Intro to Acids and Bases
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
Arrhenius Acid
a substance that, when dissolved in water, increases the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+)
Arrhenius Base
a substance that, when dissolved in water, when dissolved in water, increases the concentration of hydroxide ions (OH-).
Bronsted-Lowry Acid
a proton (H+) donor. A substance that donates a proton (H+) to another substance in a chemical reaction. This definition expands the concept of acids beyond traditional Arrhenius theory, which only classifies acids based on their ability to produce hydrogen ions in water. Must have at least one removable (acidic) proton (H+) to donate. The acidic proton is bonded to the electronegative atom.
Bronsted-Lowry Base
a proton (H+) acceptor. Any substance that can accept a proton (H+) from another substance. This theory extends the concept of bases beyond the traditional Arrhenius definition, which only includes substances that produce hydroxide ions (OH-) in water. Must have at least one non bonding pair of electrons to accept the proton (H+).
Acids & Bases Chart
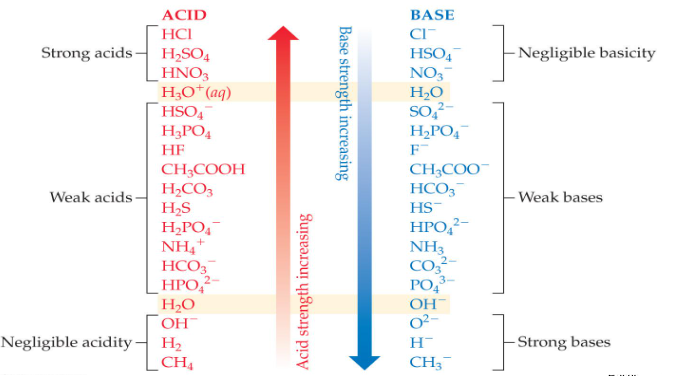
Strong Acids
HCl, HNO3, H2SO4, HBr, HI, HClO4, HClO3. Acids that completely dissociate in water, producing a high concentration of hydrogen ions (H+) and contributing to a strong acidic solution. These are acids that are strong proton donors and result in low pH solutions.
Strong Bases
LiOH, NaOH, KOH, RbOH, CsOH, Sr(OH)2, Ba(OH)2, Ca(OH)2, and Na2O. These are bases that completely dissociate in water to yield hydroxide ions (OH-). They have a strong ability to accept protons.
In every acid–base reaction, equilibrium favors transfer of the proton from the ______ to the _______ to form the _______ and the _______.
stronger acid, stronger base, weaker acid, weaker base
Polyprotic acid
Acid capable of donating more than one proton in Acid-Base reactions, EX. H2SO4, H2CO3, H3PO4
Polyprotic Base
a base that can accept more than one proton (H+) in acid-base reactions, EX. CO3²-, PO4³-
pH
a method of reporting [H+] in a solution. ( ____=-log[H+] and [H+]=10^-__)
As [H+] _____, pH _______.
decreases, increases
Neutral [H+]=
1.0×10^-7 and pH=7
Acidic [H+]>
1.0×10^-7 and pH<7
Basic [H+]<
1.0×10^-7 and pH>7
As [OH-] _______, pOH ______.
decreases, increases
pOH=
-log[OH-]
Neutral [OH-]=
1.0×10^-7 and pH=7
Acidic [OH-]<
1.0×10^-7 and pH>7 ←small concentration
Basic [OH-]>
1.0×10^-7 and pH<7 ←large concentration
[OH-] and [H+] are ________ proportional.
inversely
Indicators, including litmus paper, are used for ___________; an indicator is one color in its ________ and another color in its ________.
less accurate measurements; acid form; basic form
pH meters are used for ____________ of pH; electrodes indicates small changes in ________ to detect pH.
accurate measurements; voltage
Autoionization of water is _______.
ENDOTHERMIC and as T increases, Kw increases as well
When temperature increases, the rxn proceeds towards the products increasing [OH-] and [H+] therefore…
pH and pOH decrease.
As temperature increase in pure water, Kw _____ and [H+] and [OH-] _____ so pH and pOH ______.
increases, increase, decrease
At any temp in pure water
[H3O+]=[OH-]
Weak acids only ____________ to ions. They are ______ electrolytes.
partially dissociate; weak
Dissociation Equation for weak acids
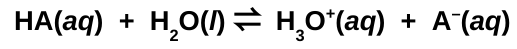
Acid Dissociation Constant (Ka)
Since it is an equilibrium, there is an equilibrium constant related to it.
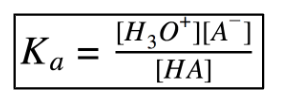
The ______ the acid, the more it _______ which means a greater _______.
Stronger; dissociates; Ka (Ka and acid strength are proportional)
Ka of an acid ______ depend on concentration.
does NOT
Ka changes only _______.
temperature
Percent ionization _______ change with concentration.
DOES
If a solution is diluted, all concentrations _______.
decrease
Percent ionization _____ as molarity ______, and percent ionization ______ as molarity ______.
increases; decreases; decreases; increases
Like weak acids, weak bases have an equilibrium constant called the…
base dissociation constant
Types of Weak Bases #1
Neutral substances with an atom that has a non bonding pair of electrons that can accept H+ EX. NH3, CH3NH2
Types of Weak Bases #2
Anions of weak acids (conjugated bases)
In every acid-base reactions, equilibrium favors transfer of the proton from the ________ acid to the ________ base to form the _______ acid and the ______ base.
stronger; stronger; weaker; weaker
Reactions between an acid and a base are called _____________ reactions. As a result _____ and a _____ (an ionic compound) are produced,
neutralization; water; salt
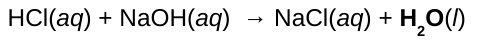
All soluble salts are ______ electrolytes, we can assume that any salt dissolved in water is completely _______.
strong; dissociated
Many ions can react with water to create H3O+ or OH- ions. The reaction with water is called ________.
hydrolysis
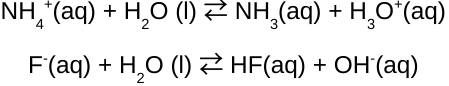
The acid-base properties of salt solutions depend on the nature of _______ and _______.
cations; anions
The cation can be _____ or ______.
basic; neutral
The anion can be _______, ______ or _______.
acidic; basic; neutral