13. visual function and effect of ageing
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/93
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 12:28 PM on 4/11/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
94 Terms
1
New cards
bipolar cells
cells in the retina which transmit impulses from photoreceptor cells to ganglion cells
2
New cards
blind spot
point at the back of the eye where optic nerve exits
3
New cards
cone cell
photoreceptor cell in retina that is responsible for colour vision
4
New cards
fovea
centre area of the macula that contains only cone cells
5
New cards
ganglion cells
cells in retina that transmit impulses from bipolar cells to brain
6
New cards
generator potential
depolarisation of receptor plasma membrane which reaches threshold and initiates action potential
7
New cards
infraction
tissue death caused by lack of blood supply
8
New cards
iodopsins
Photoreceptor proteins in cone cells
9
New cards
Macula
area of retina with most cone cells
10
New cards
rhodopsin
Photoreceptor protein in rod cells
11
New cards
rod cells
light sensitive photoreceptor cell in retina that functions in low light
12
New cards
transducers
sensory receptors that convert light to electrical energy
13
New cards
sclera
tough white outer layer containing collagen that protects the eye
14
New cards
choroid layer
layer behind retina which absorbs light, rich blood supply
15
New cards
retina
innermost layer containing photoreceptor cells
16
New cards
fovea centralis
area of retina with high concentration of cone cells for best visual acuity
17
New cards
optic nerve
bundle of neurones carrying impulses from eye to brain
18
New cards
blind spot
point where optic nerve exits and there is no photoreceptor cells
19
New cards
conjunctiva
protective layer at at front of eye kept moist by film of fluid
20
New cards
iris
coloured tissue at front of eye which controls light entering pupil by smooth muscle
21
New cards
pupil
black hole in centre which lets light in
22
New cards
cornea
clear part of sclera at front that covers iris and pupil which helps focus light
23
New cards
lens
stacks of long, narrow, transparent cells which focus light
24
New cards
ciliary body
muscle which holds lens and alters its shape
25
New cards
suspensory ligament
inelastic ligaments that attach ciliary muscle to lens
26
New cards
vitreous humour
gelatinous fluid within eye which exerts pressure outwards to maintain eye shape
27
New cards
aqueous humour
watery fluid in front of lens which helps maintain shape
28
New cards
conjunctivitis
inflammation or infection of a part of the eye where the blood vessels become dilated or haemorrhage appearing pink or red
29
New cards
dim light
more light let in, radial muscles contract, circular muscles relax, sympathetic nervous system
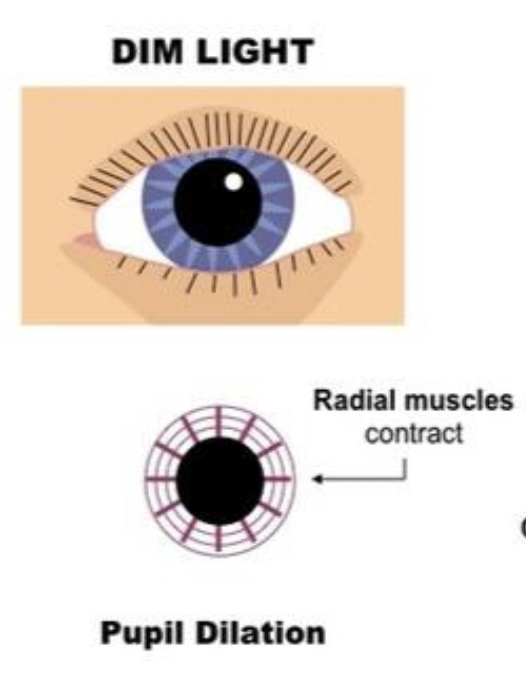
30
New cards
bright light
reduces light entering, radial muscle relax, circular muscle contract, parasympathetic nervous system
31
New cards
refracting surfaces of eye
cornea, front and back of lens
32
New cards
distant object
circular ciliary muscles relax, suspensory ligaments taut, lens pulled thin, less refraction of light
33
New cards
near object
circular ciliary muscles contact, suspensory ligaments slackened, lens bulge, more refraction of light m
34
New cards
myopia
elongated eyeball, light from distance focus in front of retina, treated with concave lens, laser eye surgery, or lens implant
35
New cards
types of cone cells
cells sensitive to red, blue or green
36
New cards
rod cell
longer photoreceptor cell
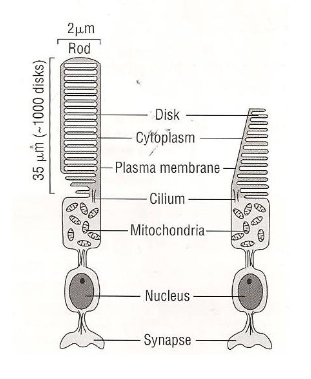
37
New cards
order of retina cells
optic nerve axons, ganglion cells, bipolar cells, photoreceptor cells, pigment epithelium
38
New cards
retinal
absorbs a photon of light and is converted to trans-isomer from cis-isomer. activates opsin
39
New cards
opsin
protein in rhodopsin with retinal
40
New cards
bleaching
when rhodopsin spits due to retinal changing isomers, reversed by re synthesis with ATP
41
New cards
ATP produced for re synthesis of rhodopsin
many mitochondria in inner segment of rod cells
42
New cards
vitamin A
vitamin needed to to re synthesise retinal into rhodopsin
43
New cards
iodopsin
photosynthesis pigment in cone cells which eolith absorbs red, green, or blue light
44
New cards
s cone
short wave light blue light - 420nm
45
New cards
m cone
medium wavelength green light - 543nm
46
New cards
l cone
long wavelength red light - 564nm
47
New cards
bipolar cells
synapse with many rod cells or single cone cell, and ganglion cell on other
48
New cards
summate
when many rod cells combine to depolarise bipolar neurone
49
New cards
glutamate
inhibitory neurotransmitter which causes the adjacent bipolar neurone to become hyper polarised
50
New cards
glutamate
causes ganglion neurone to become depolarised creating generator potential
51
New cards
visual acuity, colour vision, pupil response
3 aspects of eye tests
52
New cards
every 2 years
routine eye test carried out
53
New cards
snellen chart
letters chart, big to small, viewed at 6m, one eye covered

54
New cards
20/20 visual acuity
ability to ready letters 1cm high at 6m
55
New cards
near vision test
reading card with different size blocks of text at 30cm
56
New cards
presbyopia
near vision loss. lens is less flexible as older (40+) so less able to focus near objects
57
New cards
colour blindness
absence of one or more types of cone, recessive sex linked condition affecting makes more
58
New cards
protanopia
absence of red cone cells
59
New cards
deuteranopia
absence of defect in green cone cells
60
New cards
Ishihara colour vision test
individuals with colour blindness don’t see numbers, different colour combinations
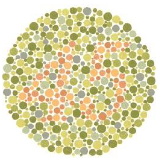
61
New cards
Farnsworth-munsell 100 hue test
caps sorted into hue order, red, green, blue and yellow

62
New cards
optical coherence tomography
OCT, non invasive, beam of near infra red light, detects reflected light, scattered removed with interferometry, 3d image of retina, map and measure thickness
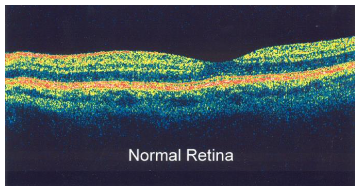
63
New cards
neurones die
loss of synaptic connections at about age 20
64
New cards
brain volume and mass
brain decrease by 10% at 90, frontal lobe and hippocampus effected most

65
New cards
thinner cortex
thins from age 20, due to loss of synaptic connections
66
New cards
white matter
decreases with age, leading to reduced speed of cognitive processing like memory, attention, action, problem solving, and decision making
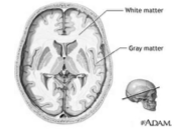
67
New cards
ventricles
enlargement with age, more significant with dementia
68
New cards
neurotransmitters
effects memory due to less synthesis of receptor proteins and…
69
New cards
onset of dementia
age related memory loss is temper lapses of memory however severe disruptive loss indicates…
70
New cards
slow age related memory loss
regular exercise, manage stress, crosswords
71
New cards
worsen age related memory loss
smoking and alcohol
72
New cards
effect of ageing on reaction times
simple involuntary reflex, different ages, unpaired t test
73
New cards
presbycusis
age related hearing los, gradual from 18 years, loss of sensitive share cells in cochlea and neurone in auditory nerve
74
New cards
high frequencies
frequencies most effected by age related hearing loss
75
New cards
range of normal speech
autograph carried out between 250 and 8000Hz
76
New cards
normal hearing level
up to 25dB
77
New cards
glaucoma
tunnel vision, optic nerve damage, increased eye pressure as aqueous humour doesn’t drain, eye drops, laser, medication, or surgery
78
New cards
chronic open angle
drainage channels slowly come blocked, reduced visual field
79
New cards
acute closed angle
less common, rapid onset, pressure in eye pushes edge of iris against cornea blocking drainage channels
80
New cards
age related macular degeneration
ARMD, loss of central vision due to degeneration of macula, dry- debris from pigments not broken down, retina detaches, wet- blood vessels grow, laser treatment, strong glasses
81
New cards
cateracts
clouding of lens and loss of elasticity, blurred vision, worse in low light, denaturation and aggregation of lens proteins, age related, stronger glasses and brighter lights, replacement lens
82
New cards
alzheimers
degenerative disease of nerve system effecting frontal and temporal lobes
83
New cards
early Alzheimers
* minor memory loss eg names and location of objects
* suffers aware of memory loss
* long term memory intact
* suffers aware of memory loss
* long term memory intact
84
New cards
mid-stage Alzheimers
* personality changes, physical problems
* dependant on others for care
* no longer aware of memory loss
* impaired long term memory
* dependant on others for care
* no longer aware of memory loss
* impaired long term memory
85
New cards
late stage Alzheimers
* deterioration of personality
* loss of control over body functions
* total dependency on others
* speech severely effected
* inability to swallow and lead to death
* loss of control over body functions
* total dependency on others
* speech severely effected
* inability to swallow and lead to death
86
New cards
multifactorial
disease with many factors contributing to it eg Alzheimers, effected by age and family history
87
New cards
abnormal break down of protein
B amyloid proteins are produced from myelin sheath which accumulate and form plaques around neurones causing them to degenerate and less neurotransmitter produced.
88
New cards
tau proteins
proteins which normally stabilise microtubules in cytoskeleton, defective ones aggregates forming neurofibrillary tangles in neurones. microtubules disintegrates and transport system collapse, less neurotransmitter, nerve dies
89
New cards
cholinergic
reduction in acetylcholine levels, most treatments based on this
90
New cards
amyloid
location of even for protein precursor on chromosome 21, links it to down syndrome. maybe derrivative called ADDLs that cause damage
91
New cards
tau
abnormalities in proteins cause neurofibrillary tangles interfering with microtubules and intracellular transport in neurones
92
New cards
acetylcholine inhibitors
use to prevent breakdown of acetylcholine to treat Alzheimers
93
New cards
carers activities
help with eating, washing, dressing, going to toilet
94
New cards
carers difficulties
financial cost, ability to work, distress, patients legal maters