Female Reproductive Systems and Diseases
1/82
Earn XP
Description and Tags
ANSC 410
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
83 Terms
structures of the female reproductive system
ovary
follicle of the ovary
oviduct (uterine tube)
uterus
cervix
vagina
urethral diverticulum
vestibule
vulva
labia
what are the functions of the female reproductive tract?
produce female sex hormones
development of reproductive cells
provides site for fertilization
provides environment for fetal development
where is the ovary located?
medial to kidneys in the craniodorsal abdomen
what is the primary female reproductive organ?
ovary
function of ovary
produces an egg (ovum) and produces the hormones estrogen and progesterone
follicle of the ovary
fluid filled structure on the ovary
blister-like
ruptures to release an egg into the oviduct (uterine tubes)
ovulation fossa
indention in the ovary in the mare
site of ovulation in the mare
oviduct (uterine tubes)
tube leading from the ovary to the uterus
function of oviduct?
collects eggs; location for fertilization
what are the 4 parts of the oviduct?
infundibulum
fimbria
ampulla
isthmus
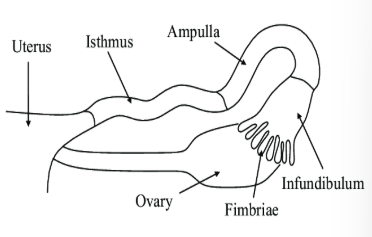
infundibulum
funnel-like
catches the ovum
located at the terminal end of the oviduct
fimbria
finger-like projections on the infundibulum
ampulla
upper 1/3 of oviduct
location for fertilization
isthmus
joins the uterine body
uterus
(womb) Y-shaped
function of uterus
site of implantation of the embryo
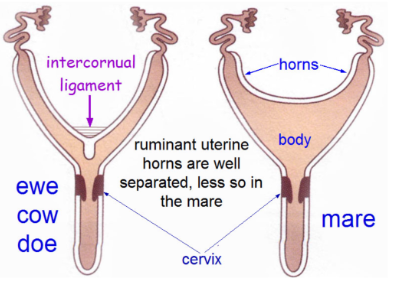
what are the 2 types of uterus?
bicornuate
bipartite
bicornuate uterus
2 distinct uterine horns; long uterine horns with smaller body
what animals have a bicornuate uterus?
dogs, cats, pigs
(true/false) bicornuate uterus can have fetus develop in both horns of the uterus
true
bipartite uterus
2 uterine horns separated by a fibrous layer; shorter uterine horns with larger body
what animals have a bipartite uterus?
ruminants - fetus only develops in 1 horn or in the body of the uterus
what are the 3 layers of the uterus?
mesometrium (serosa)
myometrium
endometrium
mesometrium (serosa)
protective outer layer of uterus
broad ligament that suspends uterus and attaches to dorsal body wall
myometrium
muscular layer of uterus
responsible for contractions during parturition
endometrium
inner mucosal layer of uterus
thickens during pregnancy
what ligament is found in the uterus?
intercornual ligament
ruminant uterus vs mare uterus
suspensory ligament of the ovary
connects the ovaries to the cranial aspect of the body cavity
very vascular and contains many nerves
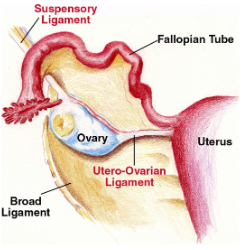
broad ligament of the uterus
attaches the uterus to the body wall
suspends the uterus in the dorsal abdomen
also connects to the ovaries
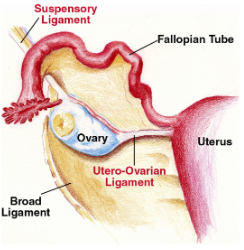
the broad ligament prevents the uterus from _______ or _________ during pregnancy
falling; prolapsing
function of vagina
area of copulation
where is the most common location where semen is deposited in natural breeding?
in the vagina
urethral diverticulum
urethral opening on the vaginal floor
for urination
vestibule
caudal (posterior) to the urethral diverticulum
vulva
exterior extension of the vagina
enlarges during parturition and estrus
labia
lips of the vulva
stages of oogenesis
oogonia
primary oocyte
secondary oocyte
oocyte
ovum
steps of the estrous cycle
proestrus
estrus
metestrus
diestrus
anestrus
proestrus
before coming into heat (estrus)
influenced by FSH
what is the beginning of follicular growth?
proestrus
estrus
heat; receptive to the male; influenced by FSH
metestrus
occurs after ovulation; influenced by LH
when does the formation of Corpus Hemorrhagicum take place?
in metestrus
Corpus Hemorrhagicum
blood clot
last about 5 days
diestrus
resting phase/pregnancy; influenced by LH
when is Corpus Luteum completely formed?
diestrus
Corpus Luteum
yellow body
rich source of progesterone (maintains pregnancy)
anestrus
period of no activity
estrous cycle of cows?
polyestrous
list the hormones of the female reproductive tract
estrogen
progesterone
follicle stimulating hormone (FSH)
luteinizing hormone (LH)
prostaglandin
estrogen
starts estrus; production is stimulated by FSH
where is estrogen produced?
ovary
progesterone
rest or pregnancy; production stimulated by LH
where is progesterone produced?
ovary
follicle stimulating hormone
increases follicular growth; causes the ovary to produce estrogen; superovulation
where is FSH produced?
pituitary gland
luteinizing hormone
causes ovulation
where is LH produced?
pituitary gland
prostaglandin
luteolytic (destroys Corpus Luteum); decreases FSH production; signals uterine contraction and menstruation
where is prostaglandin produced?
uterus
what is a free martin?
when a female calf is born as a twin with a male
over 90% of the time, the female is infertile due to…
the influence of male hormones in utero
clinical effects of free martin?
female possesses masculine behavior and non-functioning ovaries
female reproductive organs may be smaller than normal
genetic female with male characteristics
what is the most common cause of non-inflammatory infertility in cattle?
Free Martin
research shows that free martin can occur in what animal?
goats
is uterine neoplasia common in cows?
not as common as in other species
how can uterine neoplasia be identified?
rectal palpation, ultrasound or slaughter
what are the most common types of uterine neoplasia?
leiomyosarcoma and lymphosarcoma
clinical signs of uterine neoplasia
anestrus
abnormal heat cycles
male-like behavior
vaginal discharge
chronic weight loss
brucelloses
(aka Bang’s disease) contagious, zoonotic, bacterial disease
caused by the bacteria Brucella abortus
clinical signs of Brucellosis
late gestation abortions/stillbirths
retained placenta
infertility
weak calves
reduced milk production
transmission of brucellosis
contact with aborted fetus, afterbirth
ingestion
cuts in mucous membranes
diagnoses for Brucellosis
blood test or milk sample
prevention for Brucellosis
test and slaughter
vaccinate heifer calves under 12 mo.
modified live vaccine — humans can get the disease from the vaccine
Campylobacteriosis (Vibrosis)
Campylobacter fetus; bacterial, venereal disease
clinical signs of Vibrosis
infertility
repeated breeding
prolonged calving season
transmission of Vibrosis
asymptomatic bulls
prevention of Vibrosis
vaccination
using virgin bulls on virgin heifers
screen bulls before introducing into the herd
trichomoniasis
protozoal disease; Trichomonas fetus
clinical signs of Trichomoniasis
infertility due to inflammation of the repro tract
repeated breeding
prolonged calving season
transmission of Trichomoniasis
asymptomatic bulls
natural breeding (makes this more of a problem with beef cattle)
prevention of Trichomoniasis
testing and vaccinating