Chapter 11 - DNA Replication
1/35
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
DNA Replication
The duplication of the cellular genome.
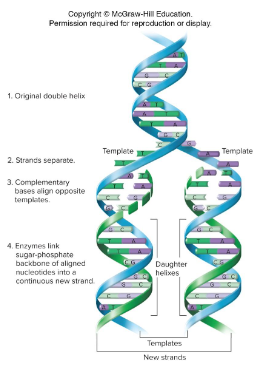
Semi-Conservative Model
A model of replication proposed by Watson and Crick. According to this model, unwinding of double helix exposes bases on each strand, where each strand can act as a template for synthesis of new strands. New strands form by insertion of complementary base pair. The end-product is two identical daughter double helices produced from a single double helix.
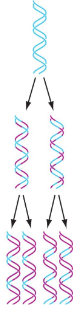
Conservative Model
Per this model of DNA replication, the parental double helix remains intact while both strands of the daughter helices are newly synthesized.

Dispersive Model
Per this DNA replication model, both strands of both daughter helices contain original and newly synthesized DNA.
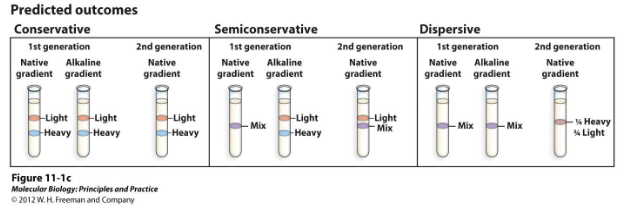
Grew E.coli in a medium with only the heavy isotope of nitrogen. They then switched the E.coli over to a medium with the light nitrogen isotope and let them replicate. They collected samples after each generation and centrifuged them. Original parent strands would have heavy nitrogen while newly made strands would have light nitrogen. They found that the DNA of each generation matched with the semi-conservative model of replication (centrifugation in first gen showed a weight marker that was a mix between the two forms).
How did Meselson and Stahl conduct their experiment determining the model of DNA replication? What were the results?
Replication Fork
The site where replication is taking place.
1) Double-stranded DNA is antiparallel with respect to each other
2) DNA polymerases always work 5’ to 3’
What are the two problems that need to be overcome with DNA replication?
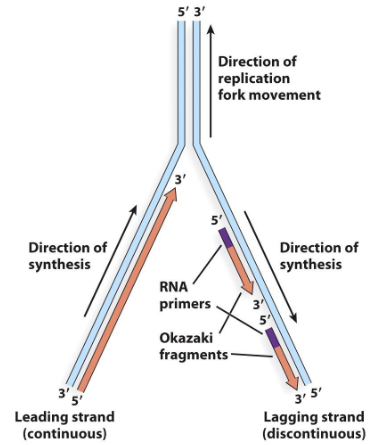
Semi-Discontinuous Replication
DNA replication in which there is a leading strand and a lagging strand.
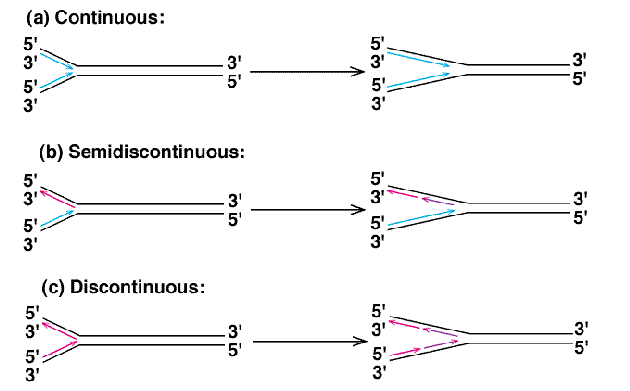
Leading Strand
The strand during semi-discontinuous replication that is made continuously and chases the replication fork.
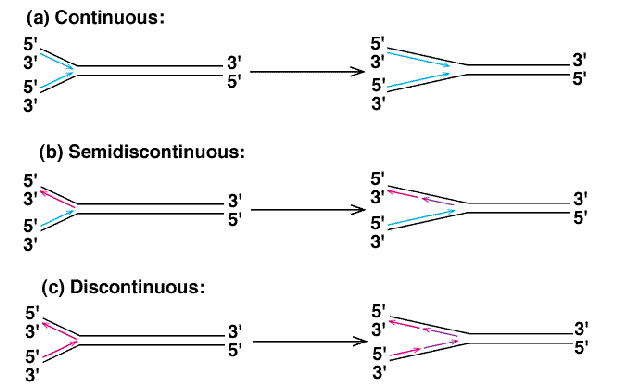
Lagging Strand
The strand during semi-discontinuous replication that is made discontinuously. Synthesis on this strand moves away from the fork.
Okazaki Fragment
Short DNA fragments synthesized on the lagging strand.
DNA Polymerase 1
Catalyzes new phosphodiester bonds during DNA replication. It has both polymerase and exonuclease activities in the same polypeptide. It can degrade DNA from the 3’ or 5’ end.
High energy phosphate bonds associated with dNTPs (hydrolysis of pyrophosphate)
The energy for DNA synthesis comes from what bonds?
Initiation
The first stage of DNA replication in which proteins open up the double helix and prepare it for complementary base pairing.
Elongation
The second stage of DNA replication in which proteins connect the correct sequence of nucleotides on newly formed DNA strands.
3’ - OH
What attacks the alpha phosphate of the incoming NTP during replication?
5’ to 3’ / antiparallel / 3’
Fill in the blank…
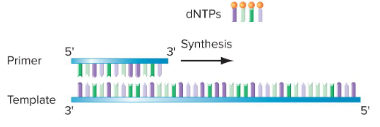
DNA synthesis proceeds in what direction? The template and newly synthesized strands are ( ). DNA polymerase adds nucleotides to ( )-OH of the new strand.
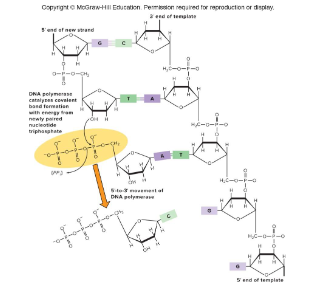
1) Four dNTPs for incorporation into the chain and for energy
2) A single-stranded template
3) A primer with an exposed 3’ hydroxyl
What are the three strict requirements for DNA polymerase action?
DNA Nucleases
Enzymes that degrade DNA.
Endonucleases
Also called restriction enzymes, these cut DNA at internal positions.
Exonucleases
Enzymes that remove bases from the ends of DNA molecules.
3’ to 5’ exonuclease activity
Exonuclease activity that will test the new DNA to make sure that the right base was put in. If not, the wrong base is removed. It removes bases from the 3’ end of the DNA and can residue on the same polypeptide as the DNA polymerase activity.
1) Polymerase slows down because of poor interactions
2) Primer template interaction is destabilized
3) The active site of the exonuclease binds and removes the mismatched base
What steps occur when there is a mismatched base during DNA replication?
5’ to 3’ exonuclease activity
This exonuclease activity is unique to polymerase 1. It degrades DNA or DNA as a new DNA strand is made (moves in direction of polymerase)
Also known as nick translation. The exonuclease makes a nick removing the wrong base and DNA polymerase fills in the nick with the correct base.
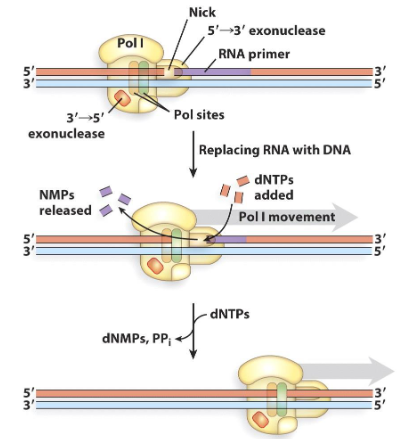
Polymerase 1
Polymerase involved in primer removal and repair.
Polymerase 3
Polymerase that replicates the chromosome.
Polymerase 2
Polymerase involved in DNA repair.
Polymerases IV & V
Polymerases that lack proofreading and make a lot of mistakes.
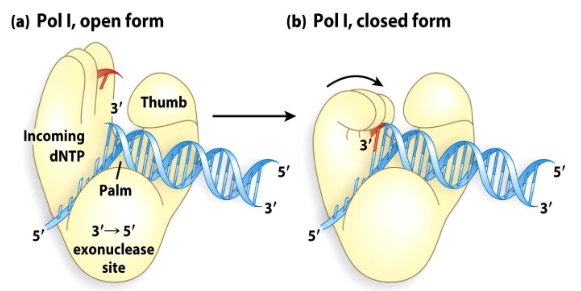
1) Palm
2) Thumb
3) Fingers
DNA polymerases have what three highly conserved domains?
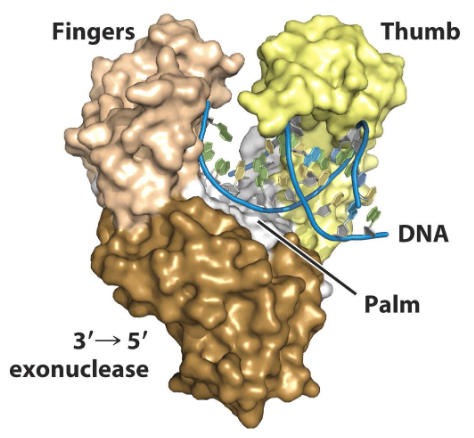
Palm
A domain of DNA polymerase that contains most of the catalytic site and monitors base pairing. The bound DNA lies here.
Fingers
A domain of DNA polymerase that is important in catalysis by binding the incoming NTP and moving it into the proper position. It bends the template to expose only the first base after the primer.
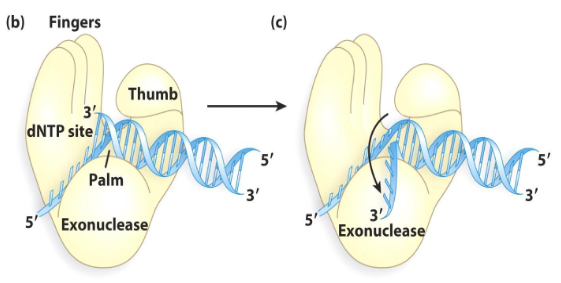
Thumb
A domain of DNA polymerase interacts with new DNA, maintaining the correct position of the primer and active site. It helps the polymerase stay on the DNA.
Closed Form
When the correct base is in the fingers, the enzyme squeezes together, forcing the NTP down to the template.
Distributive Synthesis
When DNA polymerase could dissociate from the DNA and have to rebind.
Processive Synthesis
When the polymerase simply slides forward, still attached to the DNA, after the new base is added.
Processivity Number
The average number of bases added each time an enzyme binds the primer template junction. This varies greatly between polymerases.