
Looks like no one added any tags here yet for you.
endocrine system functions and controls
reproduction
growth and development
maintenance of electrolyte, water, nutrient balance
regulation of metabolism
mobilization of defenses
food intake and digestion
amine hormone class
synthesized from: tyrosine or tryptophan
stored before release
polar and non-polar
membrane and nuclear membrane acting
ex: norepinephrine (adrenaline), thyroxin, triiodothyronine, catecholamines
peptide hormone class
synthesized from: pro-hormones (req. cleavage)
stored in vesicles
polar → free travel in blood
membrane binding and transduction of signal (second messengers)
ex: insulin, glucagon, prolactin, ACTH, oxytocin
steroid (lipid based) hormone class
synthesized from: cholesterol or arachidonic acid
released immediately due to hydrophobicity
non-polar → requires protein binding to travel in the blood
binds intracellular receptors to change gene expression directly
ex: testosterone, progesterone, cortisol, estrogen
three ways to control hormone release?
humoral stimuli
neural stimuli
hormonal stimuli
humoral stimuli mechanism
ion/nutrient levels in the blood → impacts secretion of hormones
ex: glucose levels in blood stimulate insulin secretion
blood osmolarity humoral stimuli example
high blood osmolarity (low water content)
hypo-thalamus releases ADH (vasopressin) from posterior pit.
ADH increases aquaporins in lumen side of kidney duct for increased water reabsorption → dilutes blood and decreases blood osmolarity
Calcium levels humoral stimuli example
Normal Pathway: When calcium is present in the blood
CaSR is bound by calcium → Gq11 phospholipase activation → release of intracellular Ca2+
intracellular Ca2+ blocks PTH synthesis
Kidney CaSR bound = decreased Ca2+ reabsorption
Decreased Blood Calcium Pathway:
CaSR remains unbound and inactivated → no release of intracellular Ca2+ → PTH is freed
PTH synthesized = rise of Calcium in the blood
permissiveness
one hormone must be present for another hormone to be fully expressed
hormone 1 allows/enhances effects of hormone 2
syngergism
hormone 1 and hormone 2 effects sum together allowing for greater activity
antagonism
hormone 1 opposes hormone 2 action
what are the three things target cells depend on for activation?
blood levels of the hormone
relative number of receptors on/in the target cell
affinity of binding between hormone and receptor
types of desensitization
homologous: only agonist-activated receptors are desensitized
heterologous: both agonist-activated and non-activated receptors are inactivated
situation where biological response to ligand is diminished when given continuously
mechanism of desensitization
down regulation of receptors
receptor modification (phosphate, acetyl → inactive)
receptor endocytosis (internalized receptor)
inhibition of signal transduction
functions of the hypothalamus
homeostasis; food intake, metabolism, water, temperature, sleep
endocrine control; growth, stress
autonomic control; sensory processing
limbic function; memory and emotion
hypothalamus-anterior connection
tropic hormones secreted from hypothalamus into:
primary capillary plexus
portal veins to anterior pituitary
AP releases hormones into secondary capillary plexus where they reach systemic circulation
hypothalamus-posterior connection
oxytocin and ADH are synthesized in the hypothalamus:
transported down hypothalamic-hypophyseal axon tract → posterior pituitary
oxy and ADH stored in terminals in PP
released when hypothalamic nerve signals arrive
oxytocin
nonapeptide; stimulates uterine contractions during childbirth and milk let down (positive suckling feedback)
posterior pituitary
antidiuretic hormone (ADH) ((vasopressin))
osmotic balance
blood pressure
sodium homeostasis
released when:
blood high osmolarity
drop in blood pressure
decreased circulating blood volume
ADH mechanisms
binds V1a → vasoconstriction increases blood pressure
binds V2 on principal cells of collecting duct
increased aquaporin migration to lumen membrane (increased water retention)
inappropriate ADH syndrome
excess ADH = excess water reabsorption
no edema occurs → euvolemic
body counters increased fluid by increasing sodium secretion
dilutional hyponatremia
tropic anterior pituitary hormones
TSH
ACTH
FSH
LH
What factors regulate the level of concentration of circulating hormones?
rate of release
speed of metabolism (inactivation and removal from the body)
growth hormone effects
growth of all cells, skeletal muscle and bone targets
promotes protein synthesis
promotes burning fat for fuel
direct effects: metabolic and anti-insulin
indirect effects: growth promotion
GH stimulates secretion of insulin-like growth factors (IGF-1)
gonadotropins
FSH and LH post-puberty from anterior pituitary
FSH: stimulates gamete (sperm/egg production)
LH: gonadal hormones
Stimulated by gonadotropin releasing hormone from hypothalamus during puberty
Prolactin
Secreted from lactotrophs of anterior pituitary
a. Promotes growth of mammary glands
b. Stimulates milk production
c. Release is controlled by prolactin releasing hormone and prolactin inhibiting hormone (dopamine)
d. Suckling triggers prolactin positive feedback loop
Hypothalamus Pituitary Adrenal Axis
hypothalamus releases corticotropin releasing hormone (CRH)
anterior pituitary releases ACTH
adrenal cortex releases cortisol
Adrenal Gland Overview
Cortex (outer)
corticosteroids (aldosterone, cortisol)
sex hormones (androgens)
Medulla (inner)
catecholamines (epinephrine, norepinephrine)
Adrenal Cortex Layers
Outermost:
Zona Glomerulosa = Mineralocrticoids (aldosterone)
Zona Fasciculata = Glucocorticoids
Zona Reticularis = Sex Hormones
mineralocorticoids
Secreted from glomerulosa of adrenal cortex (aldosterone)
regulate Na+ and K+ levels
Na+ = ECF volume, blood pressure, blood volume
K+ = resting membrane potential of cells
Aldosterone Mech
Mineralcorticoid- Kidney Increased Water Retention
stimulates Na+ reabsorption
stimulates K+ elimination
CYP11B2
aldosterone synthase
only found in the zona glomerulosa
How does Aldosterone Reglate Na+/H2O reabsorption
activation of intracellular mineralocorticoid receptor
increased gene transcription of:
Na+ channels
Na+/K+ ATPase
more Na+ reabsorption from urine
more intracellular K+ for excretion
regulators of aldosterone release
angiotensin II
ACTH
increased plasma K+ (hyperkalemia)
Atrial Natriuretic Peptide (ANP); inhibits renin and aldosterone secretion to decrease blood pressure
Aldosterone Renin-Angiotensin Mechanism
drop in blood pressure → kidneys release renin
renin stimulates angiotensin II release
angiotensin II stimulates the release of aldosterone
primary aldosteronism
excess aldosterone production by the adrenal gland (tumors)
excessive Na+ → hypertension
depleted K+ due to excessive excretion → abnormal muscle and neuron function
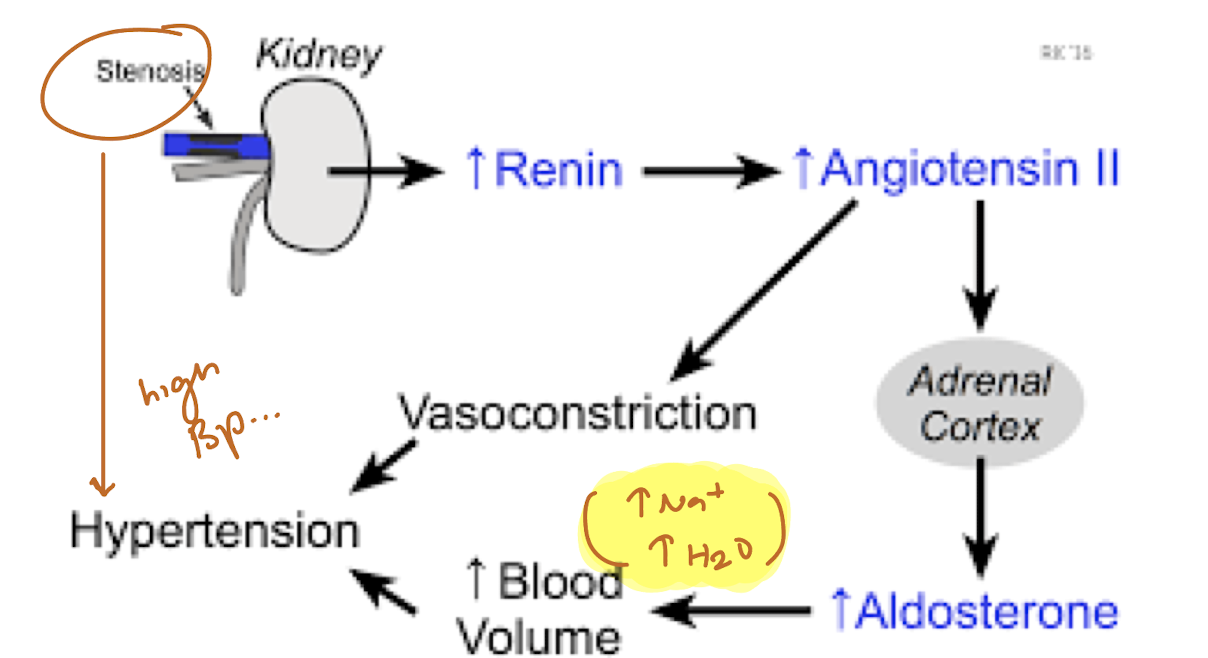
secondary hyperaldosteronism
excessive activation of renin-angiotensin-aldosterone (RAA)
caused by kidney artery stenosis
increased renin → increased angiotensin II → increased aldosterone
vasoconstriction and increased blood volume = hypertension
Glucocorticoids
Zona fasciculata adrenal cortex: stimulated by ACTH
Cortisol Primary Effect: gluconeogenesis to promote rise in blood glucose levels
keeps blood sugar levels constant
maintains blood pressure (vasoconstriction)
Cushing’s Syndrome
Hyper secretion of Cortisol
depressed cartilage/bone formation
inflammation suppression
immune system suppression
moon face/neck hump
low ACTH low CRH levels (increased cortisol neg feedback)
Addison’s Disease
Hypo cortisol syndrome
decreased glucose and Na+
weight loss, dehydration
increased ACTH increased CRH levels (unresponsive cortisol levels)
Chromaffin cells
cells of adrenal medulla
epinephrine (80%)
norepinephrine (20%)
increased vasoconstriction
increased heart rate
increased blood glucose levels
blood diversion; brain, muscles, heart
epinephrine stimulations
metabolic activities
bronchial dilation
blood flow to skeletal muscle and heart
norepi stimulations
peripheral vasoconstriction
blood pressure
regulation of growth hormone release
stimulation: GHRH binds somatotrophs AP
tetrodotoxin insenstive Na+
Ca2+ intracellular increases
exocytosis of growth hormone granules
inhibition: Somatostatin binds somatotrophs AP
opens K+ channel influx
hyperpolarize prevents growth hormone release
regulator hormones of growth hormone…
stimulators:
Ghrelin; hunger hormone of GI system
Testosterone
inhibitors:
Leptin; from adipocytes
Estrogen
growth hormone receptor layout
cytokine receptor family
dimer when bound by GH
binding = activates janus kinase (JAK2)
JAK2 promotes tyrosine phosphorylation of itself + messengers
GH Receptor JAK2 Pathways
G-Protein PLC-DAG Pathway
IRS-PI3K Pathway
STAT Pathway
RAS-MAPk Pathway
role of GH in metabolism
Protein Metabolism
increased AA uptake
increased protein synthesis
Fat Metabolism
Triglyceride Breakdown
Carbohydrate Metabolism
Gluconeogenesis
suppress insulin to prevent peripheral glucose uptake (deplete blood-glucose levels)