chem 107 lab final review
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
5 safety rules
wear googles at all times
hair is tied back
closed shoes
dispose waste properly
no eating/drinking in the lab
(1) lab items, thermometer
thermometer: measures temp
lab items, gradulated cylinder:
measures the volume of liquids
lab items, pipete
drops liquid
lab items, large tongs
holds hot items
lab items, ring stands
holds and locks in glasses used for experiments
lab items, strickers
used to light bunsen burners
lab items, gas hose
connects to bunsen burners
lab items, googles
protects eyes during labs
lab items, wire gauze
holds glass equipments while being heated
lab items,stirring rods
stirs liquids
lab items, test tube holder
holds test tubes
lab items, beakers
used for reactions, transport, and baths
erlenmeyer flasks
used to mix liquids and for a reaction t
test tubes
observe obvious solutions
small tongs
to hold test tubes
test tube brush
cleans out test tubes
filter funnel
gravity filtering
spatural
picking up solids
watch glass
used to look at solids
evaporating dish
used for solids in evaporation labscr
crucible
to heat solids at a high temp
clay triangle
to hold/suppoer a crucible
wire gauze
support glass equipment while being heated
pinch clamp
secures and controls the flow of liquids
lithmus paper
determines if solution is an acid or base
forceps
holds small objects
scale
weights solids accurately
bunsun burner
heat source
ring clamps
holds glass equipment
3 prong clamp
holds test tubes, flasks, etcc
vortex genie
shakes test tubes
burette
dripping volumes of liquids
burette clamp
holds burette
g - moles calculation
__g * 1 mole / molar mass of element
when reading a gradulated cylinder, you read
under the meniscus w
when reading a ruler, you read
make sure you’re measuring with the object starting at 0 and read where the object meet the inches line
ionic compounds
metal+non-metal, compound with the net charge = 0
EX) BaCl2
ionic compounds with transition metal
compound with the net charge = 0 AND with roman numerals
EX) CuCl = copper (I) chloride
molecular compounds
non-metal + non-metal - uses prefixes when naming
EX) CO2 - carbon dioxide
acid compunds
H+ + anion
if anion ends with -ide, add “hydro” before the root of the anion name followed by “-ic acid”
if anion ends with -ate, use the root of the anion name followed by “-ic acid”
if anion ends with -ite, use the root of the anion name followed by “-ic acid”
EX) HCl - hydrochloric acid
bunson burner parts (bottom to up)
needle, gas inlet, vents, barrel
density equation
density = mass / volume
how to calculate % in the hydrate
% H2O = mass H2O / mass of hydrate (OG)
mass H2O = total mass lost - mass of crucible, cover, and sample - mass of crucible, cover, and sample after 1st heating
mass of hydrate (OG) = mass of crucible, cover, and sample - mass of crucible and cover
double displacement
A+ B- + C+ D- → A+ D- + C+ B-
single displacement
A+ BC → AC+B
A= element
BC = compounds
molarity
moles / volume (L)
when adding/subtracting, how many sig figs are in your answer?
fewest decimal places
when dividing/multiplying, how many sig figs are in your answer?
least amount of sig figs
NH4+
ammonium
NO3-
nitrate
PO43-
phosphate
CO32-
carbonate
SO42-
sulfate
OH-
hydroxide
C2H3O2-
acetate
CN-
cyanide
describe how to determine the density of an irregular shaped solid and an unknown liquid
weigh the unknown object with a scale, record the weight
fill a graduated cylinder if a little bit of water, record this volume (Vinitial)
add the object into the graduated cylinder, record this volume (Vfinal)
subtract Vfinal - Vinitial
then plug it into the density equation
density equation
mass / volume
giga (G)
10⁹
mega (M)
10⁶
kilo (k)
1000
hecto (h)
100
deca (da)
10
deci (d)
.1 (10⁻¹)
centi ( c)
.01 (10⁻²)
mili (m)
.001 (10⁻³)
micro (µ)
.000001 (10⁻⁶)
nano (n)
.000000001 (10⁻9)
how to find % in a hydrate
% H2O = mass H2O / mass of hydrate (OG)
mass of H2O =
mass of crucible, cover and sample - the mass of crucible, cover and sample after 1st heating.
mass of hydrate (OG) =
mass of crucible, cover and sample - mass of crucible, cover
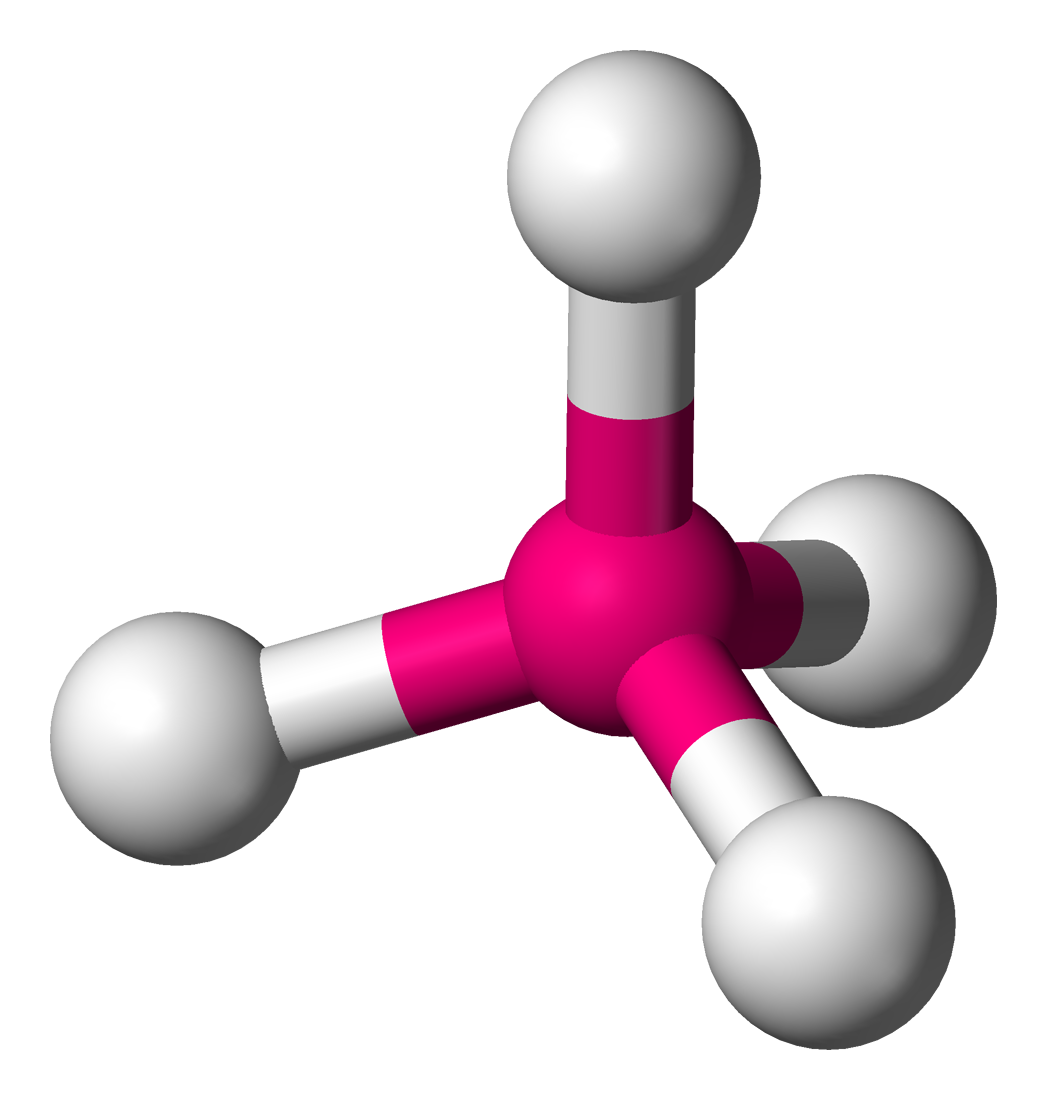
tetrahedral
4 pairs of shared electrons (4 lines)- only single bond, 109.5 degrees
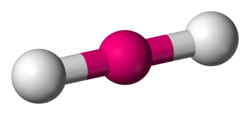
linear
2 pairs of shared electrons - both single bonds, 180 degrees
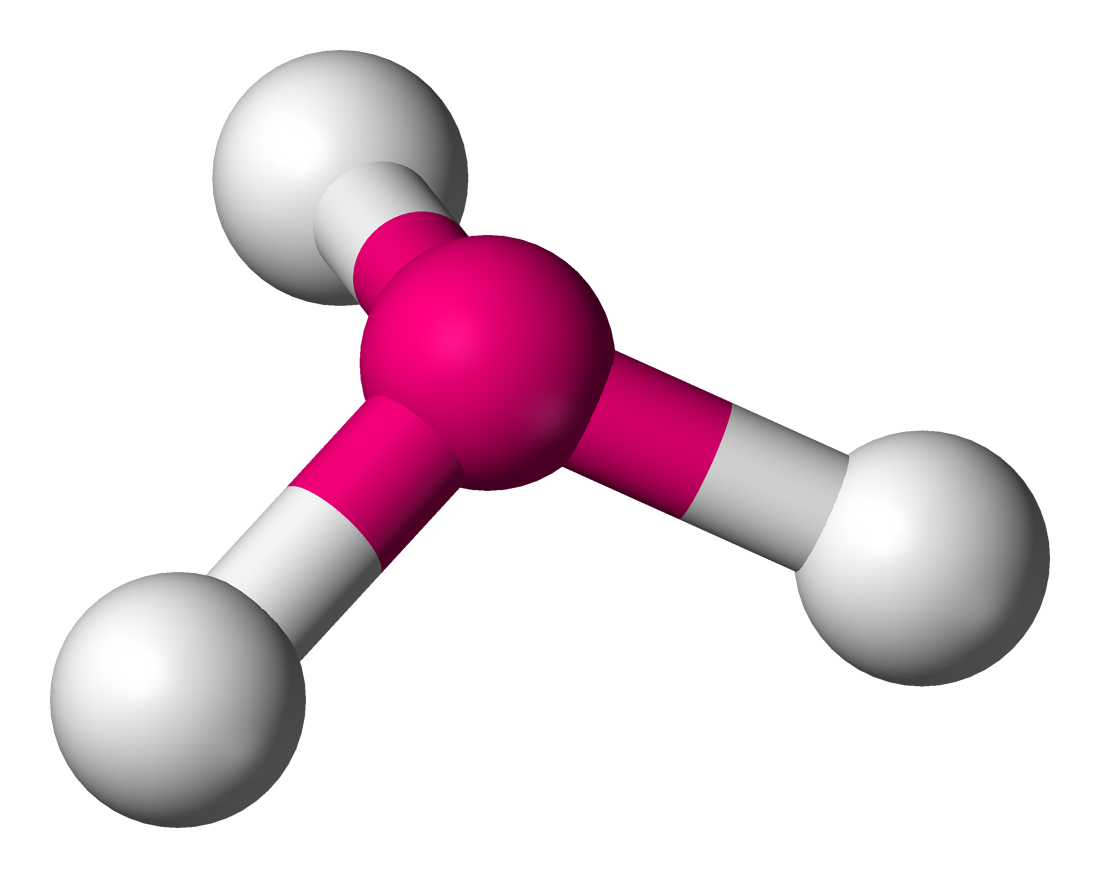
bent
2 pair of shared electrons - can both be single or double bond, 105 degrees
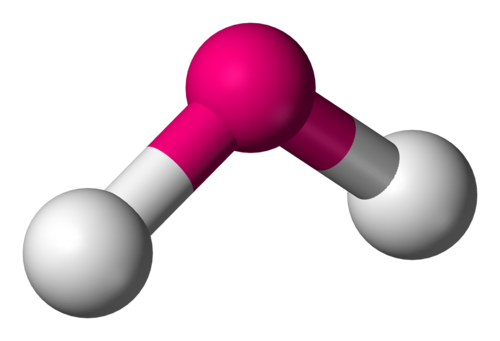
trig planer
3 pairs of shared elections - 2 single and 1 double bond , 120 degrees
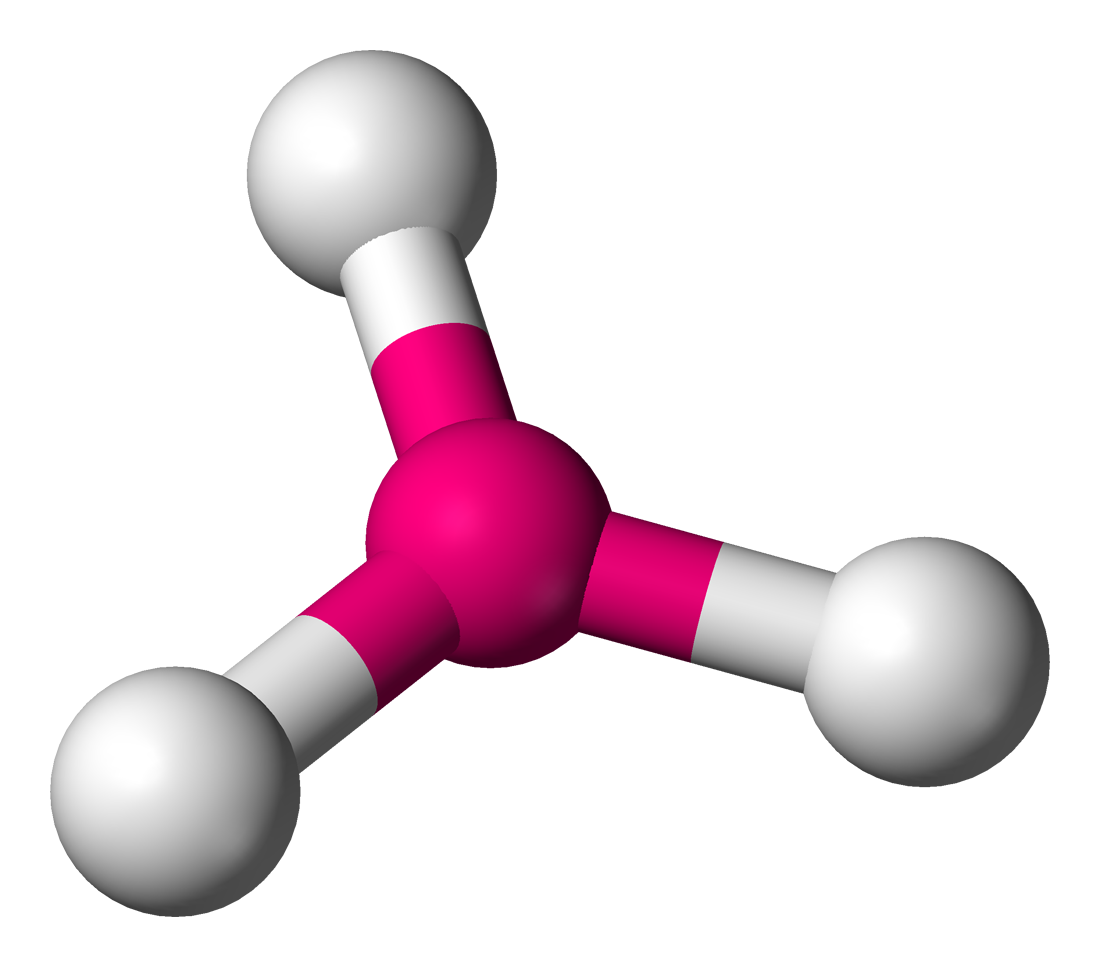
trig pyramidal
three pairs of shared electrons (3 lines), 107 degrees