Dental Anatomy Embryology Beginning
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
Odontogenesis
The process of tooth development.
Proliferation
controlled levels of cellular growth present during most of prenatal development
Appositional growth
A tissue enlarges its size by the addition of layers on the outside of a structure
Interstitial growth
Which occurs from deep within a tissue or organ
Differentiation process
A change occurs in the embryonic cells, which are identical genetically but later become quite distinct structurally and functionally.
_____ is the development of different cell types.
Cytodifferentiation
____ is the development of different histologic tissue types within a structure.
Histodifferentiation
____ is the development of the differing ____, which makes up its structure or shape, for each organ or system.
Morphodifferentiation, morphology
(Tooth Developmental Processes)
____ is the action of one group of cells on another that leads to establishment of developmental pathway in responding tissue. (Will there be a tooth or not? will a tooth be formed or not?)
Induction
____ is a controlled cellular growth and accumulation of byproducts. (Controlled cellular growth)
Proliferation
____ change in identical embryonic cells to become distinct structurally and functionally.
Differentiation
____ is the development of specific tissue structure or differing form due to embryonic cell migration or proliferation and inductive interactions
Morphogenesis
____ the attainment of adult function and size due to proliferation, differentiation, morphogenesis
Maturation
This first stage of tooth development, known as the ____, involves the physiologic process of induction, which is an active interaction between the embryologic tissue types.
Initiation stage
At the beginning of the sixth week, the embryo’s ____ is lined by ____
stomodeum (or primitive mouth), ectoderm
The outer part of the ectoderm gives rise to ____.
oral epithelium
If something goes wrong and the oral epithelium doesn’t form or function correctly:
No teeth may form at all (anodontia), or extra teeth may develop (supernumerary teeth).
Deep to the forming oral epithelium there is a type of mesenchyme known as ____ , which ids derived from neural crest cells (NCCs) that have migrated to the region.
ectomesenchyme
An important acellular structure that separates the oral epithelium and the ectomesenchyme within the stomodeum is the ____
basement membrane
During the later part of the seventh week, the oral epithelium grows deeper into the ectomesenchyme and is induced to produce a layer called the ____
dental lamina.
At this time, there are also ____ forming within each dental lamina. Each dental placode consists of plate-like thickened epithelium associated with an underlying neural crest derived mesenchyme or neuroectoderm. They function as the first signaling center for each tooth.
dental placodes
Lack of initiation within the dental lamina results in the absence of a single tooth or multiple teeth (partial) or an entire dentition (complete), producing ____ or hypodontia.
Anodontia
However, ____ is more common and most commonly occurs with the permanent third molar, maxillary lateral incisor, and mandibular second premolar.
partial anodontia
Anodontia can be associated with the syndrome of ____ because many of the components of the tooth germ are indirectly or directly of ectodermal origin. Occurs in initial stage.
ectodermal dysplasia
____ is a group of conditions in which there is abnormal development of the skin, hair, nails, teeth, or sweet glands.
Ectodermal dyplasia
Abnormal initiation may result in the development of one or more extra teeth, which are considered _____. There extra teeth are initiated from persisting clusters of the dental lamina and have a hereditary etiology.
supernumerary teeth or (hyperdontia).
Certain regions of both dentitions commonly have supernumerary teeth, such as between the maxillary central incisors (____), distal to the maxillary third molars (____,____), and in the premolar region (____) of both dental arches. (Listed in order of occurrence).
mesiodens, distomolar or “fourth molar, and perimolar
This stage is named for an extensive proliferation of the dental lamina into buds, with these three-dimensional oval masses penetrating into the surrounding ectomesenchyme.
Bud stage
Clinical Considerations with Bud Stage Disturbances
Abnormal proliferation can cause a single tooth or multiple teeth (partial) or the entire dentition (complete) to be larger or smaller than normal.
Abnormally large teeth result in ____. Abnormally small teeth result in ____.
Macrodontia, microdontia.
With true partial microdontia, hereditary factors are involved, and teeth commonly affected are the ____ and _____
permanent maxillary lateral incisor (peg lateral) and Permanent third molar (peg molar)
Complete ____ of either dentition rarely occurs but can be associated with hypopituitarism or Down Syndrome. In contrast, systemic conditions such as childhood hyperpituitarism (or gigantism) can produce complete ____.
Microdontia, macrodontia
What happens during the cap stage of tooth development?
There is unequal growth in parts of the tooth bud, forming a three-dimensional cap shape over the ectomesenchyme, still attached to superiorly to the dental lamina.
At the same time, different types of cell differentiation occur —
Cytodifferentiation (cells becomes specialized)
Histodifferentiation (tissues form)
Morphodifferentiation (the shape of the tooth develops.
What is the predominant psychologic process during the cap stage of tooth development?
During the cap stage, a tooth germ (the early form of the tooth) develops, containing all the tissues needed to form the future tooth.
The main process happening in this stage is morphogenesis, which means the shaping and organization of the tooth’s form.
Where does enamel come from?
Enamel comes from the ectoderm - it’s an ectodermal product.
What structures develop from the dental sac, and what separates it from the enamel organ?
The dental sac forms the periodontium, which includes the cementum, periodontal ligament, and alveolar process.
A basement membrane separates the enamel organ from the dental sac.
Where do the primordia of the permanent teeth develop in relation to the primary tooth germs, and what is this site of origin called?
The primordia of the permanent teeth form as an extension of the dental lamina into the ectomesenchyme, lingual to the developing primary tooth germs. This site of origin is called the successional dental lamina.
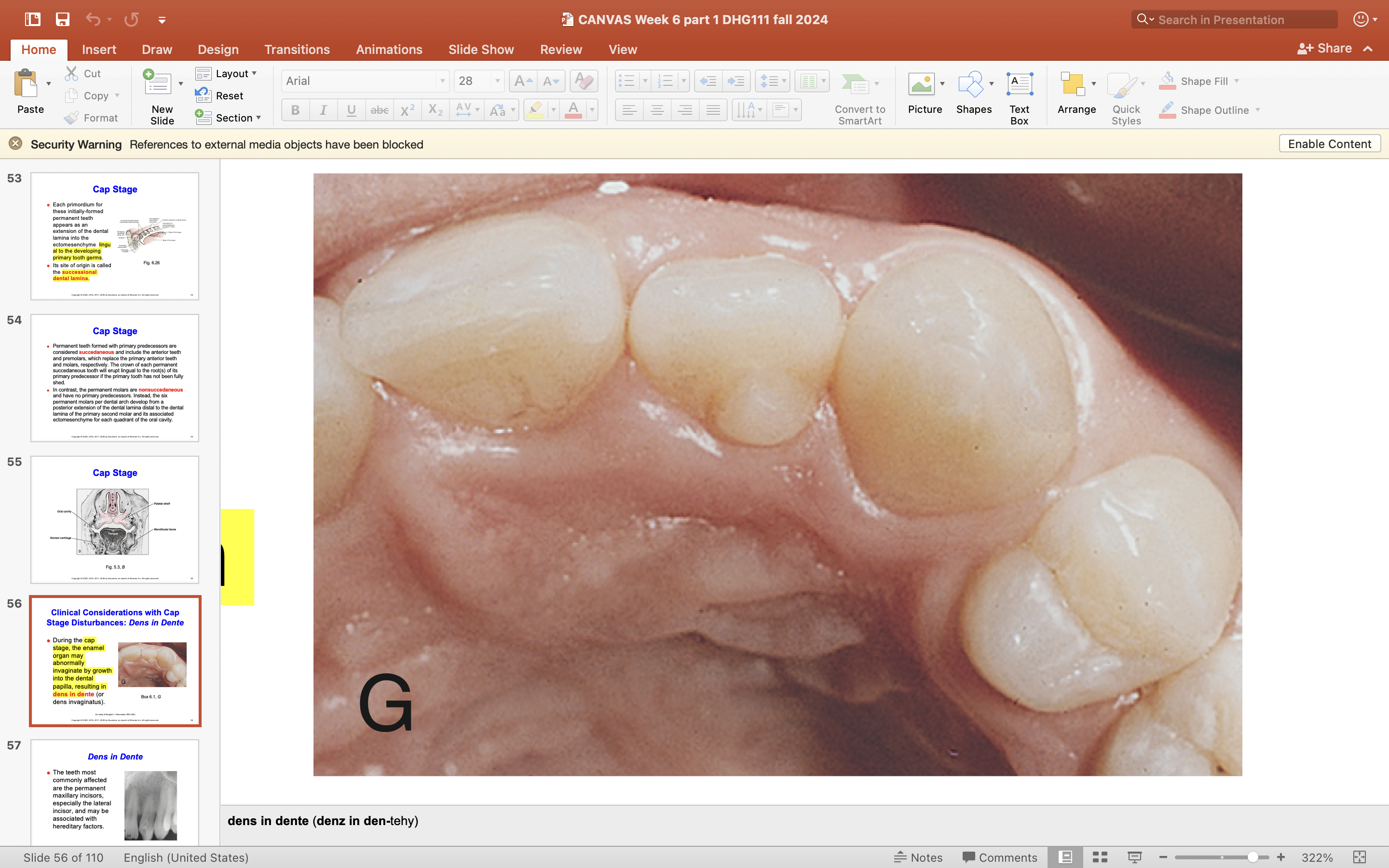
Clinical considerations with Cap Stage Disturbances
What developing disturbance can occur during the cap stage when the enamel organ invaginates by growth into the dental papilla?
During the cap stage, the enamel organ may abnormally grow inward into the dental papilla, causing a condition called dens in dente (or veins invaginatus).
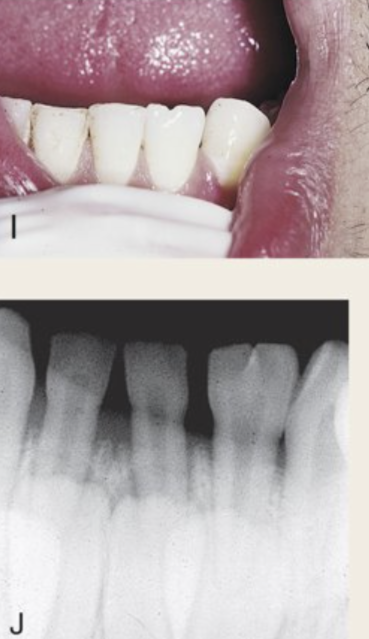
Tooth germ tries to divide and develops large single-rooted tooth with one pulp cavity and “twinning” commonly affecting crown of anteriors with correct number in primary or permanent dentition.
Hereditary
Clinical ramifications: Esthetic and spacing complications treated by orthodontic therapy
Gemination (I,J)
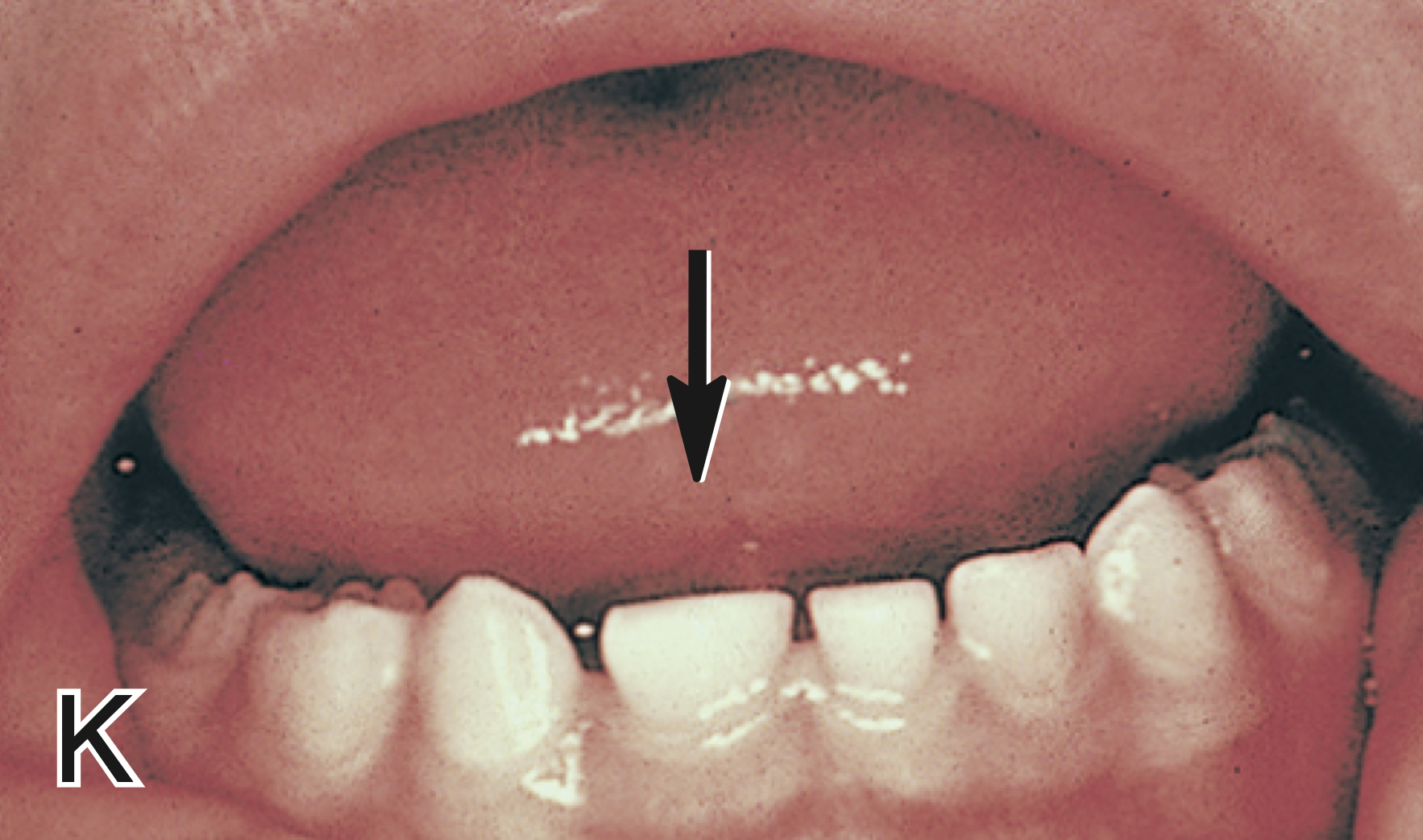
What is fusion in teeth?
Fusion results from the union of two adjacent tooth germs, possibly due to pressure, creating a broader, falsely macrondontic tooth similar to gemination. (Two combined into one)