RCC, Wilms, Dehydration, Hypervolemia
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
Renal Cell Carcinoma (RCC)
An adenocarcinoma that arises from the epithelial cells of the proximal tubulars that is more common in males in their 60s
Clear cell
Which subtype of RCC is most common and aggressive - characterized by clear cytoplasm
Papillary
Which subtype of RCC is the 2nd most common and characterized by finger like projections with a central core?
Chromophobe
Which subtype of RCC is characterized by a large, polygonal cells with halo nucleus - less common and has a better prognosis
Oncocytomas
Which subtype of RCC is usually benign and is characterized by uniform, round, and packed with bright pink granular cytoplasm
Medullary/collecting duct
Which subtype of RCC originates deeper inside the kidneys and is VERY aggressive
smoking, obesity, HTN, cystic disease, complex cyst, nephrolithiasis, analgesics (NSAIDs), environmental/occupational exposures, dialysis, von Hippel-Lindau syndrome
Risk factors for RCC (EtOH is renal protective)
Hematuria, flank pain, abdominal mass
Classic triad of RCC - seen with advanced disease
fever, night sweats, weight loss, anorexia, fatigue, HTN
Constitutional symptoms of RCC
Lower extremity edema, ascites, hepatic dysfunction, pulmonary edema
Symptoms of RCC that occur as a result of a blockage of the Inferior Vena Cava
Stauffer Syndrome
A paraneoplastic elevation of LFTs without mets
Renal pelvis urothelial cancer, hamartomas, angiomyolipomas, renal oncocytomas, renal abscess, adrenal tumors
DDX for RCC
RVT, IVC blockage, mets to adrenal glands, brain, bone, lymph nodes, lungs, liver
Complications of RCC
UA w/ culture and microscopy, CBC, CMP (renal function, LFTs, hypercalcemia), ALP (mets liver and bone)
Lab work up for RCC
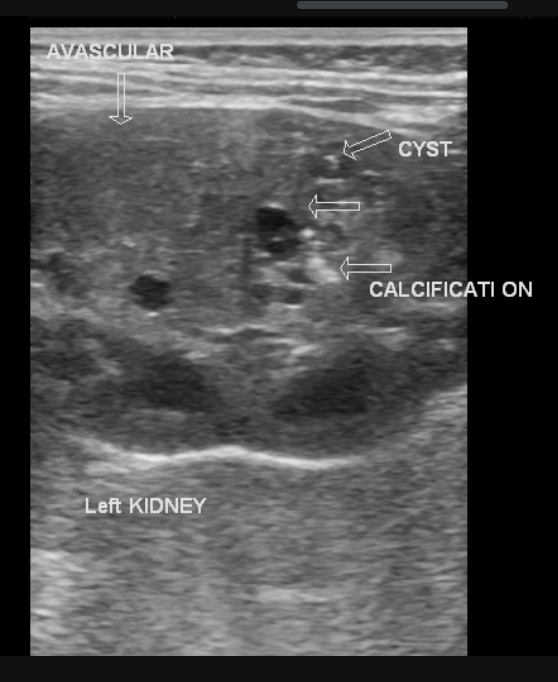
ABD U/S 🥇 (determine simple vs. complex), CT/MRI (TMN staging, mets location), CXR/Bone scan (mets), Color doppler (RVT or IVC compromise), CTA/MRA (map vascular spread pre-op)
Imaging work up for RCC
stage 1
Mass is under 7cm and is limited to the kidney
stage 2
Mass is over 7cm and is limited to the kidney
Stage 3
Mass is starting to spread out of the kidney but has not hit any other organs yet
Stage 4
Mass has spread to other organs
Active surveillance
Which treatment is good for small, localized RCC tumors, advanced disease, or poor surgical patients
Partial nephrectomy
Which localized RCC treatment is good for homies with 1 kidney, small tumors (3-4 cm), and bilateral RCC
Radical nephrectomy
Which localized RCC treatment is good for larger cancers or when partial is not feasible
Radiofrequency or cyrosurgery ablation
Alternatives to surgery with RCC
Molecularly targeted therapy (VEGF/mTOR inhibitors), immunotherapy (Nivolumab, pembrolizumab, ipilimumab), Combo, Cytoreductive nephrectomy
Which treatments are prefered for metastatic RCC - NO CHEMO
90%+ (stage 1 or 2), 50-60% (stage 3), 0-15% (lymph node involvement), 15-30% (metastatic but just 1 spot)
Prognosis of RCC
Any renal suspicious mass (urology), RCC confirmed (urologic surge), metastatic (urology/oncology)
Referrals for RCC

Wilms tumor (nephroblastoma)
The most common renal cancer, the most common ped abdominal cancer, and the 4th most common ped cancer in general
Abnormal growth of metanephric blastema - associated with chromo abnormalities (deletions in WT1 or 2)
Patho for Wilms
Hemihypertrophy/hemi-hyperplasia
Asymmetric overgrowth of half the body associated with Wilms tumor
Beckwith-Wiedermann Syndrome
Microcephaly, macroglossia, and umbilical hernia associated with wilms tumor
Wilms Tumor, Aniridia, GU abnormalities, intellectual disability
WAGR syndrome is characterized by
Wilms tumor, ambiguous genitalia, diffuse glomerular disease
Denys-Drash syndrome is associated with
UA, CBC, CMP, Renal U/S, CT chest/abdomen/pelvis, renal biopsy
5 y/o male presents to the clinic for a well child check. Parents state that they’ve recently notice a lump in his stomach when they hug him. Vitals are stable with the exception of 100.4 temp and 144/88. On physical exam you note a non-tender firm, fixed mass in the abdomen, pallor, and a varicocele. What do you want to order?
uniform and organized cells, undifferentiated cells, immature spindle cells, heterologous skeletal muscle, osteoid, fat, glomeruli
5 y/o male presents to the clinic for a well child check. Parents state that they’ve recently notice a lump in his stomach when they hug him. Vitals are stable with the exception of 100.4 temp and 144/88. On physical exam you note a non-tender firm, fixed mass in the abdomen, pallor, and a varicocele. Labs reveal hematuria, polycythemia. U/S reveals an intrarenal mass that is BOTH cystic and solid. What would be a favorable biopsy result?
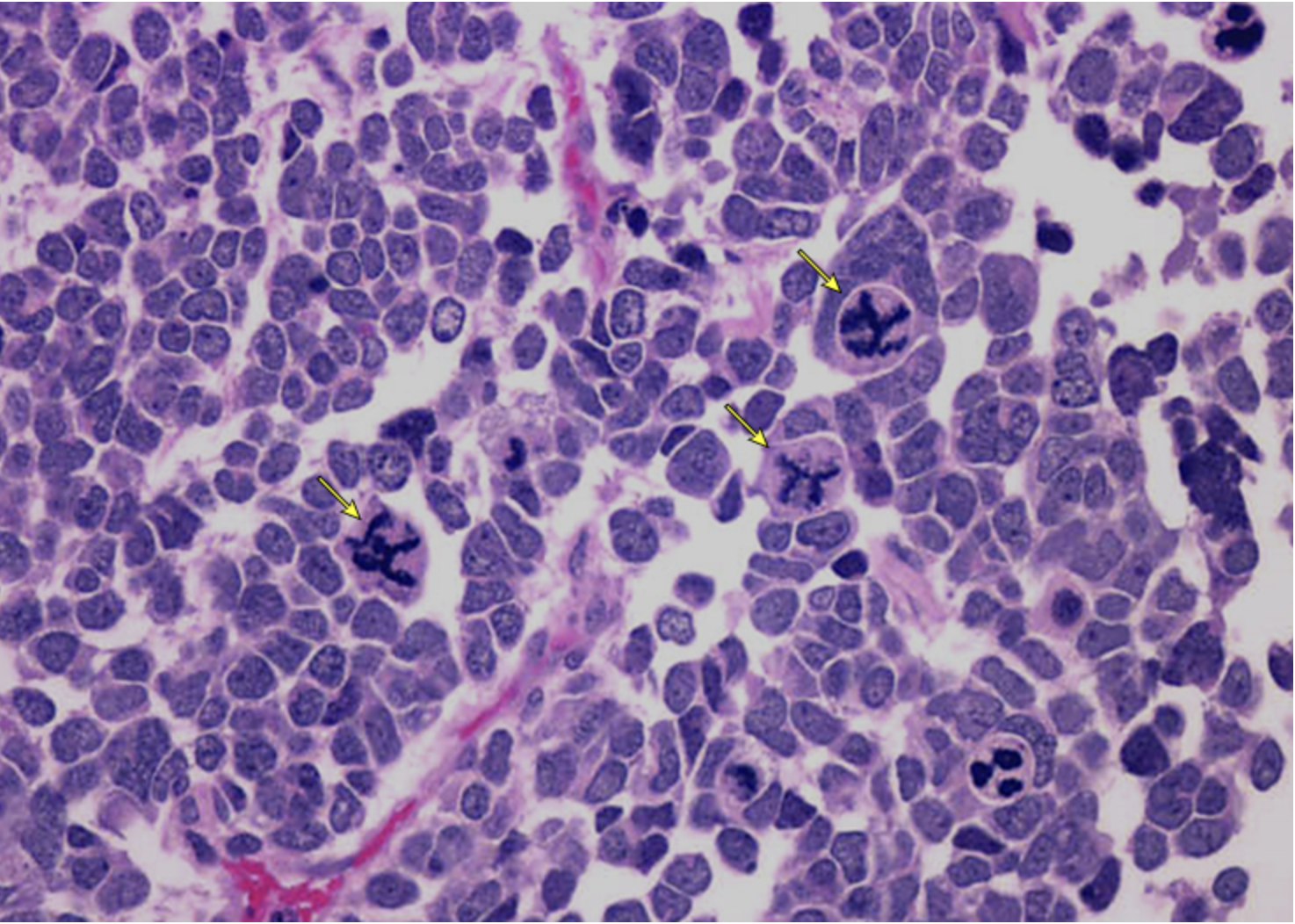
Cells are disorganized aka focal/diffuse anaplasia
What would a unfavorable biopsy of Wilms tumor look like?
surgery first then chemo
North America Approach for Wilms tumor

chemo → surgery → chemo and radiation
European approach for Wilms tumor
chemo → radical nephrectomy for the bad one, partial for the good one
Gameplan for bilateral Wilm tumor
lower stage 90%, unfavorable histology 60%
Prognosis for Wilms
cardiomyopathy, scoliosis, HTN, renal/bladder insufficiency, pulmonary and hepatic dysfunction, infertility, second malignancies
25% of survivors of Wilms tumor will get
hypovolemia
The loss of both water and salt
Dehydration
the state of net body water deficit
urination, defecation, bleeding, wound drainage, gastric draining, vomiting
What are some examples of sensible water loss?
sweat, respiration, changes in humidity, fever
What are some examples of insensible water loss?
GI loss (vomit, diarrhea, NGT, external drains), Renal (diuretics, osmotic diuresis, central/nephrogenic DI), Skin (excessive sweating, burns, severe skin disease), third-spacing (sepsis, trauma, pancreatitis, ascites)
Etiology for loss of Total body water
N/V, dysphagia, lack of access, AMS, fear of incontinence, pain, depression, eating disorders, post-op
Etiology for decreased fluid intake
thirst, dry mouth/lips, fatigue, lethargy, oliguria
Mild signs and symptoms of dehydration
increased thirst, HA, lightheaded, postural dizziness, fatigue, muscle cramps, oliguria with dark urine
Moderate signs and symptoms of dehydration
profound weakness, AMS, disorientation, confusion, chest/abd pain, tachypnea, seizures, coma, anuria
Severe signs and symptoms of dehydration
CBC, CMP, UA, VBG, serum osmolality
56 y/o male presents to the ED after passing out at work. His coworker states they had been working outside in 104 degree heat. Vitals are stable with the exception of 134 bpm and 22 RR. On physical exam you note decreased turgor, dry mucous membranes, delayed cap refill, and the patient is disoriented. What labs you want?
Rapid bolus of isotonic fluids (NS/LR), frequent reassessment, daily weights, monitor labs, treat the underlyin
56 y/o male presents to the ED after passing out at work. His coworker states they had been working outside in 104 degree heat. Vitals are stable with the exception of 134 bpm and 22 RR. On physical exam you note decreased turgor, dry mucous membranes, delayed cap refill, and the patient is disoriented. Labs are as follows, increased Hgb/Hct, hypernatremia, minor hyperkalemia, increased BUN/SCr, Serum osmolality is over 295, and the urine specific gravity is 1.030, What is your treatment plan?
oral hydration with oral rehydration solution (pedialyte)
Treatment plan for mild dehydration
elderly, HF, renal failure peeps
When treating dehydration which patients do we have to be careful to avoid fluid overload?
0.9% NS, 5% dex in saline, D5W
Give me some examples of isotonic crystalloids (raise ECF)
0.45% saline, 0.33% saline, 0.225% saline
Give me some examples of hypotonic crystalloids (cells in a hypertonic environment)
3-5% saline, 5% dextrose in 0.9% saline, 5% dextrose in 0.45% saline
Give me some examples of hypertonic crystalloids (cells in a hypotonic environment)
Albumin, FFP, hydroxyethyl starch, dextran, geletans (like blood)
Examples of Colloids - usually hypertonic and reserved for severely hypovolemic peeps
cheap, available, safe, good for rehydration, non-allergenic, t1/2 30-60
Pros for Crystalloids
Shifts in Na and osmolality, large volumes of NaCl increase the risk of hyperchloremic acidosis, increased risk of hyperglycemia and C/I with hyperkalemia (LR), Need a seperate line if blood is running
Cons for Crystalloids
replaces fluid volume, remain intravascular long, t1/2 is hours to days
Pros of Colloids
Anaphylaxis, expensive, coagulation abnormalities, excessive use can lead to cardiac or renal failure
Cons of Colloids
Hypervolemia
A state of excess body water and sodium blood vessels
intake exceeds loss, excessive sodium/fluid (or retention), decreased output, 3rd spacing
Etiology for hypervolemia
UA, CBC, CMP, BNP, Serum osmolality, CXR, echo
Wow you’re back in the Burn ICU at BAMC checking out your patient with full thickness burns on 55% of his body. Vitals are stable with the exception of 112 bpm. 144/92, and 24 RR. On physical exam you note pitting edema, bilateral crackles and rales, elevated JVP and an S3. What diagnostics you want?
CHF (most common cause of fluid overload), Pulmonary edema, pericardial effusion, cerebral edema, cutaneous edema, periorbital edema, lymphedema, liver failure
Complications of Hypervolemia
Fluid and Na restriction, loop diuretics (most common), treat the underlying; monitor daily weights, strict I&Os, vitals, lung sounds, JVP, edema assessment, electrolytes, intermittent pneumatic compression devices
Treatment plan for hypervolemia