Body Regions
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
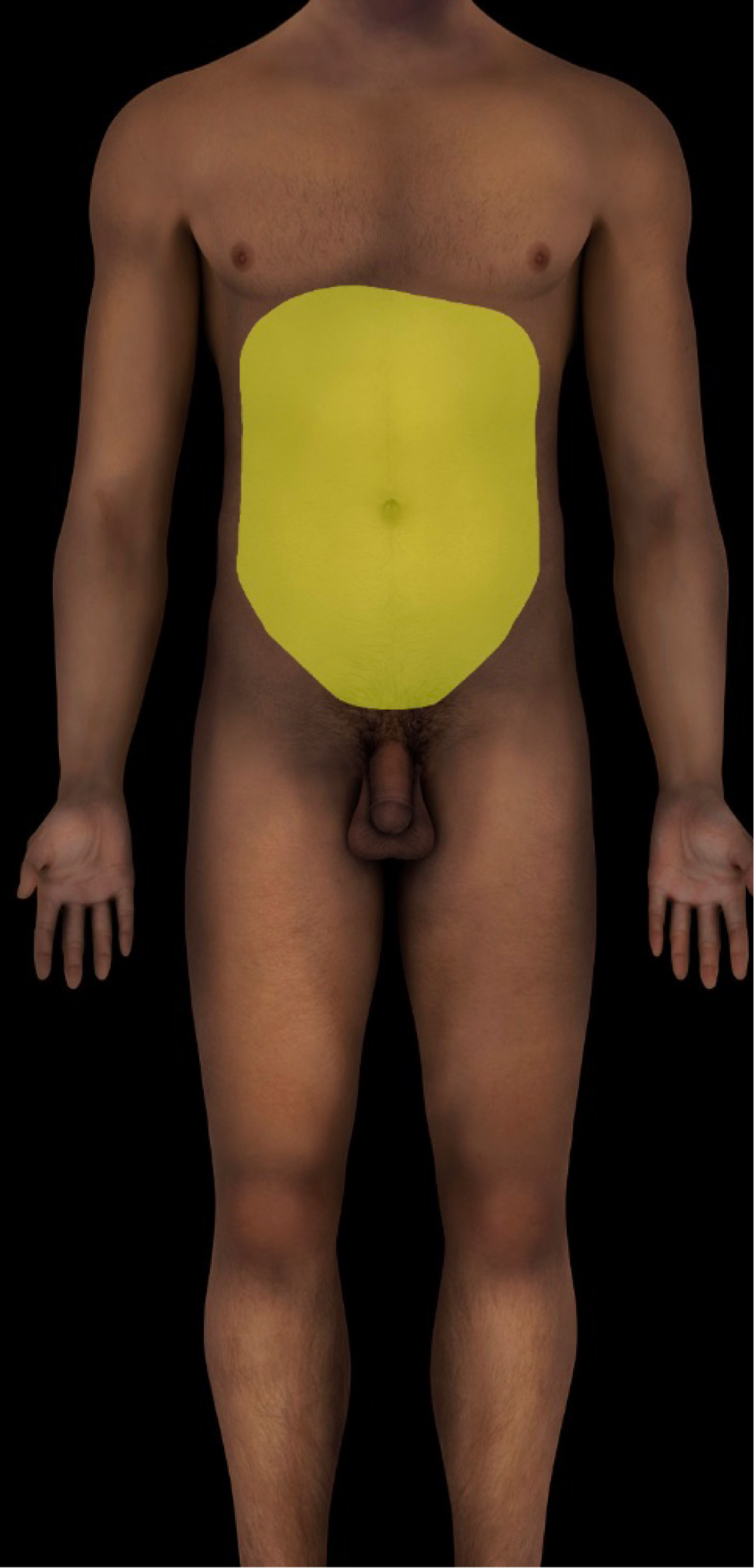

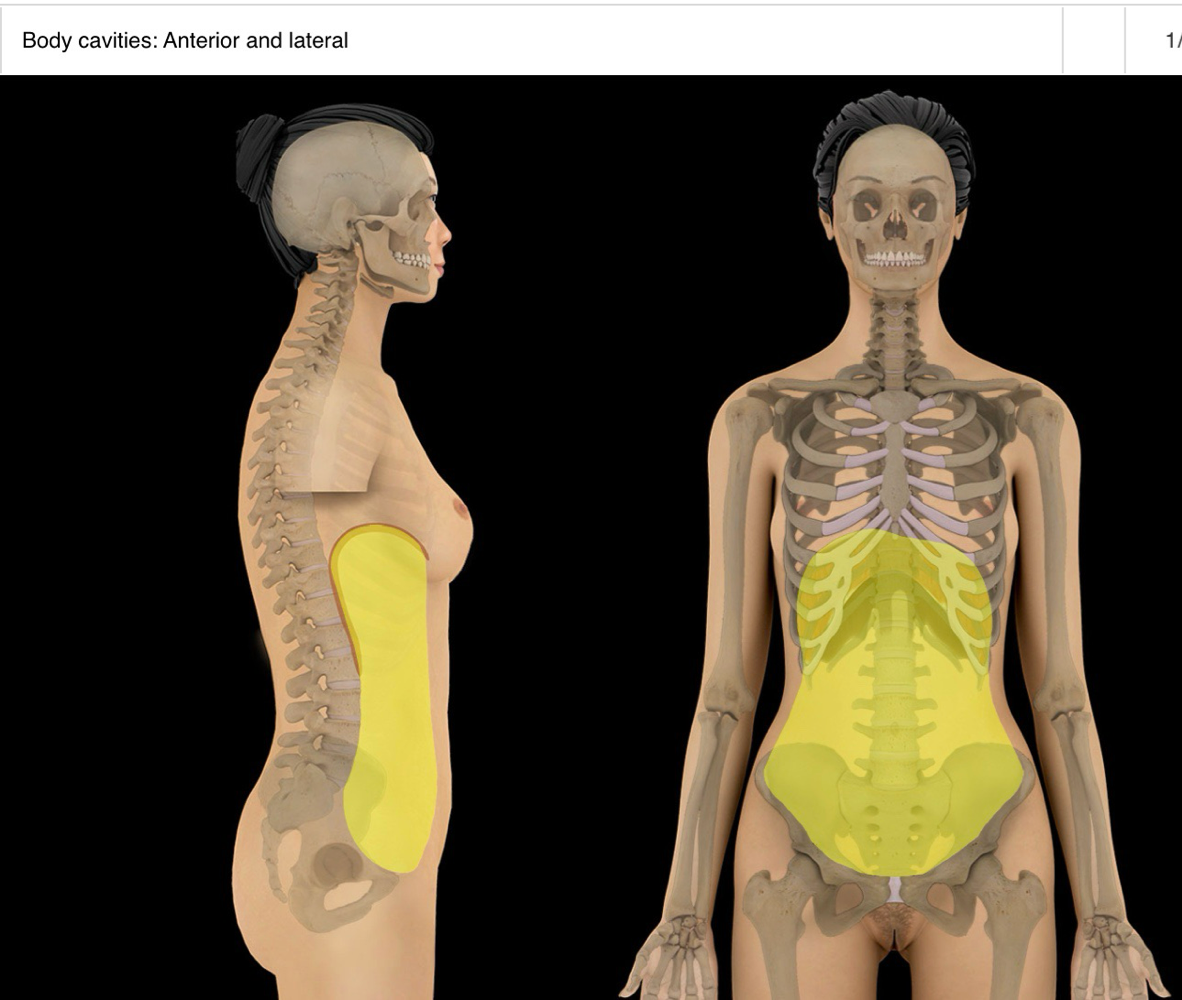
abdominal cavity
-bounded by abdominal walls, thoracic diaphragm (superior), and pelvic brim (inferior)
-major organs include:
stomach
intestines
liver
gallbladder
spleen
pancreas
kidneys + ureters
suprarenal planes
aorta
inferior vena cava
lumbar nerve plexus
-locale: abdominal region
-inferior part of abdominal cavity is the greater (false) pelvis (eg btwn iliac fossa, superior to pelvic inlet)
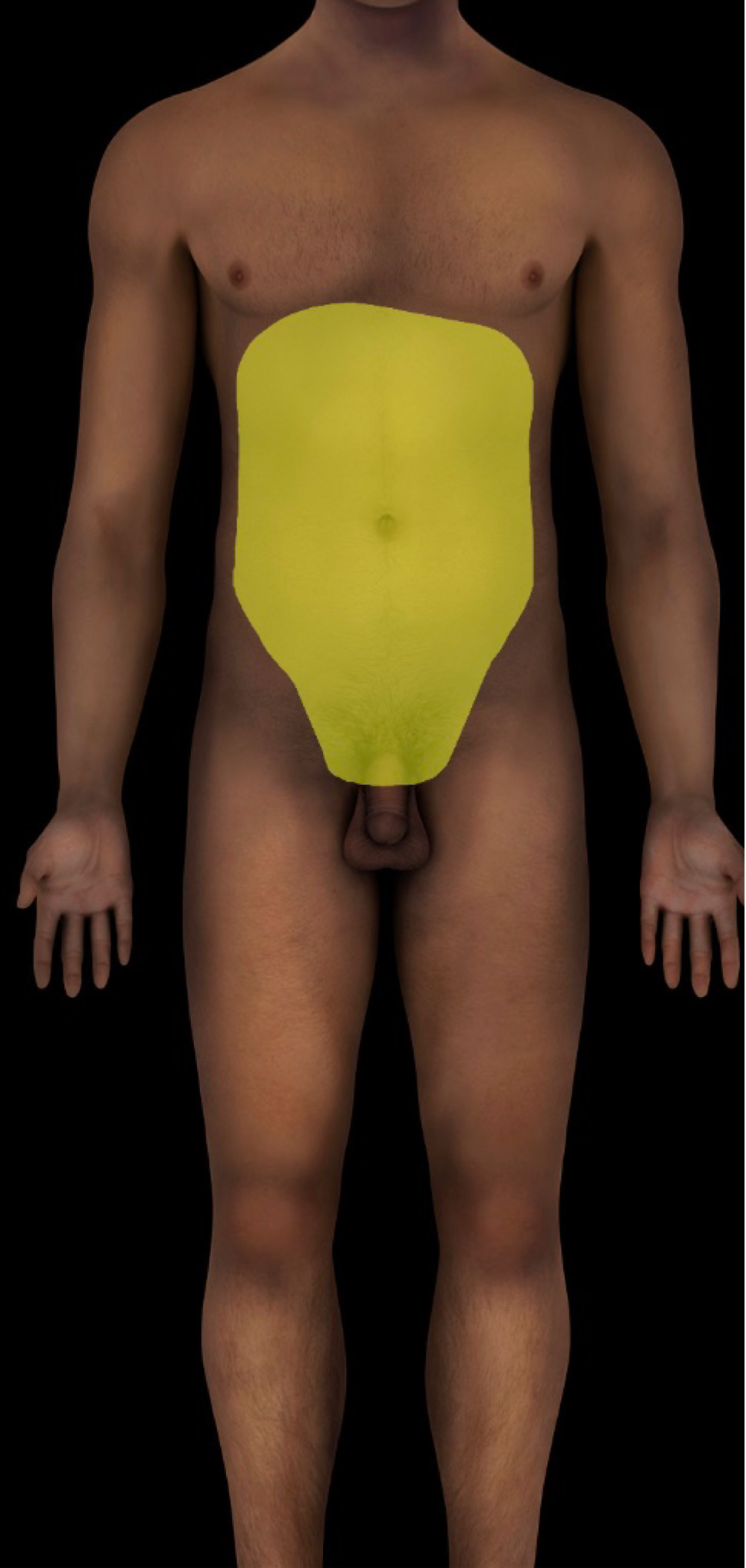

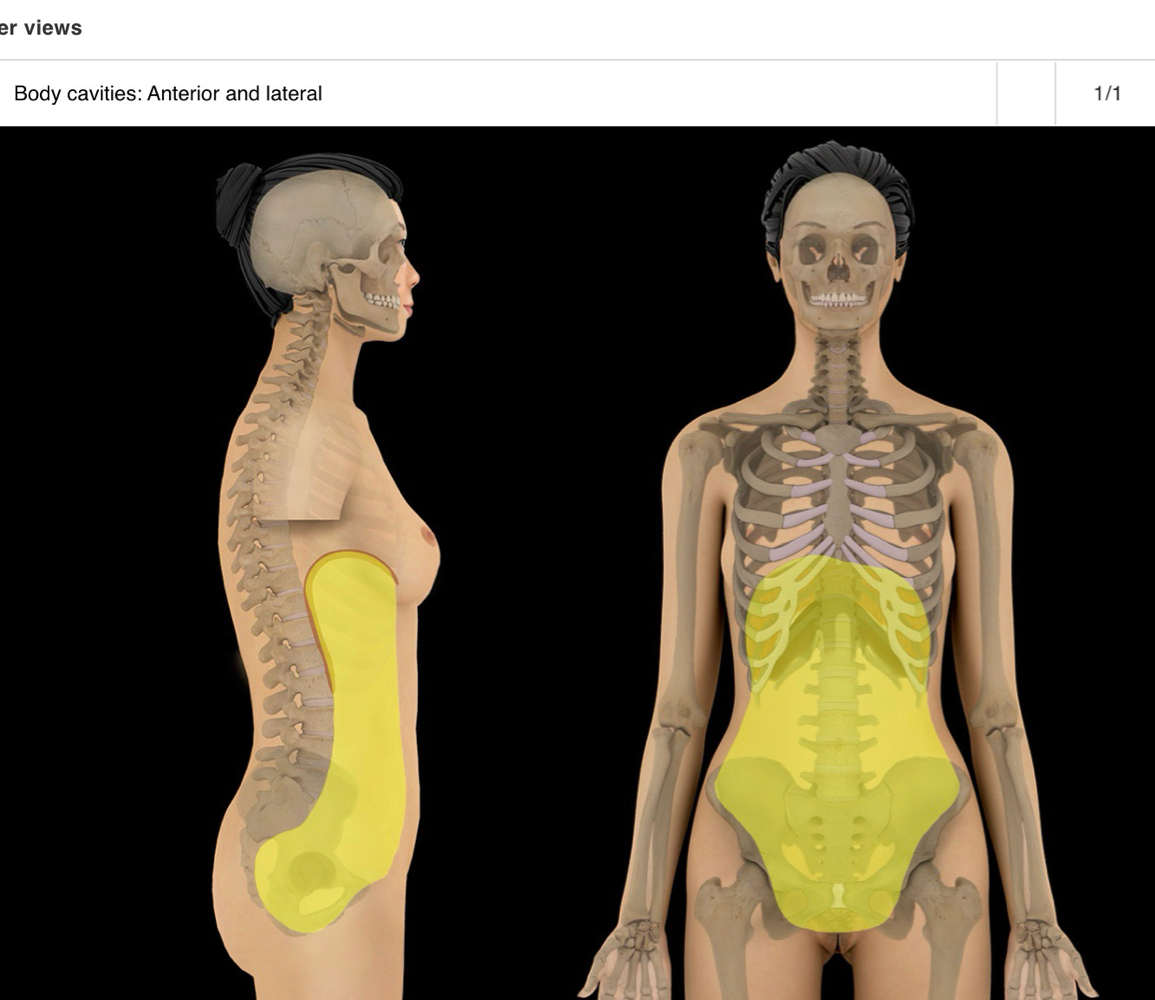
abdominopelvic cavity
-continuous cavity formed by abdominal and pelvic cavities
-locale: trunk, btwn thoracic and pelvic diaphragms
-major abdominal organs:
stomach
intestines
liver
gallbladder
spleen
pancreas
kidneys + ureters
suprarenal planes
aorta
inferior vena cava
lumbar nerve plexus
-major pelvic organs:
urinary bladder
loops of small intestine
interior part of sigmoid colon
rectum
reproductive organs:
ovaries, uterus, vagina - female
prostate and seminal glands.- male
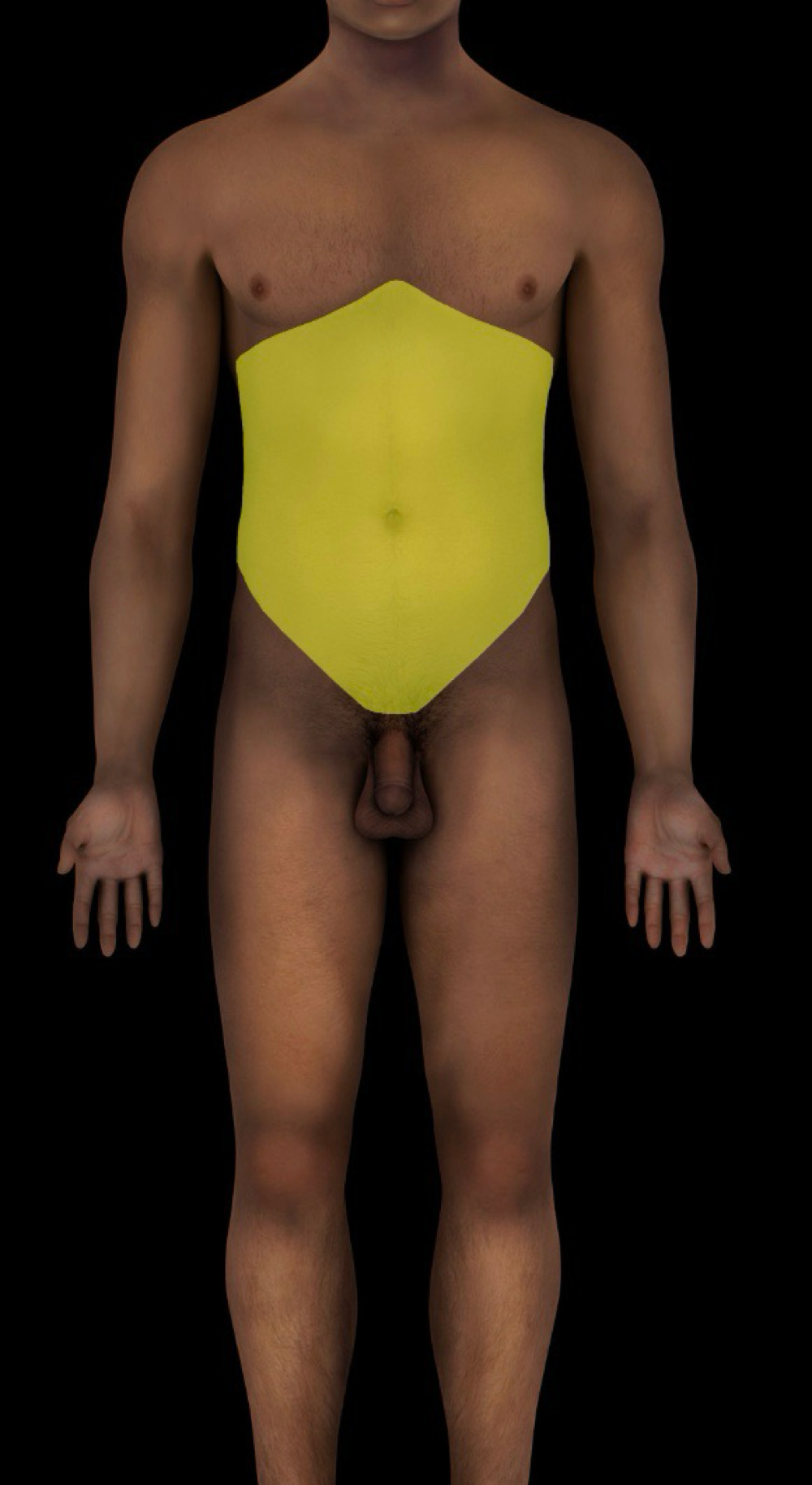

abdominopelvic region
topographic (surface) subdivision of trunk
-locale: trunk, inferior to thoracic region
-abdominal cavity contains:
stomach
most of intestines
liver
gallbladder
spleen
pancreas
kidneys and ureters
suprarenal glands
inferior vena cava
-greater (false) pelvic cavity (inferior part of abdominal cavity) is located btwn iliac fossae, superior to pelvic inlet
-lesser (true) pelvic cavity is located between pelvic inlet (superiorly) and pelvic outlet (interiorly) and it contains:
urinary bladder
reproductive organs: (ovaries, uterus, vagina - females) (prostate, seminal vesicles - males)
loops of ileum
sigmoid colon
rectum
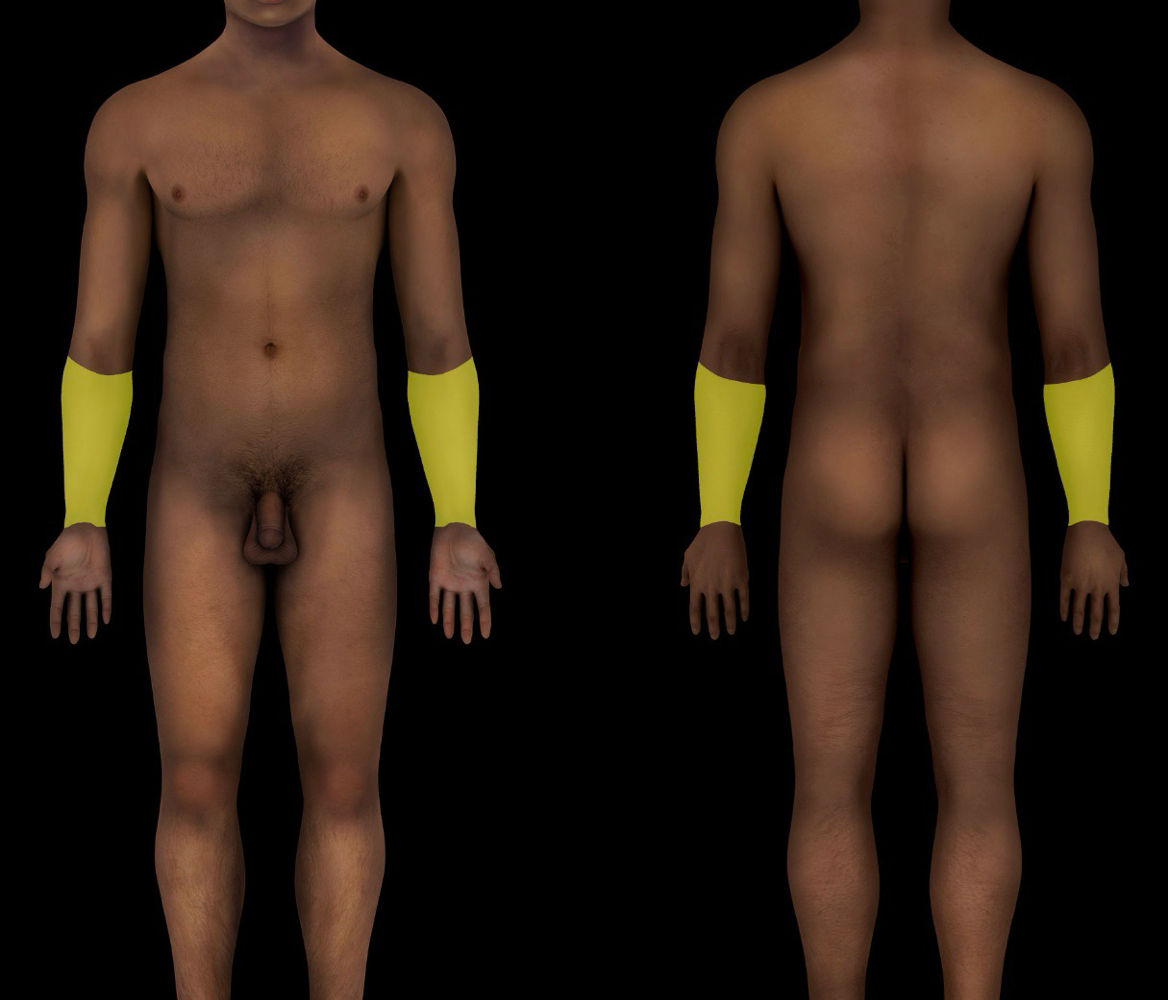
antebrachial region
-subdivision of upper limb
-contains:
skin
nerves
muscles
vessels around radius and ulna
-locale: upper limb (distal); btwn elbow and wrist joints
-aka - forearm region

auricular region
-region of external ear
-locale: head (external cranial region)
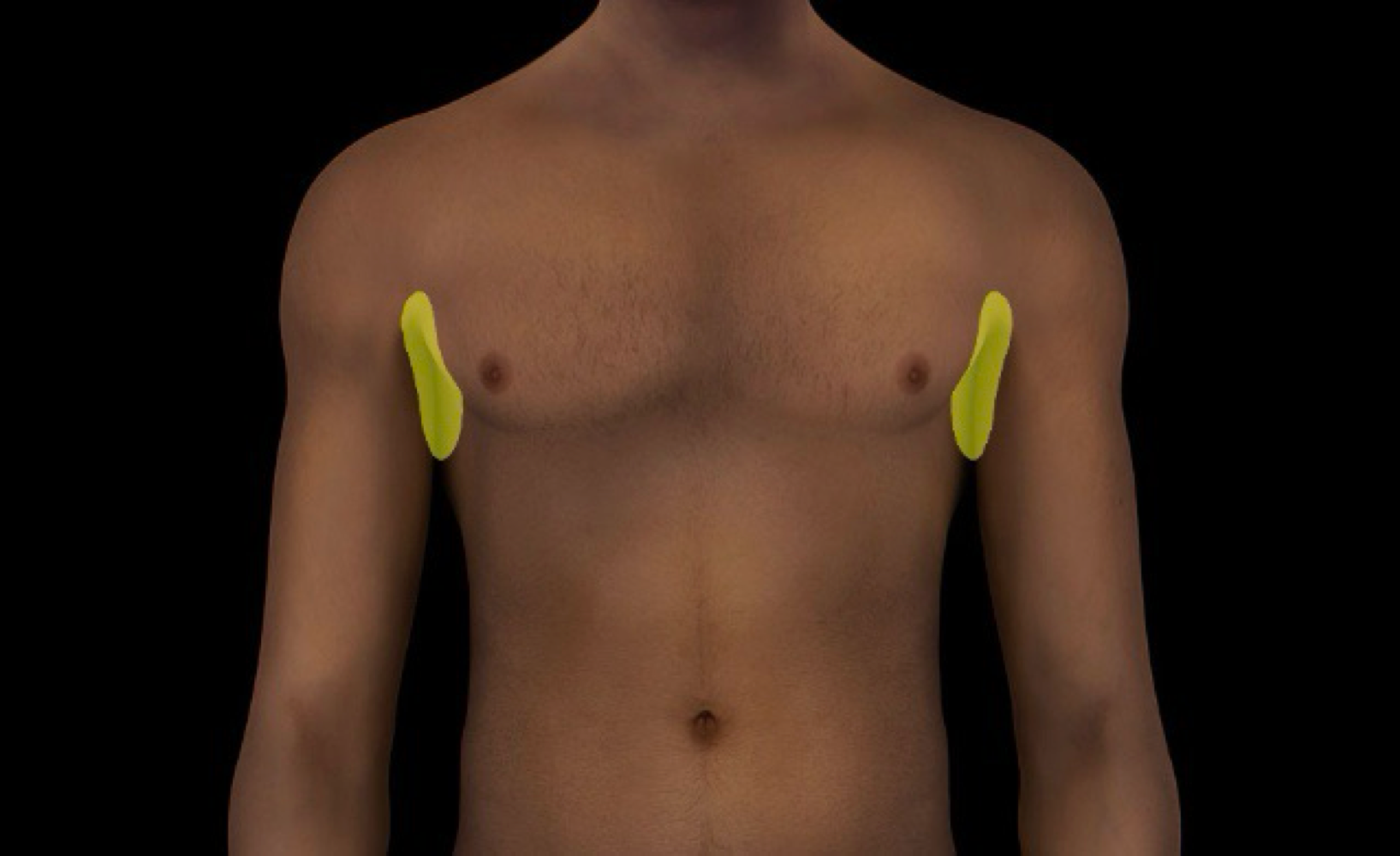
axillary region
-subdivision of thoracic region that includes axilla
-axilla is a pyramidal space
-anterior boundary: pectoralis muscles and claripectoral fascia
-posterior boundary: scapula and subscapularis, teres major, and latissimus dorsi muscles
-medial boundary: serratus anterior and upper lateral thoracic wall (ribs 1-4 intercostal muscles)
-lateral boundary: humerus (intertubercular sulcus)
-locale: thoracic region (inferior to shoulder joint); btwn upper arm and lateral thoracic wall
-base:
skin
subcutaneous tissue
axillary (deep) fascia
-apex: passage btwn neck and upper limb (cercivoaxillary canal) formed by rib1, clavical, and superior border of scapula
-contents of axilla:
axillary artery, vein and nerves
intraclavicular part of brachial plexus
areolar tissue
-axilla aka - armpit
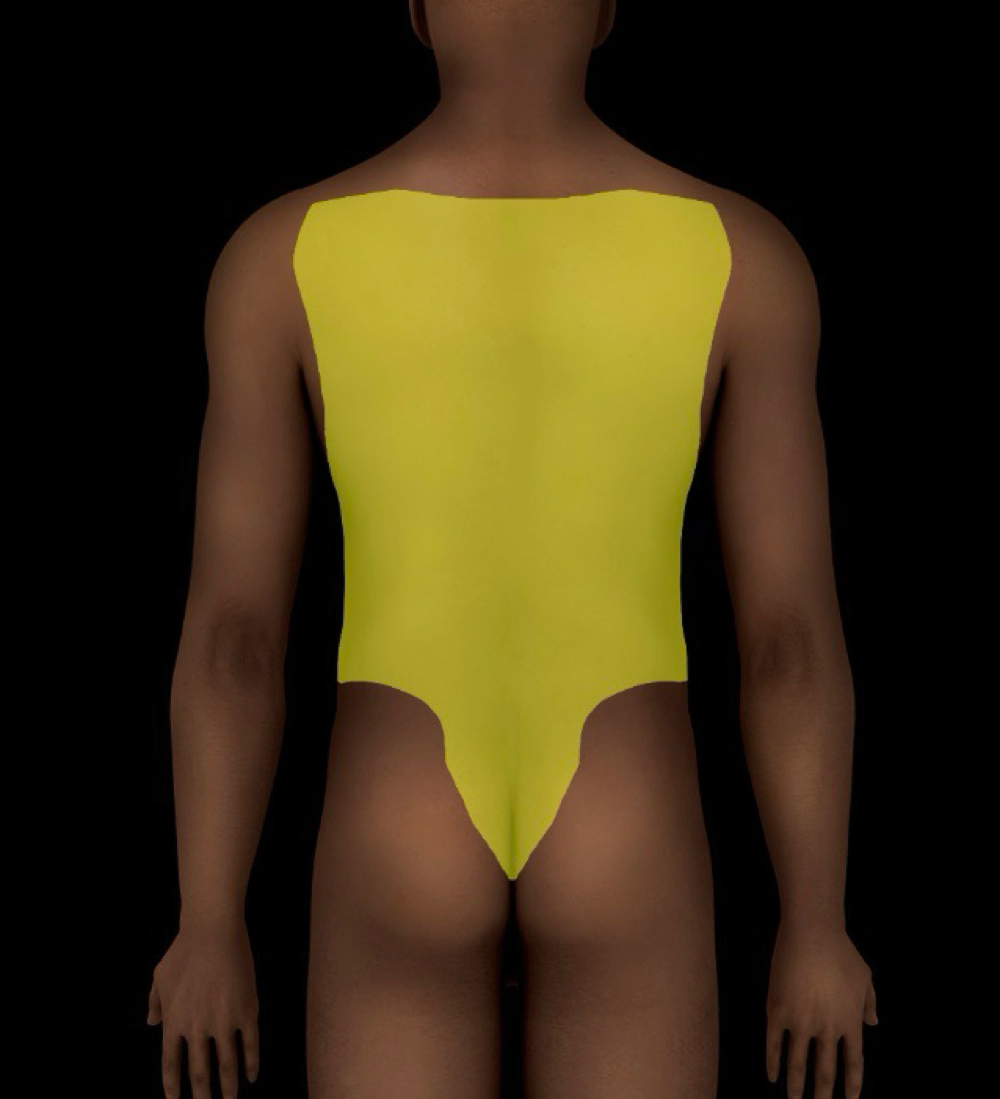

back
-formed by skin and subcuteneous tissue, muscles, vertebrial column (inferior to cervical region), ribs (thoracic region) and spinal cord and meninges
-locale: trunk (posterior); between neck region and tip of coccyx
muscles in back include extrinsic group that acts on upper limb and intrinsic group that acts on vertical column and head
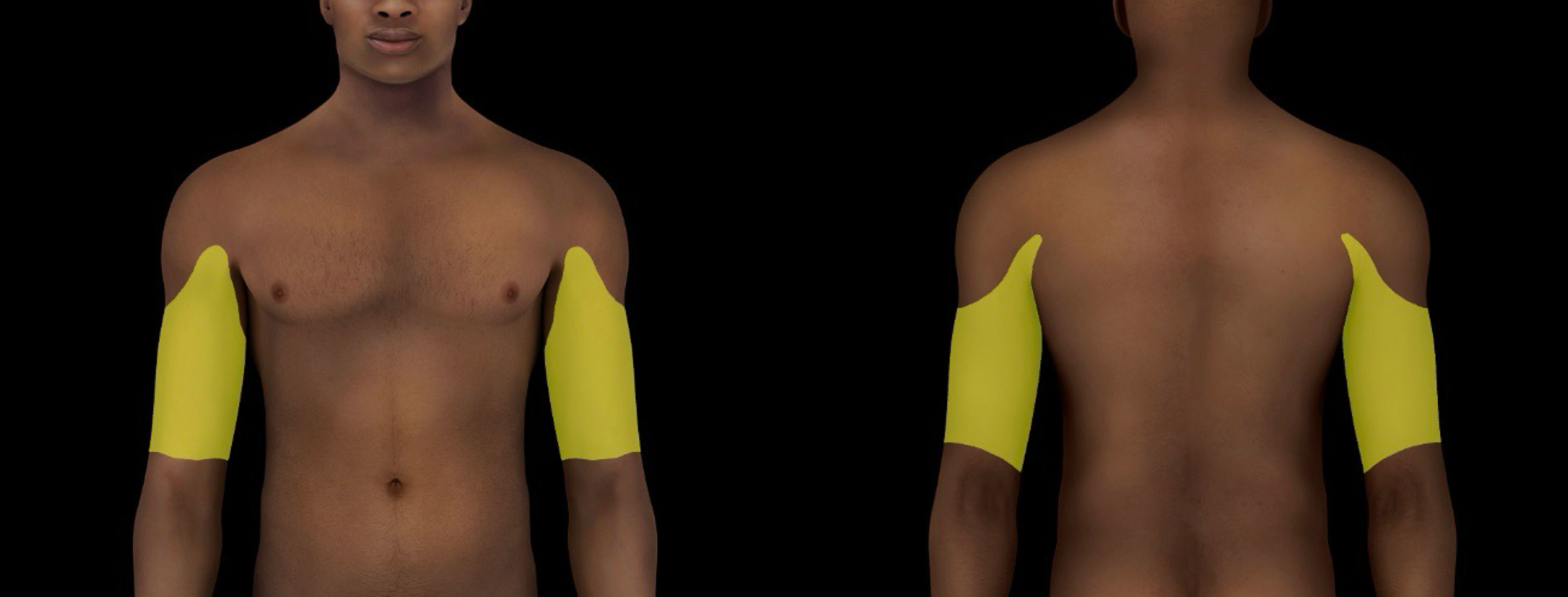
brachial region
-subdivision of upper limb
-contains:
skin
muscles
nerves
vessels around humerus
-local: upper limb (proximal); between glenohumeral (shoulders) and elbow joint
-aka - arm region
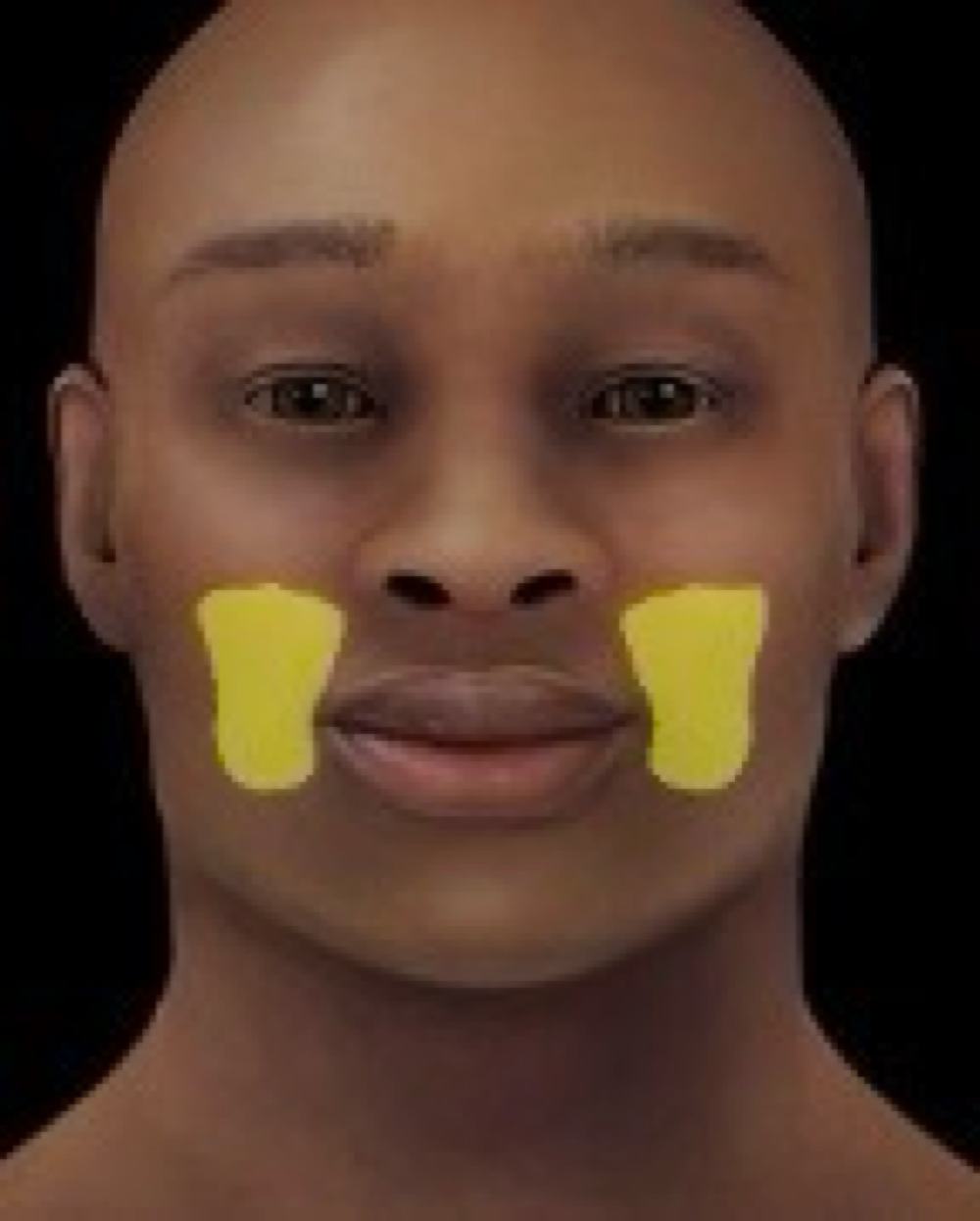

buccal region
-region of cheek
-locale: head (lateral face)
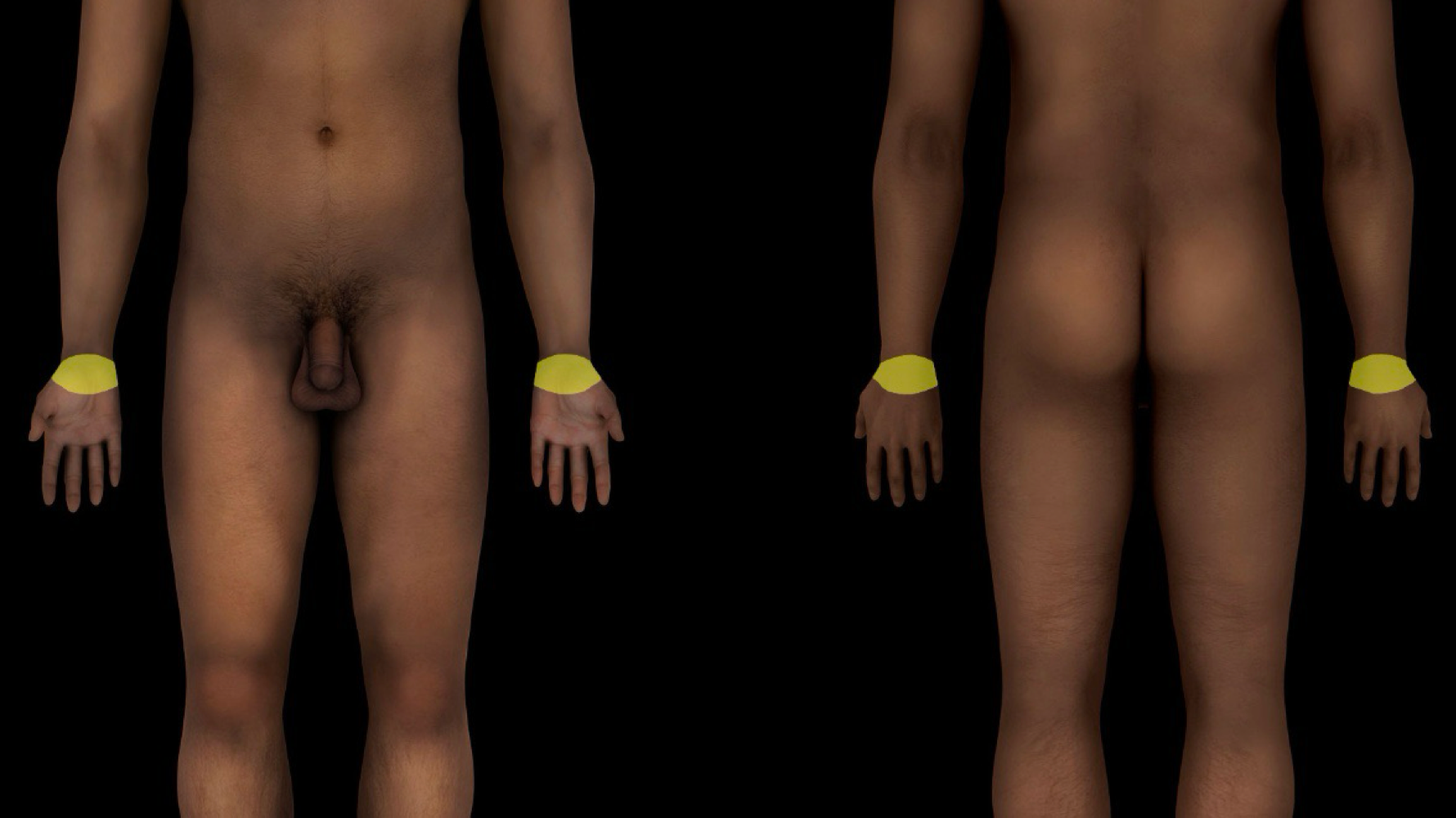
carpal region
-skin, muscles, nerves, and vessels around carpal bones
-locale: upper limb (distal); between antebrachial and hand regions
-aka - wrist region
-wrist joint distinct from carpal region, includes articulations between distal ends of radius and ulna and proximal row of carpal bones (i.e., scaphoid, lunate, and triquetrum)
-carpal (intercarpal) joints include articulations between carpal bones
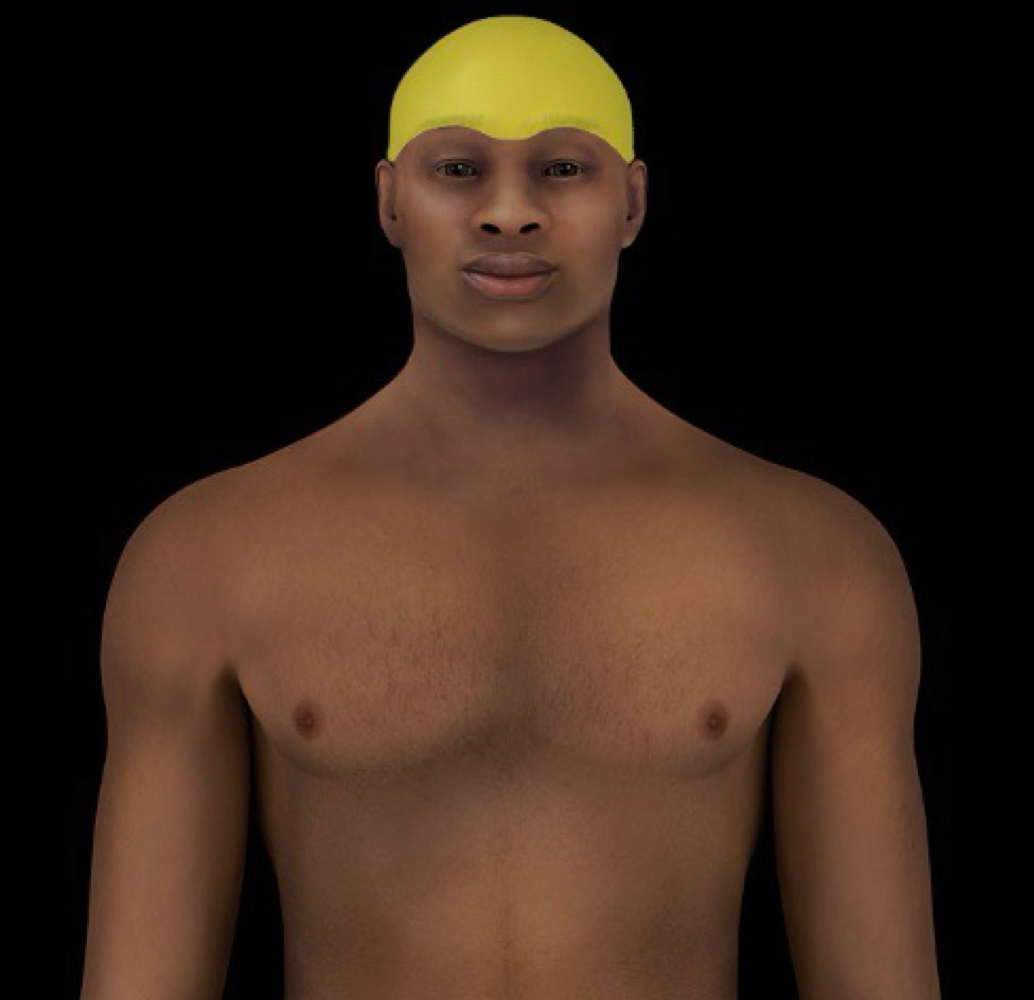

cranial region
-region of cranial cavity (i.e., surrounding brain)
-locale: head (superior part)
-cranial cavity is part of skull that contains brain
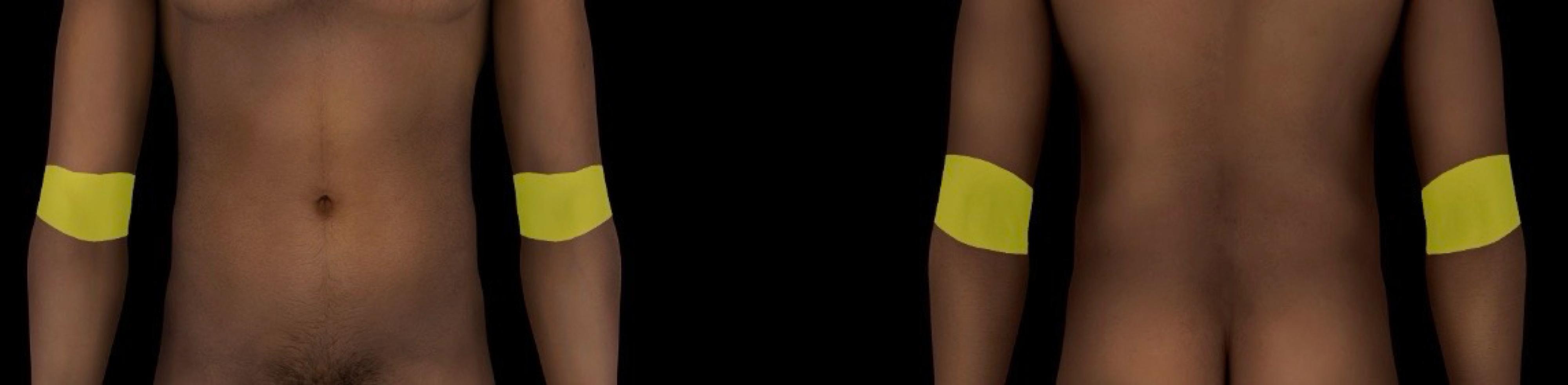
cubital region
-subdivision of the upper limb
-contains:
skin
muscles
nerves
vessels around distal end of humerus and proximal ends of radius and ulna
-includes:
cubital fossa
shadow triangular depression on anterior aspect of elbow
important structures related to cubital fossa include:
median cubital vien
brachial artery and primary branches (e.g., radial and ulnar arteries)
median and radial nerves
biceps and brachis tendon
-locale: upper limb; anterior and posterior aspects of elbow
-aka - elbow region
-cubital region subdivided into anterior and posterior regions of elbow
-cubital fossa is part of anterior region of elbow
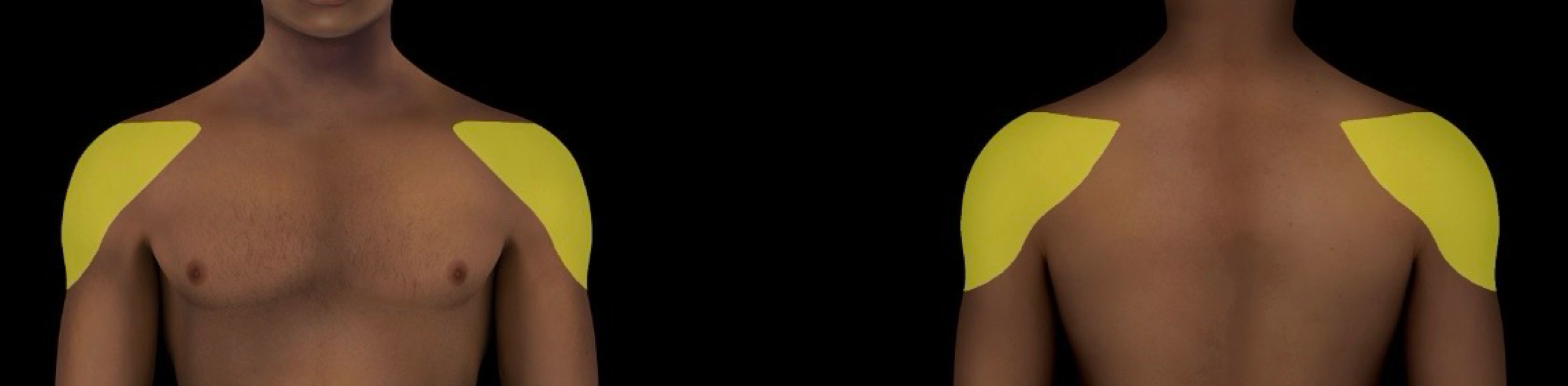

deltoid region
-subdividsion of upper lumb over deltoid muscle
-includes:
skin
muscles
nerves
vessels and glenohumeral joint
-locale: upper limb (proximal end)
-aka - shoulder region
-sometimes referred to as “shoulder)
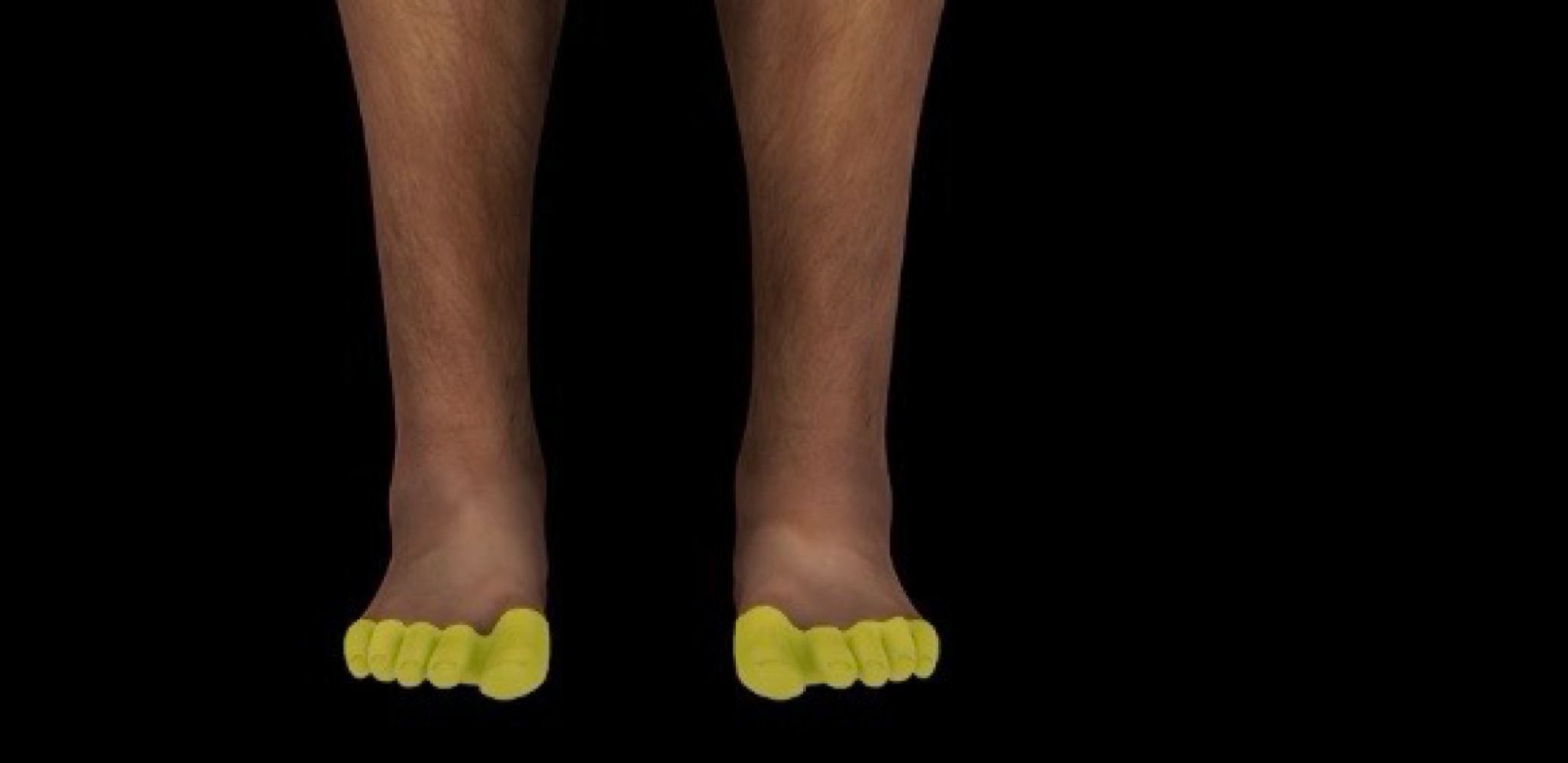
digits of the foot