Chemistry Unit 2 Test Flashcards
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
Proton ; location ; charge symbol ; mass
Subatomic particle ; nucleus ; p+ ; 1 amu
Neutron ; location ; charge symbol ; mass
Subatomic particle ; nucleus ; n⁰ ; 1 amu
Electron ; location ; charge symbol ; mass
Subatomic particle ; orbital ; e- ; amu undetermined
Law of Definite Proportions
Every sample of a compound is made with the exact same elements with the same proportions
Law of Conservation of Mass ; example
Mass is neither created or destroyed in chemical reactions ; 2H₂ + O² → 2H₂O
Law of Multiple Proportions
Compounds always have a whole number ratio of one element to the other by mass
Ex: NO = 1N:1O
NO² = 1N:2O
Dalton’s First Atomic Theory Statement
All matter is composed of atoms
Dalton’s Second Atomic Theory Statement
Atoms of the same element are identical
Dalton’s Third Atomic Theory Statement
Atoms of different elements are all unique in properties
Dalton’s Fourth Atomic Theory Statement
Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed
Dalton’s Fifth Atomic Theory Statement
In chemical reactions, atoms are combined, separated, or rearranged
Ions (charged atoms)
Atoms of the same element with different amounts of electrons
Anions
Negatively charged ions with more electrons than protons
Cations
Positively charged ions with more protons than electrons
Average atomic mass definiton ; Equation
The average mass of all the isotopes of the same element ; (Mass)(%) + (Mass)(%)/100
Radioactivity
The spontaneous emission of radiation by the nucleus of unstable isotopes undergoing nuclear decay to become more stable
How does the nucleus of a radioactive isotope attempt to become more stable?
By emitting alpha particles, beta particles, gamma rays, or energy
Non ionizing radiation
Does not affect our DNA
Ionizing radiation
Removes electrons from DNA which breaks our molecules up
Alpha Radiation ; What is it? ; What blocks it?
Weak ionizing radiation ; A gas similar in mass to Helium ; thick plastic, paper
Beta radiation ; What blocks it?
Medium ionizing radiation that turns a neutron into a proton ; wood, aluminum
Gamma radiation ; What is it? ; What blocks it?
High ionizing radiation; Small pure energy; Lead, 3 meters of concrete
Nuclear Fusion ; Where can it occur?
Lighter nuclei are fused together ; Inside stars like the Sun
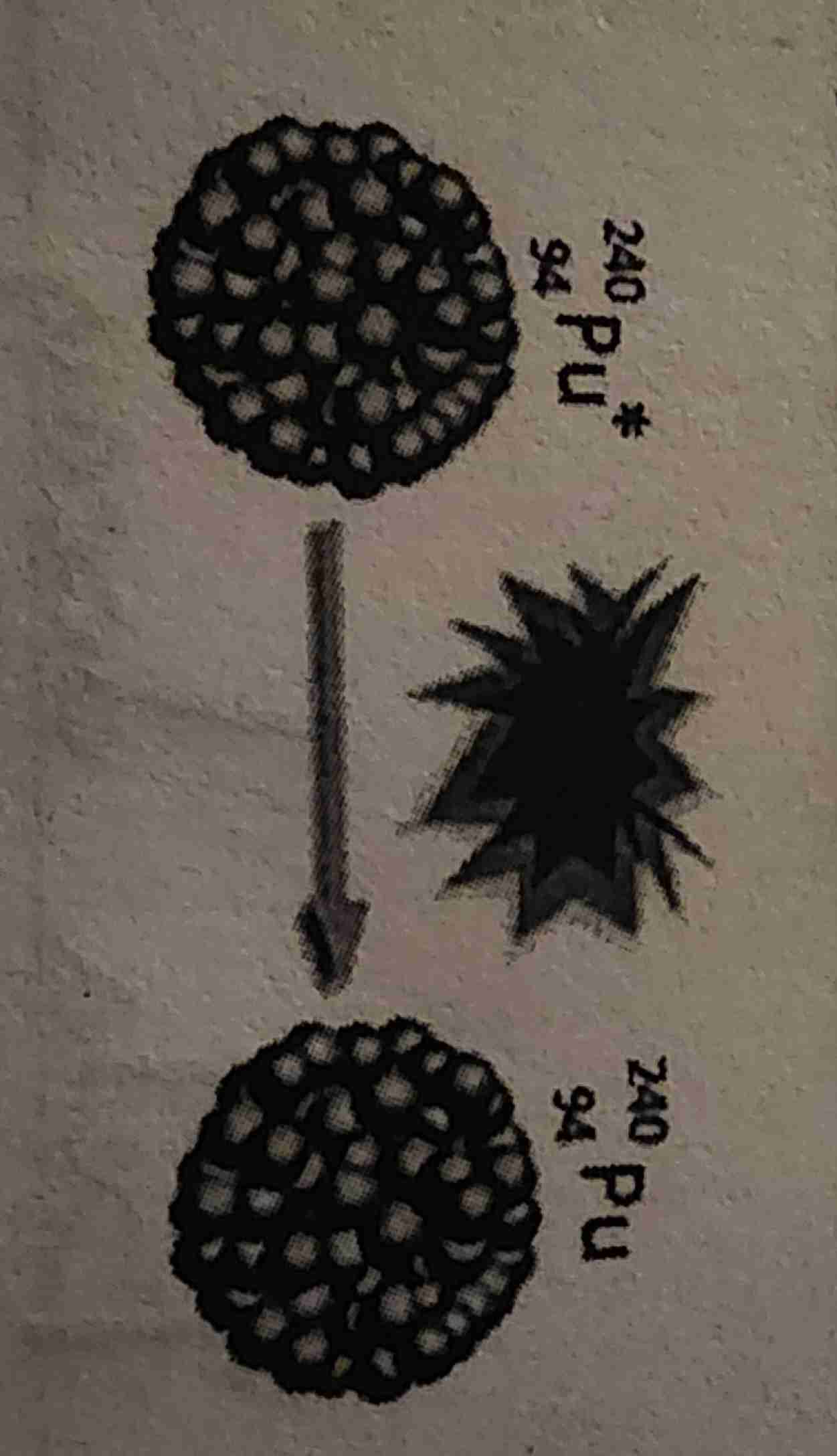
Nuclear Fission ; Where can it occur?
Heavy nucleus is split into smaller nuclei ; Nuclear power plants
What do both nuclear fusion and fission release?
Energy
What else is released in nuclear fission besides energy?
Neutrons (chain reaction)
The mass of an atom is always _____ than the sum of its _____
less ; subatomic components
Mass Defect
The difference between the sum of the masses of the components and the measured atomic mass
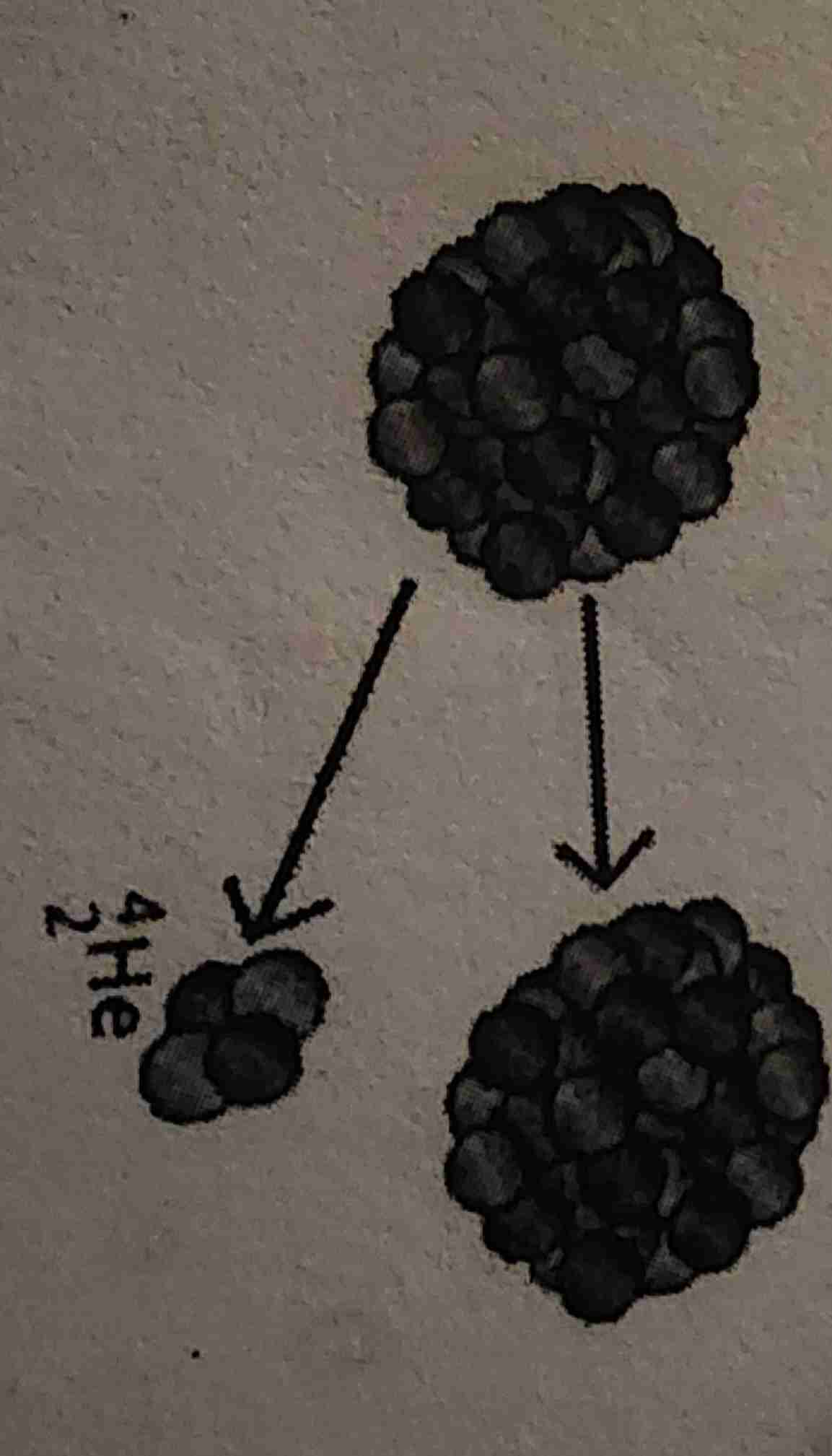
Alpha decay

Nuclear fusion
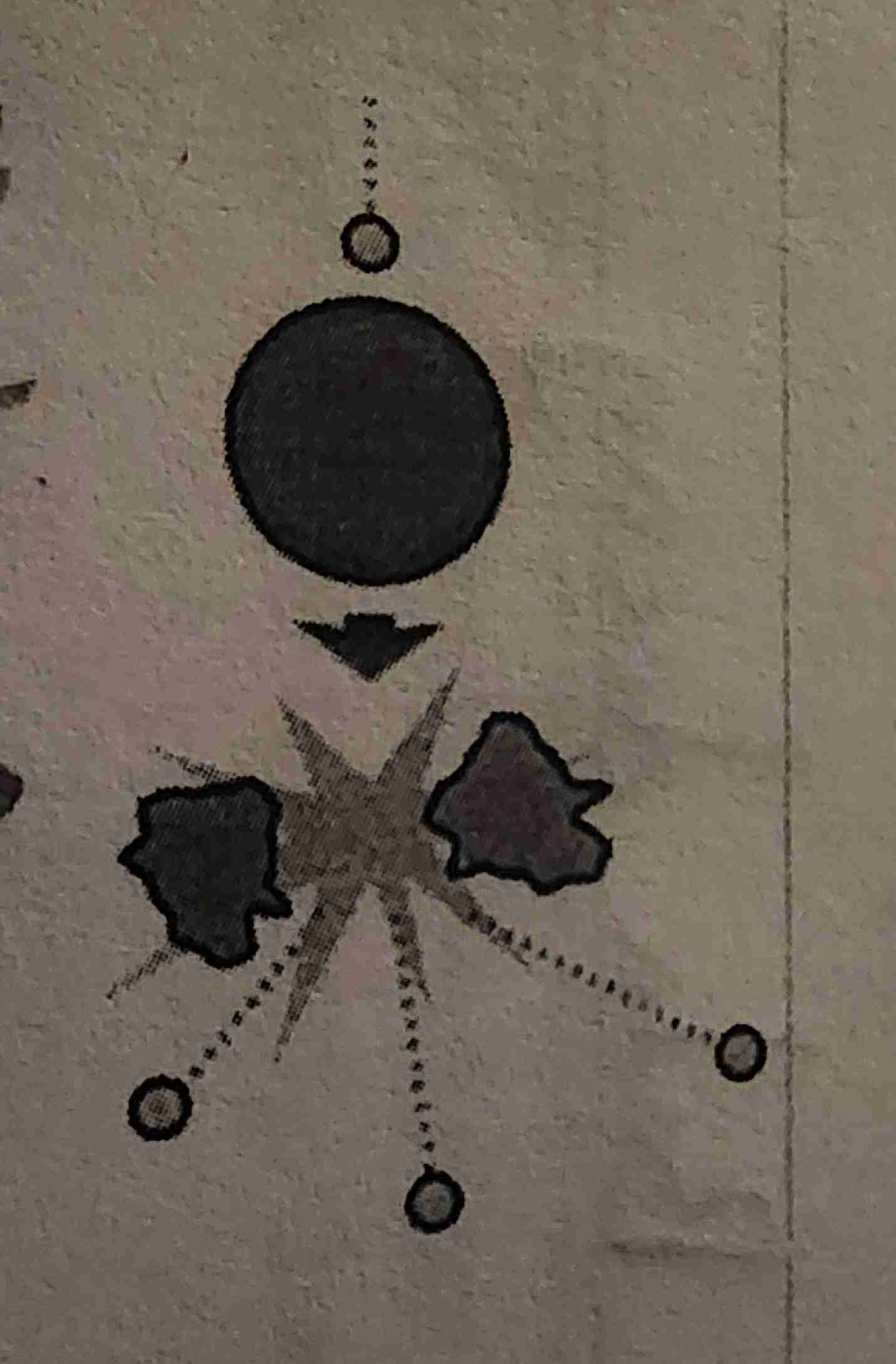
Nuclear fission

Gamma decay
Change in _____ corresponds to chnage in _____
mass ; energy
What do the letters mean in Einstein’s equation: E=mc²
E = energy ; m = mass ; c² = speed of light (squared because its a huge number)
Who first discovered the phnomenon of Radioactivity?
Henri Bacquerel
Who were the first to use the term Radioactivity?
Pierre Curie and Marie Curie
Electron Capture
Electron from inner orbital is captured by nucleus of atom and combined with a proton to form a neutron
What causes atoms to be radioactive
When ratio of protons and neutrons is unbalanced
When radioactive isotopes decay, they do so _____
exponentially
Half Life
The time it takes for half of a radioactive sample to decay
Mass of Alpha radiation
4 amu
Mass of Beta radiation
.00054 amu
Mass of gamma radiation
0 amu

Gamma ray

Neutron

Beta particle

Alpha particle

Beta particle

Alpha particle

Proton
Positron
What subatomic particles determine the stability of an atom?
Protons and neutrons
Is the Law of Conversion of Mass violated when a gas is formed?
No
What kind of elements will undergo fission or fusion?
Elements lighter than Iron-56 will undergo fusion and heavier will undergo fission
2-1 Lab: Conservation of Mass
The individual mass of Sodium Carbonate and Calcium Chloride was equal to the mass of both poured in a beaker, proving the law of conservation of mass.
The burning steel wool experiment proved the law of conservation of mass because while burning, the iron in the steel wool reacts with oxygen from the air, forming iron oxide which increases the mass by adding the mass of the oxygen atoms along with the steel wool.
2-2 Skittle Isotopes
Adding up all the weighed masses of isotopes 64-68 of Calorium by the equation (% distribution) x (mass of isotope)/100 helped figure out the average atomic mass of Calorum.
PHET Build An Atom Simulation
Charge: ratio of protons and electrons
Element: # of protons
Mass #: protons + neutrons
Stability: too many/too few neutrons: proton ratio
2-3 Modeling Nuclear Reactions
Big marshmallow = proton
Big marshmallow with little marshmallow on top = neutron
Little mashmallow = beta particle
Radioactive elements emit particles/ energy from their nucleus to become more stable
Lab 2-4 Half Life (How does a graph showing nuclear decay be used to find the half life of a radioactive substance)
How much time does it take for half of the sample to decay
Lab 2-4 Half Life Part 2 (Why do nuclear reactions produce so much energy?)
The strong nuclear force holding protons and neutrons together in the nucleus is significantly stronger than the electromagnetic forces holding electrons in orbit around the nucleus, and during nuclear reactions, all that energy is released.
2-4 Half Life (Part 3) (Can you predict when a single atom will decay?)
No because the decay of a single atom is spontaneous. And just like the lab, to roll any number with a dice is based on probability (random).