LO5 - cells
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
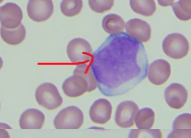
What is this?
blast
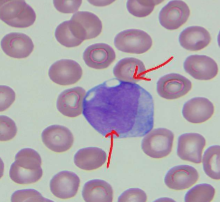
What is this?
blast
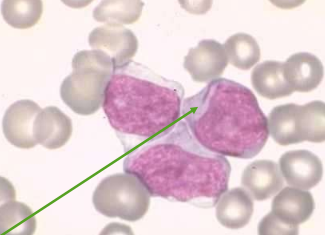
What is this?
myeloblast
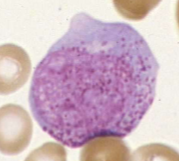
What is this?
promyelocyte
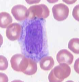
What is this?
myelocyte
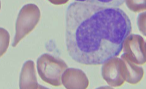
What is this?
metamyelocyte
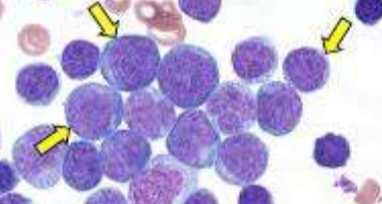
What is this?
lymphoblast
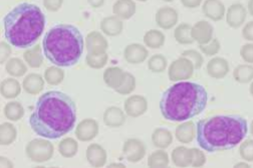
What is this?
prolymphocytes
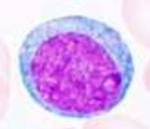
What is this?
monoblast
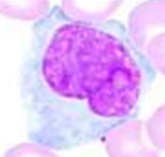
What is this?
promonocyte
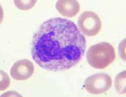
What is this?
toxic granulation
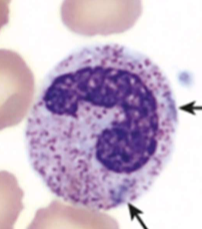
What is this?
dohle bodies
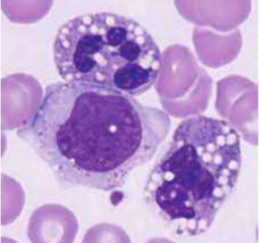
What is this?
toxic vaculation
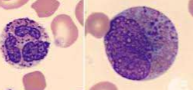
What is this?
harlequin cells
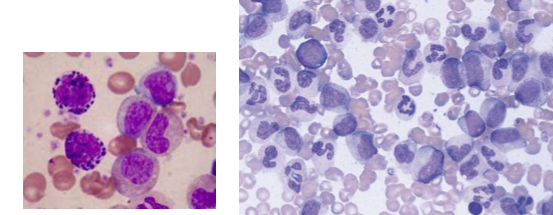
What is this?
abnormal granulocytes
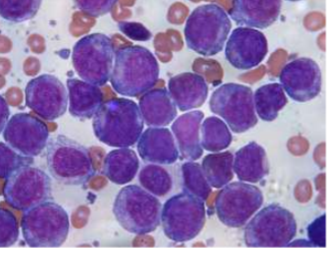
What is this?
acute myeloid leukemia
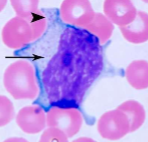
What is this?
reactive lymphocyte
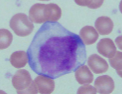
What is this?
reactive lymphocyte
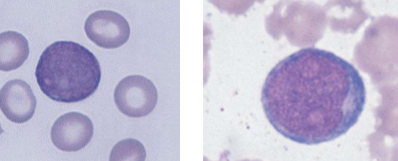
What is this?
acute lymphoblastic leukemia
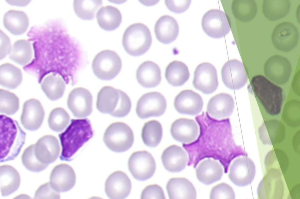
What is this?
smudge cells
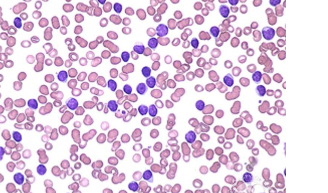
What is this?
smudge cells
What is an immature cell?
normal in bone marrow - not normal in peripheral blood - can indicate a serious condition
What is a leukamoid reaction
benign condition that mimics leukemia (malignancy) - caused by virus or bacterial infection - cells may be immature but can indicate normal reactive response
What is leukemia
cancer (malignancy) of the blood - cells may be immature or abnormal
What is a blood cell formation
CFR stem cell - immature undifferentiated hematopoietic cells derived from the pluripotential stem cell - gives rise to cells of bone marrow
What does CFU stand for? What does the GEMM acronym represent
Colony forming unit - Granulocyte, erythrocyte, monocyte, megakaryocyte
As cells mature, what is the change in size
they get smaller as they age
As cells mature, what is the change in nucleus
becomes smaller - cytoplasm is more abundant - lover N/C ratio
As cells mature, what is the change in cytoplasm
becomes less basophilic - more blue
As cells mature, what is the change in granules
Myeloid Series: appearance if granules as cell matures - None to primary to secondary
As cells mature, what is the change in chromatin
increasingly condensed
As cells mature, what is the change in nuclear chromatin pattern
goes from smooth (euchromatin) to course clumps (parachromatin) - nucleus stains darker as cells mature (light reddish purple to darker bluish purple)
What is the nucleoli of a cell
small round or irregular shaped - light blue area surrounded by a fine darker rim
What are blasts? Is there nucleoli? What is the chromatin like?
large immature looking cells - prominent nucleoli - fine lacy chromatin (no clumps)
What is the progression of granulocytic maturation
myeloblast to promyelocyte to myelocyte to metamyelocyte to band neutrophil to segmented neutrophil
Myeloblast - Nucleus? Chromatin? Nucleoli? Cytoplasm? Granules?
Large nucleus - nuclear chromatin is fine, lacy - 2-5 nucleoli - small amount of blue cytoplasm, no granules - abnormal bundles of primary granules
What is the unique thing that may distinguish a myeloblast? What does it diagnose?
Auer rods - diagnostic of non-lymphocytic leukemia
Promyelocyte - Size? Nucleus? Chromatin? Nucleoli? Cytoplasm? Granules?
slightly larger that a blast, largest in myeloid series - round to oval nucleus - smooth nuclear chromatin - 1-3 nucleoli - slightly more blue cytoplasm - stains moderately blue cytoplasm (azurophilic) - primary/non specific granules contain enzymes
Myelocyte - Nucleus? Chromatin? Nucleoli? Cytoplasm? Granules?
oval or slightly indented nucleus - slightly clumped chromatin - not visible nucleoli - moderate amount of blue-bluish pink cytoplasm - secondary granules formed (eosinophilic, basophilic, neutrophilic)
Metamyelocyte - Nucleus? Chromatin? Nucleoli? Cytoplasm? Granules?
nucleus is indented (bean shaped) - clumped chromatin - cytoplasm is pale blue to pink - specific abundant secondary granules that characterize cell (eosinophil, neutrophil, basophil)
Band Neutrophil - Nucleus? Chromatin? Nucleoli? Cytoplasm? Granules?
S-shaped/curved nucleus - very clumped chromatin - specific secondary granules
Segmented neutrophil - Nucleus? Chromatin? Nucleoli? Cytoplasm? Granules?
2-5 distinct lobes - dense chromatin compact - abundant lilac cytoplasm - fine, specific neutrophilic secondary granules - phagocytic
Eosinophil
2-3 lobe nucleus - large specific eosinophilic (reddish-orange) secondary granules - antihistamine (allergic response)
Basophil
bi-lobed - obscured granules - specific large dark basophilic (blue-black) secondary granules - water soluble - heparin, histamine, kallikrein
What does myeloblast and promyelocyte associate with
leukemia or malignancy
what does myelocyte and metamyelocyte associate with
leukamoid reaction: infection, trauma, or stressW
What does the presence of immature granulocytes indicate
left shift
Lymphoblast - Nucleus? Chromatin? Nucleoli? Cytoplasm? Granules?
large nucleus, round to oval - nuclear chromatin is fine, lacy - 1 or more nucleolo - small amount of blue cytoplasm - no granules
Prolymphocyte - Nucleus? Chromatin? Nucleoli? Cytoplasm? Granules?
large nucleus, round to oval - nuclear chromatin, slight clumping - nucleoli less prominent - small amount of blue cytoplasm - no granules
What is the monocyte maturation
monoblast to promonocyte to monocyte
Monoblast - Nucleus? Chromatin? Nucleoli? Cytoplasm? Granules?
round to oval cell shape - round more regular nucleus - 1 or 2 distinct nucleoli - grey to cloudy blue, few red granules
Promonocyte - Nucleus? Chromatin? Nucleoli? Cytoplasm? Granules?
indented or lobulated, more irregular nucleus - 1 or 2 less distinct nucleoli - grey to cloudy blue, few red granules cytoplasm
Monocyte - Nucleus? Chromatin? Nucleoli? Cytoplasm? Granules?
indented, oftern reniform or folded, maybe ne round, oval, lobulated nucleus - no nucleoli - abundant grey or grey blue cytoplasm - may contain fine azurophilic granules