Chap. 10 - Adverse Selection in Real Markets
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Positive Correlation between Risk and Coverage
As level of risk increases, so does the amount of coverage (riskier people will seek coverage more)
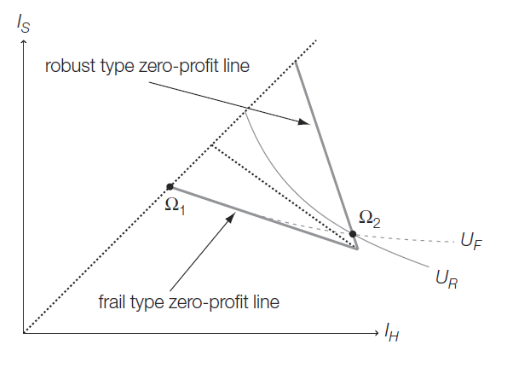
Rothschild-Stiglitz
Separating equilibrium —> high-risk types have full insurance (Ω1), low risk types have incomplete insurance (Ω2
Bulk discounts
a lower per-unit price for a large purchase of commodity
Bulk markups
a higher per-unit price for large purchases of a commodity
Insurance companies
__________ use bulk markups to protect themselves from risky customers who want a lot of insurance (what Rothschild model predicts!)
Adverse selection death spiral
both frail and robust individuals are pooled together, frail types are indirectly subsidized by robust individuals but robust types leave the pool (they are paying more due to the frail ppl even though they are healthy!) cycle repeats
predict health care costs
since people can do this more accurately than insurance companies, families with high predicted costs were more likely to was supplemental insurance (RAND HIE)
negative correlation
US workers with employer-sponsored insurance, medicare beneficiaries
life insurance
negative risk-coverage correlation: people with life insurance live longer! (some studies show that it is positively correlated but some don’t)
Viatical settlements
a firm purchases a life insurance contract from a sick person and collects the payout when he dies
why would adverse selection not occur
customers mispercieve their own risk
customers do not act on their private information
insurers can accurately observe customer risks
“advantageous selection”
customers misperceive their own risk
→ US novice drivers demand less insurance bc they believe they are safer than average driver
→ men aged 85-89, 31% think they will live to 100 but only about 3% will
customers do not act on their private information
→ Real customers have more important things to think about than small bargains on insurance
→ fail to realize their advantage
insurers accurately observing risk
→ Long-term care insurers, with access to historical data and a team of analysts, are better at predicting whether middle-aged customers will eventually need nursing home care than the customers themselves
→ all models rest on an assumption of information asymmetry
Advantageous selection
→ healthier, less risky people are sometimes more likely to buy insurance
→ more risk averse, higher income, better understanding of insurance benefits
cognitive ability
→positively correlated with medigap insurance purchase
→ negatively correlated with health expenditures
adverse selection
a situation in markets where one party, typically the buyer or seller, has more information about their risk or value than the other party
Ex post risk
risk that remains after an event has occured or after insurance contract is purchased.
Ex ante risk
reflects the uncertainty before the event, before insurance is purchased