Inheritance 1.0
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
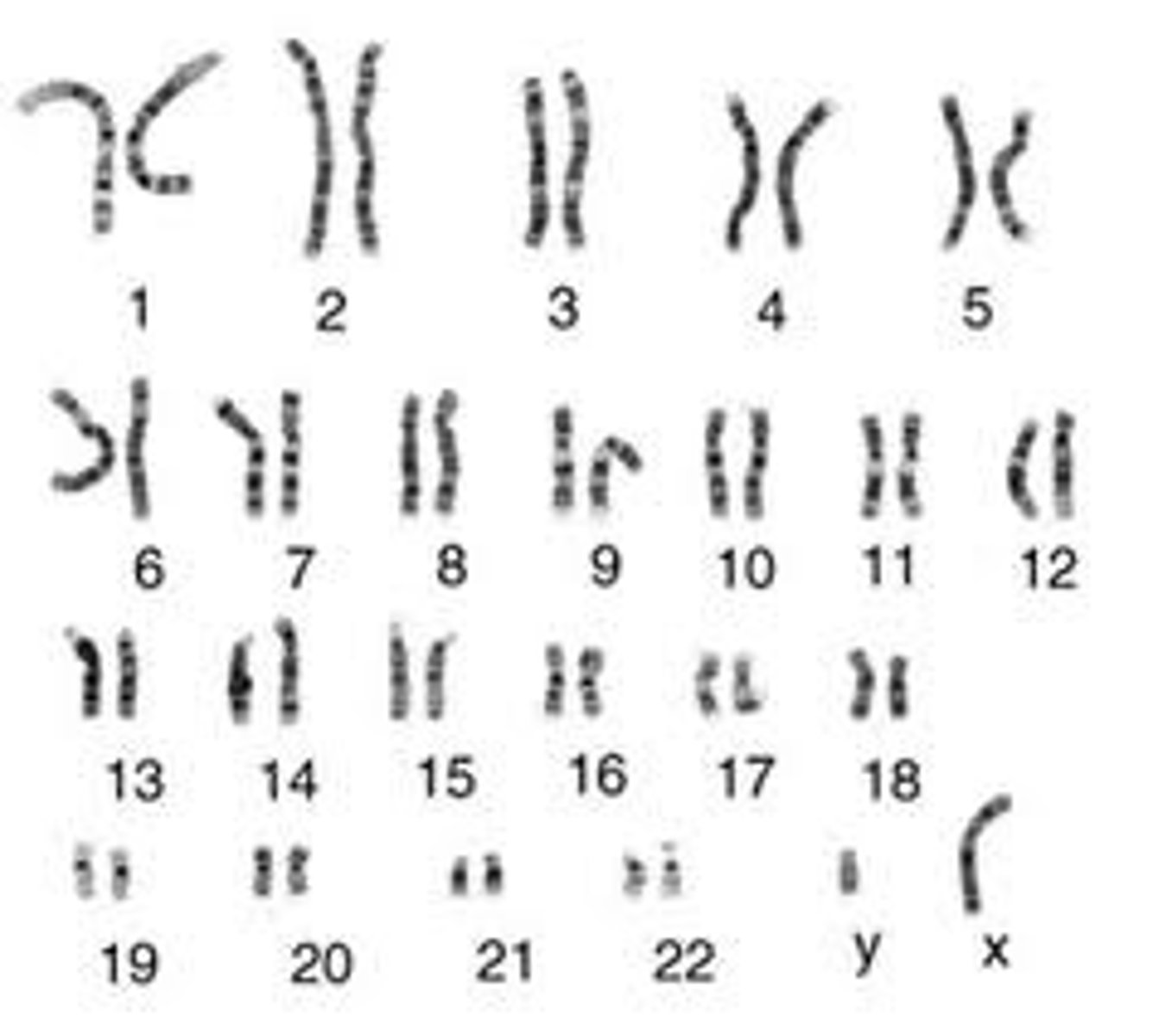
Karyotype
A picture of homologous chromosome pairs (one each from biological mom and dad) that can show mutations and gender.
Heredity
The process of passing down traits found on DNA from parent(s) to offspring
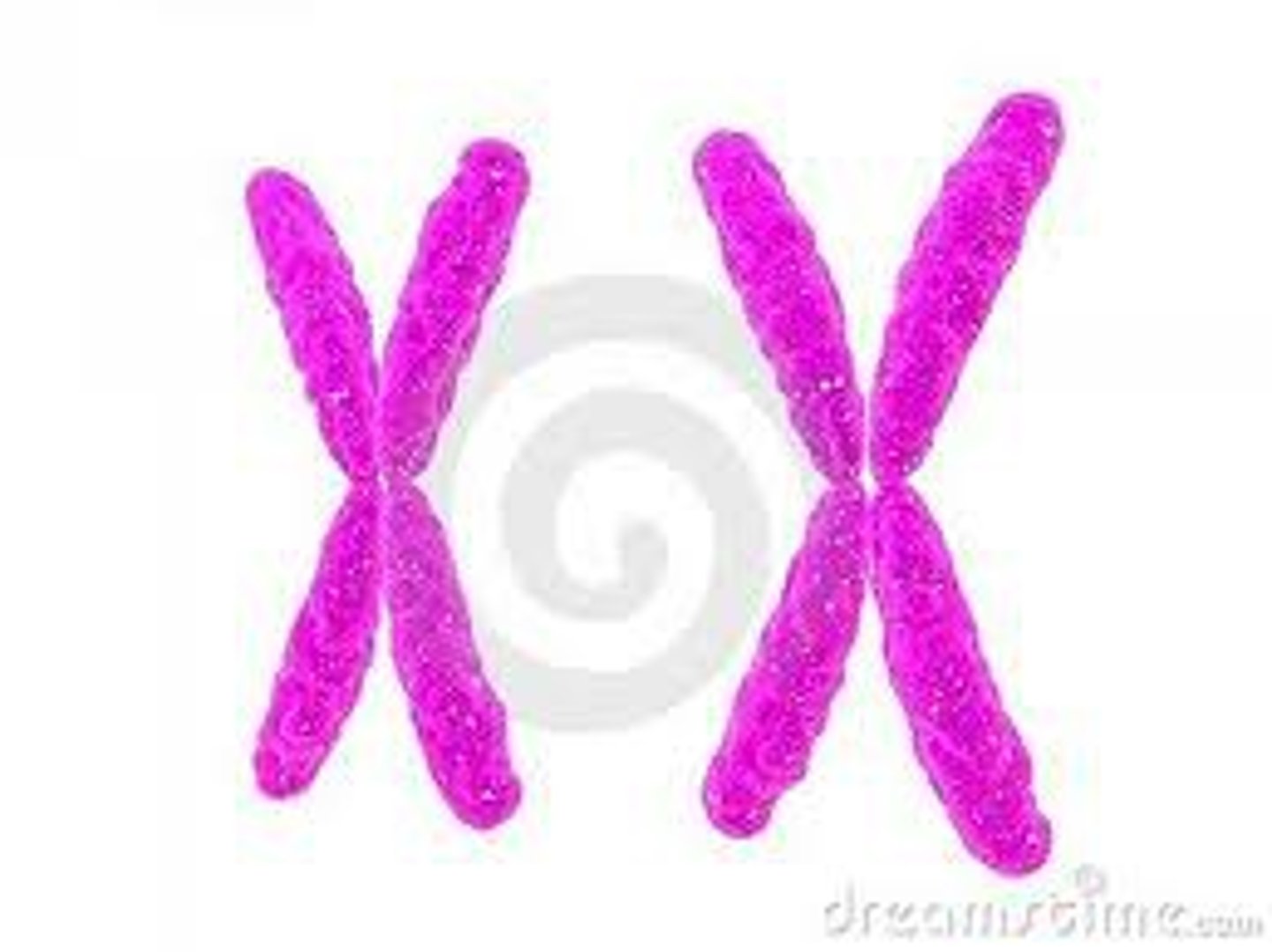
XX
Female Sex chromosomes

XY
Male Sex Chromosomes

46
The number of chromosomes in a human's somatic cells
23
The number of chromosome pairs in a human's somatic cells
Gametes
Sex cells (egg and sperm)
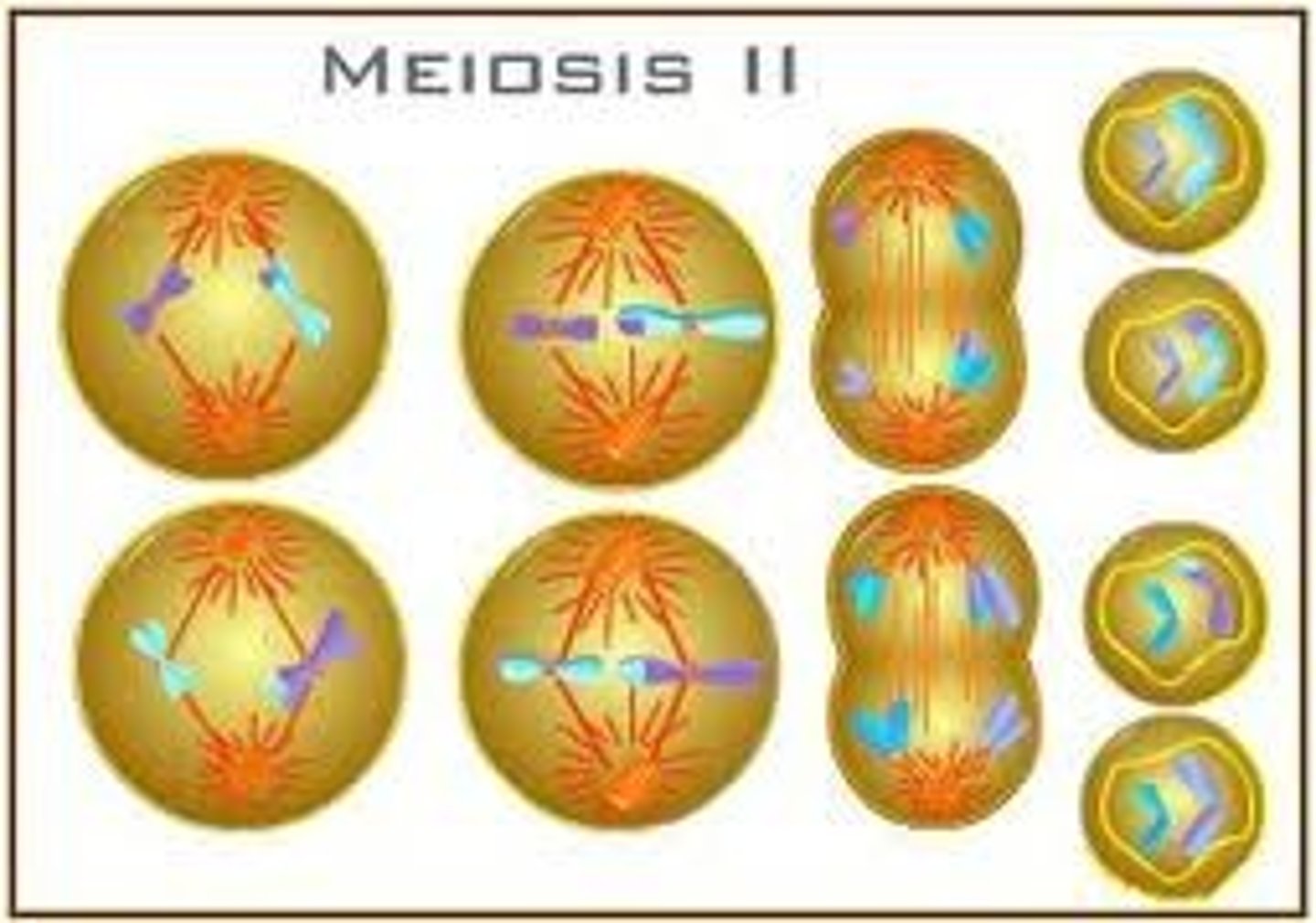
Meiosis
Cell division that makes 4 haploid sex cells (egg or sperm)
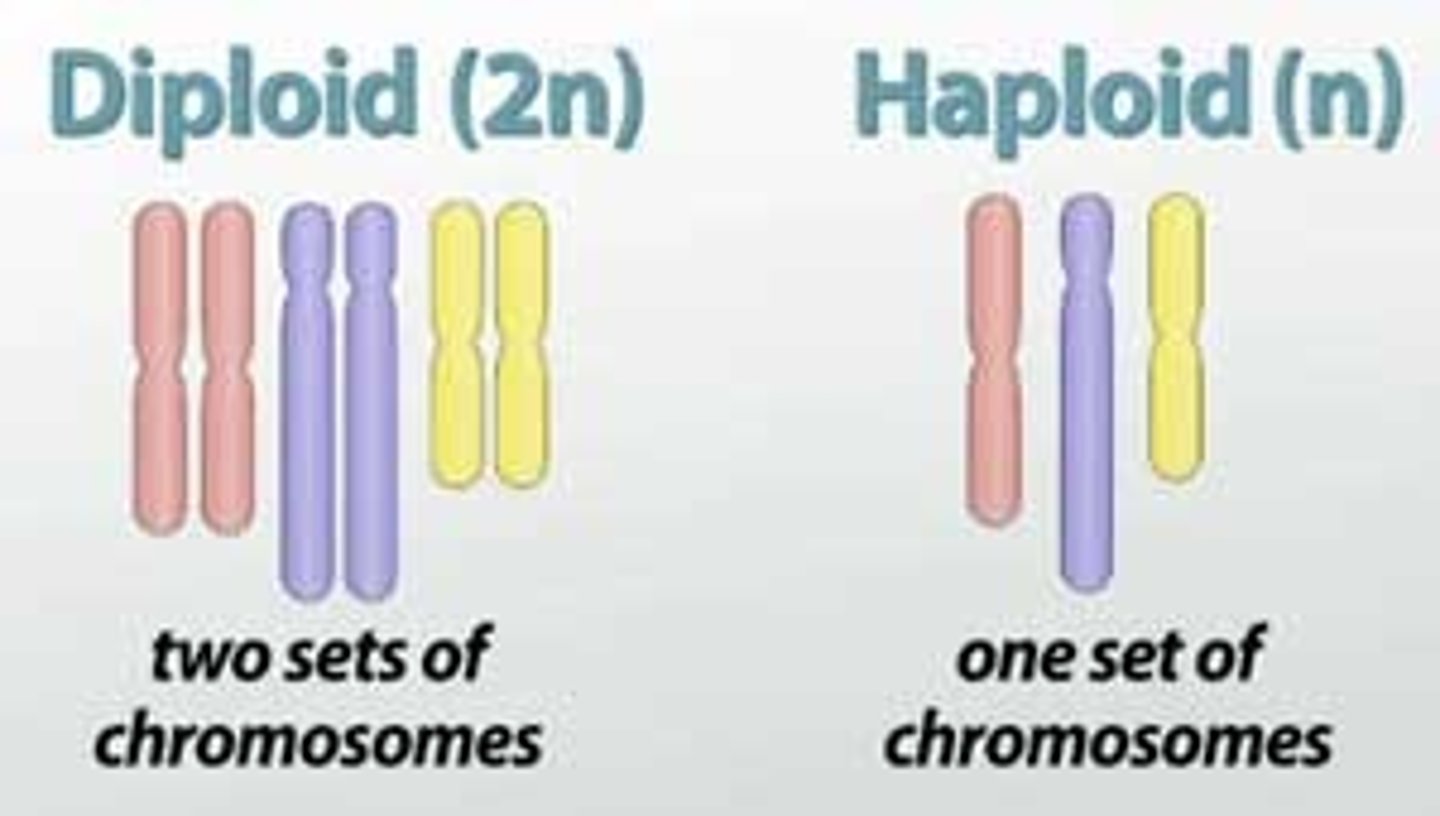
Haploid
One set of chromosomes
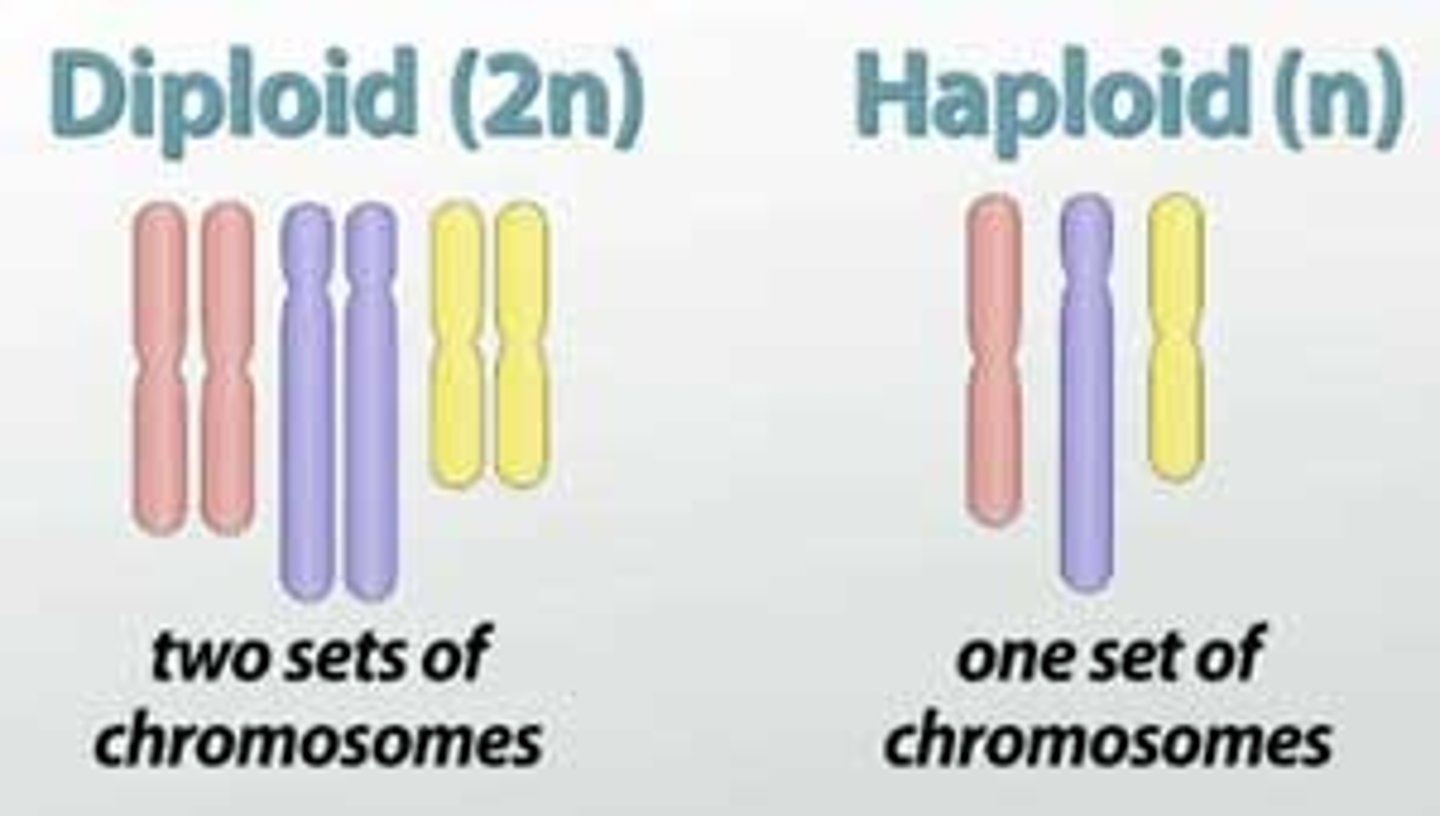
Diploid
Two sets of chromosomes
Mitosis
Process of cell division that makes 2 identical body cells. This can be used for growth and repair.

Genotype
The Allele combination (the letters) of a trait
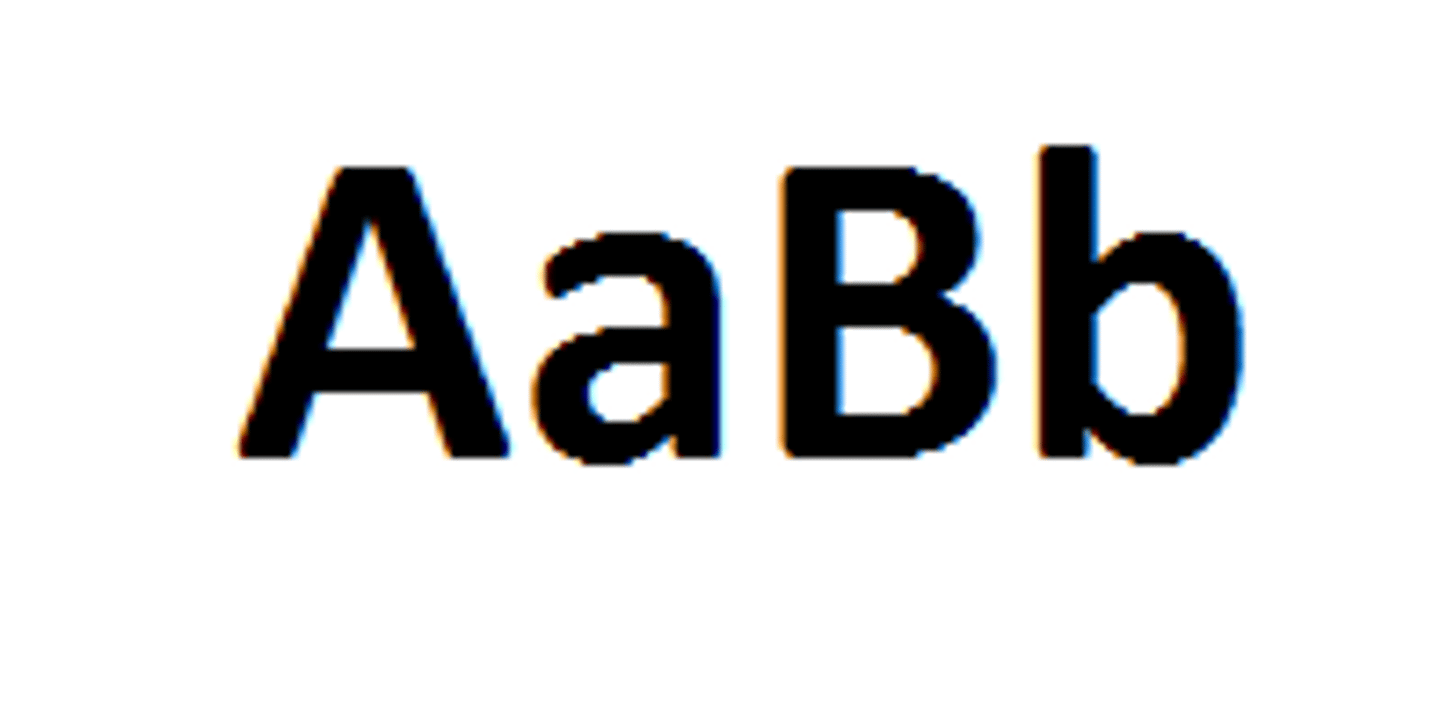
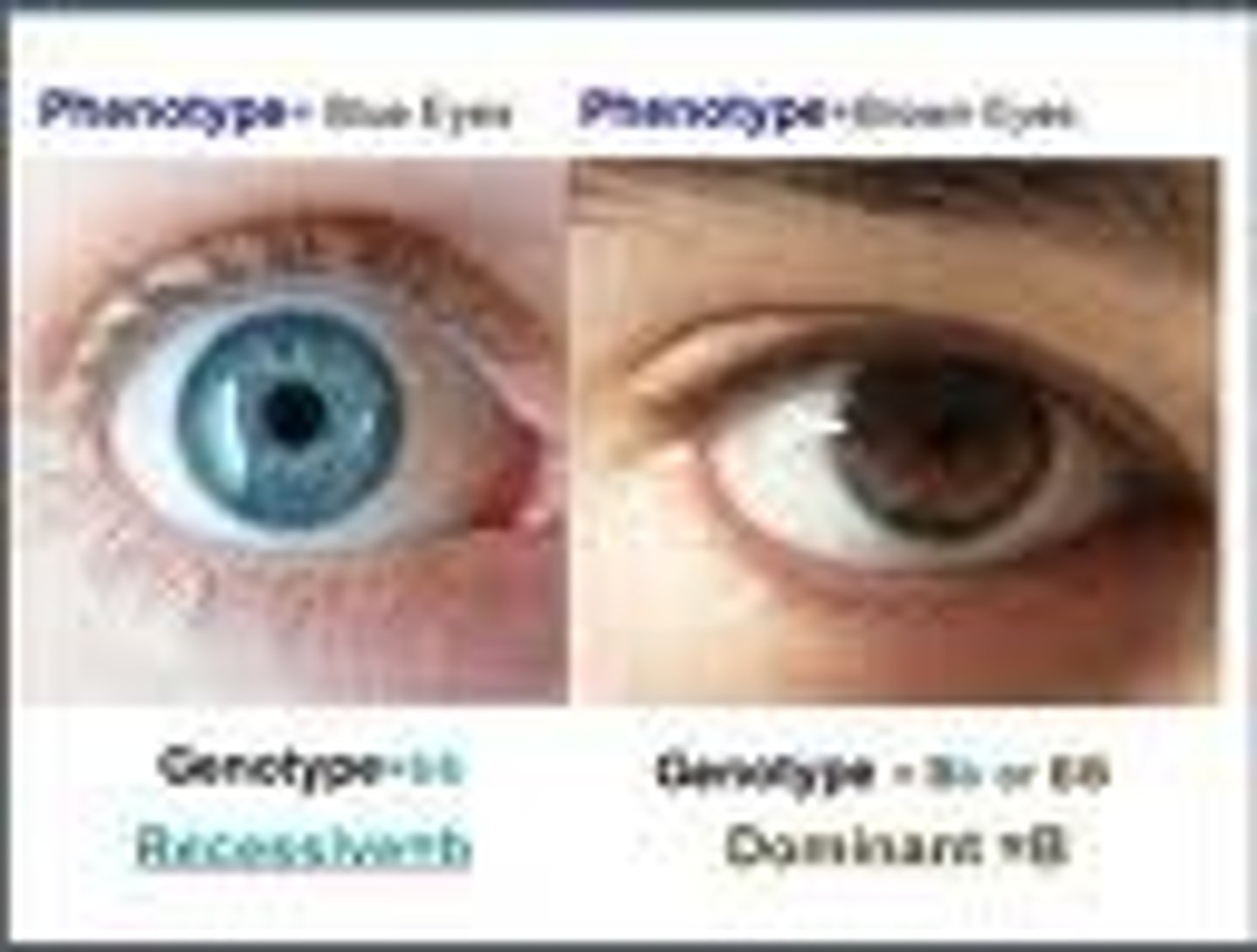
Phenotype
The outward expression of a trait (ie how it looks)
allele
A number of alternative forms of the same gene. (represented by letters).

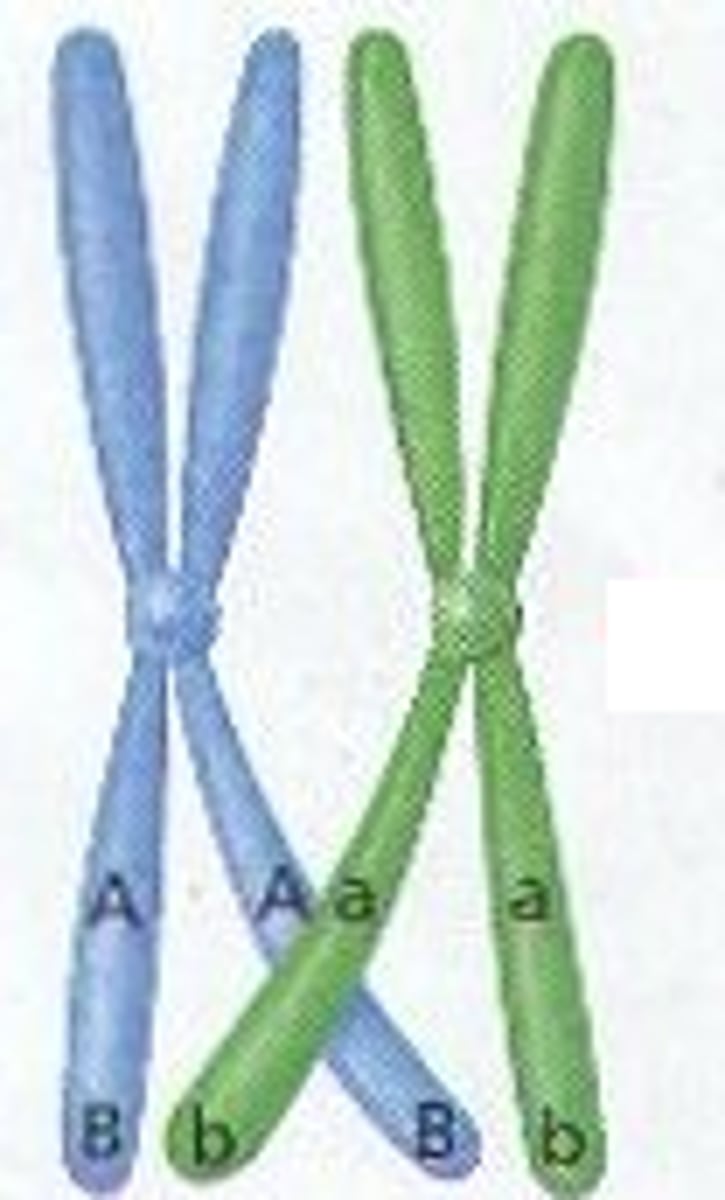
crossing-over
when two homologous chromosomes exchange pieces of their DNA in prohase I; creates genetic variation and makes new combinations of alleles on the chromosome.
Dominant
An allele that is "stronger" and can cover up another allele. Only 1 copy is necessary to show the trait; It is represented by a capital letter.

Recessive
An allele that is "weaker" and can "hide" behind a stronger allele. Two copies are necessary to show the trait; represented by a lowercase letter.
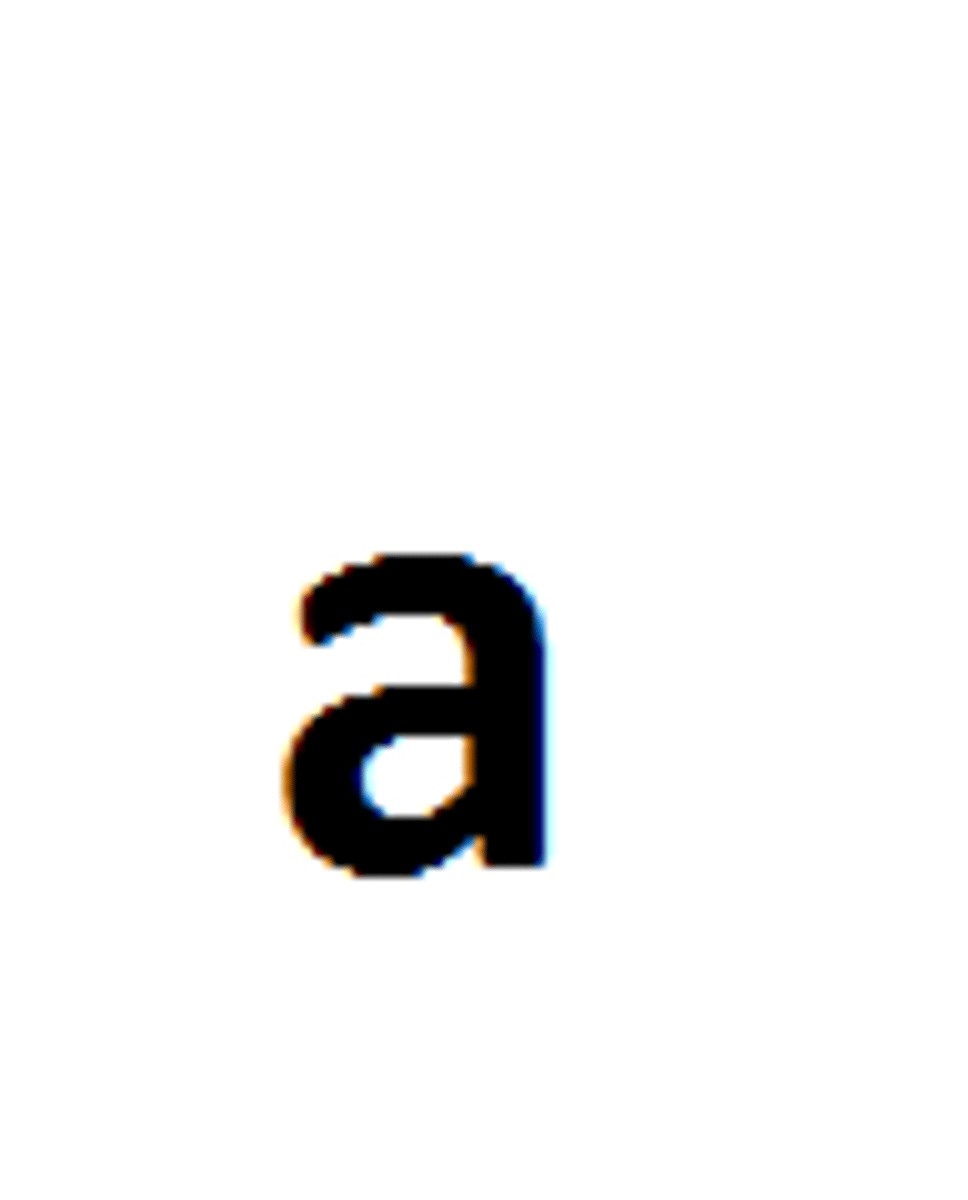
Homozygous Dominant
Two copies of the same dominant allele. It is represented by two Uppercase letters.

Homozygous Recessive
Two copies of the same recessive allele. It is represented by two Lowercase letters.

Heterozygous
An organism has two different alleles of a gene. It is represented by an upper case and a lower case letter Aa; AKA hybrid
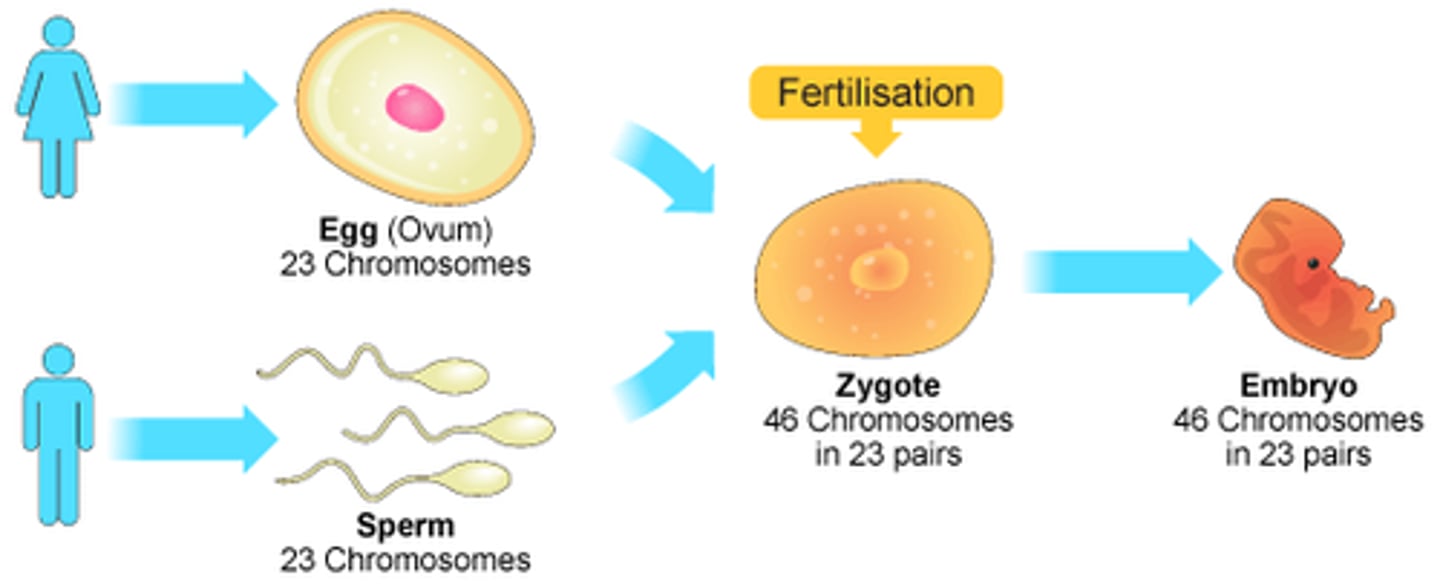
Fertilization
The process that occurs when a sperm combines with an egg. Two haploid cells join together to form one diploid cell.
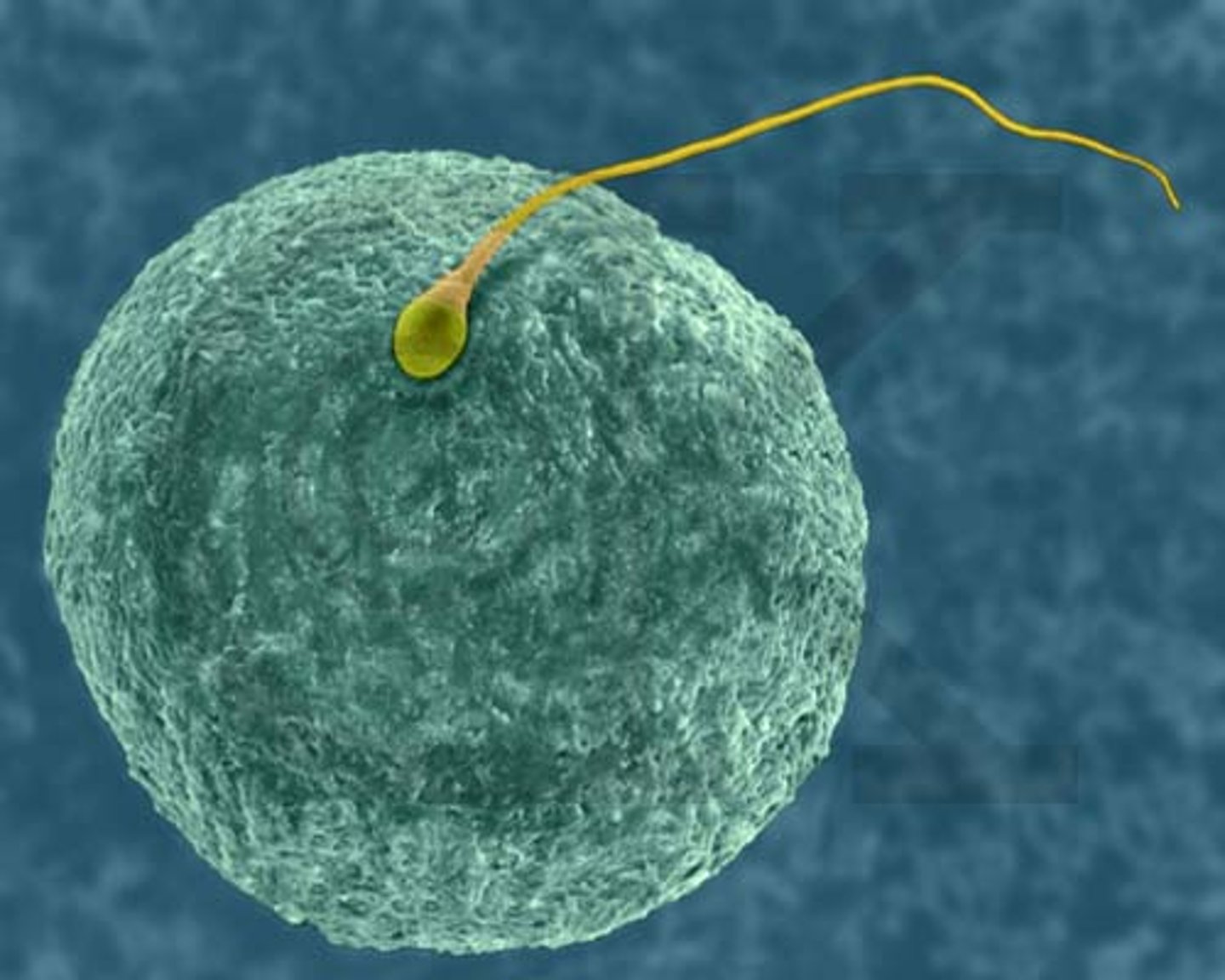
Zygote
A fertilized egg.
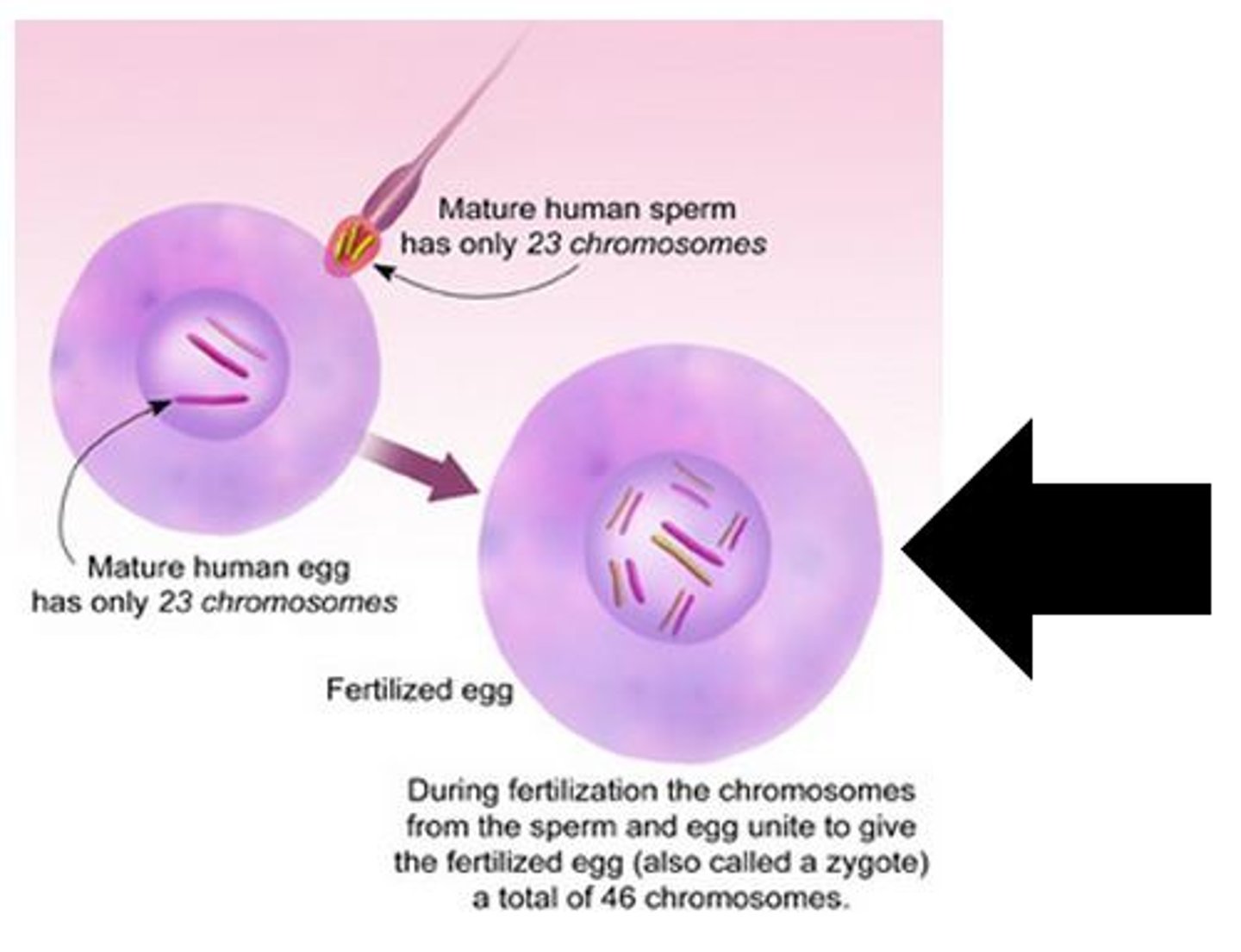
Variation
An advantage of sexual reproduction. This causes genetic differences in the offspring.

Sexual Reproduction
When two haploid sex cells or gametes (egg and sperm) come together to form a zygote.
Asexual Reproduction
A form of reproduction that needs only one individual that makes two identical daughter cells.
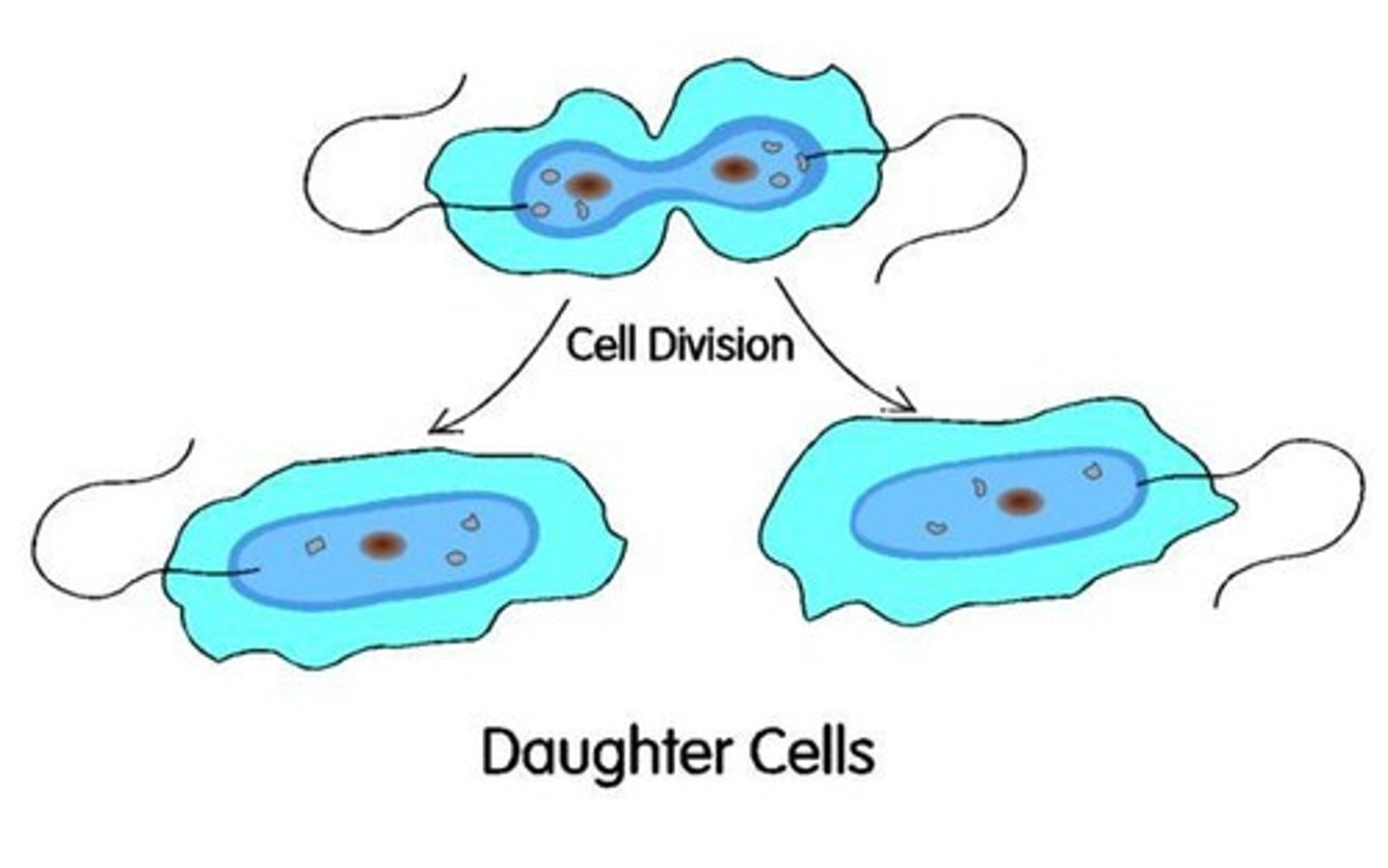
Carrier
Someone who has the recessive allele for a trait, but the trait does not show in their phenotype.
Punnet Square
A diagram used to predict the outcome of a particular cross or breeding experiment. Used by biologists to determine the probability of an offspring having a particular genotype.
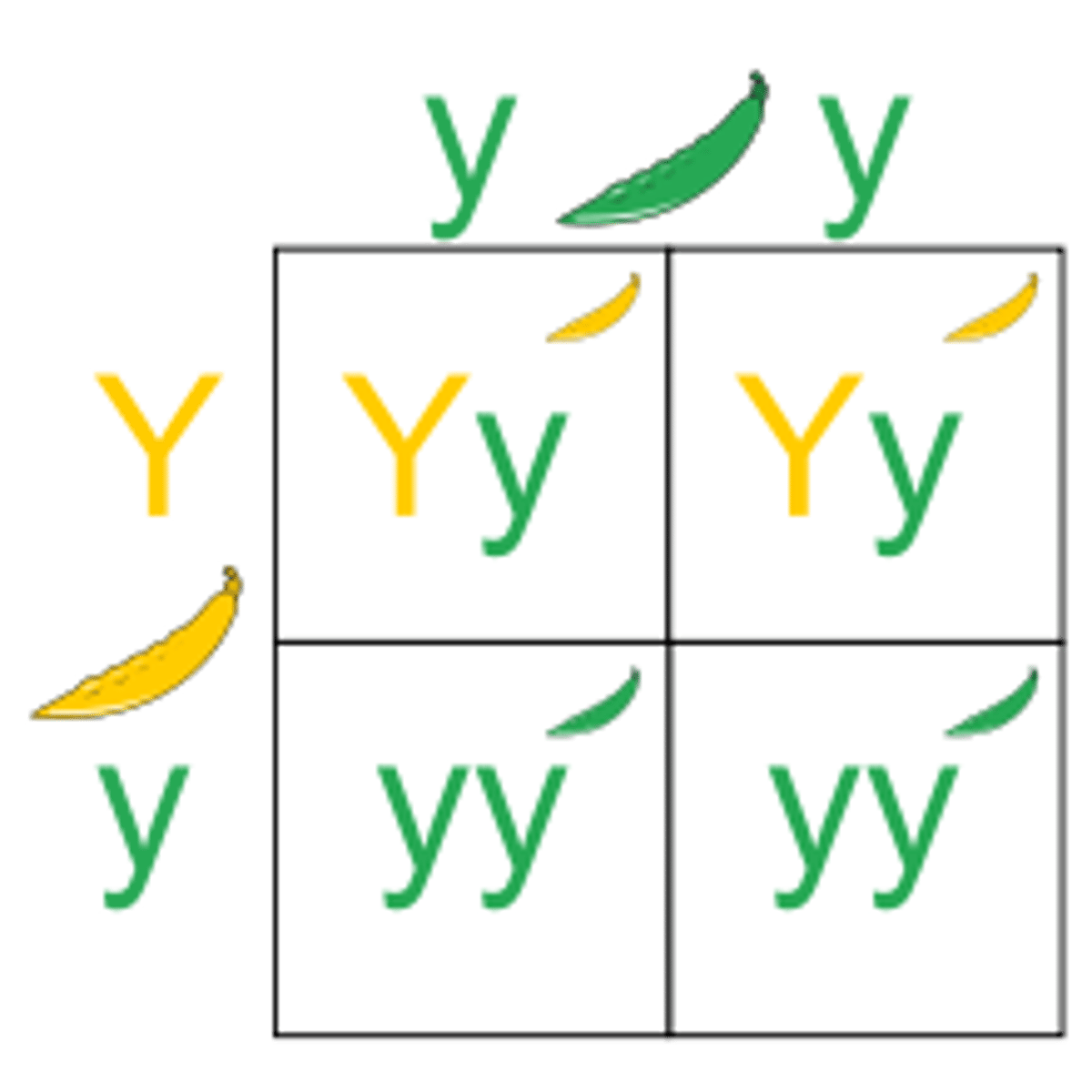
homozygous
An organism that has two identical alleles for a trait
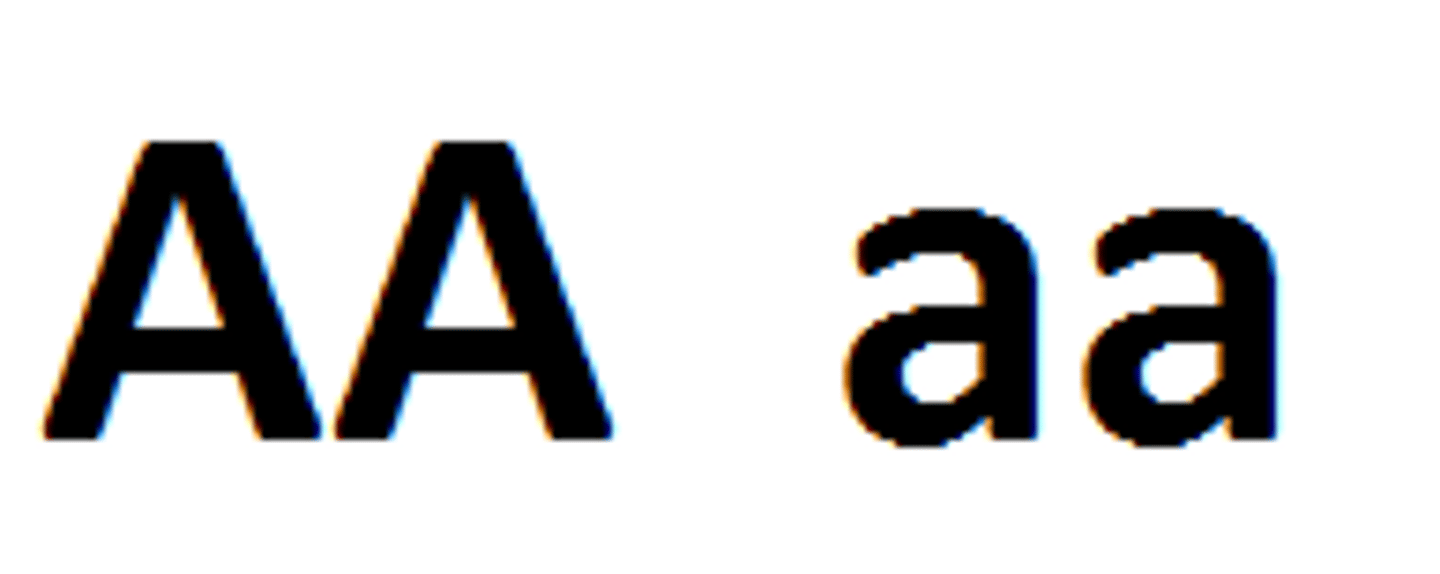
Genotypic ratio
The number of times a genotype would appear in the offspring after a test cross. For example, when 2 heterozygous organisms are crossed, the ratio of the possible genotypes would be 1:2:1.
phenotypic ratio
The number of times a phenotype would appear in the offspring after a test cross. For example, when 2 heterozygous organisms are crossed, the ratio of the possible phenotypes would be 3:1
gene
a segment of DNA that codes for a trait
P1 generation
the original, parent generation
F1 generation
the first generation of offspring
F2 generation
the 2nd generation of offspring
Principle of Dominance
The idea that some alleles are dominant and others are recessive; the recessive allele appears to "skip generations" when paired with a dominant allele
monohybrid cross
a cross of two parents that are both heterozygous for ONE trait
Independent assortment
alleles for different traits are distributed to sex cells independently of each other; for example, the genes for brown eyes and brown hair do NOT stay together.
sex-linked traits
genetic traits that are found on the sex chromosomes (X or Y) and thus are sex-based