Stats- test 1
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
What is the goal of statistics
to make inferences about populations using samples
Define statistics
the science of collecting, organizing, summarizing, and analyzing information to draw conclusions or answer questions
What is data
the information gathered used to draw a conclusion
what are recorded characteristics referred to as
variables
What are the two encompassing variables
qualitative and quantitative
What are the types of quantitative variables
discrete
continuous
What is a discrete variable
a countable variable, a whole number
What is a continuous variable
an uncountable variable, a decimal
What is an explanatory variable
the independent variable, the variable that is purposefully changed
What is a response variable
the dependent variable, the variable that changes in response to the purposefully manipulated variable
Describe and observational study
a study that does not attempt to manipulate anything but rather observes the relationship between the response and explanatory variable
What kind of relationship can you claim with an observational study
association or correlation
Describe a designed experiment
A designed experiment is where a a researcher purposefully manipulated the explanatory variable and controls the rest of the other variables in order to determine the relationship between the response and explanatory variable
What relationship can you claim with a designed experiment
causal
What is the group of people being studied called
population
What is the smaller group being used to study the population referred to
sample
What should the sample size always be in relation to the population
it should always be smaller
What are all statistical methods based on the notion of what
randomness
What is the gold standard of sampling
simple random sample
What is simple random sampling
A sample of size n from o population of size N is obtained through simple random sampling if every possible sample of size n has an equally likely chance of occurring
What is stratified sampling
separate the population into the non-overlapping groups called strata (the individuals in each group should be as similar as possible). Then choose a random individual from each stratum for your population
What is cluster sampling
make random clusters and pick a cluster, and that is your sample
What is systematic sampling
selecting every kth individual from the population. The first individual selected is a number between 1-k (like every 5th person is chosen)
What is convenience sampling
getting a sample based on convenience to the researcher, only gets to claim association
What is a lurking variable
a variable that was unaccounted for that could influence the results of a study
What is a confounding variable
a variable that cannot be separated from the explanatory variable and therefore cannot determine a true causal relationship.
When is a variable at the nominal level of measurement
if the variable’s values allow for categorizing, labeling, or naming but not ranking in a specific oreer
When is a variable at the ordinal level of measurement
when the variable’s values allow for both naming/categorizing/labeling (like the nominal level) and ranking in a specific order
When is a variable at the interval level of measurement
When the variable’s values allow for labeling/labeling/categorizing and ranking in a specific order (ordinal) and the differences in the values hold meaning. Addition and subtraction can be performed on this variable
When is a variable at the ratio level of measurement
When a variable’s values allow for naming/labeling/categorizing, being ranked in a specific order, the differences in values of the categories having meaning, substraction and addition can be done to the values (interval), and the ratios of the values have meaning, multiplication and division can be done one these values
Describe a cross sectional study
an observational study that collects information a specific point in time/ short period of time
Describe a case control study
a retrospective study where the researcher looks back in time by asking individuals to recall specifics or looking at pre-existing records
Describe a cohort study
First the study identifies a group of individuals to participate in the study and those individuals are observed over a long period of time and their characteristics recorded- making these studies prospective

What does this variable represent?
population arithmetic mean
What is a parameter in statistics
something that describes the entire population
What is a statistic in statistics
describes a sample set of data
Is u a parameter or a statistic
parameter
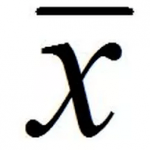
What does this symbol represent
the arithmetic mean of the sample
What does N represent?
the size of the population
What does n represent
the size of the sample
What does M represent
the median
When is a numerical summery of data resistant?
extreme observations (outliers) do not heavily affect the numerical summery
if the mean is smaller than the median then the graph is
skewed left
if the mean is larger than the median then the graph is
skewed right
if the mean and median are roughly equal
graph is symmetric
what is dispersion
the degree to which the data are spread out
what does R represent
range
what does sigma represent
standard deviation of the mean
what is the variance of a variable
s2
what is the population variance
sigma2
What is the empirical rule
approx 68% of data will lie within 1 standard deviation of the mean (mew-1 sigma)
apporx 95% of the data will lie within 2 standard deviation of the mean (mew-2 sigma)
approx 99.7% of the data will lie within 3 standard deviation of the mean (mew- 3 sigma)
How do you find IQR
3 Q - 1 Q
What does IQ R tell us
spread of middle 50%
large IQR- middle values are more dispersed
small IQR- middle values closer together
What is s
sample standard deviation
how does sample standard deviation differ from population standard deviation
sample is divided by n-1 and population is divided by N
what does variance of a variable show
how spread out dad points are from the mean