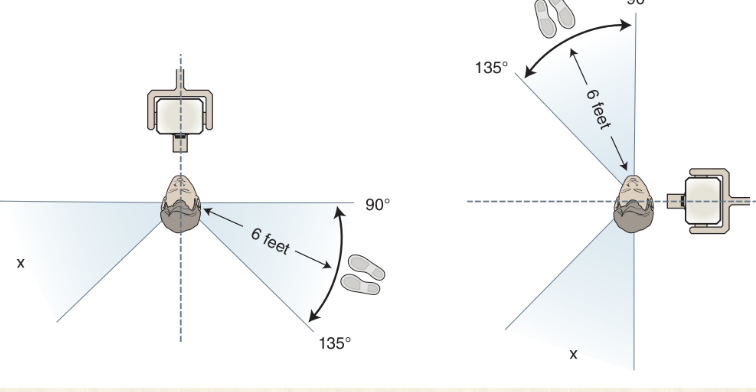
Position-and-distance rule operator dose
Operator should stand 6 ft from pt at an angle of 90-135 degrees to the central ray of the x-ray beam
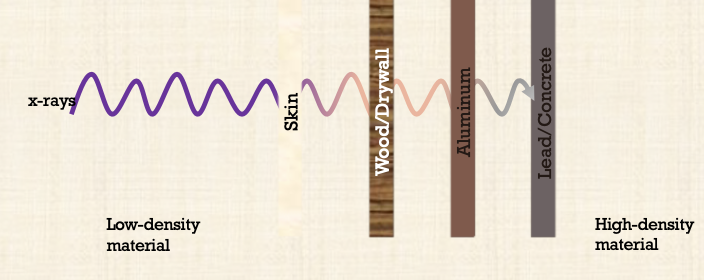
Shielding - ALARA principle
x-rays travel great distances and penetrate through low-density materials like wood and plastic
Dense materials like lead, steel, and concrete are the most effective
What does shielding look like in ALARA?
Proper shielding will greatly reduce/eliminate the dose received (lead and concrete attenuate x-rays best
Lead-lined doors/walls/windows, portable barriers
Lead aprons, gloves, thyroid collars, glasses and gonadal sheilds
Hang aprons- do not fold
Do a visual examination of leaded PPE

What did the ADA change in 2024?
Use of abdominal aprons or thyroid collars on pts when conducting dental x-rays is no long recommended
The changes apply to all pts regardless of age or health status
Leaded aprons
Reducing exposure in main beam is more important
The only radiation exposure to anatomy below the neck is through
Scatter radiation
This passes through the body internally
Gonad dose from FMX does not exceed 5 mGy
Heritable effects are insignificant
What about patient thyroid shielding during diagnostic x-rays like intraoral, panoramic, cephalometric and CBCT imaging?
They should no longer be used in routine practice for pediatric or adult patients
How do thyroid collars and abdominal shielding work
They introduce artifacts by blocking the primary beam, potentially resulting in additional radiographs being taken and do not protect against internal scatter radiation
Why can’t you use a thyroid collar with panos?
Because of the beam’s upward projection from behind the patient during production of the pano- it obscures the anterior mandible
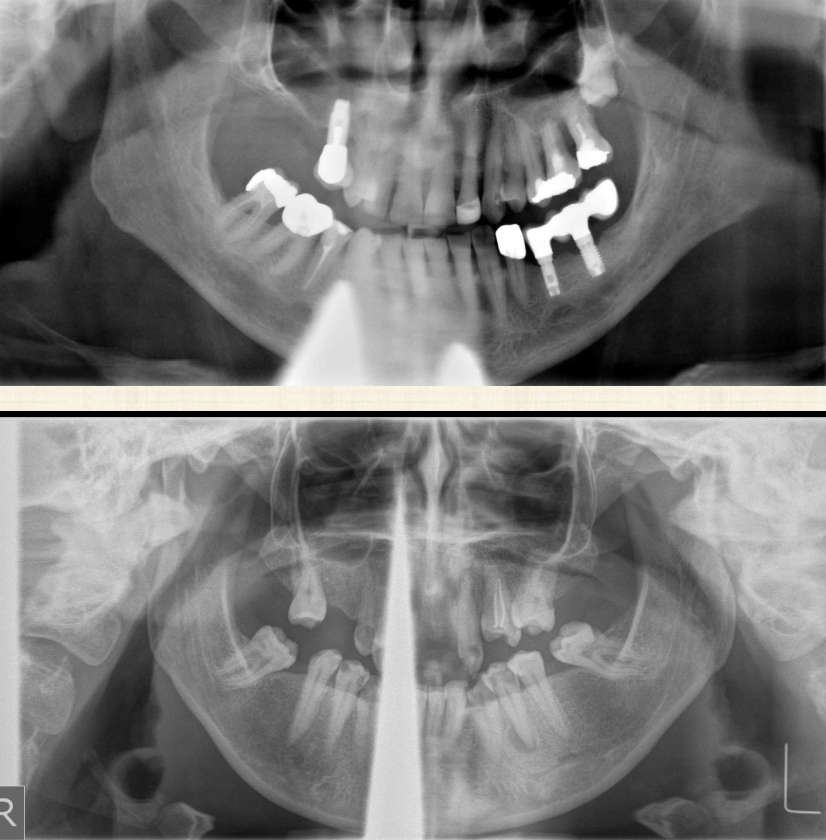
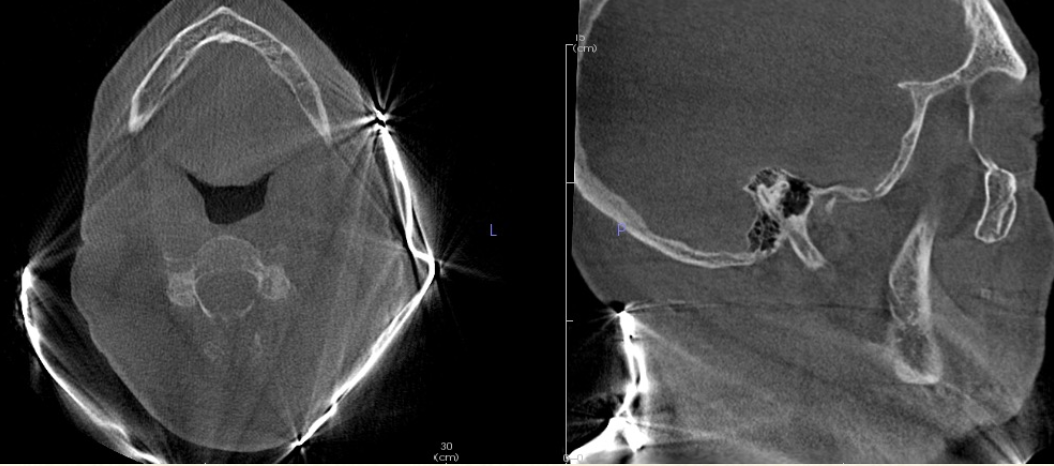
Why can’t you use a thyroid collar with CBCT?
It creates a streaking artifact and obscure anatomy
What is a collimator?
A metallic barrier with an aperture in the middle used to restrict the size of the x-ray beam and volume of tissue irritated
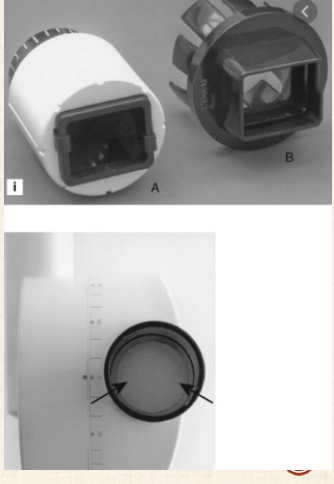
What kind of collimators are used in dentistry?
Round
Rectangular
Dental x-ray beams are usually collimated to a circle (2.75in) in diameter at the patients face
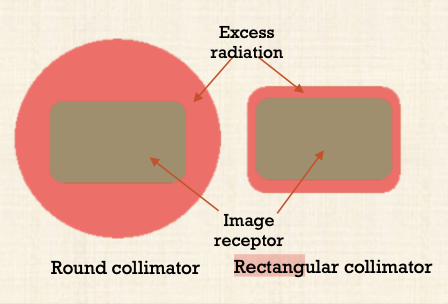
What is rectangular collimation?
Device that limits the x-ray field to dimensions large enough to cover the region of interest
Prevents exposing the patient to unnecessary primary radiation
Reduces the amount of scatter radiation to image, patient and operator
Decreases radiation dose by 5x as compared to a circular one
Radiation dose to the thyroid was less using rectangular collimation alone vs. using both a round cone and thyroid collar shield
What is the dead man switch in radiation controls?
x-rays will only be generated when the operator applies continuous pressure to the exposure switch
When released, the exposure will stop immediately
You have to release the exposure switch after the timer setting or rotation is completed and there is an audible warning signal
What are exposure indicators?
All radiation-producing devices must be equipped with visual and audible warning signals, activated when the device is emitting x-rays
-Warning lights are located on the device control panel
-Beep when x-rays are activated

What is the optimal operating potential of dental x-ray units?
60-70 kVp - kilovoltage
If everything is set correctly, what should the operator see radiographically?
Faint soft tissue outlines and they should set the amperage and time settings for exposure of dental radiographs of optimal quality
What is a dosimeter?
Recommended for workers who may receive more than 1mSv and for pregnant workers. Optically Stimulated Luminescence Dosimeter is a strip of Al2O3 radiosensitive crystal and is sensitive to 10µSv
SUMMARY - means for reducing x-ray exposure
Use digital sensors
Use holders to support films
Use rectangular collimation for PA and BWX
Replace short aiming tube with long x-ray tube
Expose with 60-70kSv
Use thyroid collars for intraoral radiographs and ceph
Reduce CBCT beam FOV to region of interest

How should you talk to your patient about radiation?
