Ch 10
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
what is corporate governance
Rules that influence manager decision making
what is the stick method
threat of removal
what is carrot method
compensation
what are the three pillers of coporate goverance
transparency
accontability
security
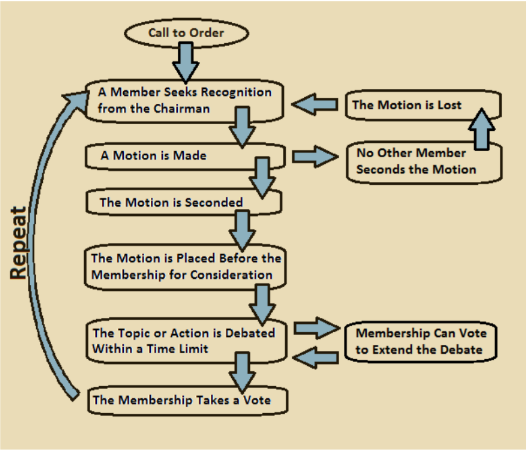
Robert’s Rules of Order
when is a agency relationship created? (2)
hiring someone to perform a service
give them decision making authority
If you are the only employee, and only your money is invested
in the business, would any agency problems exist?
NO
does a agency problem exist in these situations?
when the manager own less than 100 pf the firm’s stock
firms borrows
yes
yes
Would hiring additional people
create agency problems?
yes
who bears the costs?
manager/owner owns all the stock
outside stockholder
mangager/owner
partly the stockholder
what is agency cost or minority discount?
minority shareholder may pay less for stock
does minority shareholders have more or less say in corporate goverance
less
can borrowers make decision that affect lender? how
yes
invest in risky projects
what do if creditors anticipate possible harmful actions by stockholders (3)
higher interest rate
cost of capital goes up
value of company go down
What Actions Reduce Agency Cost of Debt? (2)
secure loan with company assets
restrictive convenants in debt agreement
examples of restrictive covenants in debt agreement (4)
maintain profitability ratios and RE
maintain debt ratios
not issuing more debt
personal guarantee
Six Potential Problems with Managerial Behavior
Expend too little time and effort or focus on the wrong things
Consume too many nonpecuniary (non-monetary) benefits
Conflict of Interest
Reject risky positive NPV projects to aviod looking bad if project falls; take a risky negative NPV projects trying to hit a homr run
Avoid returning capital to investors by making excess investments in marketable securities or by paying too much for acquisitions
Massafe information or manage earnings to avoid revaling bad news
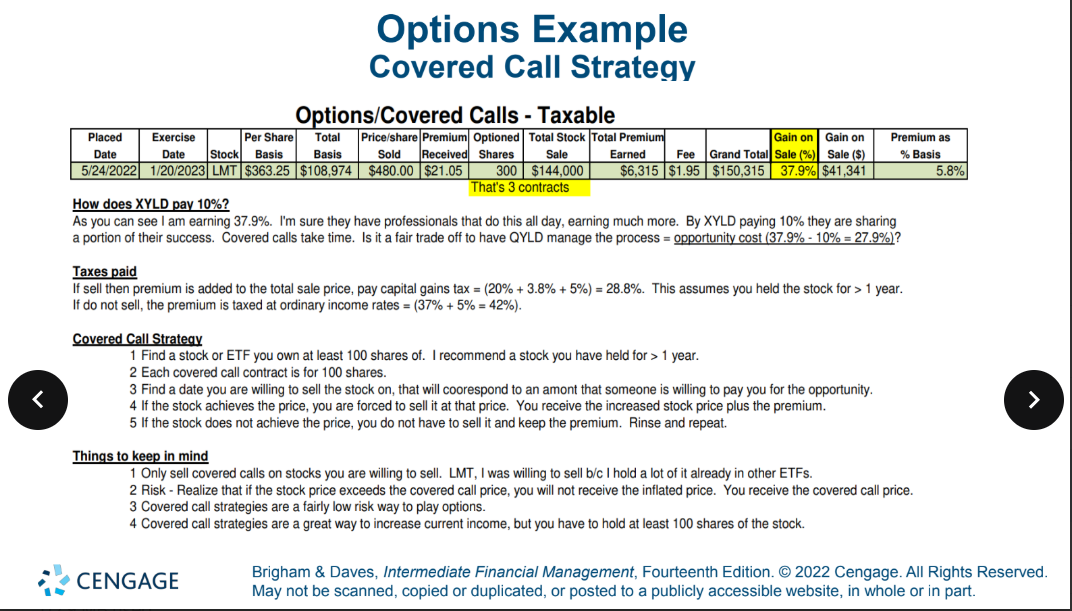
what is strike price
buy a share at a specificed price
Options that have value are called “_________”.
above or below the current stock price
would options be exericed
in the money (below current price)
below
yes
Options that have no value are called “_______”.
is price higher or lower than current stock price
will options be exercised
are the options worthless
underwater
higher
no
yes
what is a warrant?
right to buy at a certain price before a expiration date
what is the problem with manager stock options
Manager can underperform and still get rewarded from options as long as the stock price increases to above the exercise price
why is a classified board/staggered board good?
maintain institutional memory
why do you want a odd number of boardmembers?
to avoid deadlock votes
Are these effective or uneffective?
CEO is not chairman of the board (not always) and does not have undue influence over the nominating committee.
Board has a majority of outside directors (i.e., those who do not have another position in the company) with business expertise.
An inside director is a board member who also holds a managerial position in the company.
large boards
effective
effective
effective
uneffective
why do you need to aviod a interlocking board? (the ceo of one board sitting on the board of another company)
conflict of interest
what does it mean for a boardmember to be unduly busy?
too many board or too many business activities
different ways boardmembers are compsitated (4)
fixed salary
linked to firm performance or stock performance
attendance
not paid
anti-takeover provisions (3)
targeted share repurchases
shareholder rights provisions
restricted voting rights plans
what is greenmail
Target share repurchases that occur when a company buys back stock from a potential acquirer at a higher than fair market price. In return, the potential acquirer agrees not to attempt to take over the company.
what is poision pill
Shareholder rights provision allowing existing shareholders to purchase company shares at below market prices if a potential acquirer purchases a controlling interest in the firm.
what is an example of restricted voting rights plans?
own a certain amount of stock? voting rights canceled!
what is block ownership
Outside investor owns large amount/block of stock of company’s shares