Classification of Living Organisms
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
Taxonomy
The science of describing, naming, and classifying organisms
Classification
Arranging organisms into groups based on their similarities
Systematics
The scientific study of the diversity of organisms and their natural (evolutionary) relationships
Taxonomy hierarchical grouping of classification
Domain
Kingdom
Phylum (or Division)
Class
Order
Family
Genus
Species - is the basic unit of classification (but not the smallest taxonomic group)
subspecies
varieties
cultivar
Reasons to classify
To ensure that the right plants are named correctly for ease of identification and grouping
It helps identify new species
Helps to remember the diversity of plants when they’re better organized
Help us identify relationships between different plants and other organisms
Six kingdoms of life
Bacteria
Archaea
Protista
Fungi (Myceteae)
Animalia
Plantae
(BAPFAP)
Bacteria
Domain: Bacteria
E.g.: Nitrogen-fixing bacteria, cynobacteria, lactic acid bacteria, enterobacteria (in intestines of humans and other animals)
Characteristics: prokaryotic (lack distinct nuclei and other membranous organelles), singled celled, microscopic, cell walls composed of peptidoglycon
Archaea
Domain: Archaea
E.g. Halophiles (live in salt ponds), thermoacidophiles (live in hot sulfur springs), methanogens (live in swamps, digestive tracts of humans and other animals)
Characteristics: prokaryotic (lack distinct nuclei and other membranous organelles), singled celled, microscopic, cell walls without peptidoglycon, different from bacteria chemically, adapted to extreme environments such as hot springs and undersea thermal vents
Protista
Domain: Eukarya
E.g. Euglenoids, Dinoflagellates,Diatoms, Golden brown algae Yellow-green algae Green algae, Brown algae, Red algaelgae, slime molds, water molds, prolozoa
Characteristics: Eukaryotic (posses distinct nuclei and other membranous organelles), single celled or simple multicellular, varied modes of nutrition (some photosynthetic, some consume food, some absorb nutrients)
Fungi
Domain: Eukarya
E.g.: Mushroom, puffball, mildews, yeast, disease causing fungi, mycorrhizae
Charcteristics: Eukaryotic, multicellular, photosynthetic, multicellular reproductive organs, cell walls of cellulose
3 Main Types:
Biotrophs: obtain nutrients from other organisms without killing them
Necrotrophs: Attack attack living hosts virulently, killing the hosts and then absorb released nutrients
Saprotrophs: obtain nutrients from dead organisms
• Some important fungi:
1. yeast
2. disease causing fungi, e.g. rot, rust, damping-off, powdery mildew, downy mildew, in plants.
3, edible fungi, e.g mushrooms (class: basidiomycetes)
4. mycorrhizae
Plantae
Domain: Eukarya
E.g. Mosses, ferns, pines, flowering plants
Characteristics: Eukaryotic, multicellular, no cell walls, nonphotosynthetic, consume other organisms, move about by muscular contraction, specialized nervous tissue to coordinate responses
Vascular plants:
(A) seedless plants
phylum Lycopodiophyta (club mosses)
Phylum Pteridophyta (ferns, whisk ferns, horsetails)
(B) seed plants
plants with naked seeds (gymnosperms)-
phylum coniferophyta (conifers)
phylum cycadophyta (cycads)
phylum ginkgophyta (ginkgoes)
phylum gnetophyta (gnetophytes)
plants with seeds enclosed within a fruit
Phylum Anthophyta (angiosperms or flowering plants)
Class is eudiocotyledones (eudicots) OR DICOTS
Class Monocotyledones (monocots)
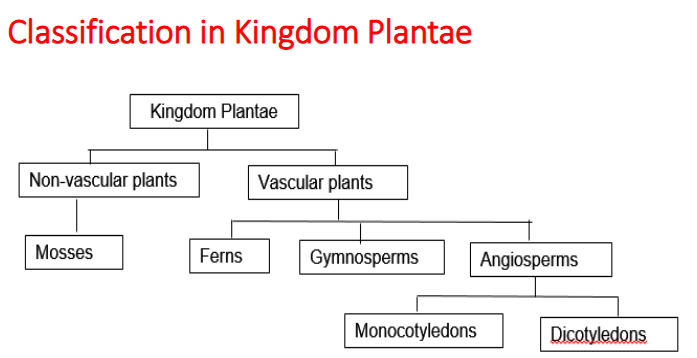

Plantae: Non-vascular plants
Phylum Brophyta (mosses) - dominant generation
Phylum Hepatophyta (liverworts)
Phylim Anthocerophyta (hornworts)
Gymnosperms
cone-bearing,
vascular non-flowering (naked seeded)
E.g. pines, have male cones and female cones, no flowers
Angiosperms
flowering plants, dicots and monocots
Monocotyledon
Commonly referred to as Monocots
One of the two main classes of flowering plants
Monocot seeds contain a single cotyledon (one seed leaf)
Usually have parallel leaf venation
The parts of monocot flowers usually occur in multiples of threes, e.g. three sepals, three petals, six stamens, e.g. their sepals, petals, stamens, etc. usually occur in multiples of three
Includes grasses, orchids, onions, lilies and palms
Dicotyledon
Commonly knows as Dicots (Eudicots)
One of two main classes of flowering plants.
Dicot seeds contain two cotyledons (have two seed leaves)
net leaf venation
Flower parts e.g. and their sepals, etc. usually occur in multiples of 4 or 5