visualising microorganisms
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
73 Terms
the human eye cannot see structures smaller than…
100um
morphology of pseudomonas aeurogenosa
rod/bacillus, 1 × 2-5um
prokaryotic microorganisms
archaea, bacteria
eukaryotic microorganisms
protozoa, algae, fungi
eukaryotic microorganisms range between what sizes ?
800nm - 4cm
diameter of RBC
8um (4x E.coli)
spherical
cocci
rod
bacilli
oval
coccobacilli
comma
vibrio
spiral
spirilla
corkscrew
spirochetes
variable
pleomorphic
example of microorganism with cocci shape
staphylococcus aureus
what shape are E.coli ?
bacillus (rod)
syphilis is caused by what microorganism ?
treponema pallidum
magnification
increase in apparent size of image
resolution
ability to distinguish detail between 2 distinct objects
what kind of sample would you visualise using a dark field microscope ?
thin, transparent or unstained
what kind of microscopy is used for visualising live cells and why ?
phase contrast - doesnt require stain
sarcina
cocci grouping of 8+ cells in cuboidal shape
example of coccobacilli shaped microorganism
haemophilus influenzae
why are vibrio curved ?
asymmetric cell wall growth
what is the advantage of a spirilla shape ?
helps microorganism navigate through environment
how has helicobacter pylori evolved ?
spirilla shape helps survive extreme low ph of gastric acid in stomach
what is the advantage of a spirochete shape ?
useful for burrowing through viscous environments
why do pleomorphic microorganisms not have a defined shape ?
absent cell wall
example of a pleomorphic microorganism
mycoplasm pneumoniae
subcellular structures can be seen with what type of microscope ?
electron
what is the fundamental resolution limit for light microscopy ?
400nm
what is the wavelength of visible light ?
400 to 750 nm
refraction
slowing down and bending of light due to change in medium and thus refractive index
refractive index
measure of how much light changes direction when moving between 2 different materials
higher refractive index means light is moving…
slower - more bend
microscopes utilise refraction through the means of…
parabolic glass lenses
what is the refractive index of a parabolic glass lens ?
1.5
“empty” magnification is said to lack…
resolution
resolution of light microscope
0.2um
total mag =
ocular x objective lens
what is a compound microscope ?
system of multiple low powered lenses that correct for aberrations
aberrations
distortions
what is meant by compound microscopes are parafocal ?
maintain focus when switching between objective lenses
purpose of oil immersion
enhances resolution by reducing light refraction at glass-slide interface
how does oil immersion improve resolution ?
refractive index of oil similar to that of microscope slide
when using bright field microscopes specimens appear…
dark against light background
when using dark field microscopes specimens appear…
light against dark background
phase contrast microscopy
enhances contrast in transparent, unstained specimens by exploiting difference in refractive index
how do fluorescent microscopes work ?
fluorophores absorb energy, move to higher energy state, when returning back to lower state emit light at longer wavelength, producing visible fluorescence
electron wavelength is what compared to that of visible light ?
100,000x shorter
what must be done to samples for electron microscopy to work ?
coated in heavy metals to allow for absorption of electrons
what is the purpose of sample prep ?
increases contrast, detection and resolution
fixation
cells immobilised on slide
what are the 2 methods of fixation ?
heat and chemical
what is the main issue with heat fixation ?
distorts morphology - more so than chemical
simple staining
single dye uniformly colours cells increasing visibility eg. methylene blue
differential staining
1 or more dyes to distinguish between cell types or structures eg. gram stain
methylene blue binds to…
negatively charged components via electrostatic interaction
what % v/v is methylene blue ?
1
what are the 2 subtypes of gram stain ?
crystal violet (+) safranin (-)
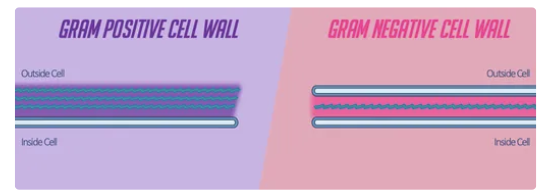
what is the difference between gram pos and neg ?
gram pos lack an outer mem but thick layer of peptidoglycan, gram neg has 2 cell walls thinner peptidoglycan
what % v/v of crystal violet and safranin are used ?
0.5
crystal violet is fixed with what and how ?
iodine - CVI complex trapped in thick peptidoglycan layer of gram pos
why can crystal violet not penetrate all bacterial cells ?
water based - some bacteria have waxy lipid rich (hydrophobic) cell walls
what type of bacteria does acid fast identify ?
those with waxy mycolic acid-rich cell walls
spore differentially stains…
spores and vegetative cells
vegetative cells
any cells of body except those which take part in production of gametes
subtypes of light microscopy
bright / darkfield
phase contrast
fluorescence
which has a higher resolution SEM or TEM ?
TEM - 0.1nm
SEM only 1 - 10
fluorophore
fluorescent dyes or proteins that absorb light at specific (excitation) wavelengths and emit it at longer ones (emission)
role of iris diaphragm in light microscopes
allows for control of light level and angle
differential interface contrast (DIC) microscopy
contrast of sample increased by identifying steep changes in refractive index
no staining required
produces 3D image
light source in fluorescent microscopy
lasers or xenon arc lamps (as opposed to halogen lamp)
SEM samples are fixed and preserved using…
glutaraldehyde and osmium tetroxide