GI Pathology: Esophagus, Forestomachs, Stomach
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
Cats/ horses
Dogs
___ and ___ have both skeletal muscle and smooth muscle in their esophagus. __ only have skeletal muscle in their esophagus?
Cat and dog
What species will not have keratinized esophagus?
Regurge
Emaciation
Dehydration
-Aspiration pneumonia
What are clinical signs of megaesophagus?
Persistent R aortic arch - entrapped esophagus leading to segmental dilation cranial to the heart
What is going to cause congenital megaesophagus?
German Shepards
Newfoundland
Great Dane
What breeds are predisposed to congenital megasophagus?
Polymyositis
Myasthenia gravis
Hypothroidism
Lead/ thallium tox
What are some methods of acquired diffuse megaesophagus?
Nematode parasites in canines will migrate from stomach -> aorta -> esophagus and will mature in the esophagus wall leading to granulomatous and fibrotic inflammation
Explain the pathogenesis of how Spirocerca lupi will cause esophagitis?
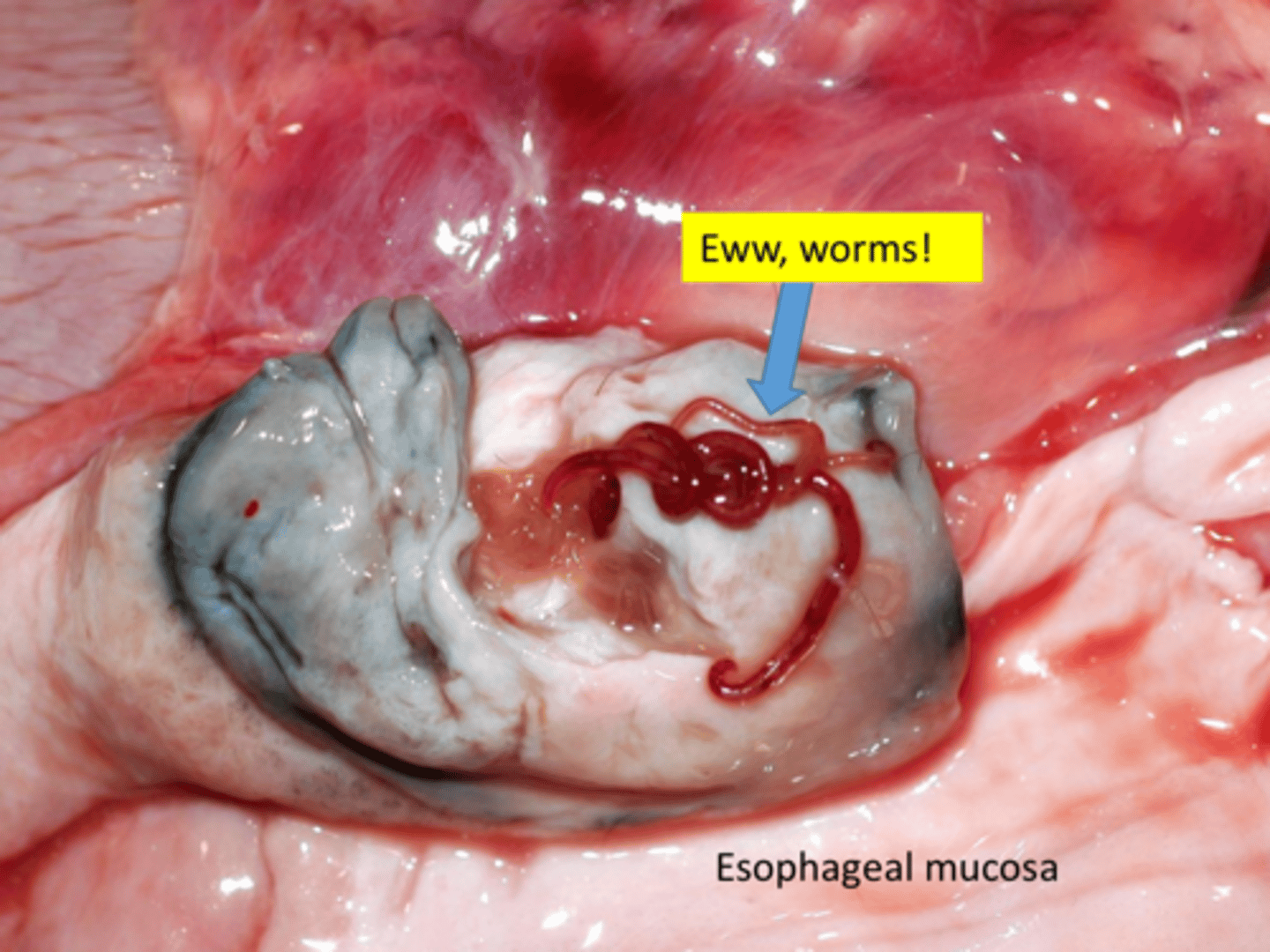
Fibrosarcomas
What is a possible neoplastic changes that can be seen w/ Spirocerca lupi?
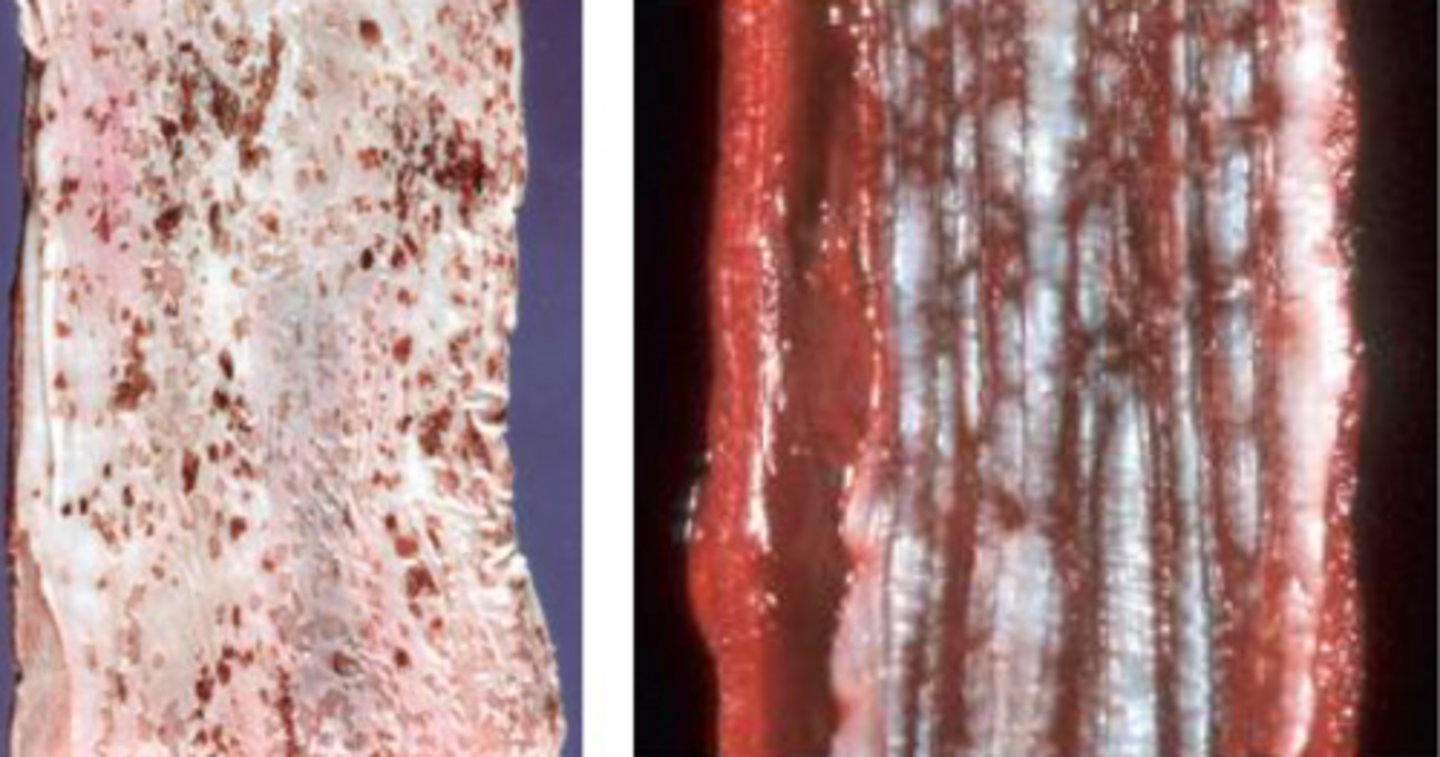
Pressure necrosis leading to perforation of stricture
What are possible sequela of food bolus/ FB in the esophagus?
Caustic substances
Viral infections (BVDV)
What are causes of ulcerative esophagitis?
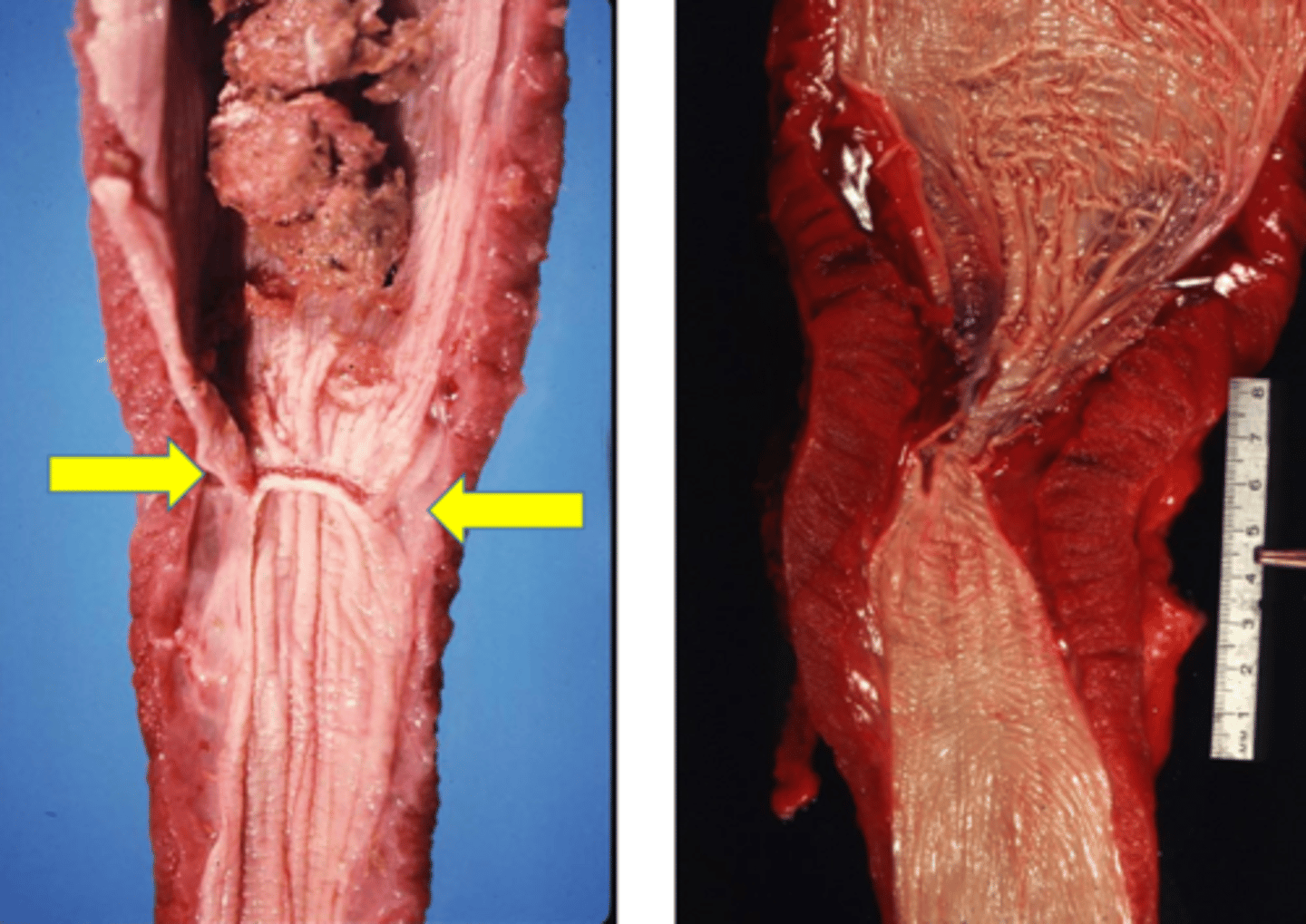
Esophageal stricture
-chronic inflammation/ ulceration leading to fibrosis
Identify the pathology?
Stratified squamous epithelium
What is the rumen forestomach lined with?
-High grain diet selects for microbes that produce lactic acid.
-Increase of lactic acid lowers pH leading to increased runimal osmotic pressure and hypovolemia
-Circulatory collapse occurs
What is the pathology of ruminal acidosis?
Truperella pyogenes
Fusobacterium necrophorum
-abscesses in the rumen/ liver
What are the most common culprits of bacterial rumenitis?
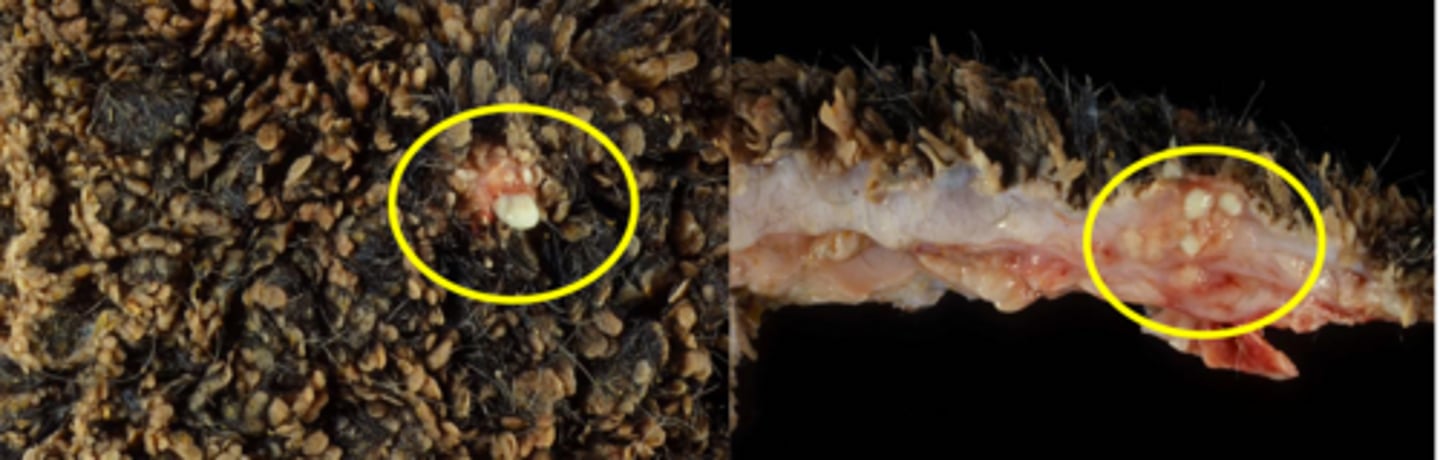
Aspergillus
Zygomycetes
What are the most common agents in mycotic rumenitis?
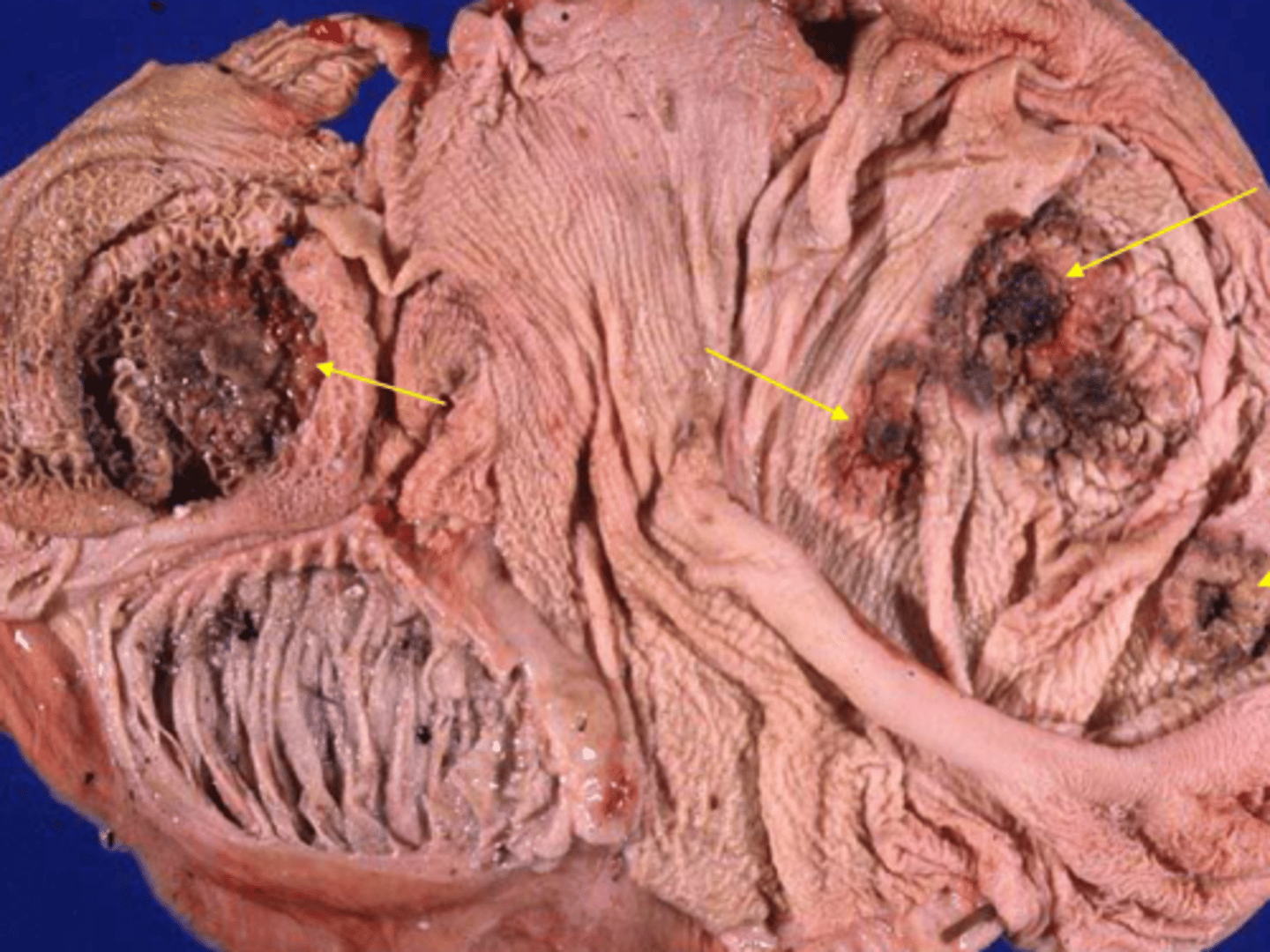
Bacterial translocation/ inflammation
Why does traumatic reticuloperitonitis/ pericarditis cause fibrinous inflammation in the heart/ peritoneum
Frothy bloat - too many legumes
What causes primary bloat?
Physical/ functional obstruction
What causes secondary bloat?
- Decreased/ lack of eructation
- Gas builds up leading to luminal distension and compression of the diaphragm
- increased intraabdominal and intrathoracic pressure leading to a decreased venous return to the heart
Explain the pathogenesis of bloat?
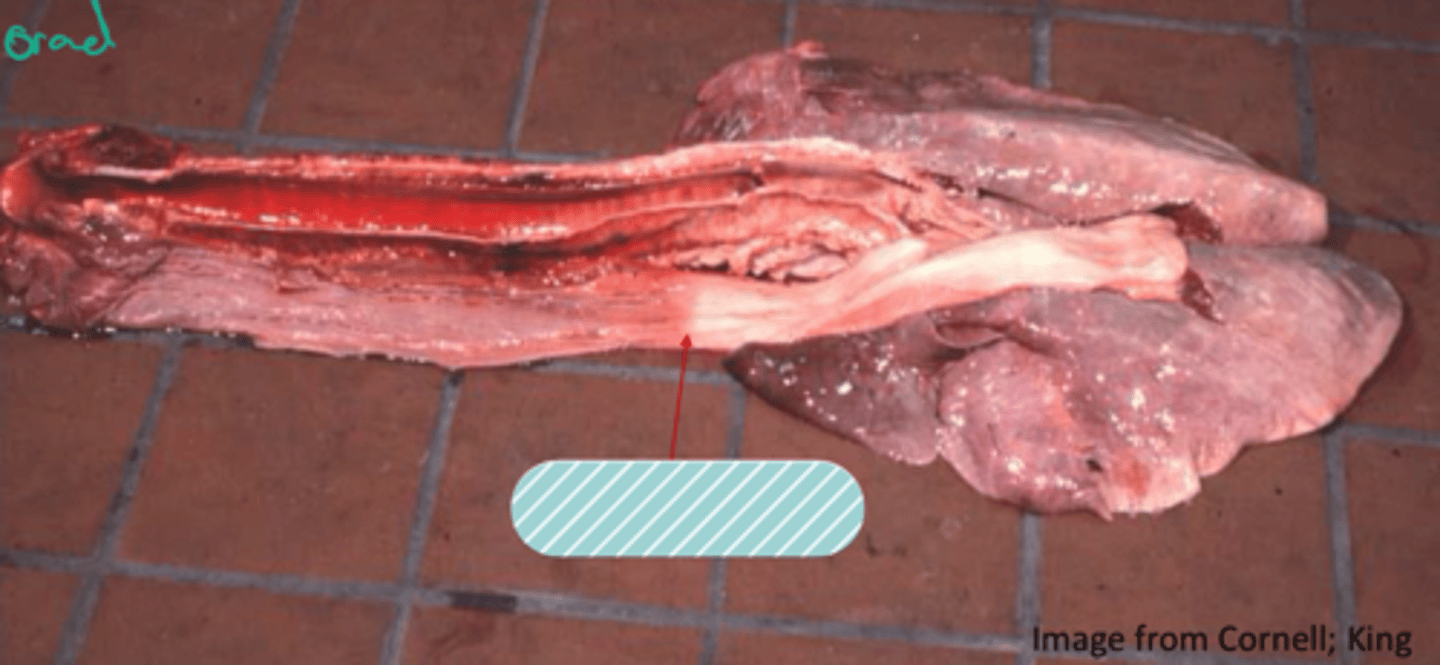
Bloat - (arrow pointing to bloat line where congestion is showing)
Identify the pathology?
Mucus - protects epithelium
Mucous cells will secrete:
Hydrochloric acid
Parietal cells secrete:
Pepsin - digestive enzyme
Chief cells secrete:
Hormones - gastrin
Enteroendocrine cells secrete:
Swine
What animal will we find a torus pyloricus?
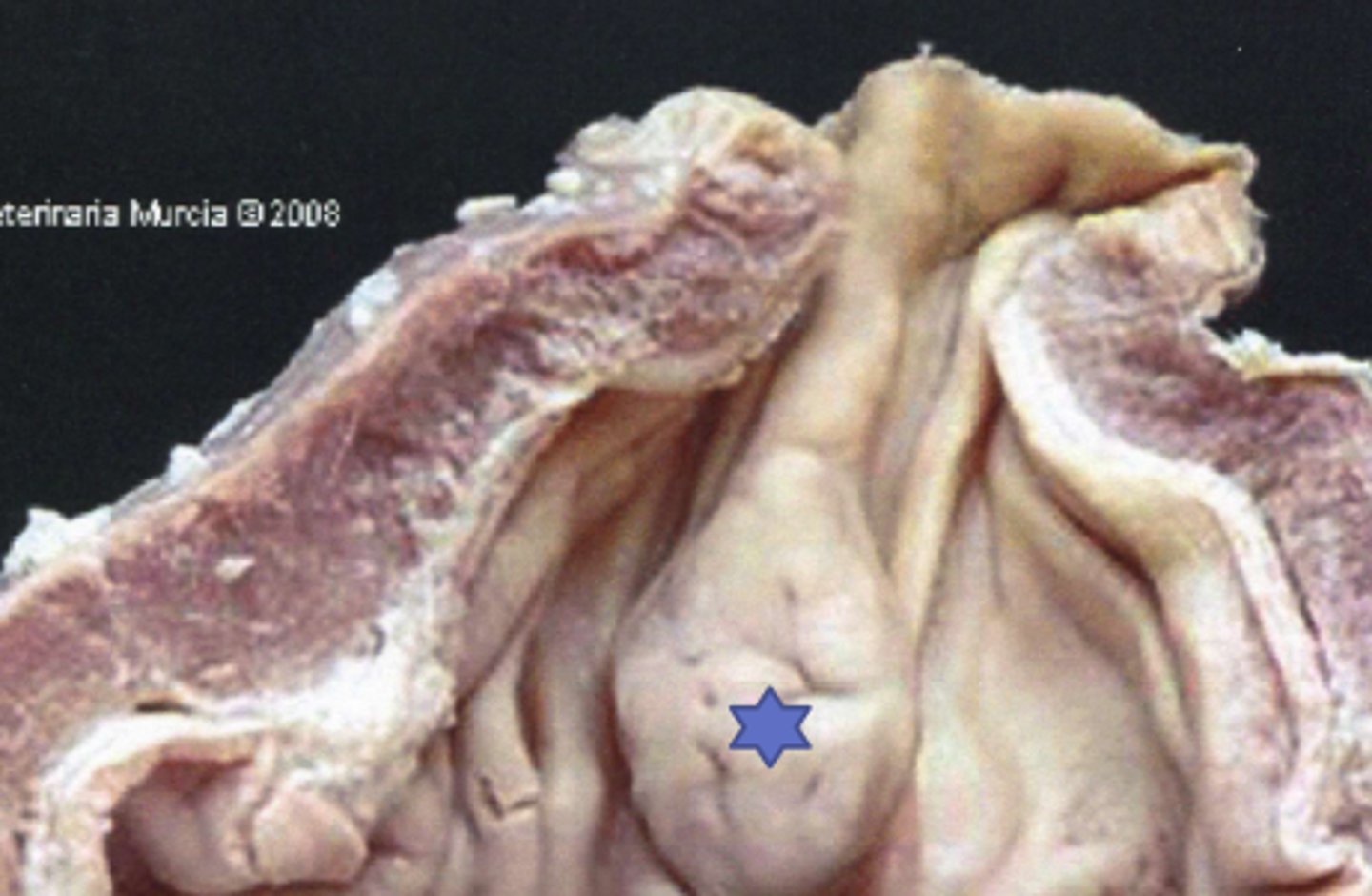
An equine structure that separates non-glandular stratified squamous stomach to gastric stomach
What is the margo plicatus?
Clostridium septicum/ perforinges
What agent will kill calves that are 2-6w old after short sings of abdomen distention?
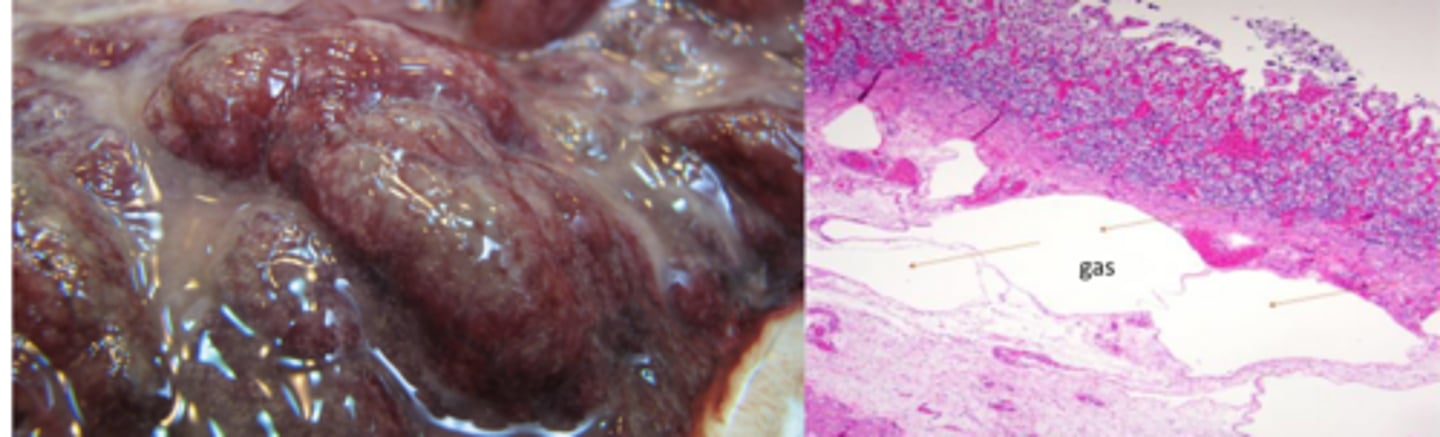
Hemorrhage
Necrosis
Gas bubbles
What lesions will you see in the abomasum of calves affected by C. perferingens or septicum?
Common in dogs due to dietary indiscretion
What is chronic gastritis?
Lymphoplasmacytic gastritis
What microscopic findings will you see in chronic gastritis?
Calcification of glands - mineralization of vessels
What will you see in uremic gastritis?
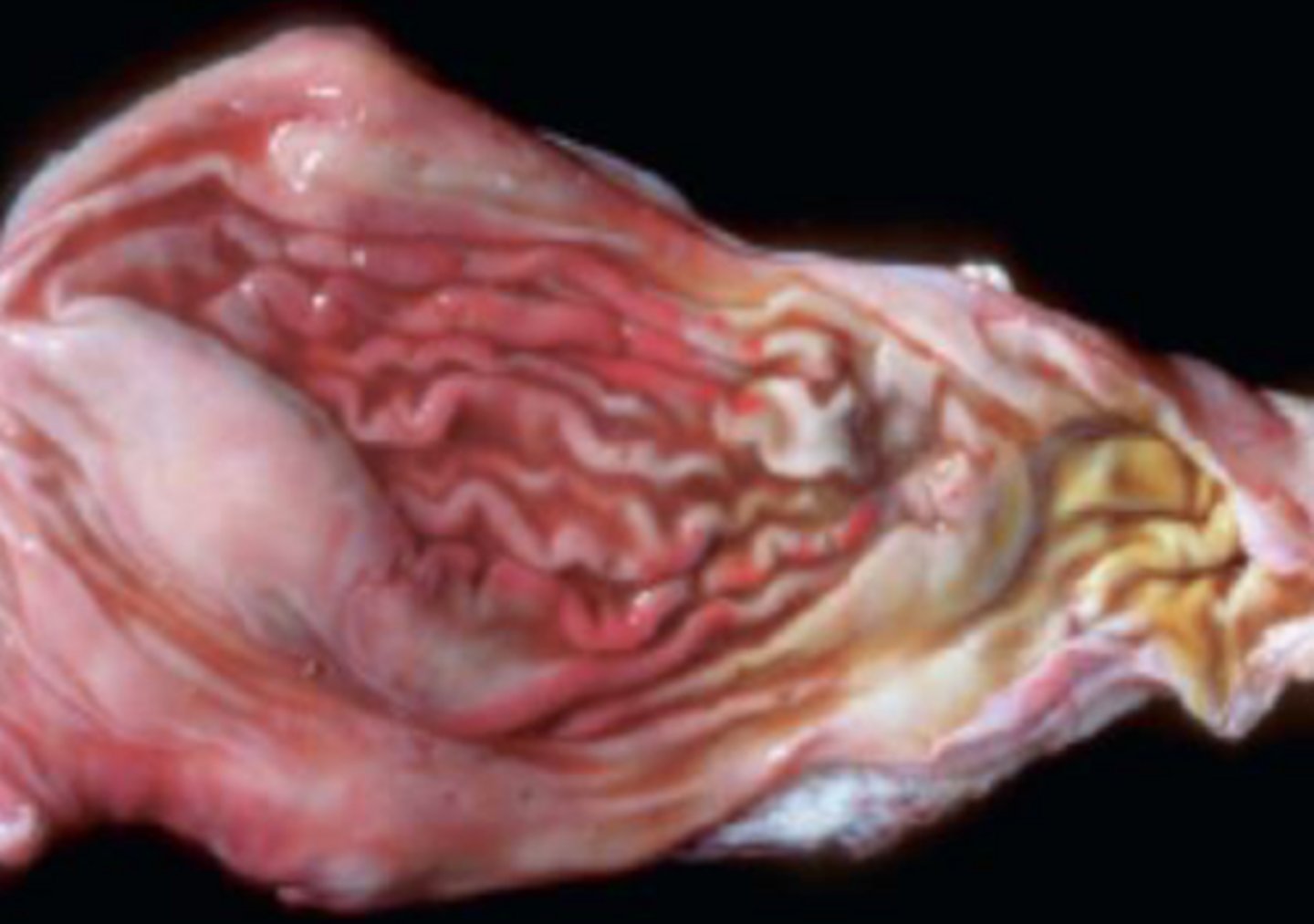
Hemonchus contortus
Ostertagia ostertagi
What gastric parasites seen in ruminants?
Draschia megastoma
What is the most common parasite seen in horses?
Blood sucking nematodes in the abomasum
-severe anemia
-hypoproteinemia
-decreased oncotic pressure
-pale mucus membrane
-effusions
-SQ edema
-Bottle jaw
What signs will you see in hemonchus contortus?
Thickened cobblestone appearance of abomasa mucosa
proliferation of mucosal cells
Eosinophilic gastritis
What are symptoms of ostertagia ostertagi?
Brood pouch - mass like lesions
What lesions will we see in a horse affected by Draschia megastoma?
Grain feeds - rapidly growing pigs
What are common causes of gastric ulcerations in pigs?
Mycotic,
Acidosis/ bloat
What are common causes of gastric ulceration in a cow?
Urema
NSAIDS
Paraneoplastic
What are common causes of gastric ulcerations in a a dog?
Gastrinomas-gastrin
MCT - histamine
What are two paraneoplastic causes of gastric ulcerations in dogs?
NSAIDS
Stress
What causes gastric ulcers in horses?
Gastroduodenal ulcers - at the pylorus
Where is the most common location of an ulcer in a dog?
Canine gastric dilation and volvulus (GDV)
- Large breed/ deep chested
Identify the pathology?

Fundus twists and greater curvature is displaced ventrally and duodenum will be moved dorsally and caudally
Explain the pathology of GDV?
Decreaed blood flow to heart leading to pulmonary and Cardiovascular depression -> shock/ myocardial dysfunction
How dose GDV lead to death?
hyper motility
Displacements in ruminate are common w/ what?
Parturition
Abomasum displacement most commonly occurs after __?
Metabolic alkalosis - chloride sequestration
What will a volvulus lead to in ruminants?
Rupture/ sepsis
What are consequences of gastric ilation/ displacement?
Dog
-Strictures in the stomach
Name the animal most likely to get the following neoplasia of the stomach:
Adenocarcinoma?
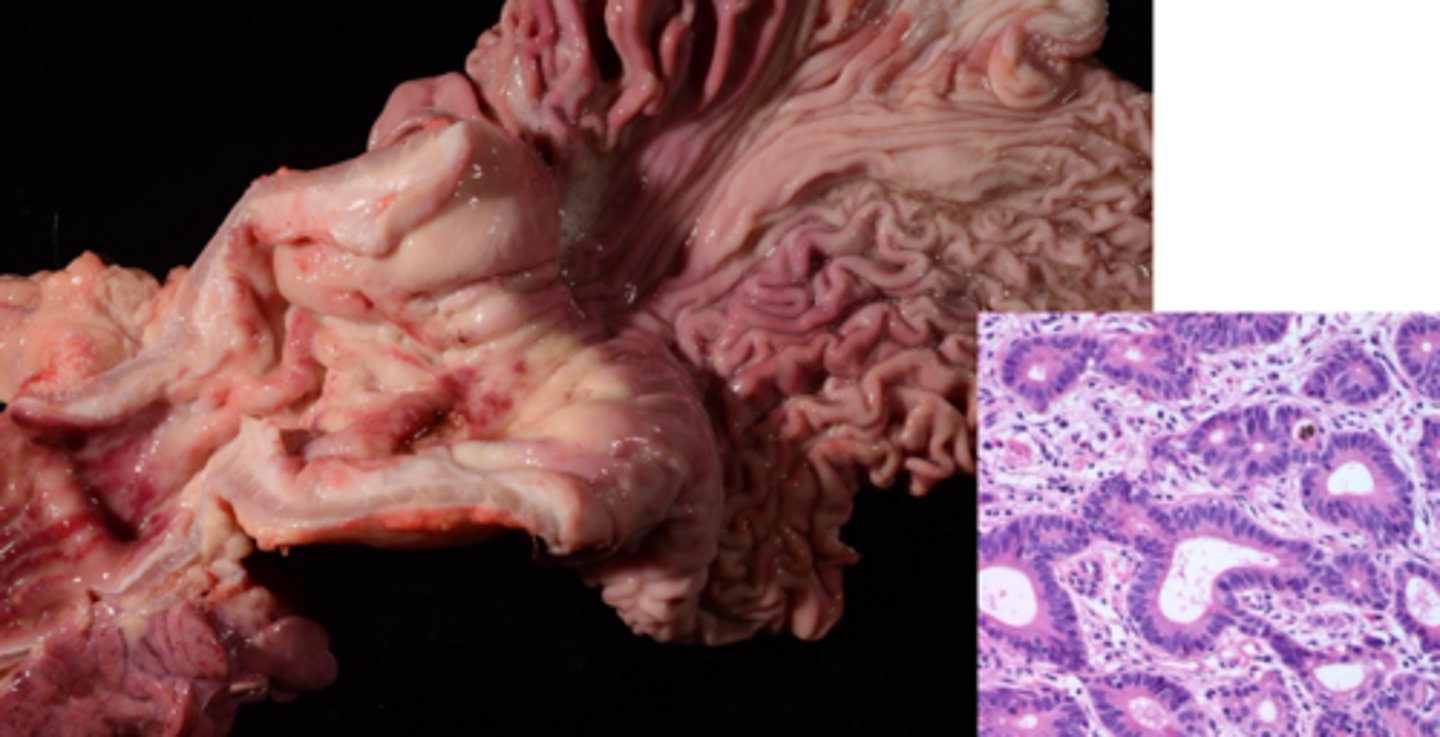
Horses
-nests/ islands making keratin
Name the animal most likely to get the following neoplasia of the stomach:
Squamous cell carcinoma
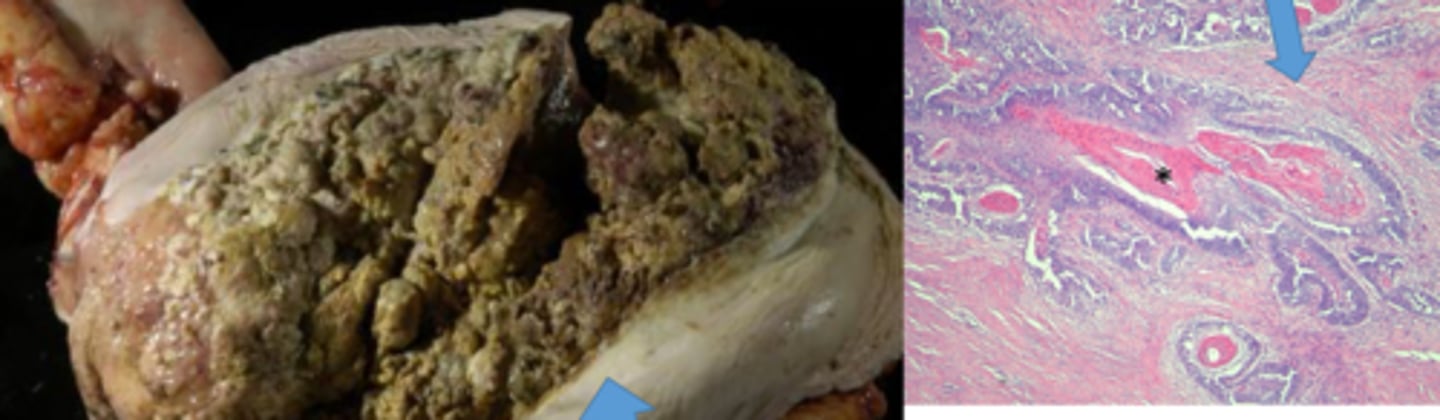
Cows
Cats
Dogs
Name the animal most likely to get the following neoplasia of the stomach:
Lymphoma
Dogs
-non-infultrated
-in the stomach wall
Name the animal most likely to get the following neoplasia of the stomach:
Leiomyoma, leiomyosarcoma
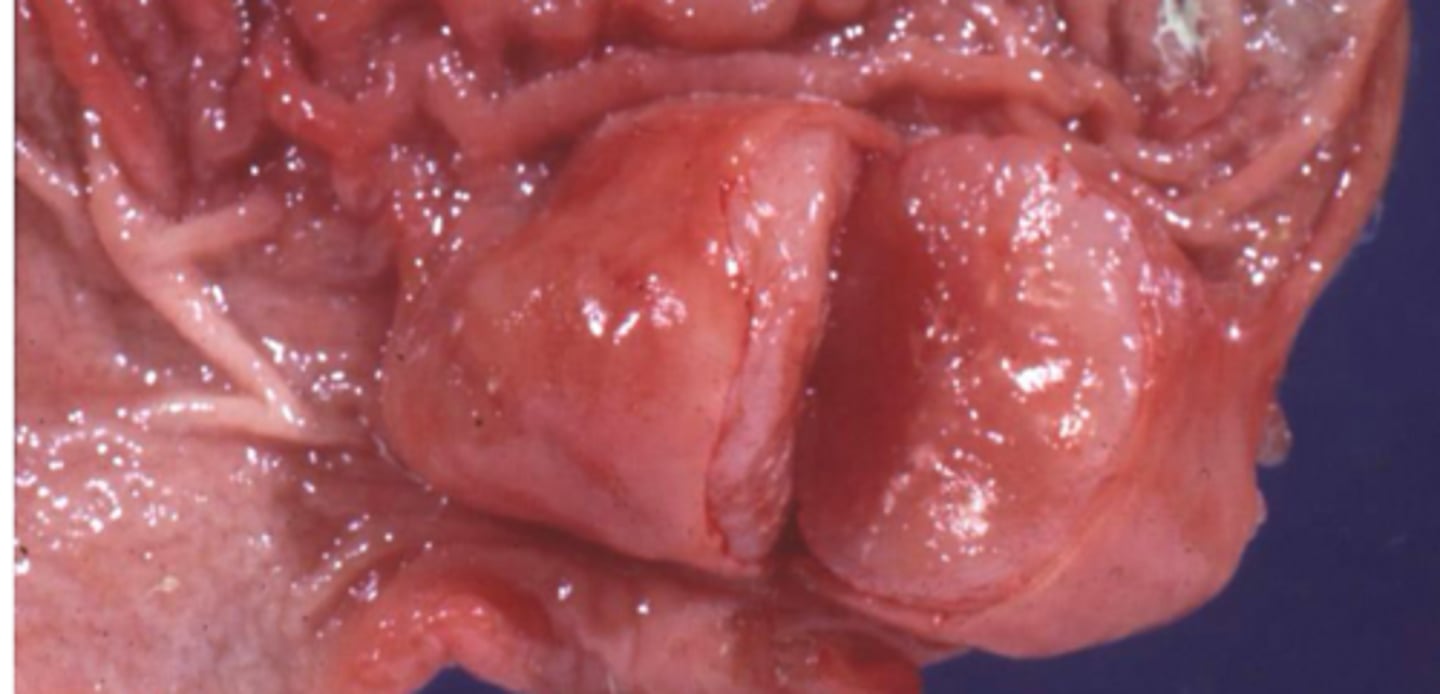
Spontaneous
Bovine leukemia virus induced
GI lymphoma in cats is ___ and in cows is ___?