Chapter 12: The Cell Cycle
1/32
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
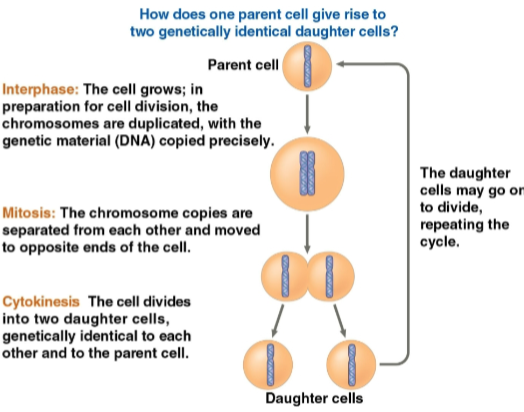
Interphase
Phase of the cell cycle in which the cell grows in preparation for cell division
Chromosomes are duplicated
Genetic material is copied precisely
Mitosis
Phase of the cell cycle where the chromosome copies from interphase are separated from each other and moved to opposite ends of the cell
Cytokinesis
Phrase of the cell cycle where the cell divides into two daughter cells, genetically identical to each other and the parent cell
Daugher cells may go on to divide after interphase, restarting the cell cycle
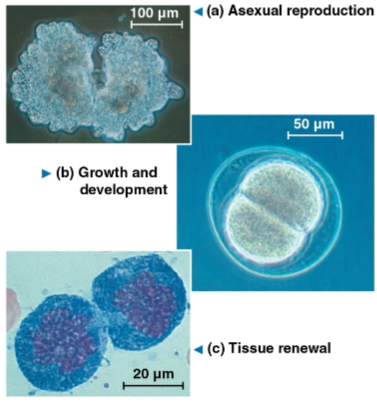
Cell division
The reproduction of cells to ensure the continuity of life
Is the characteristic that distinguishes living things from nonliving matter
Seen in:
Single-celled organisms giving rise to new organisms
Multicellular eukaryotes undergoing embryonic division as well as renewal and repair for the fully grown
Genetic material (DNA)
Instructions for the cell’s function within a eukaryote’s nucelus or prokaryote’s interior
Cell division is remarkably accurate in passing this from one generation to the next
Genome
All the DNA within a cell
Consists of a single DNA molecule (common for prokaryotes) or a number of DNA molecules (common in eukaryotes)
Chromosome
The packaging form for DNA molecules in a eukaryotic cell
Carries several hundred to a few thousand genes
Every eukaryotic species has a characteristic number of these in each cell nucleus
Chromatin
A complex of DNA and protein that condenses during cell division in eukaryotic chromosomes
Somatic cells (nonreproductive cells)
Cells that have two sets of chromosomes
Gametes (reproductive cells)
Cells that have half as many chromosomes as somatic cells
Produced by a variation of cell division called meiosis
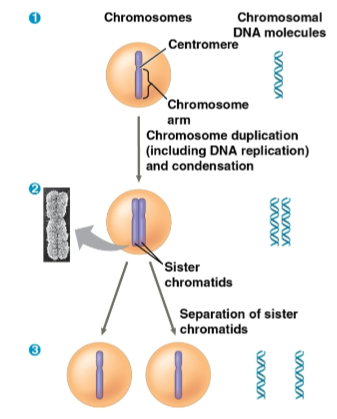
Sister chromatids
Joined copies of the original chromosome created during DNA replication in preparation for cell division
These separate and move into two nuclei during cell division, thus turning into chromosomes
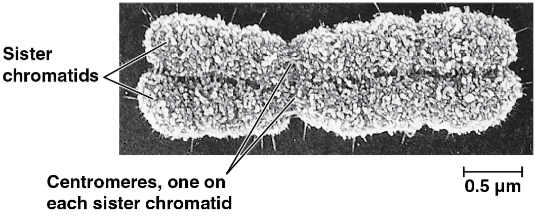
Centromere
The narrow “waist” of the duplicated chromosome where the two chromatids are most closely attached
Meiosis
The variation of cell division that creates gametes
Yields nonidentical daughter cells with half as many chromosomes as the parent cell
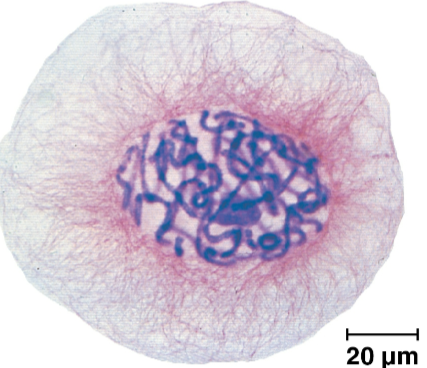
Walther Flemming
The German anatomist who developed dyes to observe chromosomes during mitosis and cytokinesis in 1882
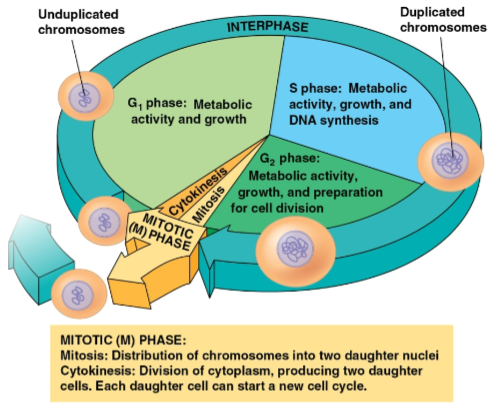
Cell cycle
Consists of:
The mitotic (M) phase (mitosis and cytokinesis)
Interphase (cell growth and copying of chromosomes in preparation for cell division)
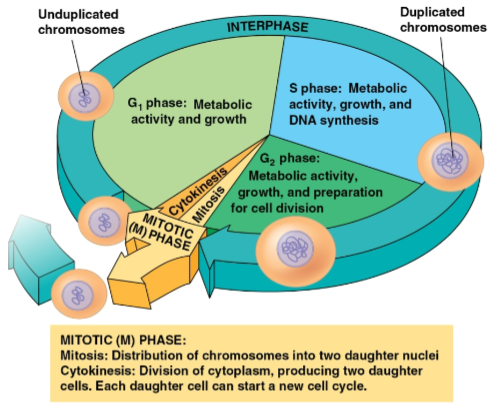
Mitotic phase
Phase of the cell cycle that includes mitosis and cytokinesis
Divided into five stages:
Prophase
Prometaphase
Metaphase
Anaphase
Telophase
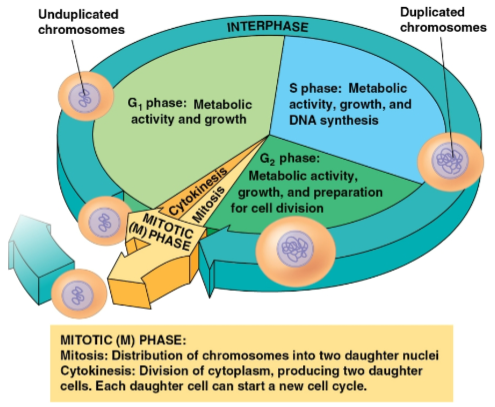
Interphase
Phase of the cell cycle where cell growth and chromosome duplication occurs in preparation for cell division
Divided into three phases:
G1 phase (first gap)
S phase (synthesis)
G2 phase (second gap)
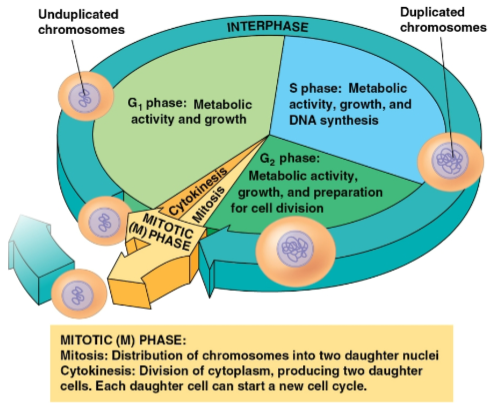
G1 phase
Phase of interphase where metabolic activity and growth occurs
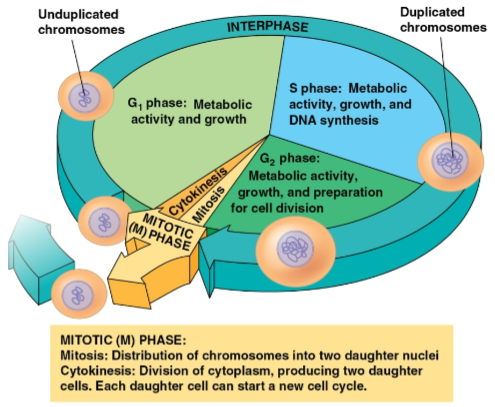
S phase
Phase of interphase where chromosomes are duplicated
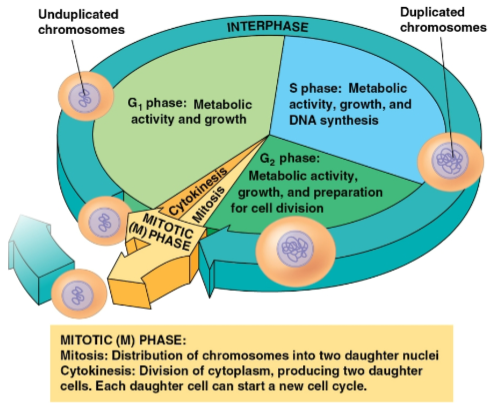
G2 phase
Phase of interphase where metabolic activity, growth, and preparation for cell division occurs
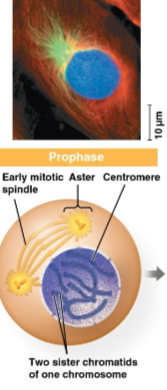
Prophase
Phase of mitosis where sister chromatids joined by a centromere become visible as the mitotic spindle develops
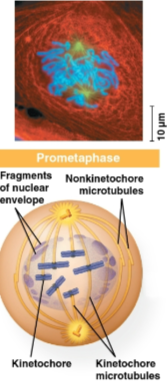
Prometaphase
Phase of mitosis where the nuclear envelope dissolves and kinetochore microtubules extend over the chromosomes
Centrosomes are at opposite ends of the cell by the time of this phase’s completion
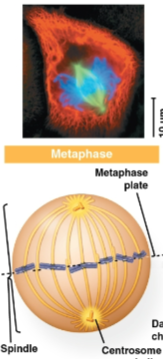
Metaphase
Phase of mitosis where the mitotic spindle is developed with centrosomes at the pole and centered chromosomes
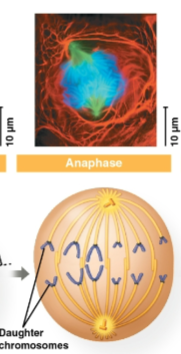
Anaphase
Phase of mitosis where daughter chromosomes are pulled apart towards the poles of the cell by centrosomes
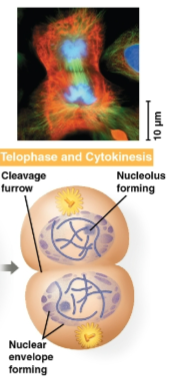
Telophase
Phase of mitosis where cytokinesis starts to occur as the nucleus reforms and the cell divides
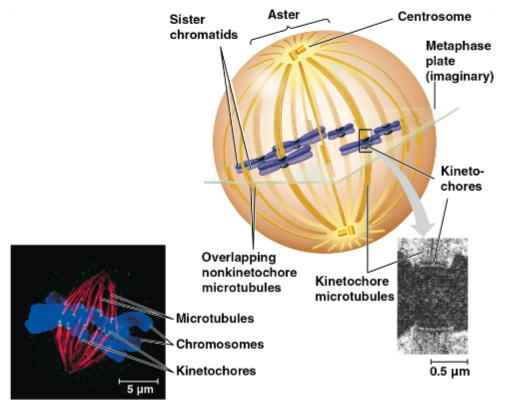
Mitotic spindle
A structure made of microtubules that controls chromosome movement during mitosis
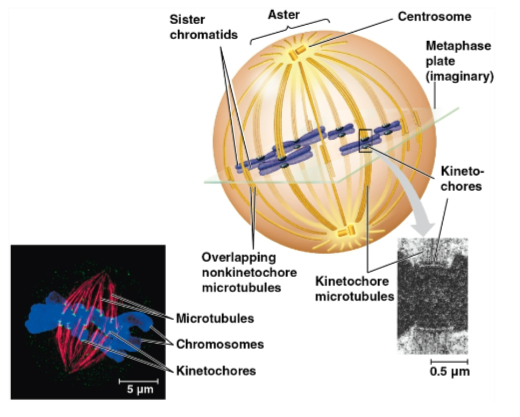
Centrosome
An assembly of spindle microtubules at the poles of each cell for organization
Replicates during interphase and migrates during prophase and prometaphase
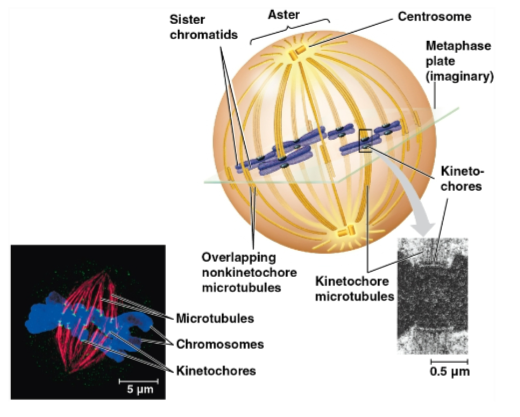
Kinetochore
A protein complex associated with centromeres, assigned to each sister chromatid
Spindle microtubules attach to these during prometaphase
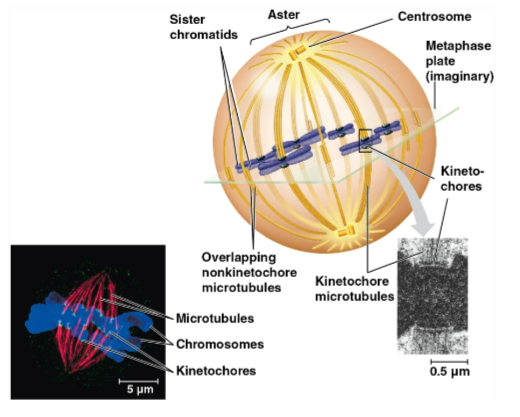
Metaphase plate
Plane midway between the spindle’s two poles where the chromosomes are all lined up
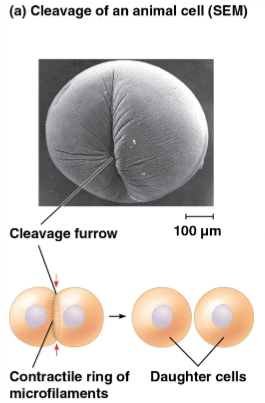
Cleavage
Process that causes cytokinesis in animal cells
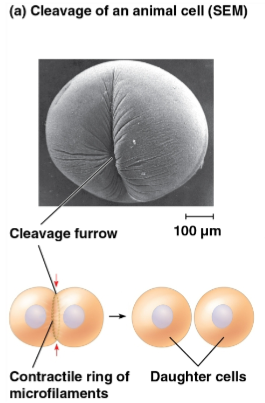
Cleavage furrow
The first sign of cleavage in an animal cell, marked as a shallow groove in the cell surface near the old metaphase plate
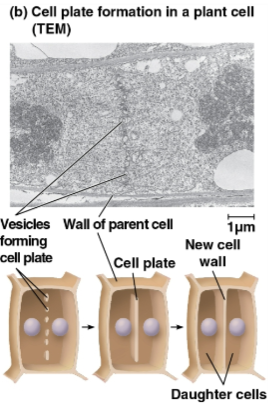
Cell plate
Sign of cytokinesis in plant cells after cell division
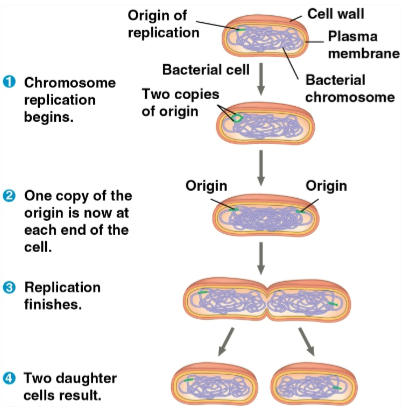
Binary fission
The type of cell division conducted by prokaryotes such as bacteria and archaea
Replicates the chromosome, then actively moves them apart as the plasma membrane pinches inward for division
Likely the basis for mitosis in eukaryotes through evolution