Electric Physics
1/36
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Electric Physics Ex...brrr...plained.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
⚛ Protons & Electrons
Protons → Positive (+)
Electrons → Negative (-)
Electrons move more easily than protons
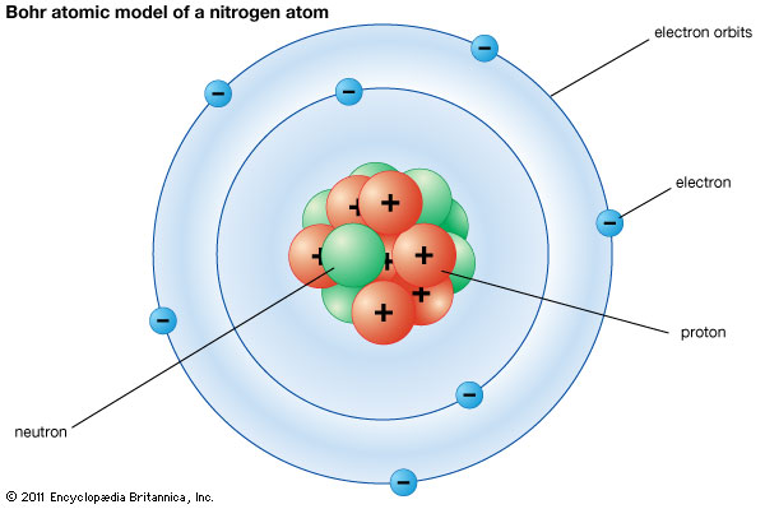
⚖ Neutral Atoms vs. Ions
Neutral Atom: Electrons = Protons
Ion: Electrons ≠ Protons
Anion (-): Extra electrons
Cation (+): Fewer electrons
🔋 Elementary Charge & Coulomb
Elementary charge (e) is defined as the charge of one electron (-e) or one proton (+e):
𝑒 = 1.6 × 10⁻¹⁹ C
Where C = Coulomb
1 C = 6.24 × 10¹⁸ protons/electrons
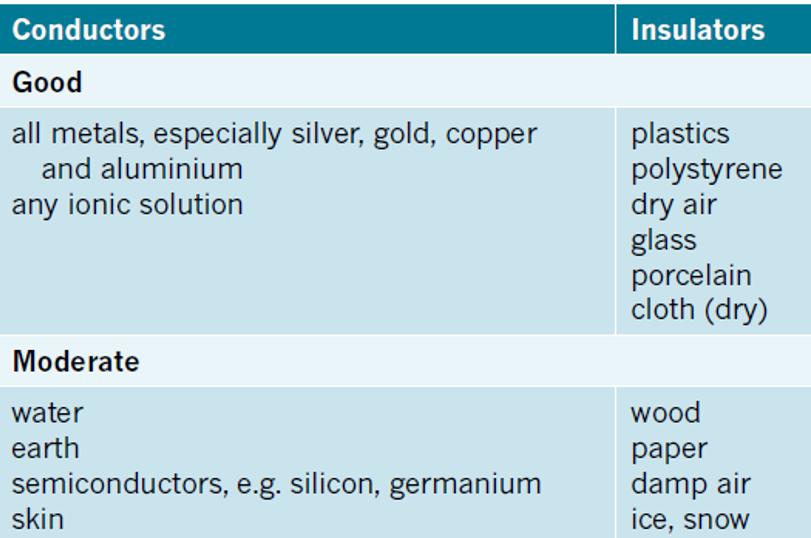
⚡ Conductors vs. Insulators
Metals (Conductors): Free-moving electrons through the lattice of positive ions.
Non-metals (Insulators): Tightly bound electrons
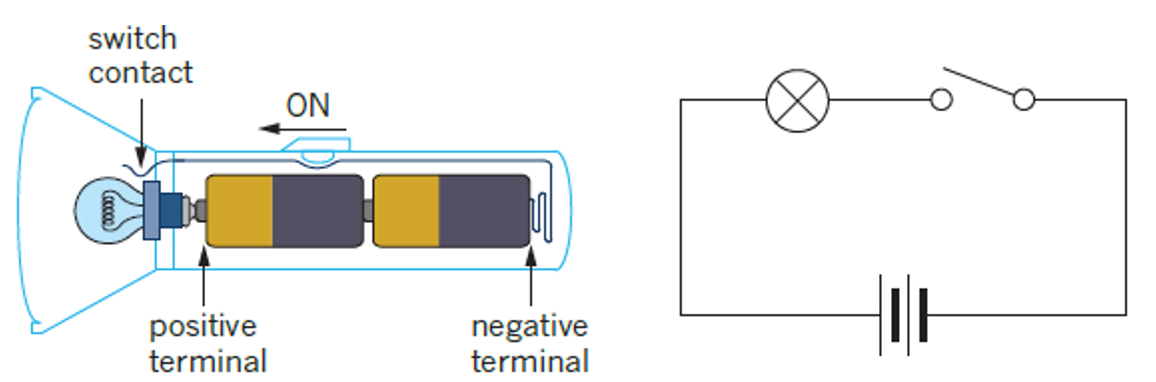
⚡ What is Current?
Rate of flow of electric charge
Carried by electrons (in wires) or ions (in solution)
Requires a complete circuit
All circuits require an energy source, wires, and a circuit element.
🔄 Conventional vs. Electron Flow
Conventional Current (I, current): + to -
Electron Flow (electron current): - to +
Note: + = LONG SIDE, - = SHORT SIDE
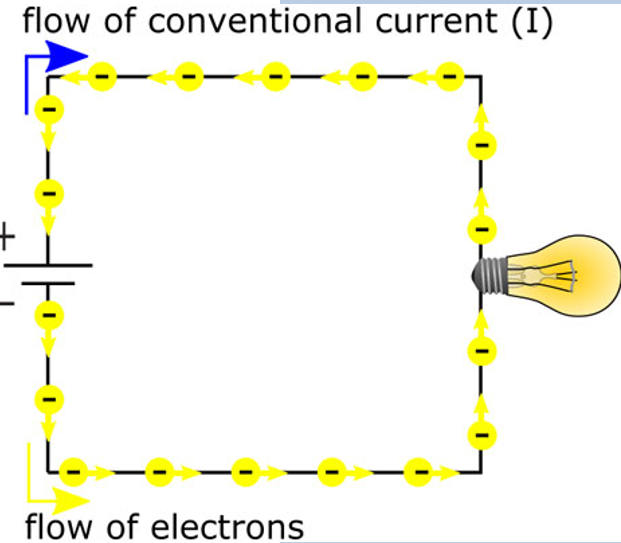
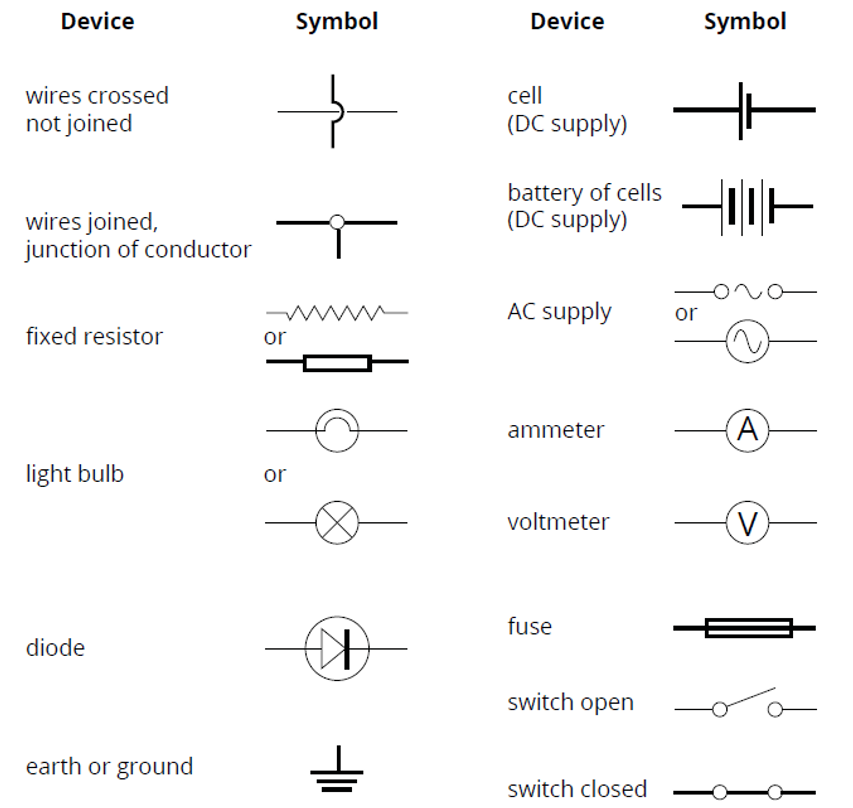
Representing electric circuits
Voltmeters: don’t allow current to pass through it. Must be put in parallel series.
Ammeters: allow current to pass through it. May be placed in series.
Diode: the triangle shows the direction at which the current flows.
📏 Current Formula
𝑰 = 𝑸/𝒕 (Charge per second), I = Current (A), Q = amount of charge and t = time (s)
𝑸 = 𝒏ₑ × 𝒒ₑ (Charge = No. of electrons × charge per electron)
Unit: Amperes (A), 1A = 1 Coulomb/s
📊 Measuring Current - Ammeter v.s. Voltmeter
Ammeter measures current
Connected in series with the circuit.
A voltmeter measures voltage
Connecting in parallel across components as it doesn’t allow current to pass through.
💧 Water Analogy for Current
Battery = Water pump
Current = Water flow
Light bulb = Turbine (converting energy)
Charges are not used up, like chain links in a bicycle
🔋 Energy for Electrons
Electrons need energy to move, provided by the battery.
When a circuit connects two ends of the battery, the battery transforms chemical energy into electrical potential energy.
⚡ Potential Energy in a Circuit - Potential Difference
Potential energy is stored as a separation of charge between battery terminals.
The amount of energy gained when moved from one to another battery.
This is called potential difference (V), measured in volts (V).
This can also be referred as: Volts / Electromagnetic Force (EM Force).
💡 Voltage Drop
Voltage drop is the energy lost by each coulomb of charge.
Equation: 𝑉 = 𝐸 / 𝑄
𝑉 = potential difference (V)
𝐸 = electric potential energy (J)
𝑄 = charge (C)
⚙ Energy in a Circuit
Energy (E) = 𝑉 × 𝐼 × 𝑡
𝐸 = energy (J)
𝑉 = potential difference (V)
𝐼 = current (A)
𝑡 = time (s)
🧮 Power Formula
Power (P) is energy used per second: 𝑃 = 𝐸 / 𝑡
𝑃 = power (W)
𝐸 = energy (J)
𝑡 = time (s)
Power equation: 𝑃 = 𝑉 × 𝐼
𝑉 = potential difference (V)
𝐼 = current (A)
Voltage and current are easily measured in a circuit.
We can then derive (from V=IR, Ohm’s Law):
Start with:
P = VI
Use Ohm’s Law: V = IR and I = V/R
P = VI = (IR) × I = I²R
P = VI = V × (V/R) = V²/R
Original: P = VI
So, the three forms are:
P = VI = I²R = V²/R
Resistance (and to the flow of charge)
Resistance is a measure of how hard it is for current to flow through a material. Conductors have low resistance, while insulators have high resistance. Resistance is measured in ohms (Ω).
Energy required:
Create an electric current: Separating electrons from atoms.
Maintain an electric current: Keeping electrons moving through the material.
Note: two resistance in a circuit means faster since more cross-sectional area.
Electron Movement
Electron movement:
Do not move in a straight line but bump into ions.
Although they move with great speed, their net speed (drift velocity/average speed) is slow.
Example:
In a 10A current through copper, the electron's net speed is 0.16 mm/s or 1.6 x 10⁻⁴ m/s.
Ohm’s Law
Georg Ohm's discovery:
Current is directly proportional to potential difference (I ∝ V).
Equation:
𝑅 = 𝑉 / 𝐼 or V = IR
Where:
V = potential difference in Volts (V)
I = current in Amps (A)
R = resistance in Ohms (Ω)
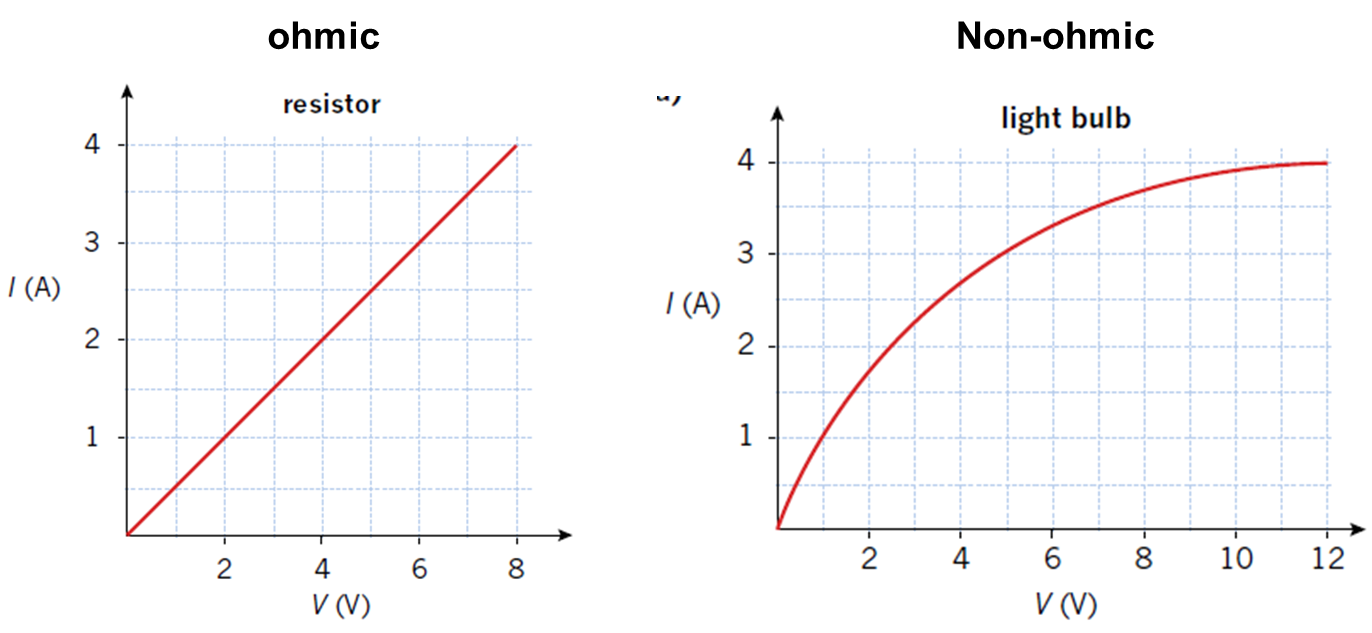
Ohmic / Non-ohmic Conductors
Ohmic conductors:
Conductors that obey Ohm's law.
Usually called resistors.
Often used to control the amount of current and the voltage drop across parts of a circuit.
Identification:
An ohmic conductor is identified by measuring the current that flows through it when different potential differences are applied.
Resistance of ohmic and non-ohmic conductors:
Can be found from the gradient of the V-I (Ohmic) or I–V (non-Ohmic) graph
Ohmic:
V ↑ → I ↑ → R ↑
V ↓ → I ↓ → R ↓
Non-Ohmic:
V ↑ → m ↓ → R ↑
V ↓ → m ↓ → R ↓
Gradient: Ohmic - just use rise/run; Non-ohmic: find avg gradient on a point from start.
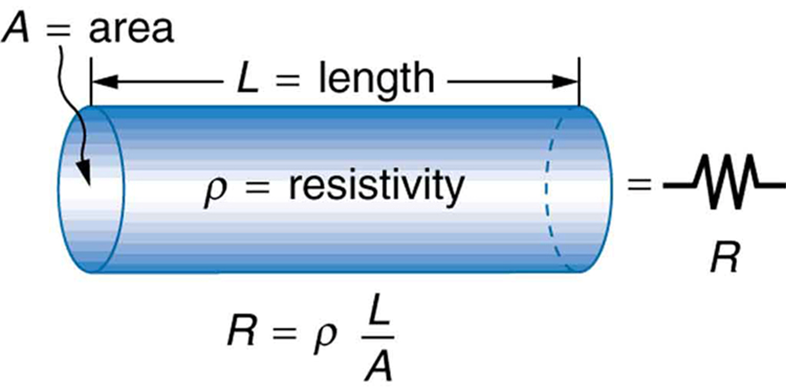
Variables that Affect resistance
Factors affecting resistance:
Directly proportional to length (l).
Inversely proportional to cross-sectional area (A).
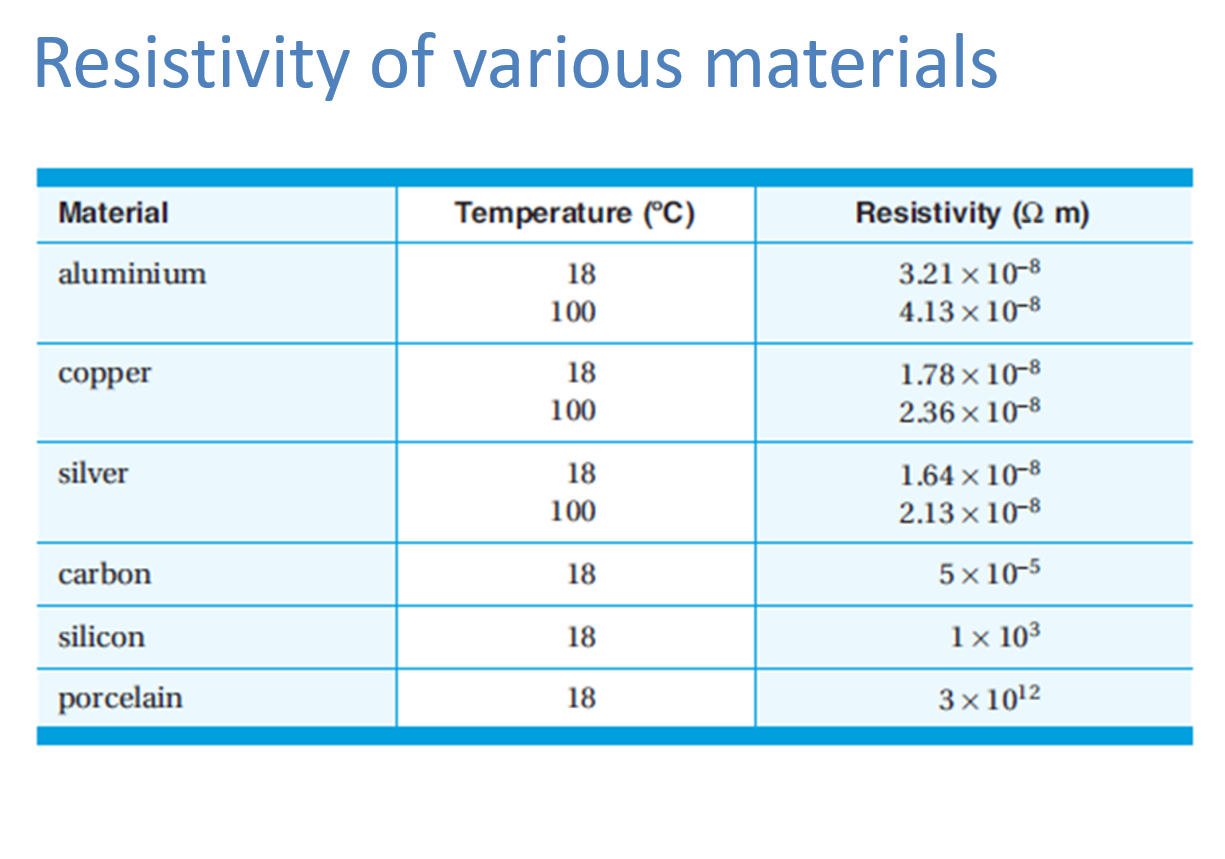
Affected by resistivity (𝜌), a property of the material.
General formula for resistance:
𝑅 = 𝜌(𝐿 / 𝐴)
R = Resistance (Ohms, Ω)
𝜌 = Resistivity (Ohm meters, Ω·m; constant)
L = Length of the conductor (meters, m)
A = Cross-sectional area of the conductor (square meters, m²)
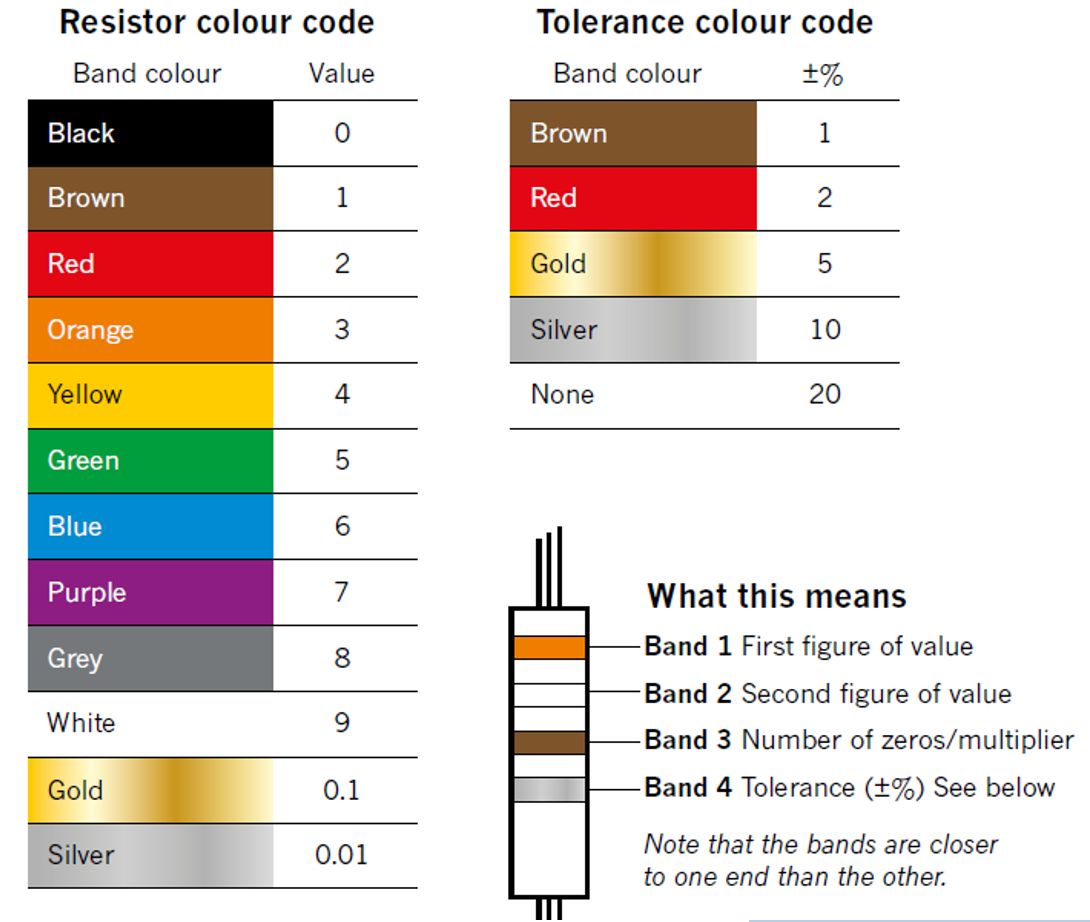
Resistors - Colours Coding
Summary of Series vs Parallel
Aspect | Series Circuit | Parallel Circuit |
|---|---|---|
Connection | Components in a single loop, one break all break. | Components in separate branches, one break others fine |
Resistance (Rₜ) | RT=R1+R2+R3+⋯+Rn | 1/RT=1/R1+1/R2+⋯+1/Rn 𝑅ₜ = (1/𝑅₁ + 1/𝑅₂ + 1/𝑅₃ + … + 1/𝑅ₙ)-1. |
Voltage (V) | VT=V1+V2+V3+⋯+Vn | Same across all branches: VT=V1=V2=⋯=Vn |
Current (I) | Same in all components: IT=I1=I2=⋯=In | Total current: IT=I1+I2+I3+⋯+IN |
Resistance Note | Increases with more resistors | Always less than the smallest resistor 𝑅ₜ < 𝑅ₛ𝑚𝑎𝑙𝑙𝑒𝑠𝑡 𝑟𝑒𝑠𝑖𝑠𝑡𝑜𝑟. |
Effect of Break | Whole circuit stops | Only the affected branch stops |
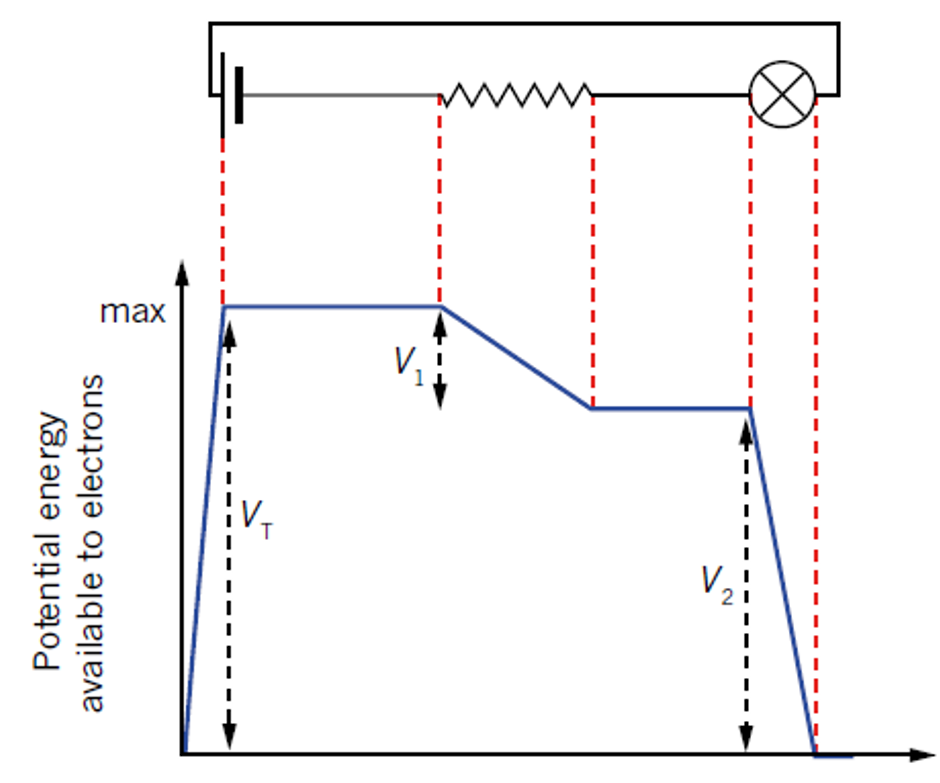
Kirchhoff’s Loop Rule
Potential difference in a closed-loop circuit:
The sum of the potential differences across all elements must be zero.
The energy gained (potential gain) equals the energy lost (potential drop) by the charges.
In a series circuit:
The sum of the potential drops (V₁ + V₂) across components like the resistor and the lamp equals the EMF.
Source of energy:
Devices that provide energy are referred to as sources of EMF (electromotive force), measured in volts.
Identical Resistors in Parallel Circuits
Identical resistors in parallel:
If there are n resistors of equal value R, the equivalent resistance is:
1/𝑅ₜ = 𝑛/𝑅
𝑅ₜ = 𝑅/n.
Kirchhoff’s junction rule
Kirchhoff’s junction rule:
The total current flowing into a junction must be equal to the total current flowing out of the junction.
Resistors and Power Formula
Resistors in parallel circuits draw more current than in series circuits, leading to higher power consumption.
Power formula:
P = V I, where:
P is the power (W)
V is the voltage (V)
I is the current (A).
Transducers
Transducer: A device that converts one form of energy into another (e.g., microphone, light bulb, speaker, battery).
→ Input transducers: convert physical signals → electrical (e.g. microphone, temperature sensor)
→ Output transducers: convert electrical signals → physical (e.g. speaker, LED, motor)
Input Transducers
Light Dependent Resistor (LDR):
A transducer whose resistance varies based on the amount of light falling on it.
Commonly used in devices like cameras, streetlights, and night lights, as well as in detectors for various applications.
Thermistor:
A variable resistor that changes with temperature, with types:
NTC (Negative Temperature Coefficient) — resistance decreases as temperature increases.
PTC (Positive Temperature Coefficient) — resistance increases as temperature increases.
WARNING: NO SLOPE = NOT THERMISTOR
Applications: Thermistors are used in temperature-sensitive devices (e.g., refrigerators, toasters).
Potentiometer:
A variable resistor with three terminals, used to adjust current/voltage or divide voltage. The wiper's position controls resistance.
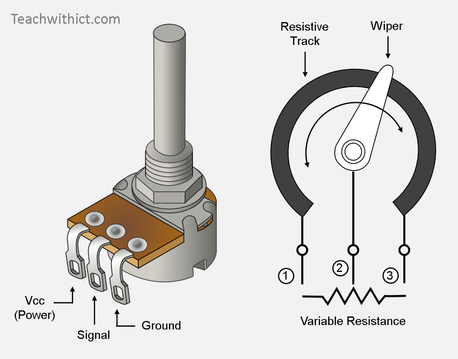
Voltage Divider
Definition: A circuit that reduces an input voltage to a desired output voltage.
Components: Typically uses two resistors in series.
Function: Divides the voltage in proportion to the resistances.
Not a transducer: It doesn't convert energy; just modifies voltage.
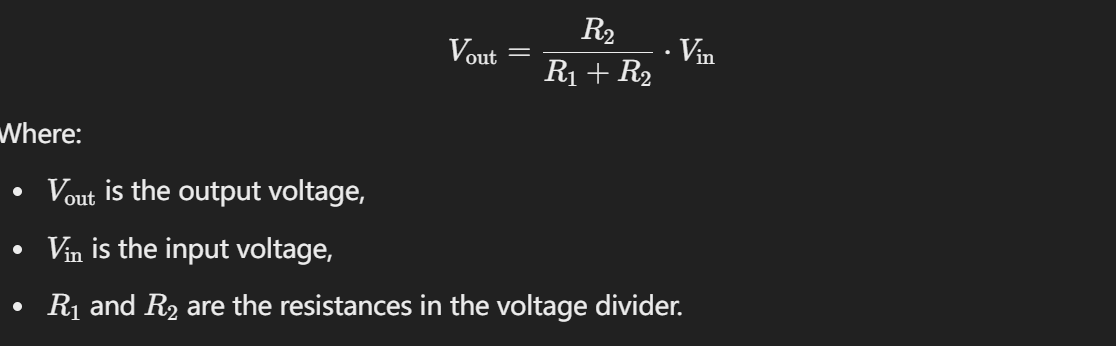
AC / DC
AC (Alternating Current):
Electrons oscillate back and forth in the circuit. Household energy is AC with a voltage of -340V to +340V, equivalent to 240V rms at 50 Hz.
DC (Direct Current):
Electrons flow in one direction only. Batteries, such as a car battery, provide DC, usually at 12V.
Root-Mean-Square (RMS)
RMS (Root Mean Square) is the effective value of an alternating current (AC) or voltage, calculated by squaring all values, averaging them, and then taking the square root, which gives the equivalent DC value that would produce the same power.
Square each value of the signal: First, you take all the values in the signal and square them (make them positive).
Find the average: Next, you calculate the average of all these squared values.
Take the square root: Finally, you take the square root of that average value.

Home Electricity
Three-pin plug color code:
Brown (or red): Active
Blue (or black): Neutral
Green/Yellow: Earth
Active wire:
Connected to 240V, oscillates between +340V and -340V.
Has a root-mean-square (RMS) voltage of 240V.
Neutral wire:
Connected to the neutral link at the switchboard and earth.
Always at 0V.
Energy Flow:
Current flows back and forth between active and neutral wires, providing energy to the appliance.
Electricity bills:
Measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh).
1 kWh = 3.6 × 10⁶ J
E = P × t
Cost = Energy × Rate
Energy Measurement:
Meters measure electrical energy supplied before distribution to various parts of the house.
Electrical Safety Devices: Fuses and Circuit Breakers
Function: Protect circuits by interrupting current if it exceeds a safe level.
Fuses: Contain a metal wire that melts when current is too high, breaking the circuit.
Circuit Breakers: Use a bimetallic strip that bends when heated, tripping a switch to break the circuit. These can be reset after activation, unlike fuses, which need replacing.
Appliance Placement: High-power appliances like ovens and air-conditioners are put on separate circuits from lights and power points.
Power Boards:
Limit: Most power boards can carry a maximum of 10 A of current.
Overuse: Overloading power boards with high-current devices can cause overheating, melting insulation, and potentially starting a fire.
Short Circuit
Short circuits occur when a low-resistance path allows current to bypass resistors, leading to excessive current flow. Overloads happen when too many devices draw current from a single circuit. Both can cause wires to heat up, potentially melting insulation and increasing the risk of fire. Faulty appliances and damaged wires can also lead to short circuits.
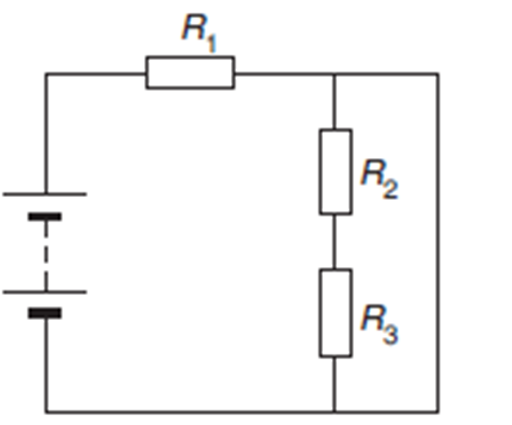
A short circuit is present in the branch parallel to R2 and R3, therefore no current will be measured across R2 and R3:
Electrical Safety and Protection Mechanisms
If the active wire inside an appliance touches the metal case, the case becomes live. An earth wire directs the current to the ground to prevent danger. A short circuit causes a large current, which trips the fuse or circuit breaker.
Double-insulated appliances have two layers of protection and don’t need an earth wire. They often have two-pin plugs.
RCDs (Residual Current Devices) detect current differences between the active and neutral wires. If there’s a leak, the RCD turns off power in 20 milliseconds.
Electrical Safety
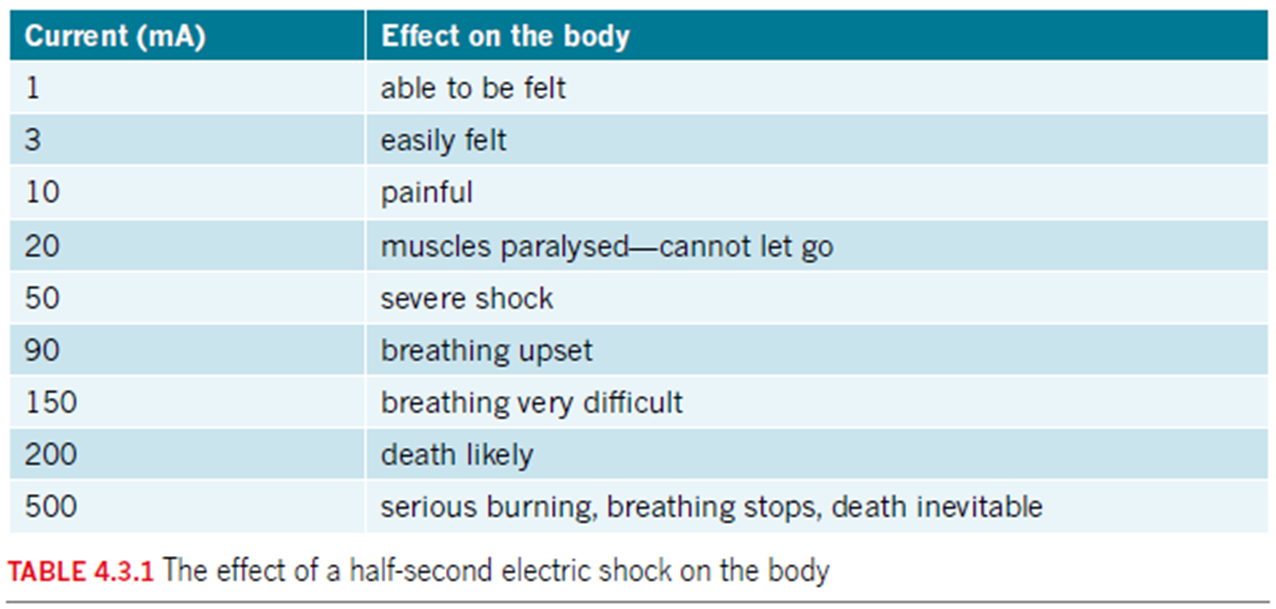
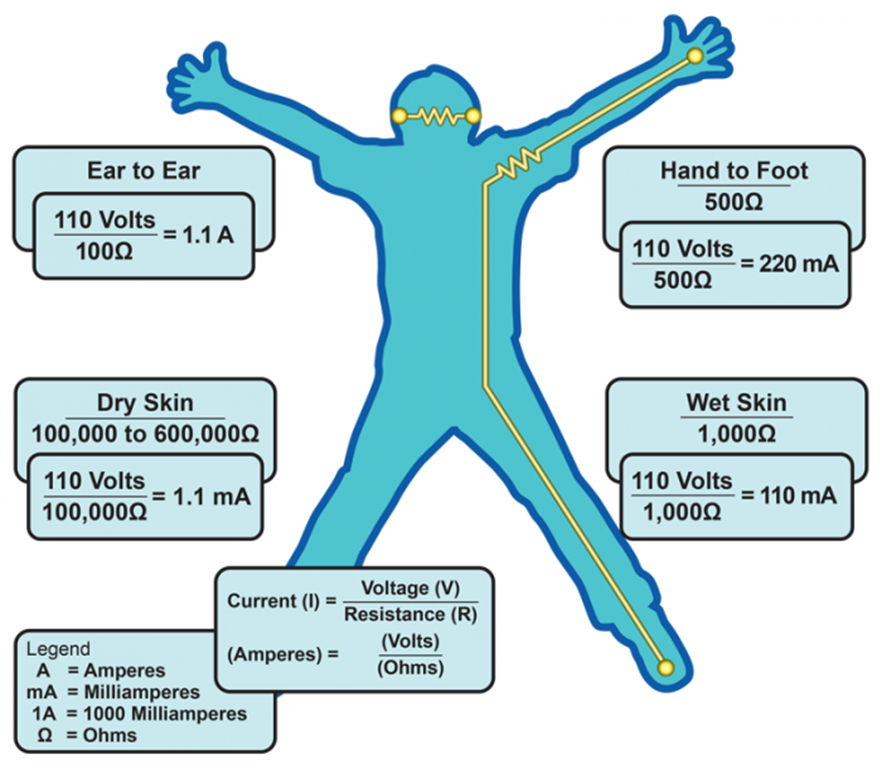
50 Australians die from electrical accidents yearly.
Shock impact depends on current, duration, and path through the body.
240V source can cause deadly current flow if contact is good (wet hands make it worse).
Electrical energy turns to heat, causing burns.
80mA current can cause heart fibrillation, often leading to death.

Current: LDR / Light bulb example
Bright light → LDR has low resistance → current bypasses bulb → bulb off
Darkness → LDR has high resistance → current flows through bulb → bulb on
💡 Current takes the path of least resistance in parallel circuits.