cell fractionation
1/10
Earn XP
Description and Tags
yum !
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
give the 4 main steps of cell fractionation:
sample preparation
homogenisation
filtration
ultracentrifugation
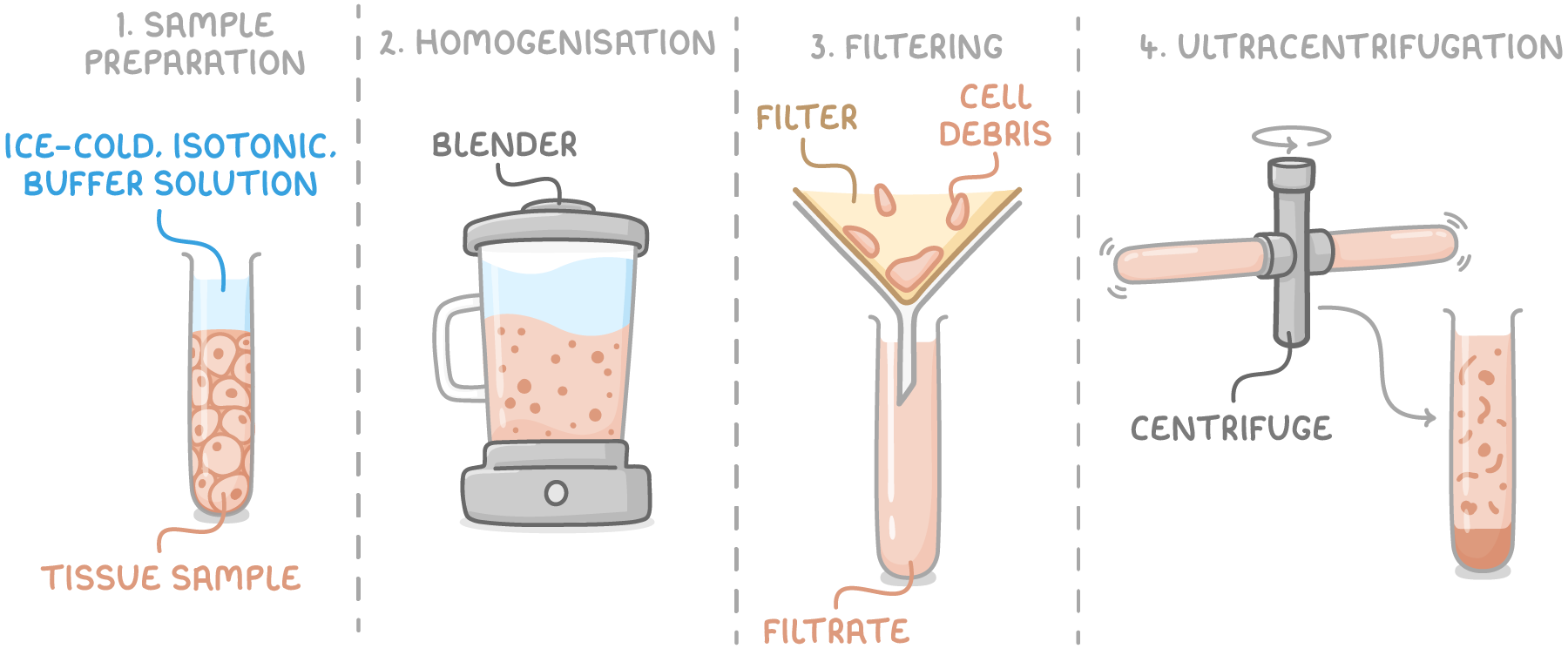
describe the sample preparation stage:
sample is placed in an ice cold, isotonic, buffered solution
why must the solution used in sample preparation be ice-cold?
reduce enzyme activity that might otherwise digest organelles otherwise
why must the solution used in sample preparation be isotonic?
ensures ψ inside and outside organelles is the same, so they do not burst as a result of osmosis
why must the solution used in sample preparation be buffered?
keeps pH constant so that organelle structures are not damaged and enzymes do not denature
describe and explain the homogenisation stage:
cells are physically broken open using a blender
this disrupts the plasma membrane, allowing the organelles to be released into the solution
describe the filtration stage:
mixture filtered to remove cellular debris and tissue fragments
filtered through a gauze - allows organelles to pass through while retaining larger debris
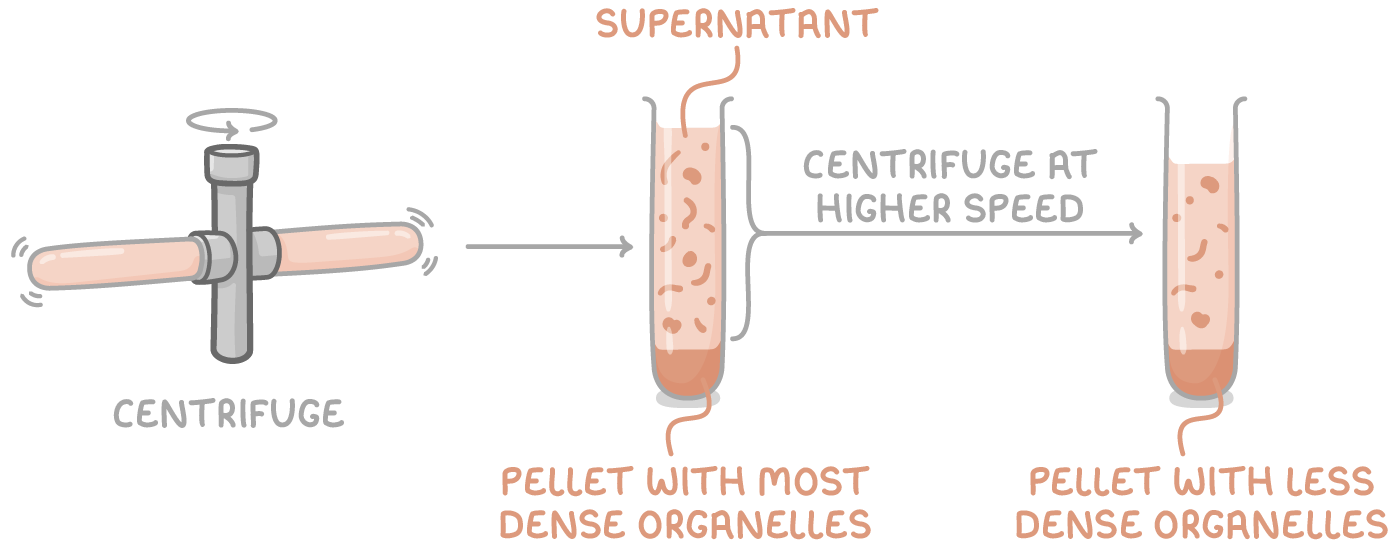
describe the ultracentrifugation stage:
filtrate centrifuged at a low speed → heaviest organelles (nuclei) form pellet at bottom of tube, lighter organelles remain suspended in supernatant
supernatant transferred to new tube and centrifuged at a higher speed → next heaviest organelles (chloroplasts/mitochondria) form new pellet
transfer supernatant into new tube and repeat entire process, increasing speed each time until all organelles have been separated into distinct layers
give the order of organelles from heaviest to lightest:
nuclei
chloroplasts
mitochondria
lysosomes
ER
ribosomes
what is the pellet?
sediment at bottom of tube - contains heavier organelles
what is the supernatant?
liquid remaining above pellet - contains lighter organelles