AP Bio Unit 4
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
How do cells communicate?
by generating, transmitting, receiving, and responding to chemical signals
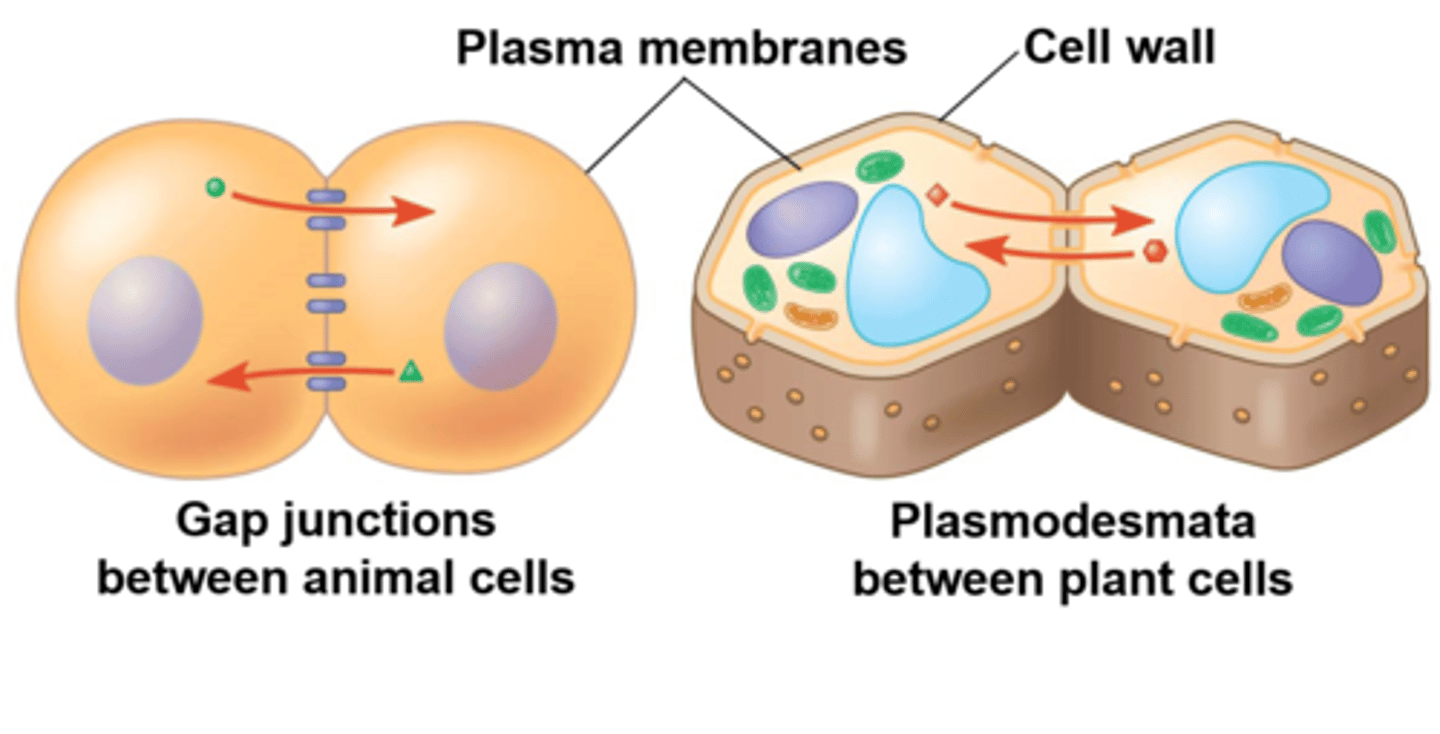
How does a cell communicate with another cell that it's touching
1. Juxtracrine signaling
2. In animals, this is done by gap junction (little holes connecting membranes)
3. In plants, this is done by plasmodesmata (little holes connecting cell wall)
4. this can also be done via proteins
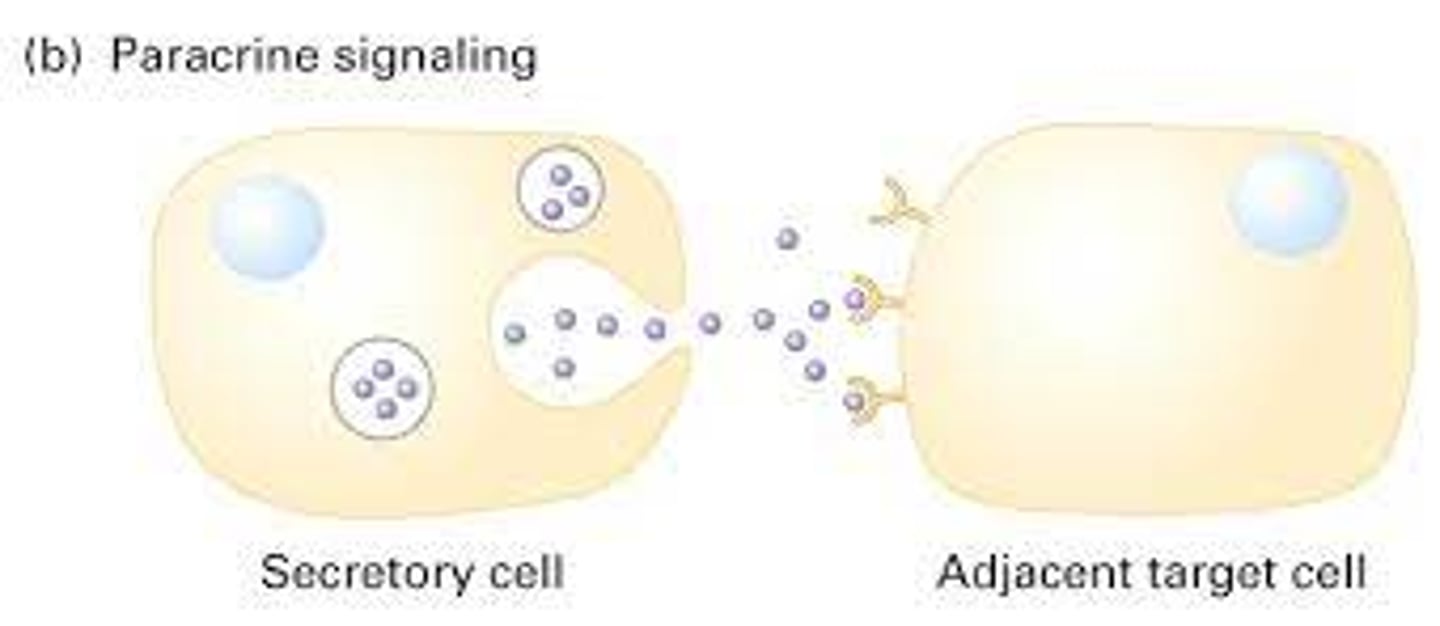
How do cells a short distance away communicate? (close but not touching)
Paracrine signaling: cell secretes a signaling molecule that will signal close by cells that have a receptor for it.
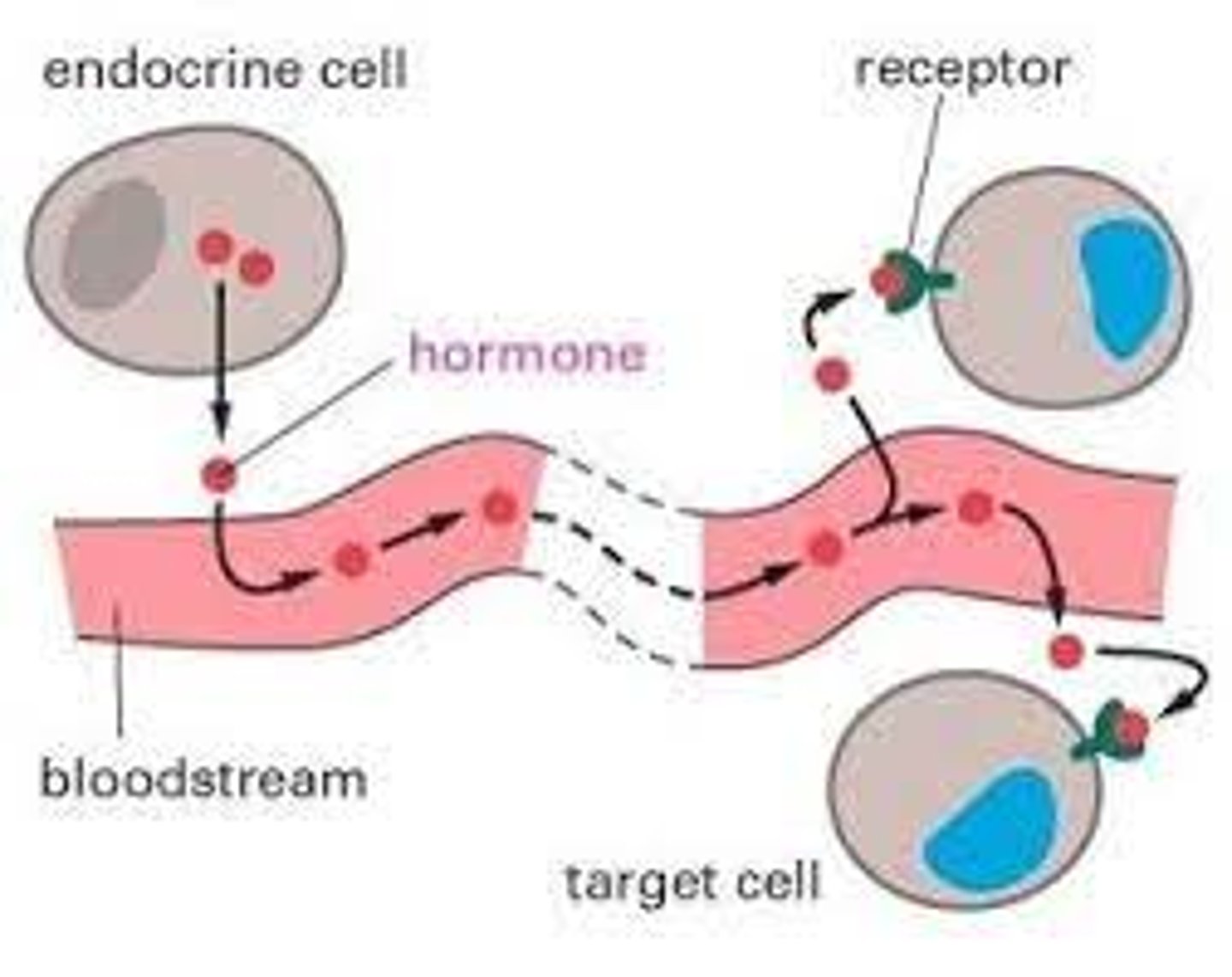
How do cells communicate with cells that are far away?
Endocrine signaling: cells secrete a signaling molecule, usually into the bloodstream, that will travel to a far away cell. The molecules are usually hormones traveling through the blood stream.
How does a cell signal itself?
Autocrine: a cell secretes a signaling molecule that binds to its own receptors.
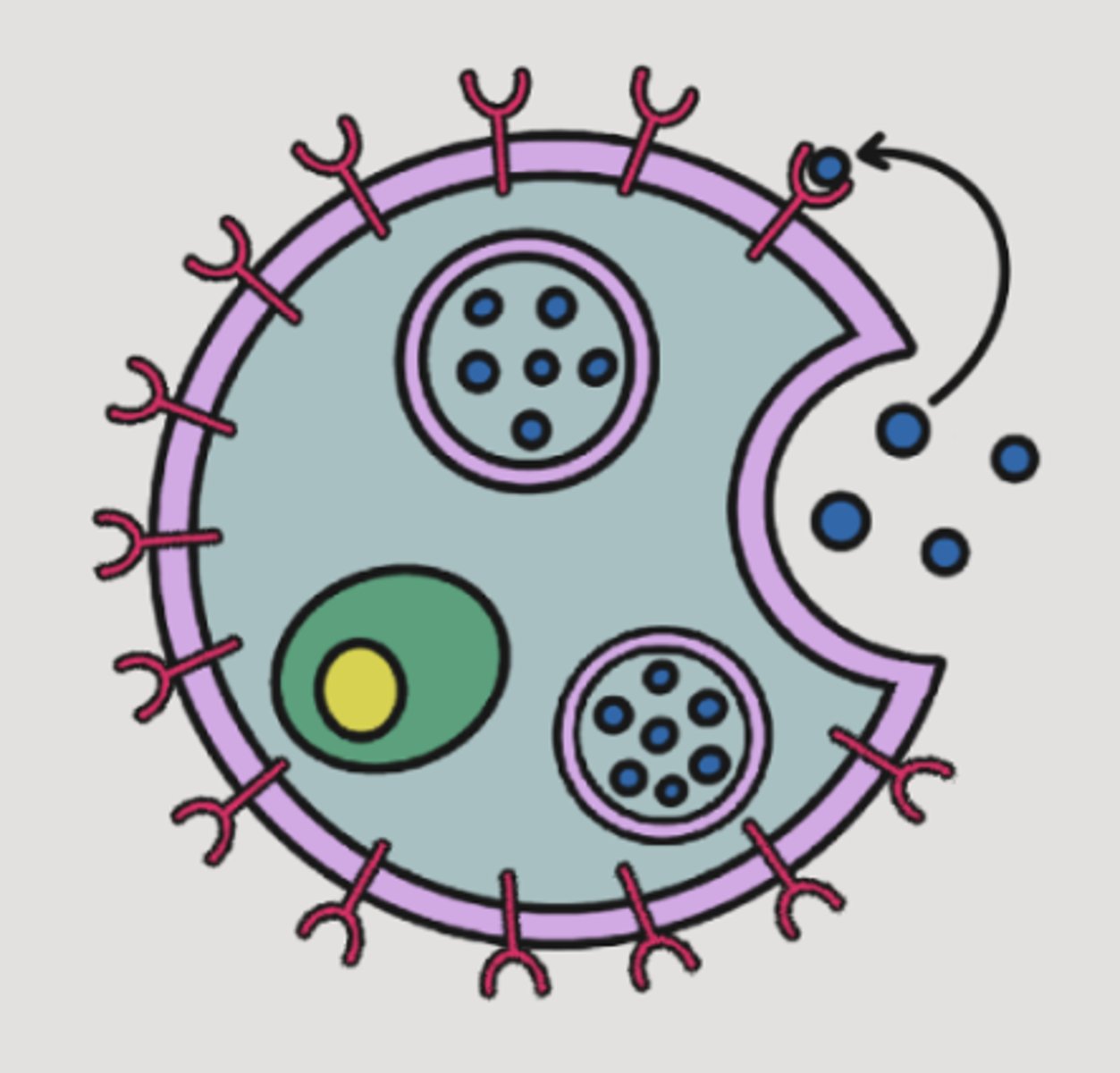
what are signaling molecules called? what do they do?
Ligands: bind to a receptor protein in or on another cell to make it do something
What are the three stages of cell signaling?
1. Reception: the signal is received
2. Transduction: a series of reactions happen in the signal transduction pathway, which amplifies the signal
3. Response: what the cell actually does
How can cell signaling be messed up?
mutations can cause cells to not be able to send or receive signals
For example, the SRY gene controls testosterone production, but mutations can mess this gene up and someone with an XY chromosome will develop into a female because they can't make the signaling molecule testosterone. This is called Swyer Syndrome.
What are the two types of feedback?
1. Negative feedback: Tries to maintain a constant level of something (homeostasis)
Ex: If blood glucose is too high, insulin will be made to decrease it, if blood glucose is to low, glucason will be made to increase it.
2. Positive feedback: tries to create more of the same response
Ex: childbirth.
The baby pushes in the cervix, stretching the uterus, which sends a signal to the brain to release oxytocin. Oxytocin causes the uterus to contract and the baby to push on the cervix more, creating a positive feedback loop.
What are the phases of the cell cycle?
1. Interphase: 90% of the cells life. Normal functions.
2. Gap 1 (G1): cell grows
3. Synthesis (S phase): DNA replicated
4. Gap 2 (G2): cell grows some more
5. Mitosis: cell duplicates
6. Cytokinesis: after mitosis, the cytoplasm is divided, separating the two cells made from mitosis.
What are the four phases of mitosis?
prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase (PMAT)
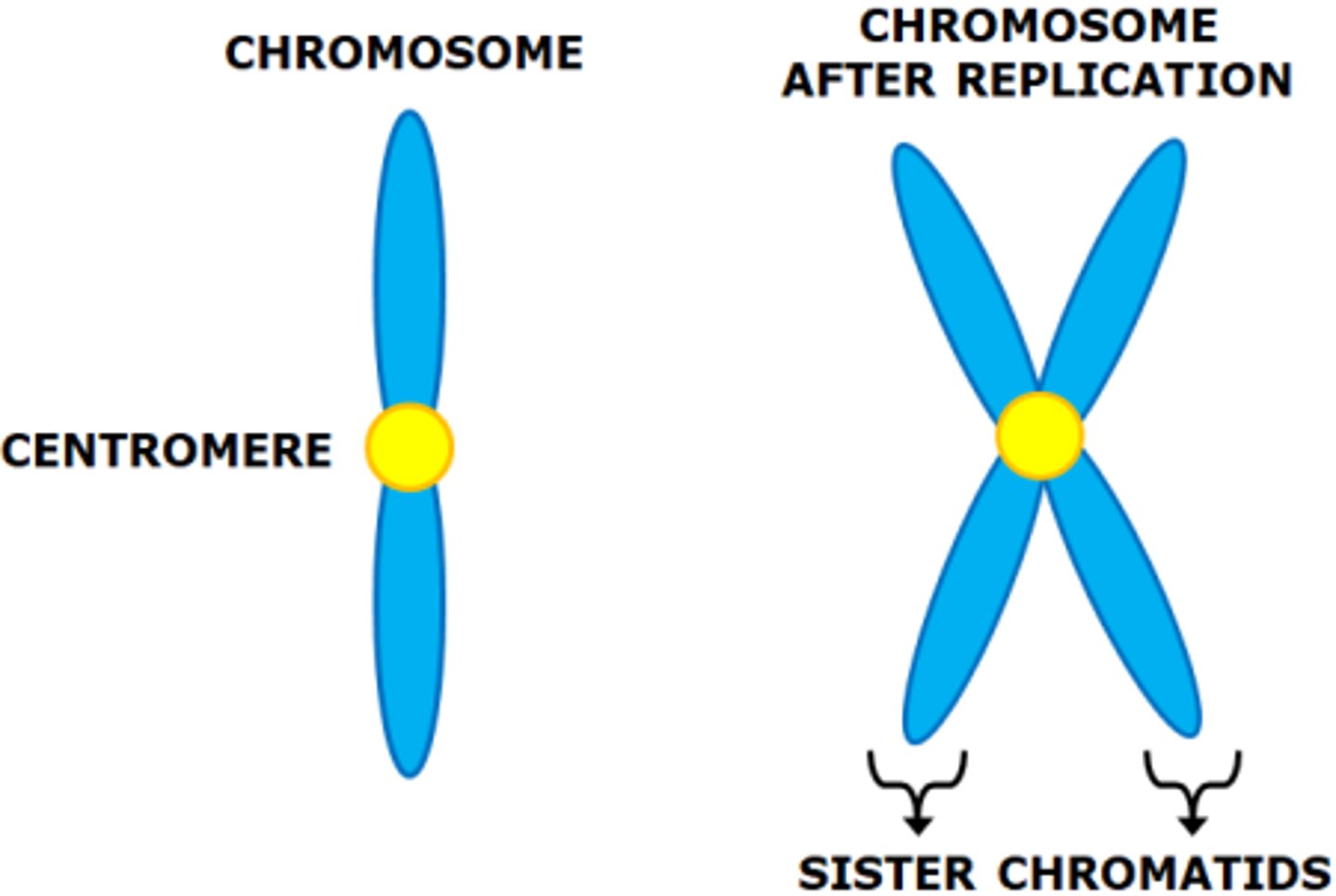
parts of a chromosome
chromosomes are counted by the amount of centromeres. A chromosome with two sister chromatids is still one chromosome, just with double DNA.
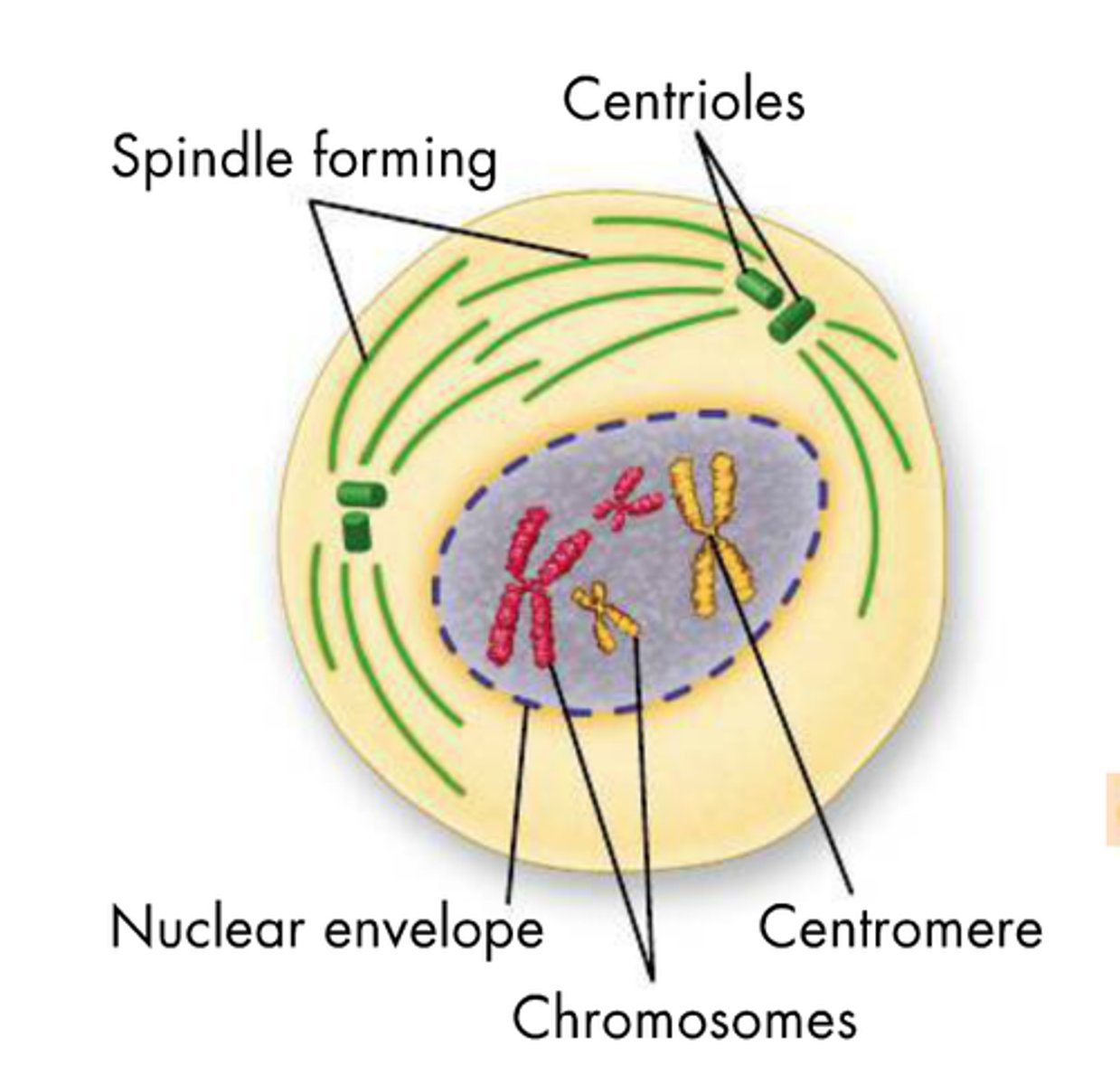
Describe prophase
1. spindle fibers form
2. nuclear envelope breaks down
3. chromatin (long strings of DNA) turns to chromosomes (nicely packed structures of DNA)
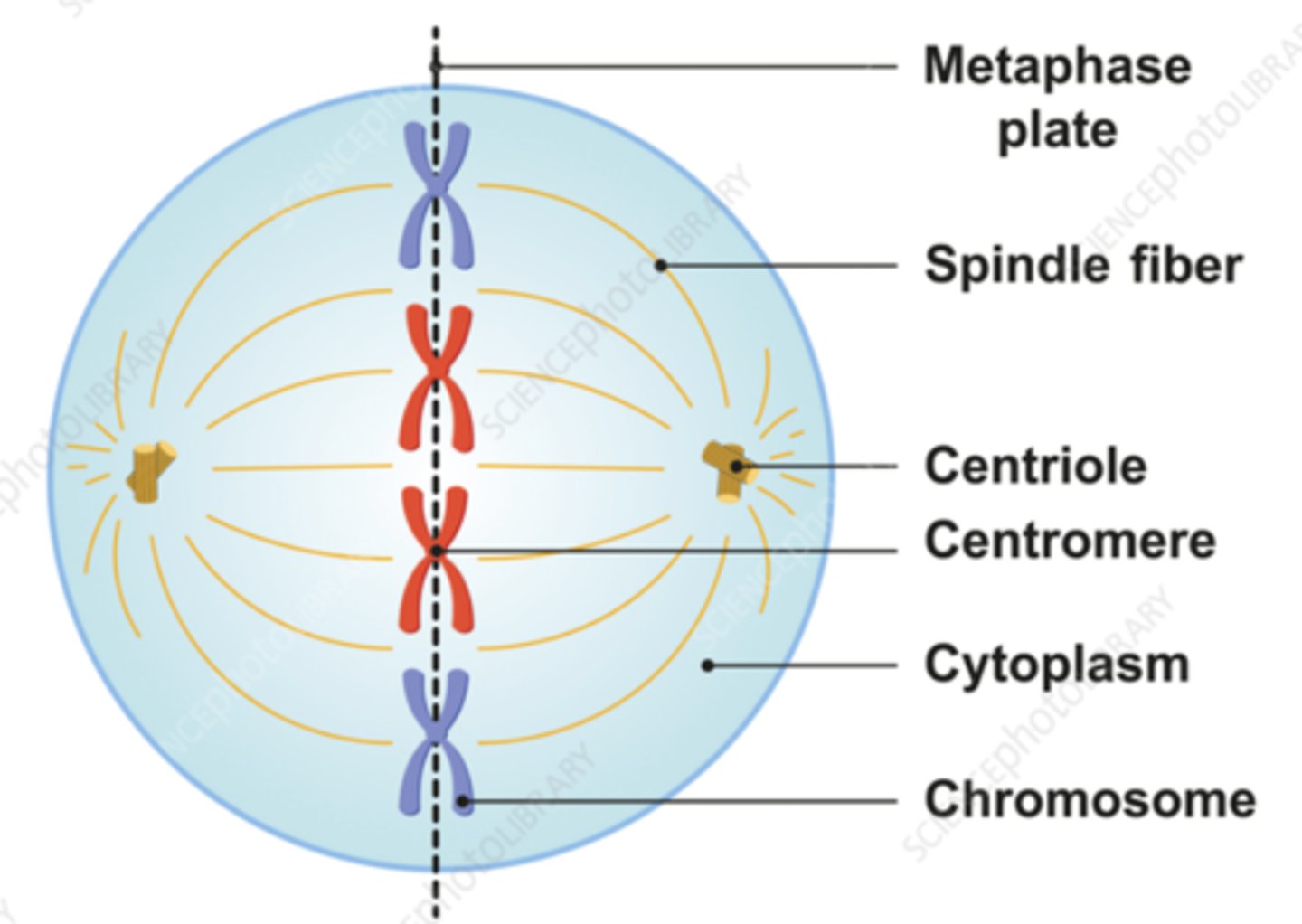
Describe metaphase
1. Chromosomes align in the center
2. centrioles go to the poles
3. spindle fibers attach to the chromosomes and centrioles
Describe anaphase
spindle fibers rip sister chromatids apart, doubling the amount of chromosomes.
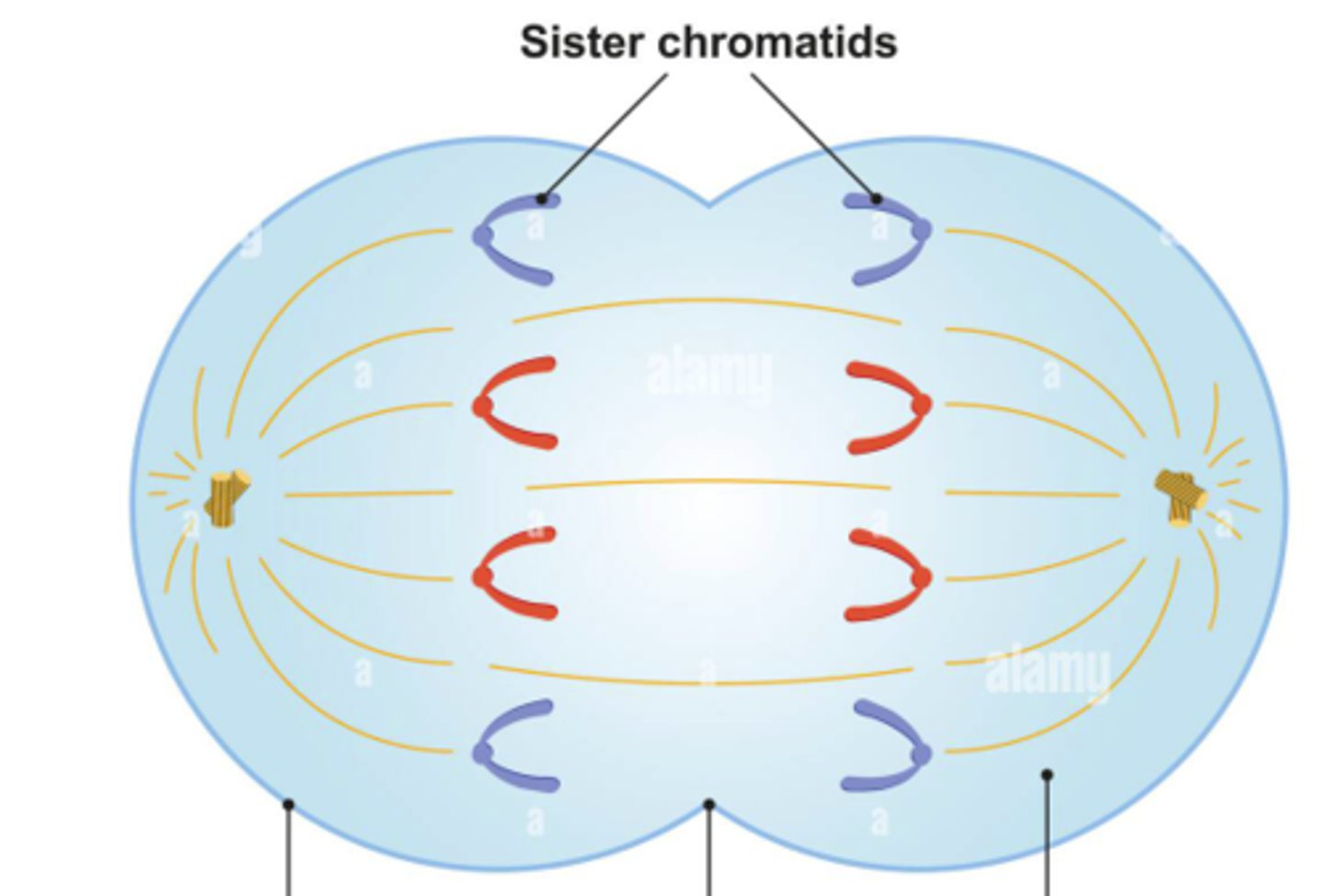
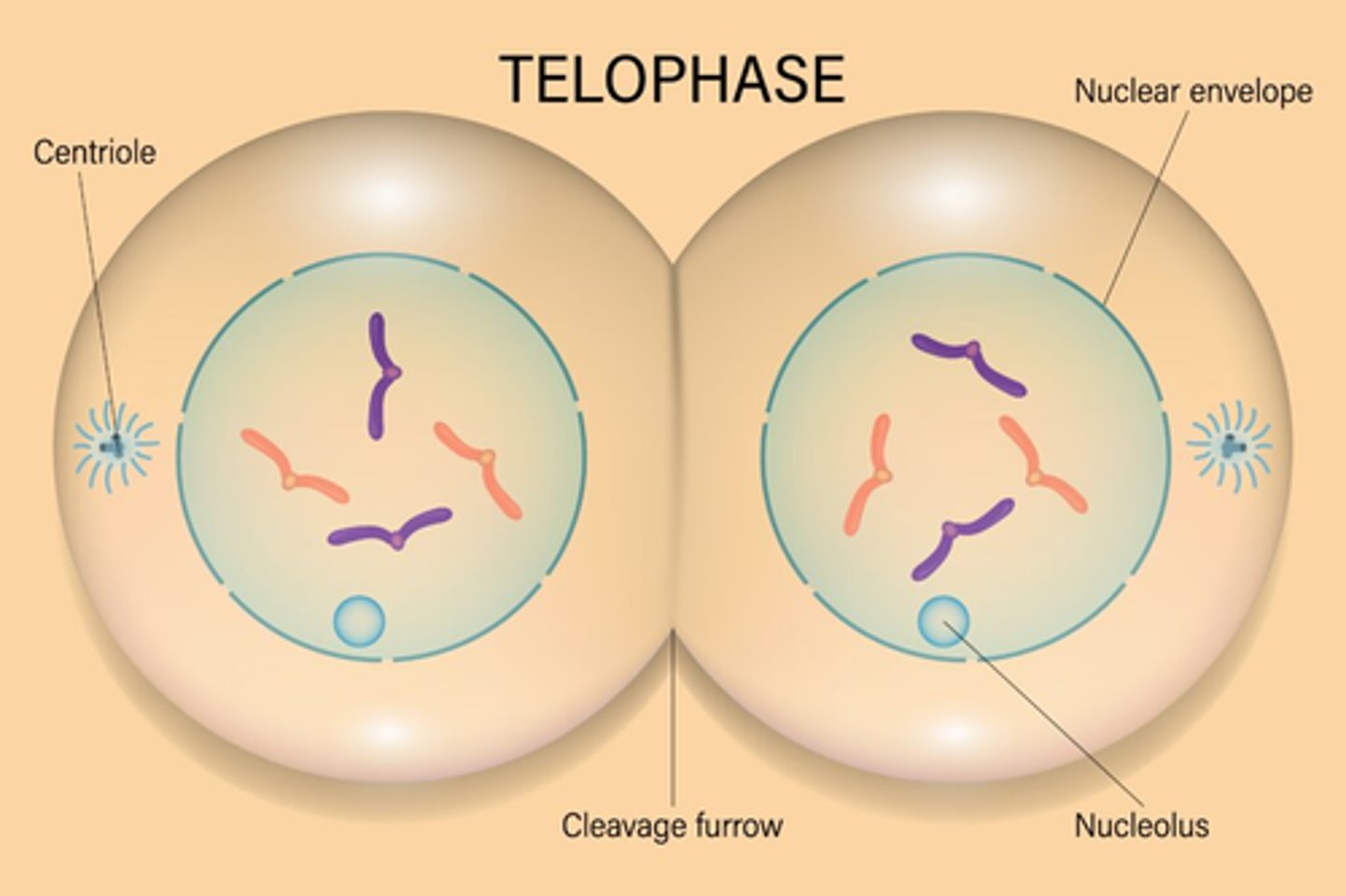
Describe telophase
1. Cleavage happens as the cell begins to split
2. Two nuclei begin to form, one for each new set of chromosomes
What is the final product of mitosis (after cytokinesis)
Two identical daughter cells
What regulates the cell cycle?
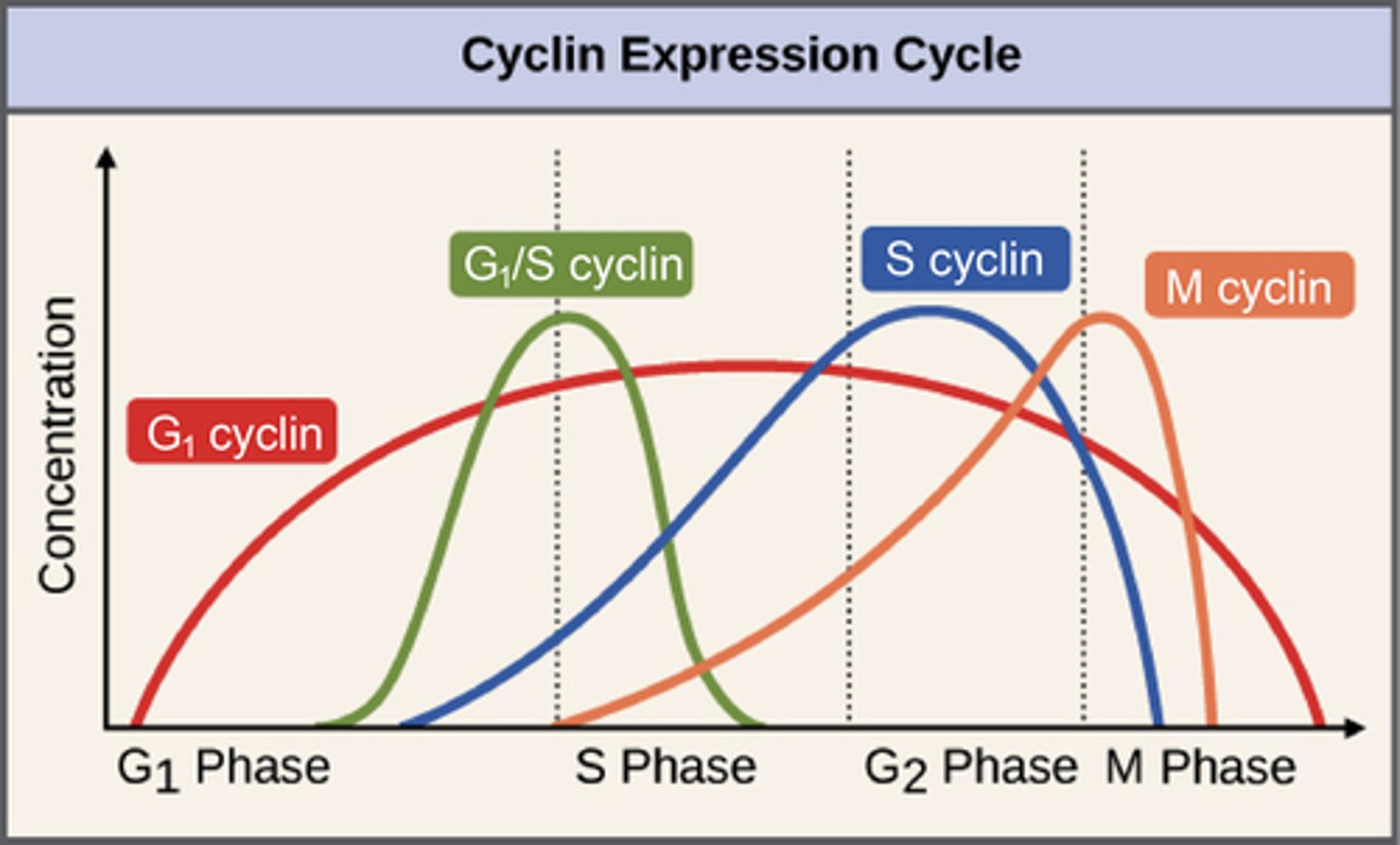
Cyclin dependent kinase (Cdks)
Cdks activate target enzymes based on what type of cyclin binds to their active site.
For example, if S-phase cyclin binds to Cdks, dna will be replicated
At what points in the cell cycle is each type of cyclin present?