Cardiovascular System
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/119
Last updated 12:05 AM on 4/4/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
120 Terms
1
New cards
What does blood transport?
Dissolved gasses, nutrients, hormones, and watsters to and from all tissues of the body
2
New cards
What does blood regulate?
Body temperature, pH, and electrolyte levels
3
New cards
Coagulate
Bloods response to an injury through the use of enzymes and other proteins.
4
New cards
How do white blood cells provide immunity?
Disabling and removing bacteria, viruses, and other foreign compounds
5
New cards
How does blood stabilise body temperature?
Absorbing heat from muscles and distributing it throughout the body
6
New cards
The three components blood is made of
Plasma, White blood cells and platelets, and Red blood cells
7
New cards
Plasma
A mixture of 92% water, proteins, nutrients, electrolytes, and wastes
8
New cards
Three proteins in plasma…
Albumin, Globulin, and Fibrinogen
9
New cards
Albumin
Helps the transportation of lipids
10
New cards
Globulin
Includes antibodies that attach to bacteria and viruses
11
New cards
Fibrinogen
Part of blood clotting
12
New cards
Erythrocytes (Red Blood Cells)
Transport oxygen from the lungs to body cells and contrints hemoglobin
13
New cards
Hemoglobin
A protein that binds to oxygen and causes the red colour of blood and red blood cells
14
New cards
Leukocytes (White Blood Cells)
Circulate throughout blood and fight disease and infection. They are larger than red blood cells and have a nucleus
15
New cards
Platelets
Fragments of cells that aid in blood clotting
16
New cards
Spleen
An abdominal organ that removes and recycles old red blood cells, holds a reserve of blood, produces antibodies, and filters bacteria and viruses
17
New cards
Antibodies
Proteins that attach to and disable bacteria and viruses
18
New cards
Lymph nodes
Contain large numbers of leukocytes that help to filter bacteria, viruses, foreign particles, and cancer cells.
19
New cards
Hematopoiesis (Erythrocyte Production)
Occurs within the red bone marrow, and is regulated by the kidneys
20
New cards
\[Negative feedback cycle\] Drop in blood O2 levels
Kidneys release the hormone erythropoietin, blood marrow releases more red blood cells
21
New cards
\[Negative feedback cycle\] Normal O2 levels
Kidneys stop producing erythropoietin, blood cell production stops
22
New cards
Antigens
The proteins that the surface of each red blood cell is covered with
23
New cards
ABO blood type
Determined by the presence of A and B antigens
24
New cards
Positive or Negative
Blood type is determined by the presence of the Rh antigen
25
New cards
Agglutination Test
Where antibodies are added to a blood sample to test what type of blood someone has.
26
New cards
What indicates a positive result in an agglutination test?
Clumping of the blood
27
New cards
Transfusions
Transfer donated blood from one individual to another
28
New cards
Hemolytic Reaction
Takes place when the immune system of the recipient attacks the blood cells from the donor
29
New cards
How can a patient safely receive blood?
Blood that contains the same antigens as them or fewer
30
New cards
What blood type is the universal donor and why?
O- because it will not cause a reaction in any patient
31
New cards
What blood type is the universal reciever and why?
AB+ because these patients can safely receive any blood type
32
New cards
Complete Blood Count (CBC)
A test that analyses the number of each blood cell and platelet
33
New cards
Anemia
Lack of red blood cells and/or hemoglobin
34
New cards
Iron Deficiency Anemia
Limits the production of erythrocytes
35
New cards
Pernicious Anemia
Caused by a deficiency in B vitamins
36
New cards
Sickle-Cell Anemia
A genetic disorder that causes misshapen erythrocytes
37
New cards
Polycythemia
A condition where the percentage of red blood cells is too high. Results in high blood pressure and a risk of blood clot formation
38
New cards
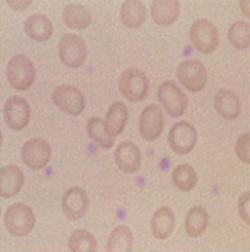
Anemia
39
New cards
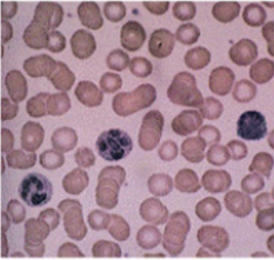
Normal Blood
40
New cards
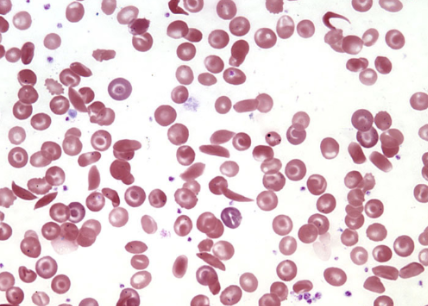
Sickle-Cell Anemia
41
New cards
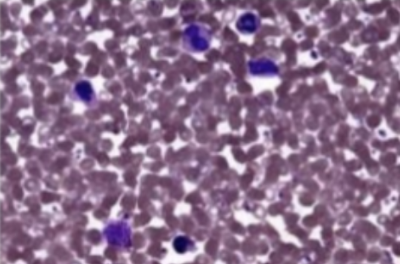
Polycythemia
42
New cards
Leukemia
a form of cancer that causes an overproduction and release of immature white blood cells
43
New cards
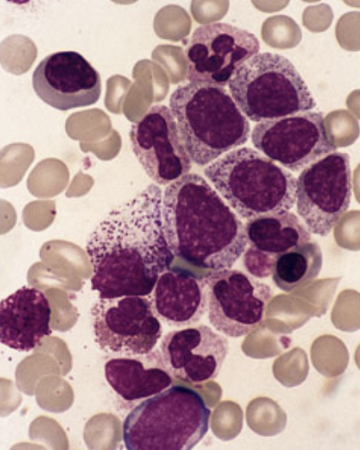
Leukemia
44
New cards
Circulatory System
Includes the heart and all blood vessels that circulate throughout the body
45
New cards
Pulmonary Circuit
Carried blood between the lungs and the heart
46
New cards
Systemic Circuit
Carries blood between the heart and the rest of the body
47
New cards
Heart
A muscular organ that serves as a double-pump for blood
48
New cards
What side of the heart pumps blood through the pulmonary circuit?
The Right Side
49
New cards
What side of the heart pumps blood through the systemic circuit?
The Left Side
50
New cards
Tricuspid Valve prevents…
Right Atrium and ventricle from backflow
51
New cards
Mitral Valve prevents…
Left atrium and ventricle from backflow
52
New cards
Aortic Valve prevents….
Aorta and left ventricle from backflow
53
New cards
Pulmonary Valve prevents…
Right ventricle and pulmonary trunk
54
New cards
Coronary Arteries
Supple the heart muscle with oxygen
55
New cards
Coronary sinus
Deoxygenated blood from the heart muscle is collected here in the right atrium
56
New cards
\[Pacemaker\] Sinoatrial Node
Originated an electrical impulse, which travels across the atria
57
New cards
\[Pacemaker\] Atrioventricular Node
Receives the signal and passes i through two bundle branches
58
New cards
\[Pacemaker\] Bundle Branches
Transmit an impulse towards the apex
59
New cards
Purkinje Fibers
Carry the contraction impulse through the muscle of the right and left ventricles, causing them to contract
60
New cards
Electrocardiograms (ECGs)
Measure electrical impulses coming from the heart, creating a graph of the output
61
New cards
P Wave
Atria Contact
62
New cards
QRS Wave
Ventricles Contract
63
New cards
T Wave
Ventricles relax and rest
64
New cards
What is the normal resting heart rate for most people?
60-100 bpm
65
New cards
Bradycardia
Heart rate that is below 60 bpm
66
New cards
Tachycardia
A contraction of the ventricles or atria at a rate above 100bpm
67
New cards
Heart attack
Caused by a blockage in one of the coronary arteries, disrupting flow of oxygenated blood to the heart muscle
68
New cards
Coronary Bypass
Transplants a vein from another part of the body (usually the leg) onto the heart. The blood gets rerouted around the blockage
69
New cards
Angioplasty
A narrow balloon is inserted into the blocked vessel. It is then inflated, expanding the vessel
70
New cards
Stent
If a vessel does not stay expanded on its on, the mesh-like object can be inserted to hold it open
71
New cards
Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
An abnormal thickening of the heart muscle wall, which decreases the heart’s ability to pump blood
72
New cards
Arteries
Carry blood AWAY from the heart
73
New cards
Veins
Carry blood TOWARDS the heart
74
New cards
Capillaries
Move blood from the arteries to veins, and allow the diffusion of oxygen and carbon dioxide
75
New cards
What had a smaller lumen, but a thicker wall of smooth muscle and elastic fibers?
Arteries
76
New cards
What has a larger lumen, with a thin layer of muscle and elastic fibers?
Veins
77
New cards
Valves
Only in veins to prevent backflow as blood flows upwards
78
New cards
What has the smallest lumen, often just large enough for blood cells to move through single file
Capillaries
79
New cards
Blood Pressure
A measurement of the pressure inside of the large arteries of systemic circulation
80
New cards
Systolic Pressure
Peak pressure caused by the contraction of the ventricles in the heart
81
New cards
Diastolic Pressure
Low pressure caused by the refilling of the ventricles in the heart
82
New cards
What is the normal blood pressure range?
120-140 / 80-90
83
New cards
Atherosclerosis
A buildup of lipids, calcium, or cell debris that gradually restricts blood flow
84
New cards
Aneurysm
A weakening of the wall of a blood vessel, causing it to bulge outwards. It can lead to the vessel bursting and/or the formation of a thrombus. More likely when a patient has high blood pressure, atherosclerosis, or a history of smoking
85
New cards
Hemostasis
The stoppage of bleeding from a break in a blood vessel
86
New cards
Platelet Plug
When Platelets attach to the wall of a broken blood vessel
87
New cards
Thrombin
A plasma protein that platelets activate
88
New cards
Fibrin
Sticks to the plug, Thrombin activates it
89
New cards
How much blood would you have to lose for Hemorrhagic shock?
More than 30%
90
New cards
How much blood can you lose with few side effects?
Less than 15%
91
New cards
Hemophillia
A hereditary disorder that impairs the body’s ability to control blood clotting. Results in minor injuries always being serious issues
92
New cards
Thrombus
A blood clot in a vessel that us not broken
93
New cards
Embolus
A thrombus that breaks away, floats in the bloodstream, and clogs a vessel farther away (e.g. the brain)
94
New cards
Hematoma
A swelling of clotted blood within a tissue
95
New cards
Foramen Ovale
Lungs are nonfunctional and are bypassed by the hole (fetal circulation)
96
New cards
Umbilical Cord
Transports oxygenated blood from the mother to the placenta
97
New cards
Umbilical Arteries
Transports deoxygenated blood from the placenta back to the mother
98
New cards
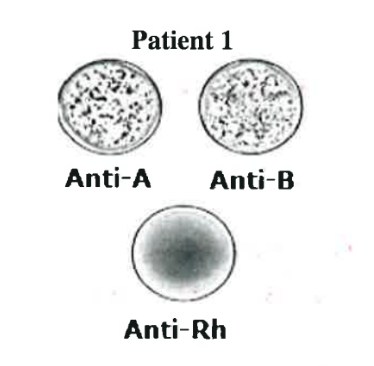
AB-
99
New cards
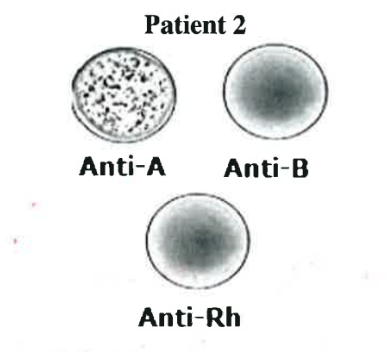
A-
100
New cards
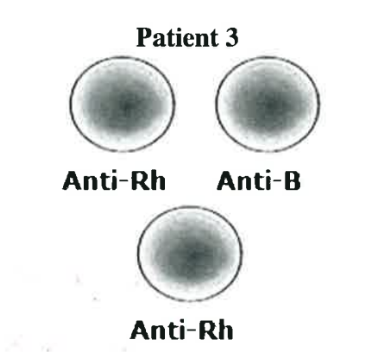
O-