AP Environmental Science: Biomes
1/20
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Freshwater Wetlands
Submerged or saturated by water for at least part of each year. Shallow enough to support emergent vegetation. Includes swamps, marshes, and bogs.
Marshes
wetlands that contain non woody vegetation, such as reeds and grasses.
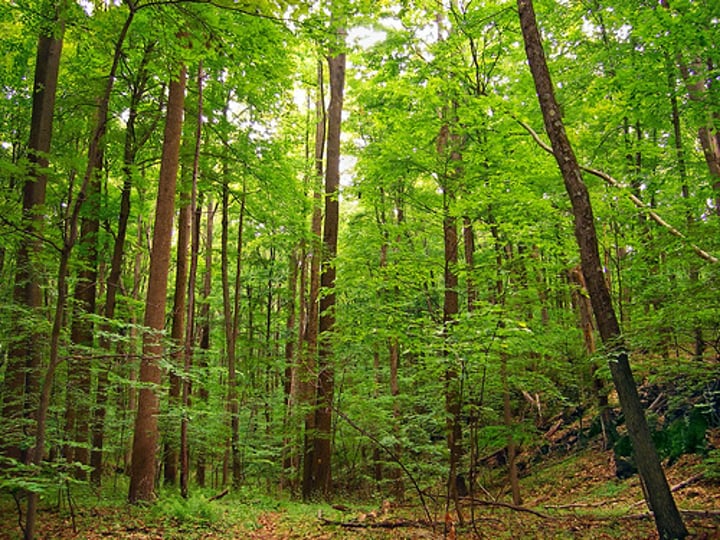
Temperate Deciduous Forest
-Cool Winters, Warm Summers (Seasonal Variation)
-Precipitation is relatively evenly spread throughout the year
-Deciduous Trees (Oak, Beech)
-Europe, China, Eastern North America
-Northern Hemisphere
-Good Soils

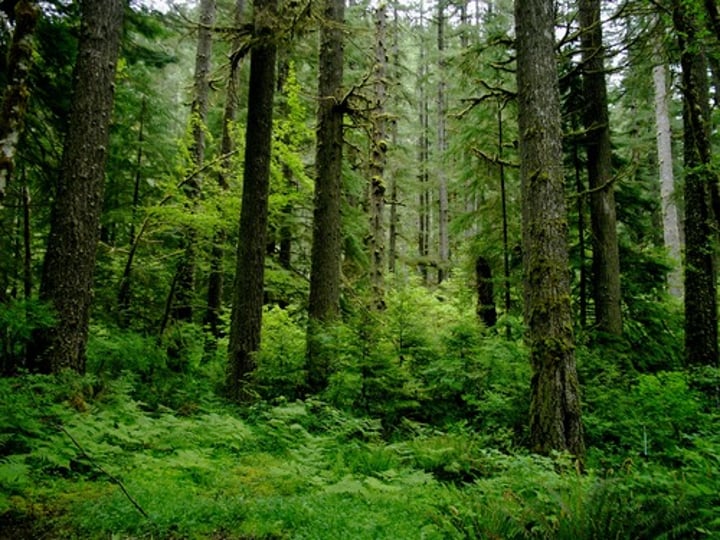
Temperate Rainforest
-Cool Winters, Warm Summers (Seasonal Variation)
-Large amount of precipitation (Less rain in winters)
-Coniferous Trees
-Provide lumber and paper
-Northern Hemisphere
-East coast of North America and Canada
-Fertile soils that are susceptible to land slides and erosion if forests are cleared

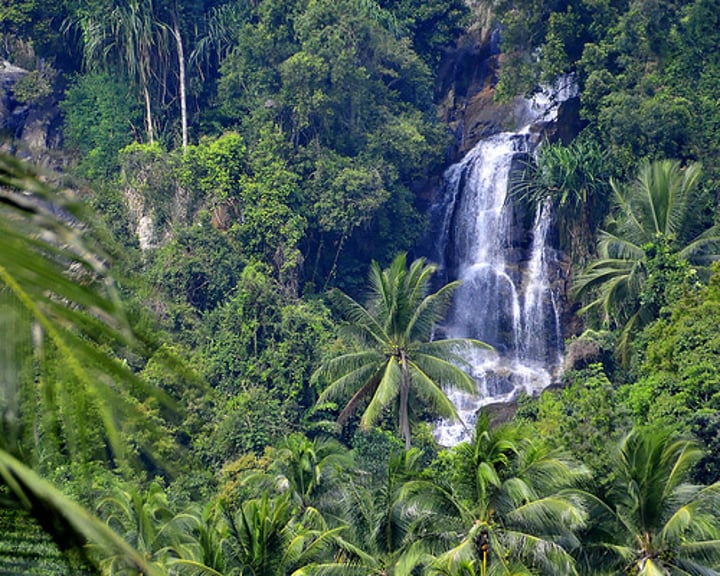
Tropical Rainforest
-Warm all year round
-Very high amount of precipitation (300-500 mm per month)
-Southern Hemisphere
-Central America, Africa, South America, Southeast Asia
-Great Biodiversity
-Poor, thin soils

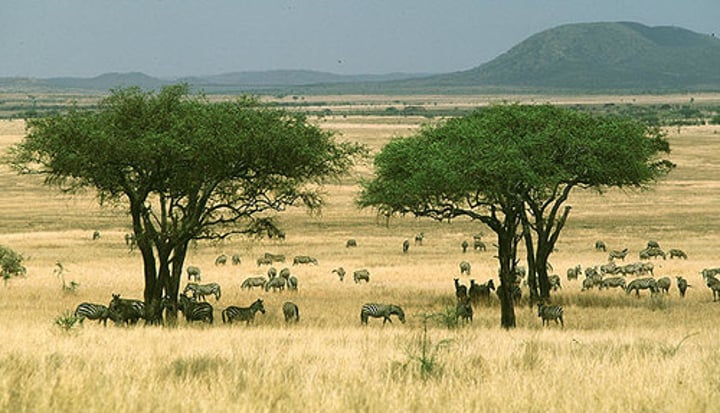
Savanna (Tropical Grasslands)
-Slight seasonal variation (warmer in summer)
-Extreme wet and dry seasons
-Wet Summer (not as wet as tropical dry forest)
-Southern Hemisphere
-Isolated Trees
-Africa, South America, India, Australia
-Zebras, Giraffes, Gazelles

Temperate Rainforest
Moderate temperatures, high precipitation. Is a coast biome. Nearly a 12 month growing season. Supports growth of very large trees.
Swamps
wetlands that contain emergent trees
Salt marshes
found along the coast in temperate climates and contain non woody emergent vegetation.
Mangrove Swamp
tropical and subtropical coasts that contain trees whose roots are submerged in water. Mangrove trees are salt tolerant and help protect coastline from erosion and storm damage.
Coral Reefs
warm, shallow waters beyond shoreline. Most diverse marine biome.
Temperate Grassland
-Cool Winters, Warm Summers (seasonal variation is more extreme than temperate deciduous forests)
-Limited amount of precipitation
-Frequent fires (no trees)
-Also called prairie or steppe
-Northern Hemisphere
-North America, Middle East, Europe, Asia
-Very fertile soils (used for agriculture)

Desert
-Driest Biome
-Barely an rainfall
-Slight seasonal variation
-Saline soils
-Little Vegetation
-Temperatures drop at night
-Northern Hemisphere
-Africa, Mexico, Middle East, Asia

Tundra
-Coldest Biome
-Warmer in summers, but still cold (5 degrees celsius)
-Freezing in winters (-20 degrees celsius)
-Northern Hemisphere
-Dry
-Slightly wet summers
-Soil is permanently frozen (permafrost)
-Also occurs as alpine tundra at the tops of mountains
-Northern Europe, Northern Canada, Northern Asia, Greenland

Chaparral
-Densely thicketed
-Highly seasonal
-Cool, wet winters and warm, dry summers
-Induced by oceanic influences
-Northern Hemisphere
-California, Chile, Australia
-Frequent fires

Climate
the weather conditions prevailing in an area in general or over a long period
Weather
The daily conditions of the atmosphere in terms of temperature, atmospheric pressure, wind, and moisture.
biome
large land regions with certain types of climate and dominant plant life
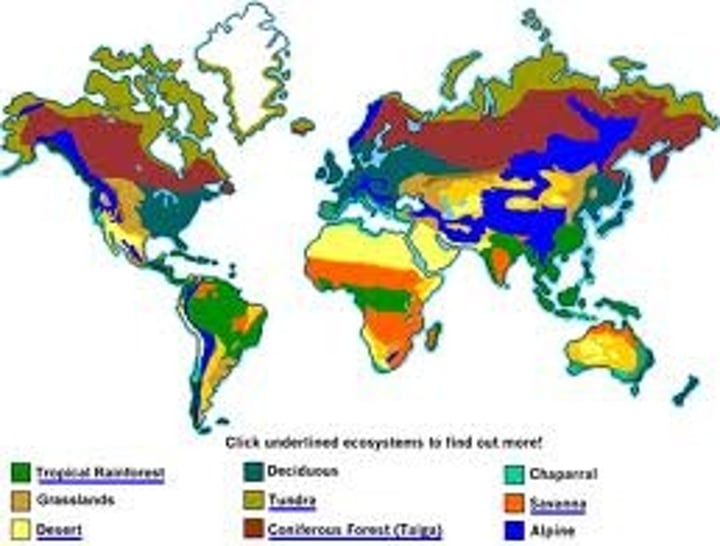
Equator
Greater biodiversity occurs in this region of the world
Tundra
Cold, treeless biome with low-growing vegetation. Soil is frozen. Permafrost is present. Annual Temperature is -6.7 degrees Celsius
Boreal Forest (Taiga)
Very cold climate, plant growth constrained by temperature, not precipitation. Soil is nutrient poor due to slow decomposition. Annual precipitation is 31.8 cm