Charlemagne and Middle Ages
1/123
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
124 Terms
This Treaty split the Empire of the Franks into three parts
The Treaty of Verdun
Who was the Pope in Rome who crowned Charlemagne in 800 CE as the Holy Roman Emperor?
Pope Leo III
The Capitulary of the Saxons noted forced baptism of this group
Infants (& some Saxons)
Carolingian Miniscule was designed to help educated Franks do this
Read texts easily - by using punctuation and upper/lower case letters
Einhard describes the fate of the Saxons at the end of 30 year war. What does he state Charlemagne did to minimize the power of the Saxons to rebel and force Christianity?
Charlemagne deported Saxons from their lands, to other areas of the kingdom
Viking raids declined in the Kingdom of the Franks but the group settled in this area of France.
Normandy
As a result of urbanization Strayer argued this political change occurred.
Stronger centralized monarchs (ie, England and France)
The division of labor in cities and towns led to an increase in economic activity because
Production could be highly specialized.
Pope Gregory VII fought with this king over the issue of investiture
Henry IV
The purpose of the Hanseatic League was to
Protect trade between guilds in cities/towns in areas of Western Europe
Oaths that were taken between lords and vassals were called
Fealty oaths
Charlemagne’s capital city and the country where this is located today
Aachen, Germany
In the early Middle Ages, Roman and Germanic cultures blended. This Germanic tradition helped to serve justice.
wergeld
Explain the connection between feudalism and manorialism
Feudalism = political and manorialism is economic
Note relationship between the nobles and peasants are key to both systems - exploitive.
Explain the three field system and note which source describes its effects
Leaving one field fallow each season to help soil.
World History: Connections to Today
Extra Credit? What is Mrs. Wallace’s favorite morning beverage?
Coffee
Extra Credit? Select the BCA faculty members who are former BCA students: Mr. Spinelli, Ms. Pagano, Mr. Walsh, Mr. Isecke, Dr. Bath, Ms. Feuss
Spinelli, Walsh, Isecke, Feuss
Extra Credit? The first academy to be formed at “BCA” was
The Academy for the Advancement of Science and Technology
Extra Credit? What is the name of the BCA Auditorium?
The John Grieco Auditorium
Extra Credit? Where is this at BCA? This subject is taught in the classroom next door.
Biology
Extra Credit? Put the following Kardashians and Jenners in order from oldest to youngest: Kylie, Kourtney, Kendall, Kim
Kourtney, 41, Kim, 39, Kendall, 24, Kylie, 22.
Extra Credit? How is the number of terms a president can serve determined in the U.S.?
2
Extra Credit? What are slugs and snails collectively called?
Molluska
Extra Credit? This individual tried to be voted in as the Speaker of the House yesterday but failed for the second time.
Jim Jordan
Extra Credit? This region of modern day Europe is home to the language of Catalan, a language with roots in the Middle Ages.
Spain
Extra Credit? The Byzantine city of Constantinople is in this modern day country, and is called?
Istanbul, Turkey
Extra Credit? The source that noted the attacks of the Viking on the Franks by year was called
The Frankish Annals
Extra Credit? Notre Dame Cathedral is in
France
Extra Credit? Vikings who settled in Russia were called
The Rus
Extra Credit? Name a place where the Vikings were not successful at plundering?
The Islamic Empire and the Byzantine Empire
This organization had a trading post in Madras and came to use this port as a headquarters.
The British East India Company
King who converted to Christianity in Gaul in 496 CE and gained support from the Church
Clovis
Role of missi dominci in Charlemagne’s Empire
monitor infrastructure, listen to grievances and ensure justice
Ran the school at Aachen, which focused on topics such as Latin, grammar, math, and logic
Alcuin
An estate of land, especially one given on the condition of feudal service
fief
In the early Middle ages, the economic activity of western European manors was largely
unproductive and agricultural
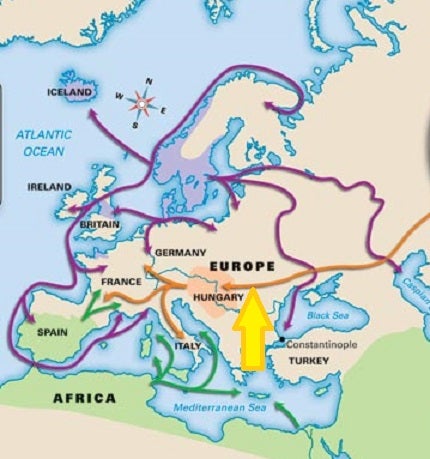
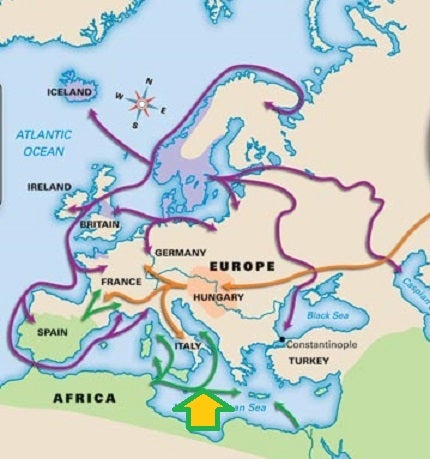
Use the LARGE, YELLOW arrow to identify the invading group in Europe circa 800 CE on the map below:
Magyars
Use the LARGE, YELLOW arrow to identify the invading group in Europe circa 800 CE on the map below:
Islamic Empire
An authoritative prohibition by the Church, such as that posed by Pope Gregory VII, against the actions of a king or lord
interdict
The Carolingian Empire declined mostly because
Charlemagne’s heirs were weak rulers, frequent Viking attacks, and local nobles gaining strength/sought autonomy from the central government
The larger purpose of the Carolingian Renaissance was to
Establish a more standardized practice of Christianity
Which activity was usually NOT found in monasteries in feudal Europe?
Masses and performance of sacraments such as confessions or baptism
The action or practice of lending money at unreasonable high rates of interest (usury)
was seen as immoral according to the Church and a violation of Canon Law
a grant by a sovereign power that allows permission for such things such as towns
charter
The Vikings primarily targeted these areas in Europe during the time period between 750 and 1000 CE
England, Franks, and Russia
Which would not be a cause of the “agricultural revolution” around 1000 CE in Western Europe?
trade
The manor economy was based mostly on
farming and self-sufficiency
What types of sources might largely tell us about the Viking raids on the Franks circa 850 CE?
Annals and Records of the Franks; Archeological digs of Viking ships; Archeological digs in Scandanavia
One of the arguments for the gradual decline of feudalism in Western Euorpe was
increasing power base of merchants in cities and towns
What was significant about the Saxons in Charlemagne’s Empire?
They did not want to convert to Christianity and rebelled for 30 years.
Which occurred last in terms of chronology?
Battle of Tour; Pope Gregory VII expands his power; Viking attacks on the Franks; Women see their roles in guilds decline
Women see their roles in guilds decline
The primary aim of guilds in the High Middle Ages was to ___
protect wages and quality within communities of craft makers and merchants
Arguments that explain decreases of women’s role in the High Middle Ages (about 1300 CE) include
technology and new descriptions for masculinity
Note an important “value” to the source written by “John of Toul”, - if you are researching the effects of feudalism.
It describes the complexity of feudal contracts and challenges for vassals
What is the message behind the “Day of Judgement” carved into the Church of Notre Dame?
Christians should resist sin to access salvation in the kingdom in of heaven
Note an important limitation for the Capitulary on Saxony - To what extent did Christianity spread under Charlemagne?
It details the laws as written in 745 CE and not the enforcement of the law.
How did the Church dominate life in the European Middle Ages and to what extent did reforms develop?
The Church dominated life in the European Middle Ages by controlling the common people’s dependency on the Church for laws and more , and made sure the local priests and nuns were watching the locals, ensuring their devotion to Christianity. The reforms developed to the extent of expanding and securing Christian rule since the Church removed outside influence from kings and nobles, made sure nuns and monks were devoted, and had friars continue to preach Christianity across Europe.
secular
worldly
sacrament
the sacred rituals of the Church
Canon Law
Church’s body of law
excommunication
not able to receive the sacraments or be buried, and shunned
interdict
exclusion of an entire town, region, or kingdom
tithe
tax equal to 10% of income (from Christians paid to Church)
anti-Semitism
prejudice against Jewish people; relating to or denoting a family of languages that includes Hebrew, Arabic, and Aramaic and certain ancient languages such as Phoenician and Akkadian, constituting the main subgroup of the Afro-Asiatic family
Roman Catholic Church
western church, headed by the Pope
Benedictine Rule
rules made to regulate life made by the monk Benedict of the Monte Cassino monastery in Italy (founder)
Dominicans
those who dedicated themselves to educating people about Church doctrines and disputing the ideas of the heretics, named after St. Dominic
charter
written document that set out the rights and privileges of the town
capital
money for investment
usury
lent money at interest
guild
associations, usually based of certain groups of professions
apprentice
trainee
Describe at least three ways in which the Church shaped life in the Middle Ages.
Three ways the Church shaped the Middle Ages were: forcing laws made by the church, some with extreme punishments such as excommunication; made people dependent on churches and monasteries for social centers, rituals, medicine/health treatment, charity, and education; and increased hatred for Jews as Christians blamed Jews for diseases, famines, economic hardships, and the death of Jesus, laying the foundations of anti-Semitism.
What views did the Church hold about women, and to what degree did these views change over time?
The views that the Church held about women were either weak women led by sin as “daughters of Eve” or modest and pure like Mary “mother of God”. In 1100s, women started to speak out more, such as Hildegard who gave advice to many in power. These views changed much over time as the Church began to restrict nuns’ activities, leving them unable to preach, hear confessions, and learn too much to follow Church’s authority blindly; few women were able to reach Hildegard’s position by the early 1400s due to these restrictions.
In what ways did monks and nuns help build Christian civilization in Europe?
Monks and nuns helped build Christian civilization in Europe by copying ancient books, spreading Christian teachings throughout Europe, giving advice, educating locals, and providing social services.
Describe one reform effort to address the role of the Catholic Church.
One reform effort to address the role of the Catholic Church was to have the Church itself choose Church officials, instead of allowing kings’ and nobles’ outside influence.
How did the economy in the Middle Ages change between the Early Middle Ages and the Late Middle Ages? What are the most significant reasons for the economic change, and how did Europeans’ lives change as a result? Who ended up with new forms of power?
The economy in the Middle Ages changed between the Early Middle Ages and the Late Middle Ages because instead of feudal towns only paying the lord in crops, farmers would sell crops and give money to lord as it was desirable to buy luxurious goods. The most significant reasons for the economic change were the increase of merchants and trade throughout Europe because lords started to desire the luxurious goods from the east that the peasants could not purchase, and peasants starting to use currencies to purchase from each other; leading to tenant farmers or hired fam laborers. Due to this, Europeans lives changed as the lords desired money, new jobs that required creating crafts and exchanging them for money that would pay the lord appeared. With the rise of new crafts came the craft guild in addition to the merchant guilds that mostly controlled the town. Merchants and guilds (or the middle class) ended up with new forms of power.
What were two effects of the agricultural revolution that increased the quality of life for Europeans?
Two effects of the agricultural revolution that increased the quality of life for Europeans were more crops, more food from said crops, and a larger population that could be feed from the increase in food due to the new agriculture technologies such as horse-pulled iron plows and windmills.
What new ways of doing business evolved in Europe during the Middle Ages? Why were these practices important?
The new ways of doing business that evolved in Europe during the Middle Ages were: merchants partnerships so that merchants can pool money for large-scale projects; insurance to reduce product risk, and bills of exchange that could be exchanged in a bank for the amount of money written of the bill to not carry gold coins that could easily be stolen. These practices were important because the risk of living as a merchant was greatly reduce as it was easier to earn profit through connections, and loss of money through incidents and thievery.
How did the growth of towns affect the rigid class system of feudalism? What does this suggest about who might hold power later in the Middle Ages?
The growth of towns affected the rigid class system of feudalism by limiting the power of the lords and the Church through charters, making the towns independent through merchants. In addition to this, the nobles found towns were a disruptive influence, and the Church found that usuries profits were immoral. This suggests those who might hold power later in the Middle Ages will need to make deals with merchant guilds, and craft guilds or take control over the guilds.
What kind of power did guilds have in some of the urban centers during the Middle Ages?
The kind of power merchant guilds had in some of the urban centers during the Middle Ages were controls over taxes and where to spend tax money, while craft guilds would ensure quality of goods, regulate hours of labor, prices of goods, help widows and children of dead members, and establish schools and hospitals.
Do you think of American workers as a group that has power in the American society today – in 2023? Why or why not?
American workers as a group have power in the American society in 2023 because without workers, the economy wouldn’t exist, nothing would get done, and money itself wouldn’t exist as money is the trust of the people in the government. This is shown through recent unions from 2023 fighting against major corporations and industries and winning, such as the UPS strike for better working conditions and pay, and the Writer’s strike for better pay.
What resources did Europe have at the dawn of the Middle Ages?
The resources Europe did have at the dawn of the Middle Ages were dense forests in the north, rich soil, and veins of rich minerals. In addition to this, the seas that surround Europe had the potential to house ports for trade.
Multiple groups invaded Europe including “Barbarians,” Islamic Empire, and the Magyars. What were some of the causes and effects of these specific invasions, according to the text?
Some of the causes of the invasions by the “Barbarians,” Islamic Empire, and the Magyars were weakened countries or territories from losts of leaders, wars, and diverted attention; while some effects were the spread of Islam, plundered lands, and trade.
What steps did Charlemagne take to improve his government and unify the Kingdom of the Franks? How successful were his efforts – given the challenges?
The steps Charlemagne take to improve his government and unify the Kingdom of the Franks were keeping control of provincial rulers by using officials called missi dominici to be up to date with each province and uphold justice and reviving the Latin language through educating his people with schools and preserving manuscripts. His efforts were successful given the challenges during his reign; however, his children were unable to follow his legacy, leading to the destruction of the Roman Empire.
What challenges did Charlemagne have in advancing the wellbeing of his kingdom, the European Kingdom of the Franks, and how successful were his efforts by the end of his reign?
The challenges Charlemagne had in advancing the wellbeing of his kingdom, the European Kingdom of the Franks were taking control of the government, keeping accurate records, and promoting education. First, to take control of the government, Charlemagne took control of provincial rulers by using officials called missi dominici to be up to date with each province and uphold justice. Charlemagne learned to read and write himself, therefore realizing accurate records would be needed to complete reports. This was a problem because education had declined. To fix this, Charlemagne had to establish a palace school with scholars who could also copy manuscripts to preserve Latin works and Christianity. By the end of his reign, his efforts were successful, though his descendants ruined his legacy.
Describe three characteristics of a “feudal” political system.
The three characteristics of a "feudal” political system are lords who could granted lesser lords’ fiefs, or land, for the lesser lord to become a vassal, the vassals themselves, and knights for war between lords.
How did the notion of chivalry affect the status of women, according to the text?
According to the text, the notion of chivalry affected the status of women as the code of chivalry made it so men would have to protect and cherish women.
What responsibilities did the peasant have toward the lord? What responsibilities did the lord have toward the peasant?
The responsibilities peasants had toward the lord were working several days a week to farm for the lord, repair the lord’s property, pay marriage fees, pay inheritance fees, pay local mill fees, pay holiday fees, and often pay with food. On the other hand, the responsibilities the lord had towards the peasants were to give the peasants food, housing, and land.
What were the pros and cons of feudalism as a political system? (Note some historians challenge the specific tenets of feudalism – the meaning of the word is broad.)
The pros of feudalism as a political system where peasants were guaranteed the right to live and protection; women were treated better; and noble women were able to get into politics. The cons of feudalism as a political system were arranged marriages; peasants being unable to leave manor without the lord’s permission or pick a lord as lords could change; and the mess caused by a lesser lord being a vassal to multiple lords who may or may not go to war or be allied.
How did feudalism and the limitations of the manor economy shape medieval life in Europe?
Feudalism and the limitations of the manor economy shaped medieval life in Europe by forcing peasants to do work for the lord with little rewards for themselves outside their own work, likely causing demotivation and demoralization. In addition to this, it is entirely possible that many of the lords were corrupt and would not treat their serfs correctly, such as ignoring their needs and having high taxes. Since lords also went to war with each other, there are likely to be many casualties for the common people and the destruction of their crops.
Clovis
King of the Franks, who remembered that his wife was Christian, and swore he would convert to Christianity if won a major battle
Islam
religion that emerged in Arabia in 632. Within 200 years, Muslims had built a great empire and created a major new civilization; enemy of Christians
Charlemagne
Charles the Great; Holy Roman Emperor after protecting Pope Leo III, converted most of Western Europe to Christianity
Alcuin
respected scholar who ran palace school; created curriculum on Latin, grammar, rhetoric, logic, arithmetic, geometry, music, and astronomy; hired scholars to copy ancient manuscripts that would be textbooks for the next 700 years
Treaty of Verdun
treaty that divided the Frankish territory into 3 parts after Charlemagne’s descendants were unable to hold the empire together
Vikings
most destructive raiders; fierce warriors, traders, sailors, and explorers from Norway, Sweden, and Denmark.
missi dominici
officials that would keep control of provincial rulers, check on roads, listen to grievances, and see that justice was done
vassal
lesser lords who would pledge loyalty and service to a greater lord in return for land
fief
estate