neurolab week 3 - brainstem, cerebellum, ventricles
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
https://www.uoguelph.ca/psychology/lab/sheep-brain/coronal-cuts
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
what makes up brainstem?
medulla
pons
midbrain
what are the cranial nerve nuclei and reticular formation
collective of cell bodies in the brainstem
difffuse reticular formation and nucleus raphe
contained in the brain stem
difffuse reticular formation = arousal and awareness
nucleus raphe = serotonergic neruons
cerebellum
little brain, houses 50% of neurons in the CNS, conain granule cells and purkinje cells
overlies the posterior part of the pons and medulla
acts indirectly to control movement and posture by adjusting the output to major descening pathways, improves accuracy of movements, and regulates rate, range, direction, and force of muscular activity in movements and postures
damage to cerebellum = jerky, erratic, uncoordinated movements
true or false the cerebellum is needed for perception and muscle contraction
false, only helps coordinate movement
two excitatory inputs that come into the cerebellum
climbing fibers > originate in inferior olivary nuclues and synapse on purkinje cells
mossy fibers > come from pons, spinal cord and excite granule cells. have parallel fibers that synapse purkinje.
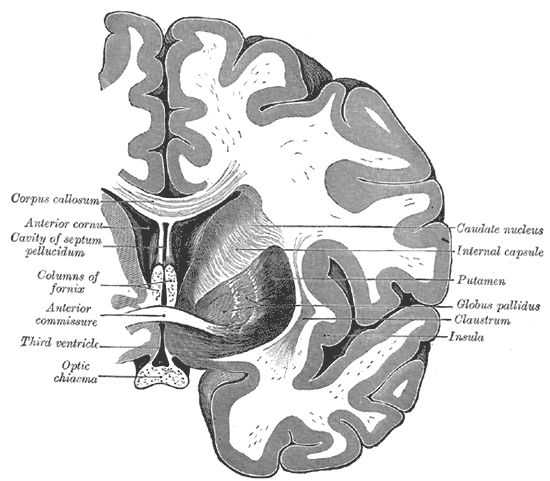
anterior commissure
above to the 3rd ventricle, it connect the thrid ventricle to olfacotory structures and miffle and inferior tempeoral gyrus posterioroly
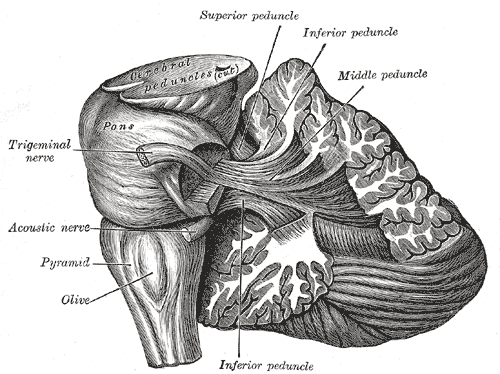
cerebellular penducles: connections of cerebellum to midbrain
which connect cere to midbrain?
cere to pons?
cere to medulla?
cere to midbrain = superior cerebellar peduncle
cere to pons = middle cerbellular peduncle
cere to medulla = inferior cerebellar peduncle
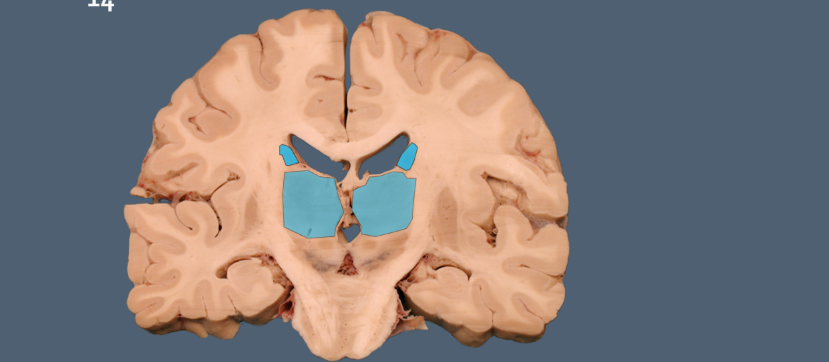
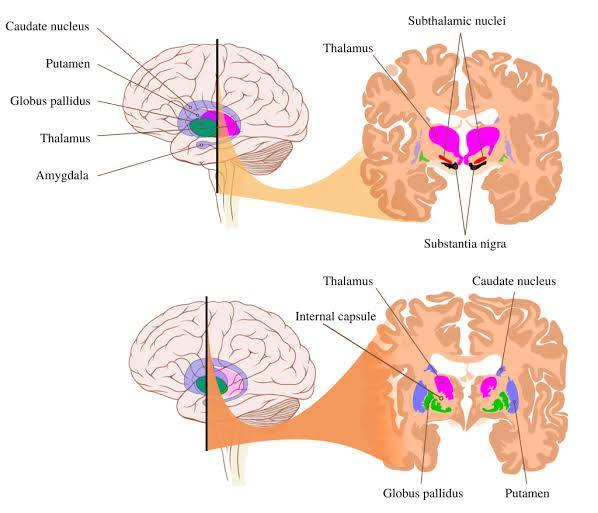
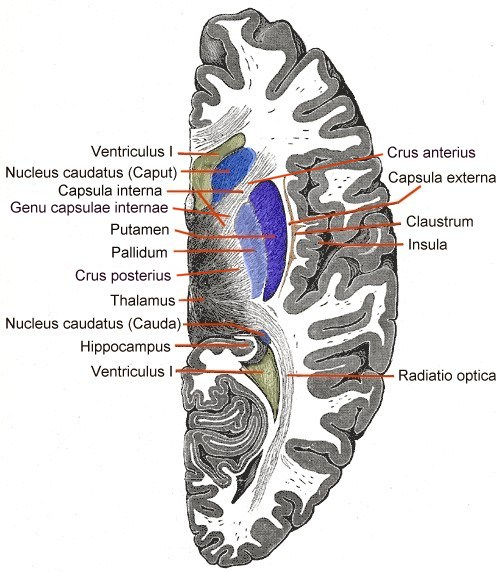
the caudate and the thalamus are sisters. how to tell them apart.
caudate is c shaped.
more posterior cut where pons seen = more thalamus seen
more forward cut = caudate more apparent.
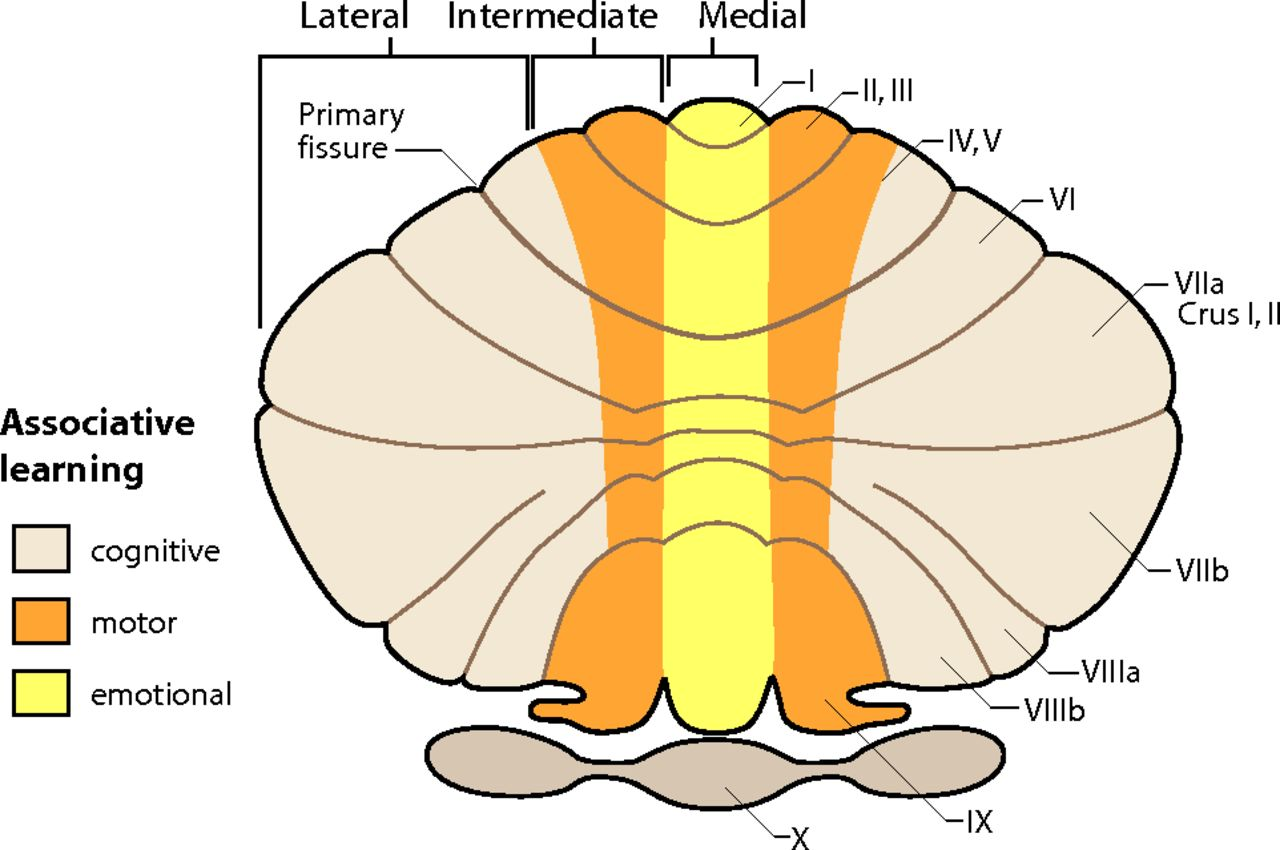
3 functional regions of cerebellum
central vermis (connects cerbellum on two hemipsheres)
intermediate zone
lateral zone
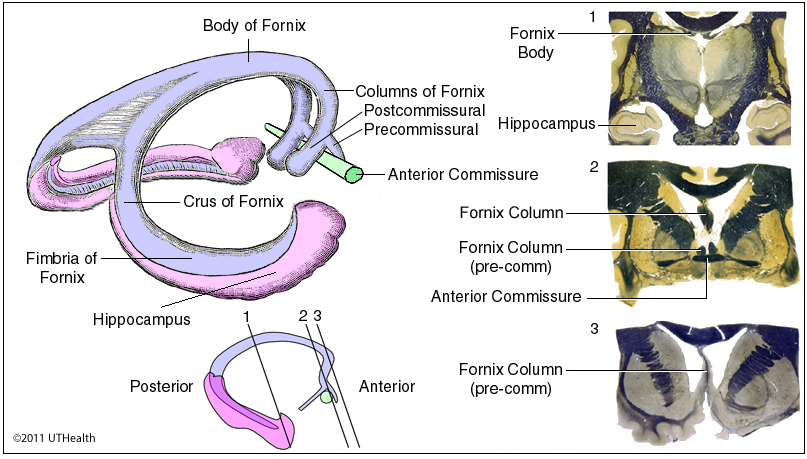
fornix fibers
C-shaped white matter tract in medial part of brain
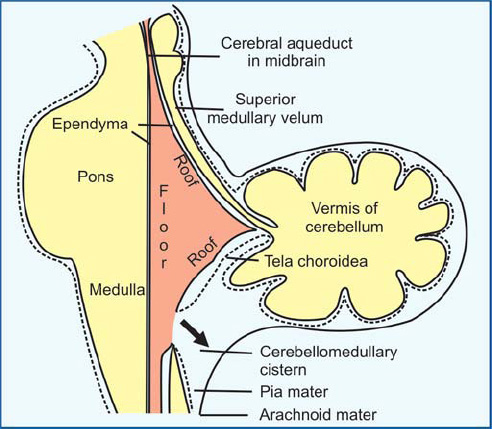
what closes off 4th ventricle
anterior medullary velum
optic radiation vs fornix fiber
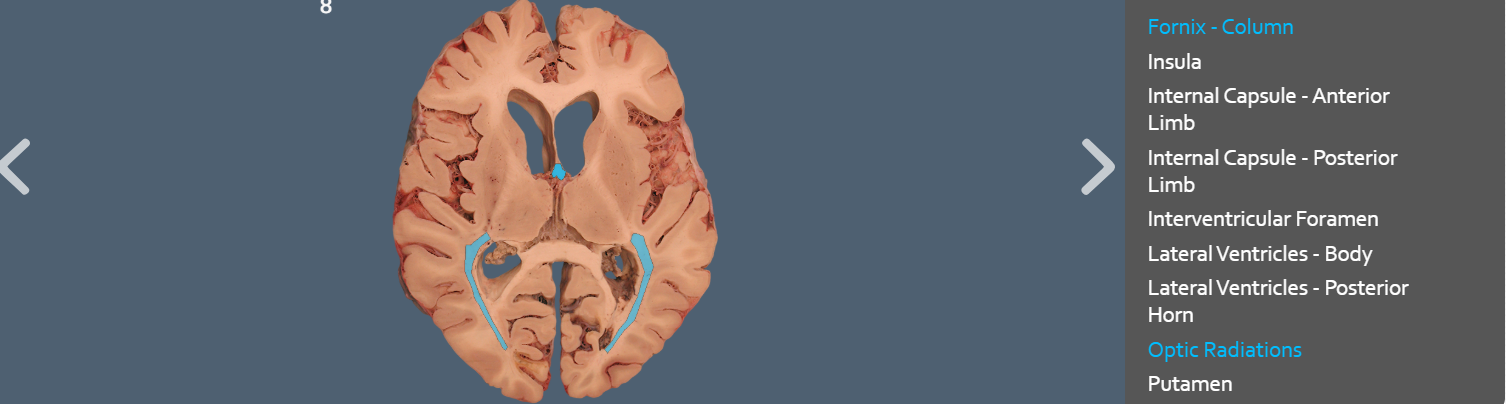
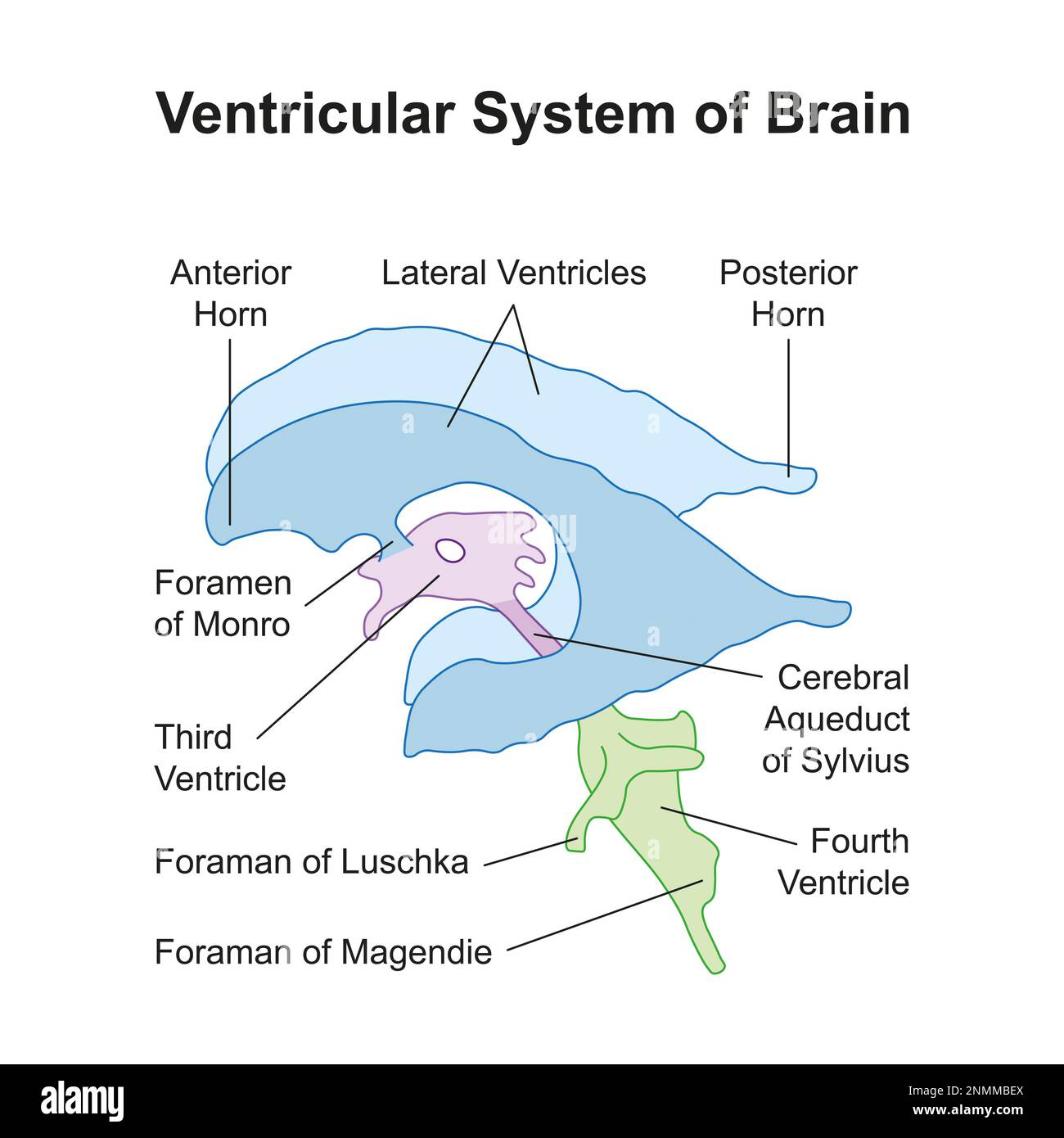
ventricle system
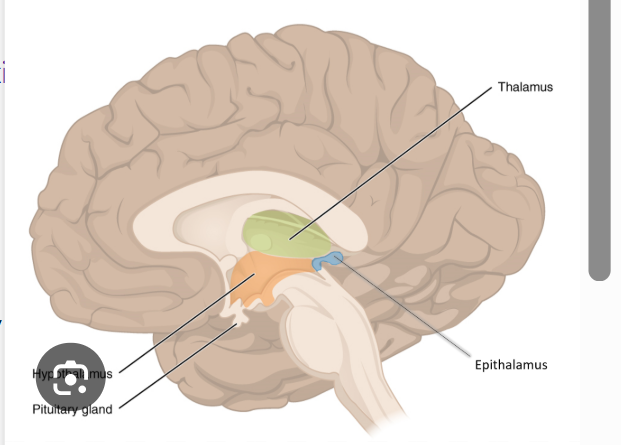
which ventricle is located vertically in between thalamus and hypothalamus?
which ventricle is located beneath the cerebellum and above the pons
thrid ventricle located vertically in between thalamus and hypothalamus
fourth ventricle is located beneath the cerebellum and above the pons
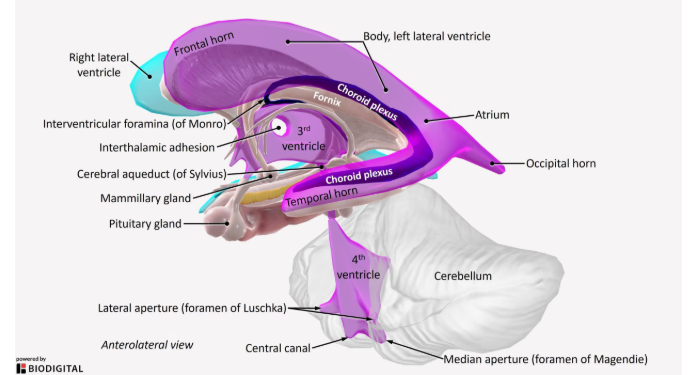
Foramen of magendie
Foramen of Luschka
formane = holes
Lushcka = lateral holes on frouth ventricle
Magendie = central tube of frouth ventricle
internal capsules
project form cortex to connect to parts of brainstem pons/cerebellum
comissural fibers: anterior and posterior commissure fibers
anterior commissure fiber > string located right above third ventricle and right below columns of fornix
posterior commisure fiber > above superior collucli and above poeing of cerebral aqeuduct
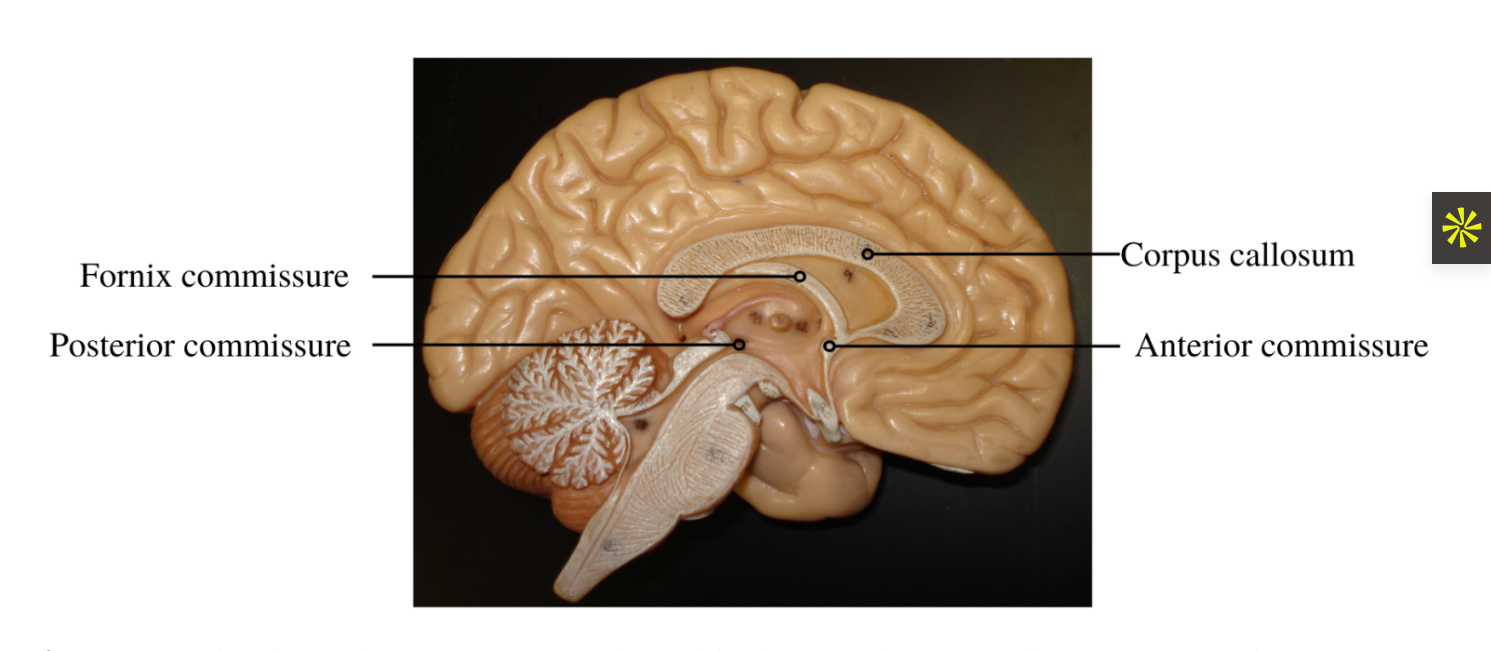
how to tell fornix fibers from septal nuclei
the columns of the fornix are thick, C-shaped bundles of white matter fibers that arch posteriorly, while the septal nuclei are small clusters of gray matter neurons located just superior to the anterior commissure and on the dorsal side of the fornix's precommissural fibers.
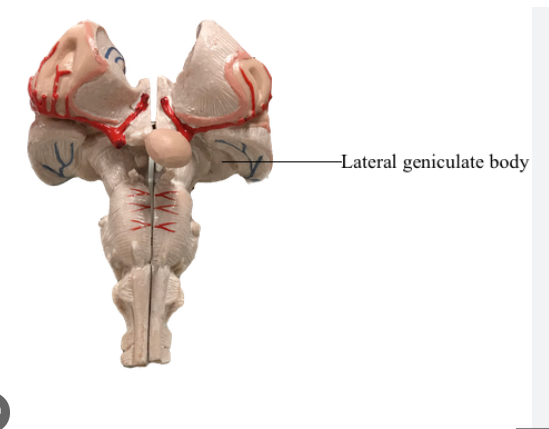
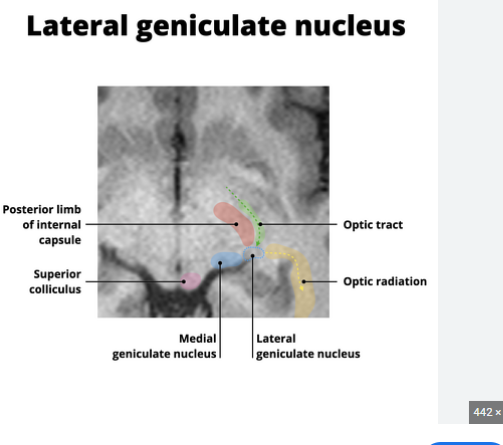
LGN
sits posterior to thalamus
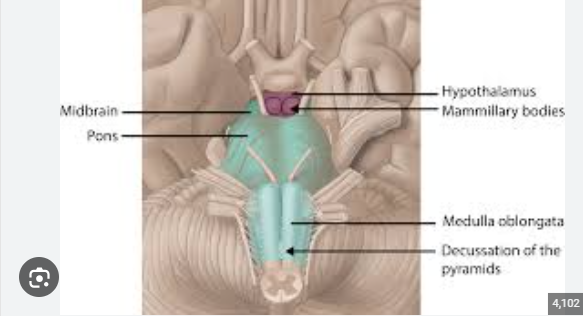
hypothal, pituitary, mamminllary body