4.4 & 4.5 Vocab Quizlet
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
personality
an individual's characteristic pattern of thinking, feeling, and acting

psychodynamic theory
theories that view personality with a focus on the unconscious and the importance of childhood experiences
psychoanalysis
Freud's theory of personality that attributes thoughts and actions to unconscious motives and conflicts; the techniques used in treating psychological disorders by seeking to expose and interpret unconscious tensions

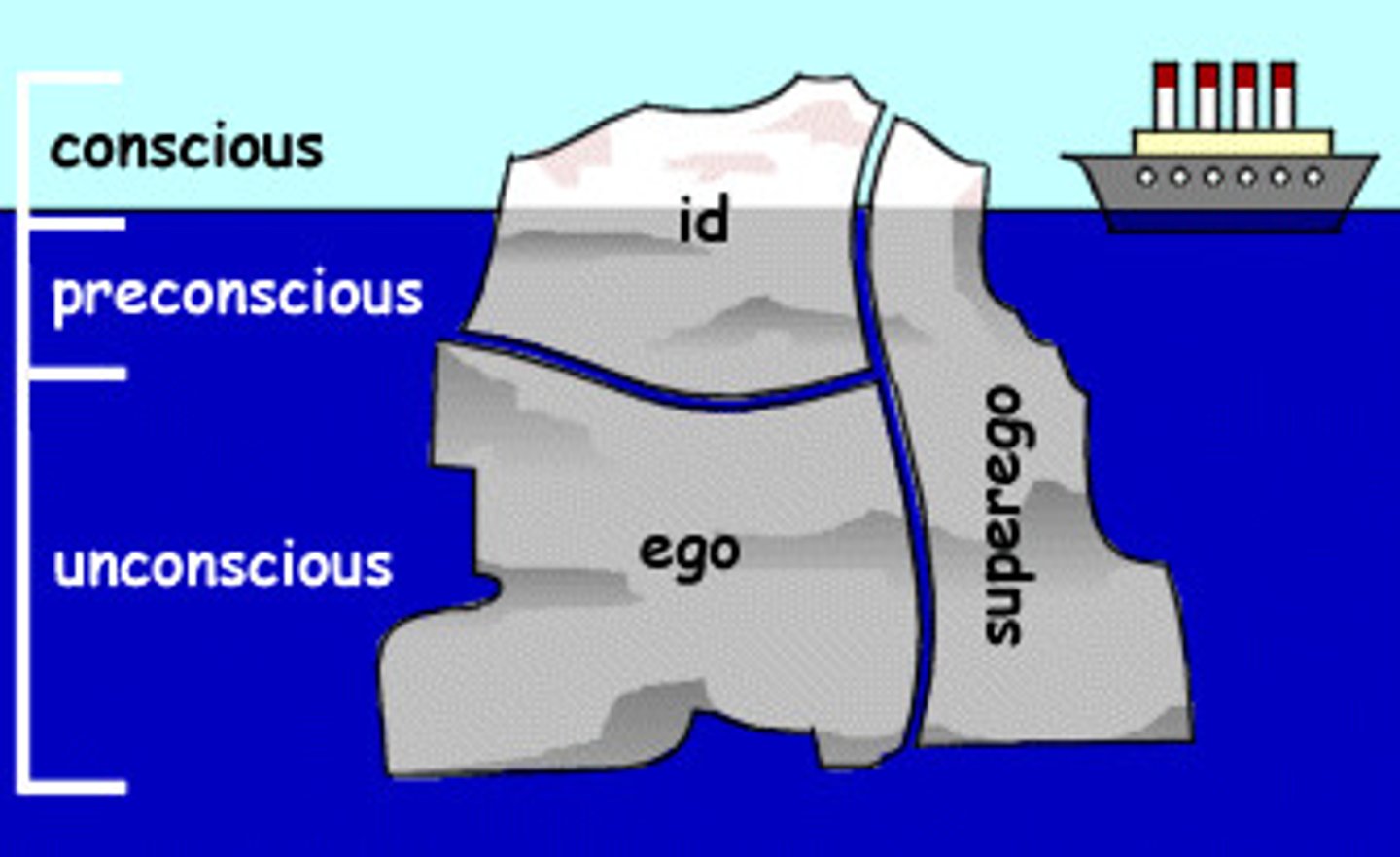
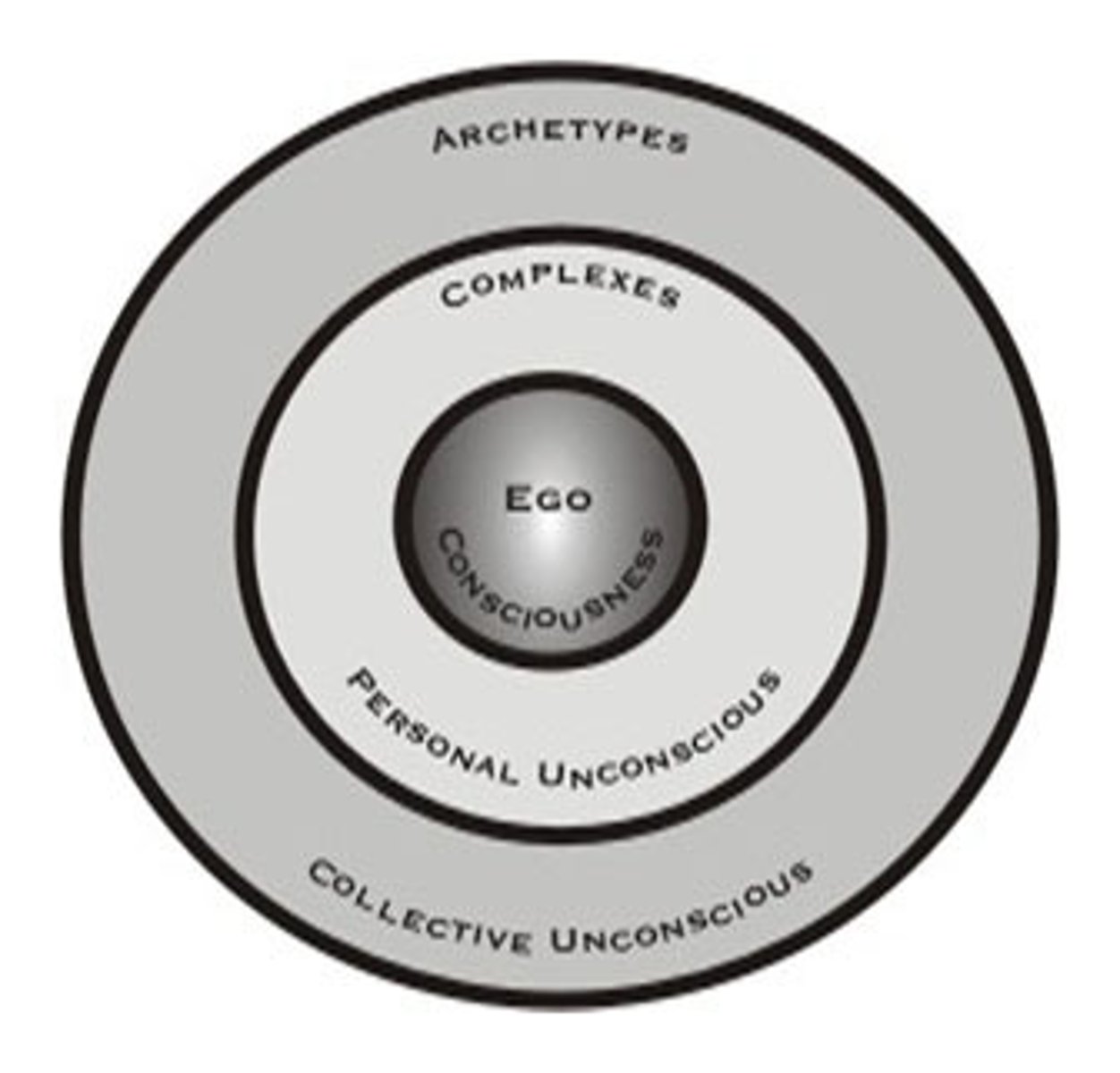
unconscious
according to Freud, a reservoir of mostly unacceptable thoughts, wishes, feelings, and memories. According to contemporary psychologists, information processing of which we are unaware.
free association
in psychoanalysis, a method of exploring the unconscious in which the person relaxes and says whatever comes to mind, no matter how trivial or embarrassing

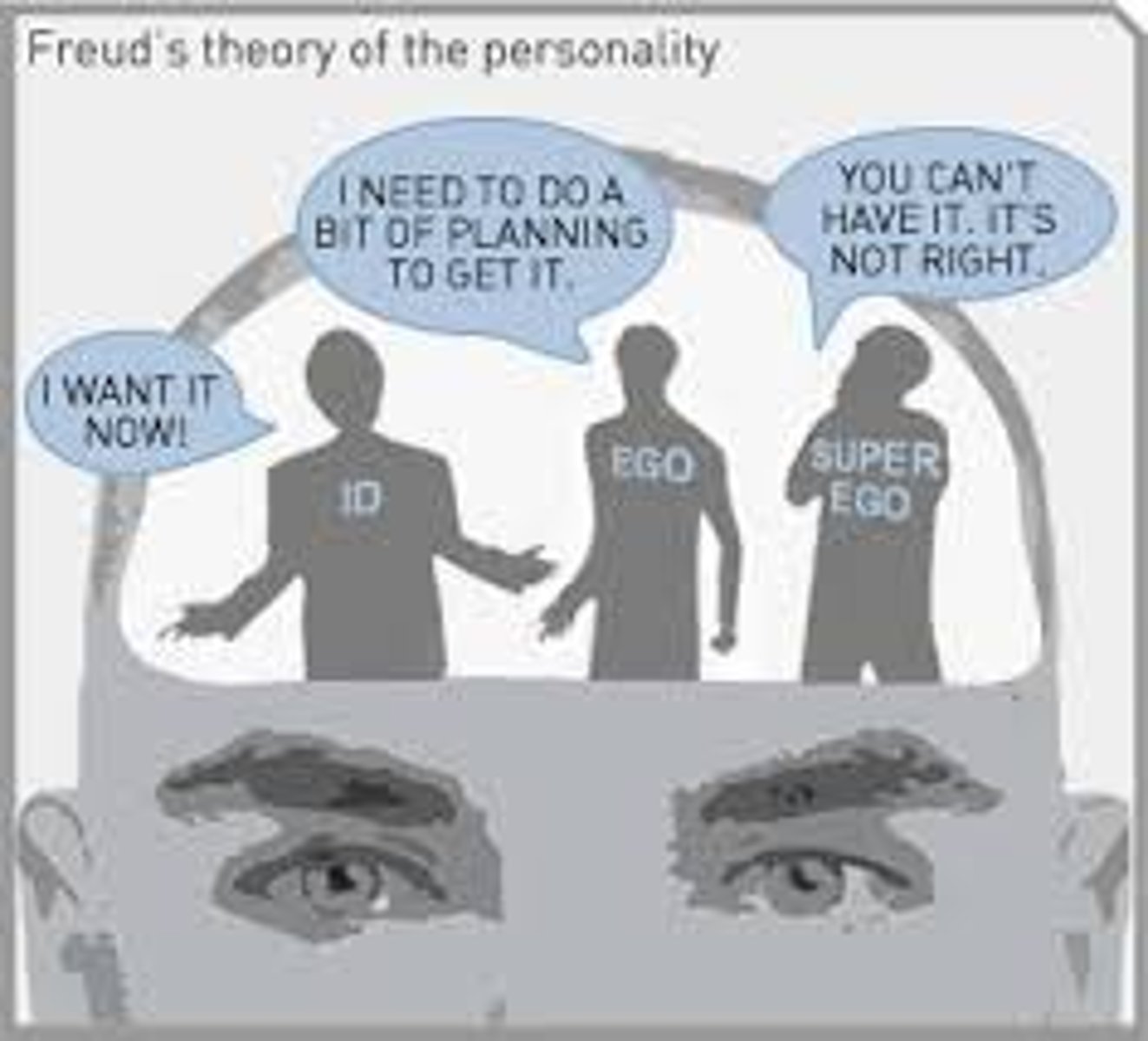
id
a reservoir of unconscious psychic energy that, according to Freud, strives to satisfy basic sexual and aggressive drives. The id operates on the pleasure principle, demanding immediate gratification.
ego
the partly conscious, "executive" part of personality that, according to Freud, mediates among the demands of the id, the superego, and reality. The ego operates on the reality principle, satisfying the id's desires in ways that will realistically bring pleasure rather than pain.

superego
the partly conscious part of personality that, according to Freud, represents internalized ideals and provides standards for judgment (the conscience) and for future aspirations.
defense mechanisms
in psychoanalytic theory, the ego's protective methods of reducing anxiety by unconsciously distorting reality

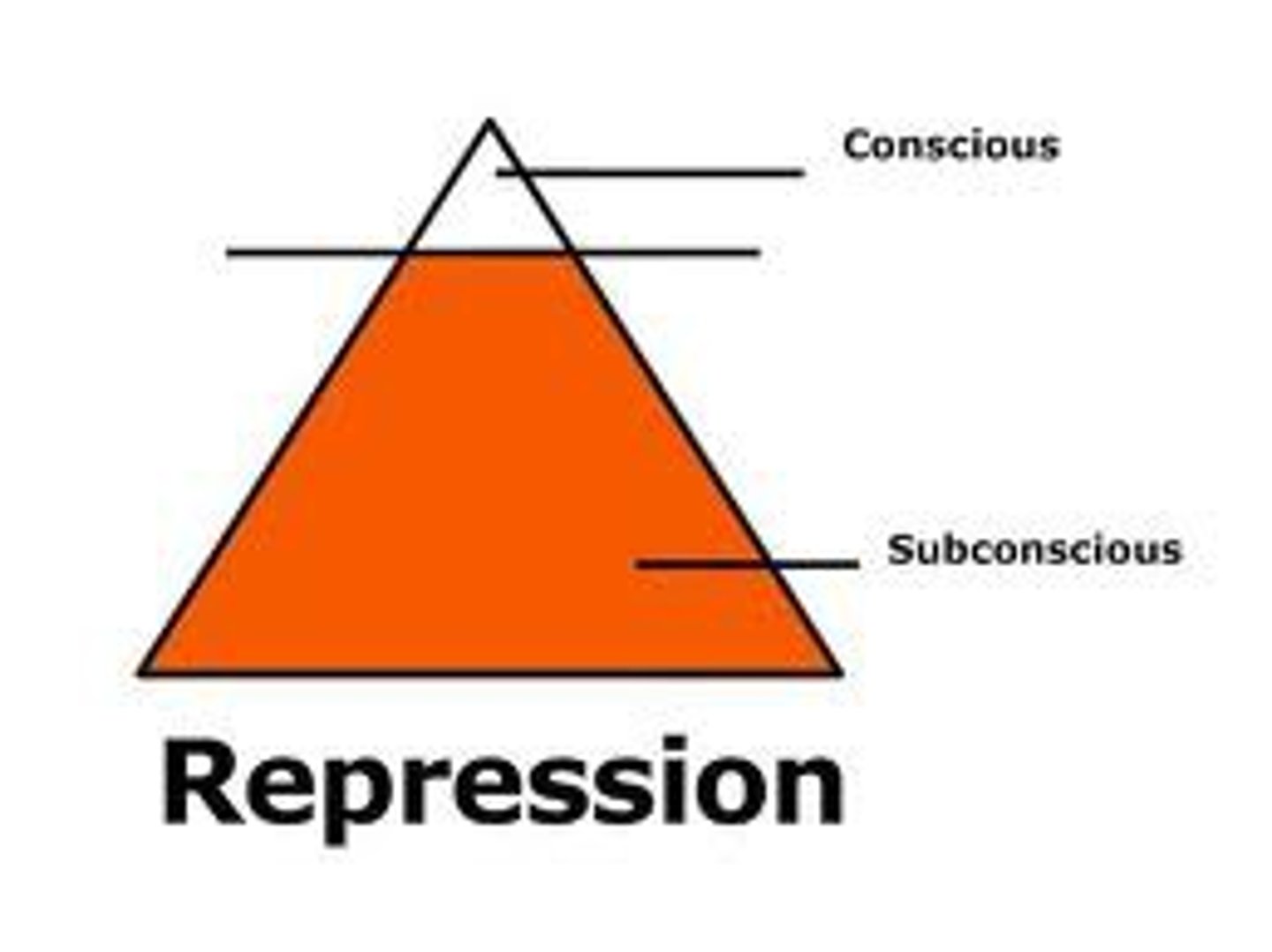
repression
in psychoanalytic theory, the basic defense mechanism that banishes from consciousness anxiety-arousing thoughts, feelings, and memories
collective unconscious
Carl Jung's concept of a shared, inherited reservoir of memory traces from our species' history
terror-management theory
a theory of death-related anxiety; explores people's emotional and behavioral responses to reminders of their impending death

Thematic Apperception Test (TAT)
a projective test in which people express their inner feelings and interests through the stories they make up about ambiguous scenes

projective test
a personality test, such as the Rorschach or TAT, that provides ambiguous stimuli designed to trigger projection of one's inner dynamics
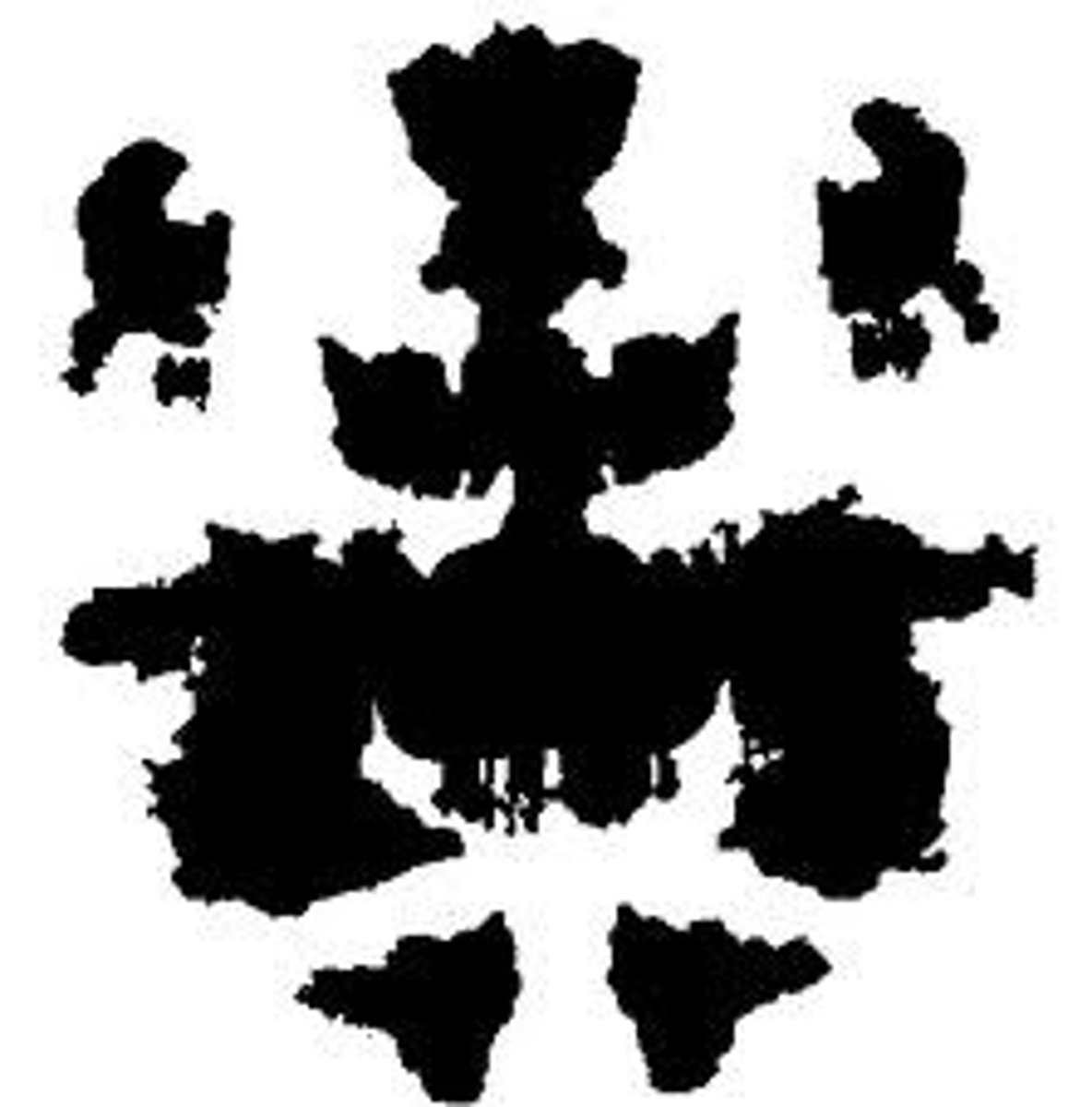

Roschach Inkblot Test
a projective test designed by Hermann Rorschach; seeks to identify people's inner feelings by analyzing how they interpret 10 inkblots

humanistic theories
theories that view personality with a focus on the potential for healthy personal growth
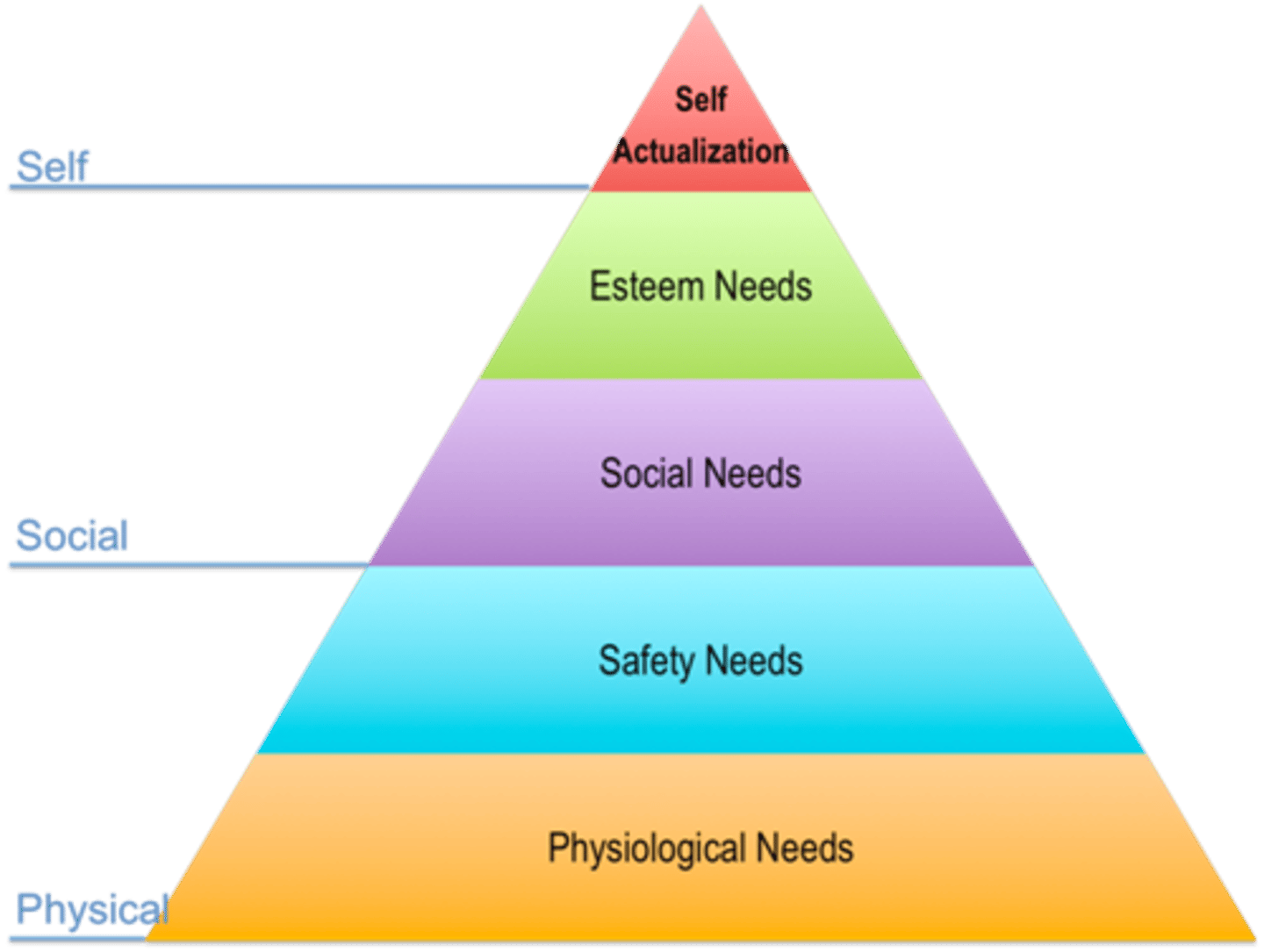
hierarchy of needs
Maslow's pyramid of human needs, beginning at the base with physiological needs that must first be satisfied before higher-level safety needs and then psychological needs become active
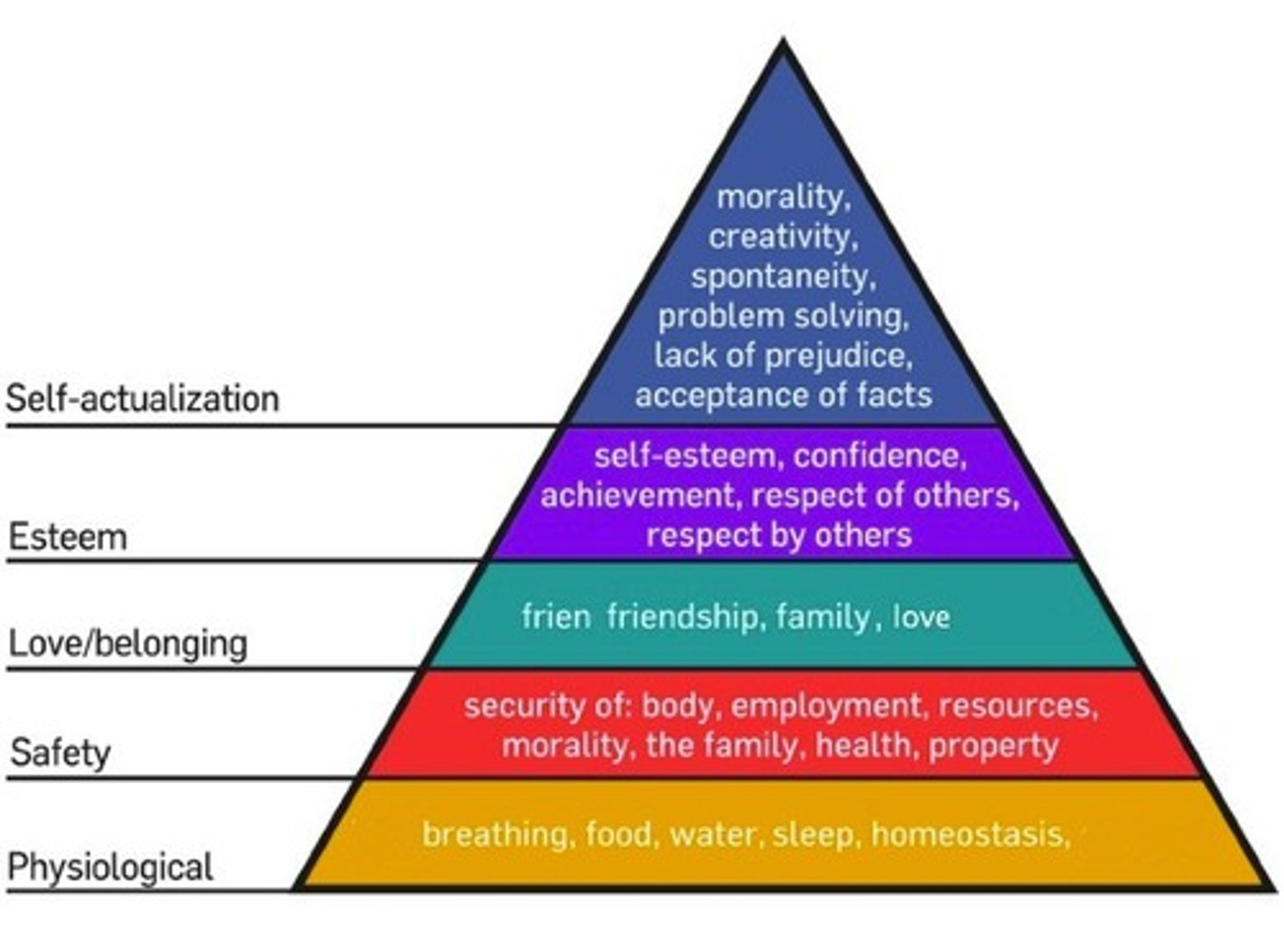
self-actualization
according to Maslow, one of the ultimate psychological needs that arises after basic physical and psychological needs are met and self-esteem is achieved; the motivation to fulfill one's potential
self-transcendence
according to Maslow, the striving for identity, meaning, and purpose beyond the self

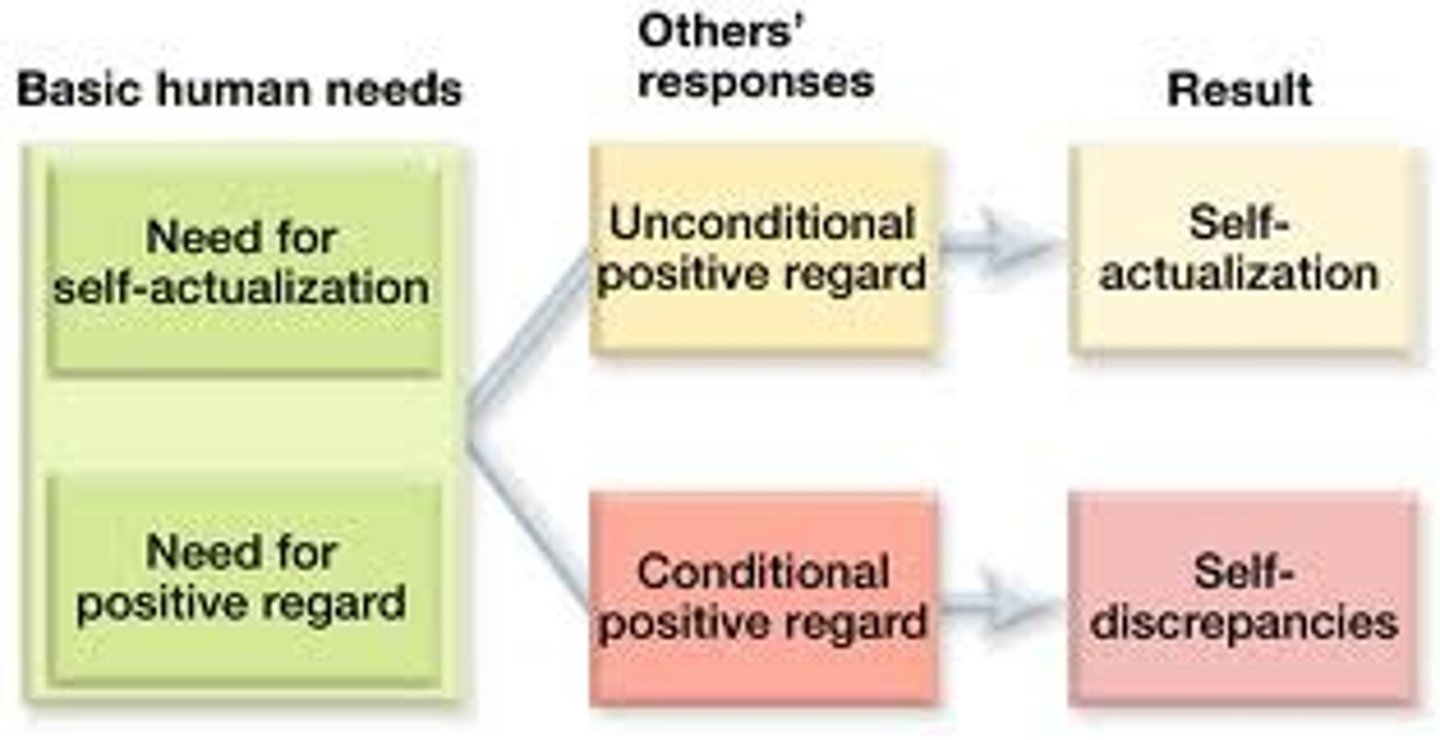
unconditional positive regard
a caring, accepting, nonjudgmental attitude, which Carl Rogers believed would help clients to develop self-awareness and self-acceptance

self-concept
all our thoughts and feelings about ourselves, in answer to the question, "Who am I?"
trait
a characteristic pattern of behavior or a disposition to feel and act, as assessed by self-report inventories and peer reports
trait theories
theories that endeavor to describe the characteristics that make up human personality in an effort to predict future behavior
factor analysis
a statistical procedure that identifies clusters of related items (called factors) on a test; used to identify different dimensions of performance that underlie a person's total score.
personality inventory
a questionnaire (often with true-false or agree-disagree items) on which people respond to items designed to gauge a wide range of feelings and behaviors; used to assess selected personality traits.

Minnesota Multiphasic Personality Inventory (MMPI)
the most widely researched and clinically used of all personality tests. Originally developed to identify emotional disorders (still considered its most appropriate use), this test is now used for many other screening purposes.

empirically derived test
a test (such as the MMPI) developed by testing a pool of items and then selecting those that discriminate between groups
Big Five Factors
CANOE, (conscientiousness, agreeableness, neuroticism, openness, extraversion)
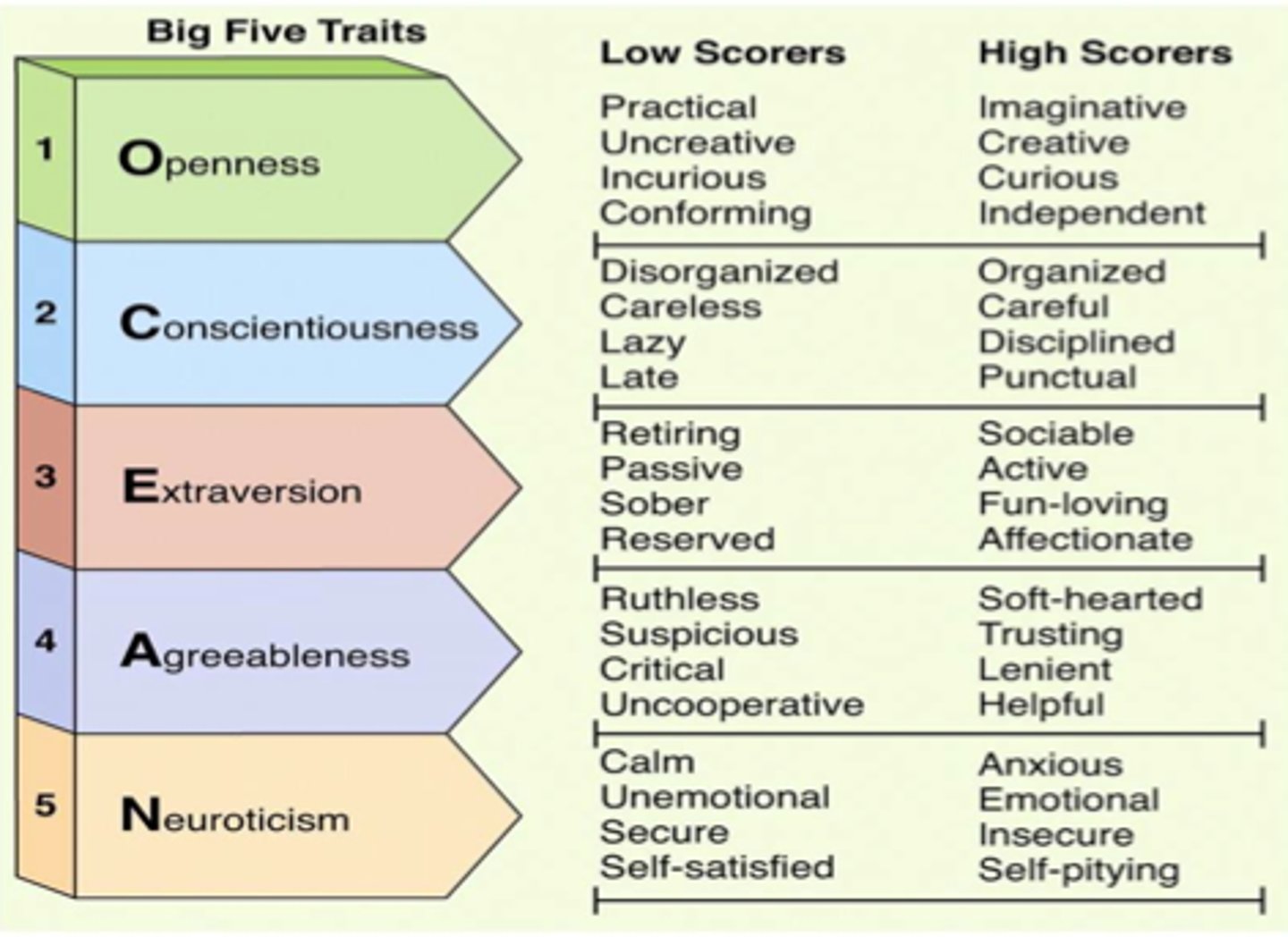
Agreeableness
The tendency to get along well with other people.

Openness to experience
willingness to try new things and be open to new experiences

extraversion
tendency to be outgoing and energetic

conscientiousness
the tendency to be organized, responsible, and deliberate

emotional stability (Neuroticism)
tendency to experience negative emotions

person-situation controversy
the question of whether behavior is caused more by personality or by situational factors
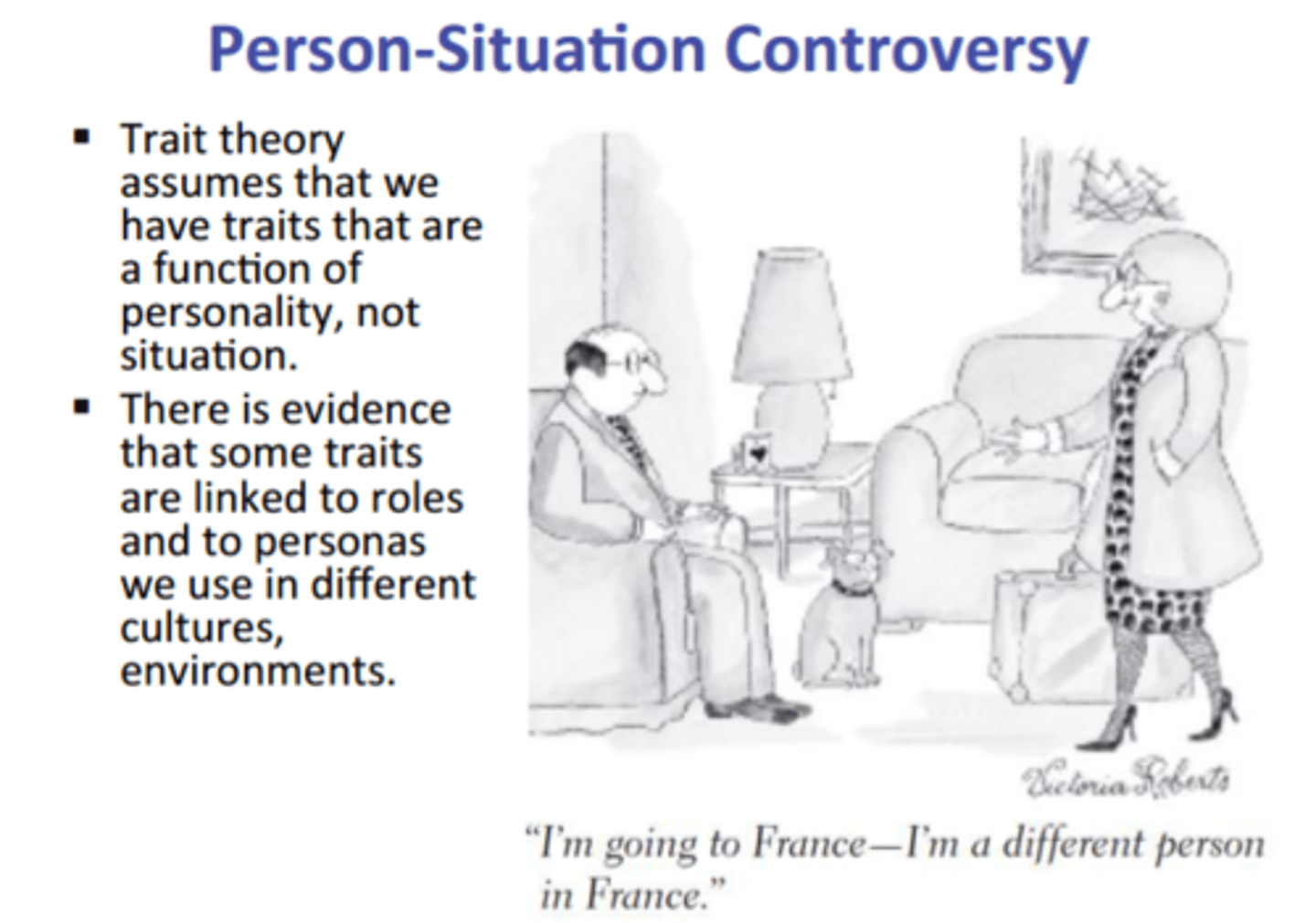
social-cognitive perspective
views behavior as influenced by the interaction between people's traits (including their thinking) and their social context.
behavioral approach
focuses on the effects of learning on our personality development
reciprocal determinism
the interacting influences of behavior, internal cognition, and environment
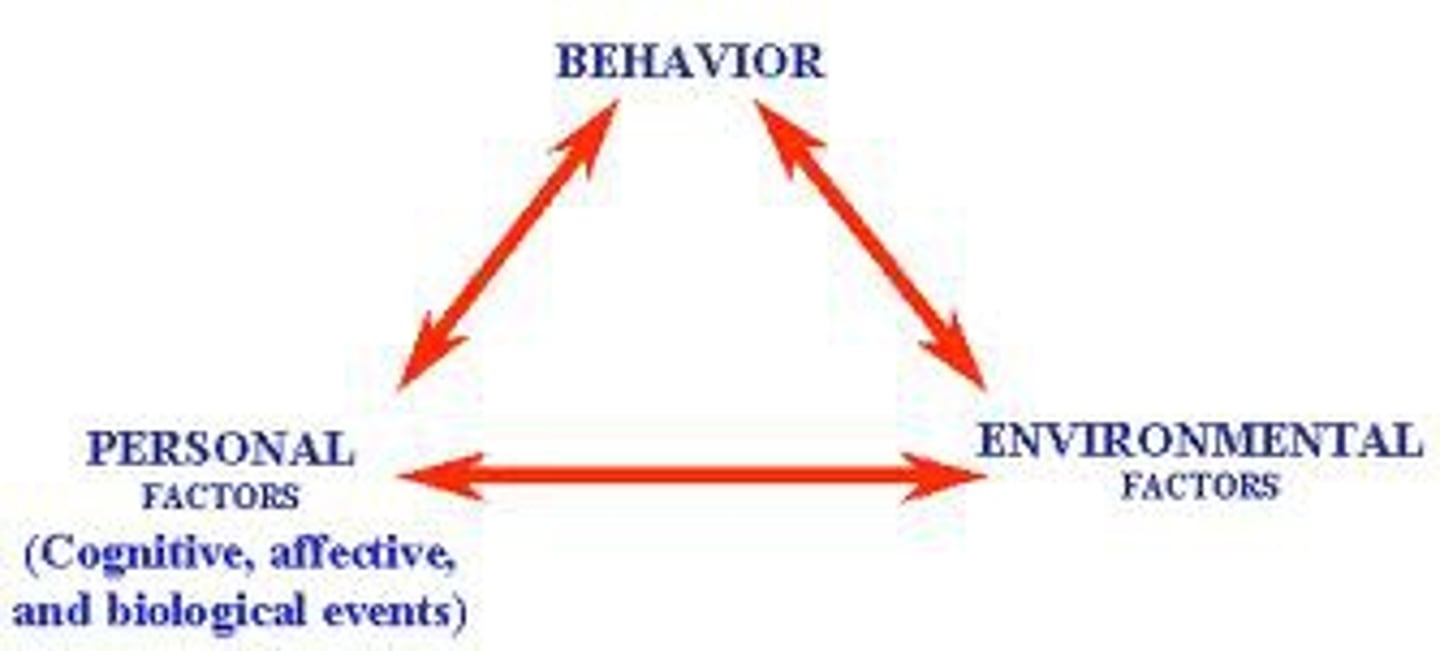
self
in contemporary psychology, assumed to be the center of personality, the organizer of our thoughts, feelings, and actions

spotlight effect
overestimating others' noticing and evaluating our appearance, performance, and blunders (as if we presume a spotlight shines on us)

self-esteem
one's feelings of high or low self-worth

self-efficacy
one's sense of competence and effectiveness

self-serving bias
a readiness to perceive oneself favorably
narcissism
excessive self-love and self-absorption
individualism
a cultural pattern that emphasizes people's own goals over group goals and defines identity mainly in terms of unique personal attributes

collectivism
a cultural pattern that prioritizes the goals of important groups (often one's extended family or work group)

culture
Beliefs, customs, and traditions of a specific group of people.

sublimation
redirecting unacceptable desires through socially acceptable channels

repression
in psychoanalytic theory, the basic defense mechanism that banishes from consciousness anxiety-arousing thoughts, feelings, and memories

regression
psychoanalytic defense mechanism in which an individual faced with anxiety retreats to a more infantile psychosexual stage, where some psychic energy remains fixated
reaction formation
psychoanalytic defense mechanism by which the ego unconsciously switches unacceptable impulses into their opposites. Thus, people may express feelings that are the opposite of their anxiety-arousing unconscious feelings.

denial
refusing to believe or even perceive painful realities

displacement
psychoanalytic defense mechanism that shifts sexual or aggressive impulses toward a more acceptable or less threatening object or person, as when redirecting anger toward a safer outlet

projection
psychoanalytic defense mechanism by which people disguise their own threatening impulses by attributing them to others

rationalization
defense mechanism that offers self-justifying explanations in place of the real, more threatening, unconscious reasons for one's actions

measurement
traits are measured used to organize item responses into traits