unit 1: levels of measurement
1/9
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
levels of measurement
rules for assigning numbers to objects (nominal→ ordinal → interval→ ratio)
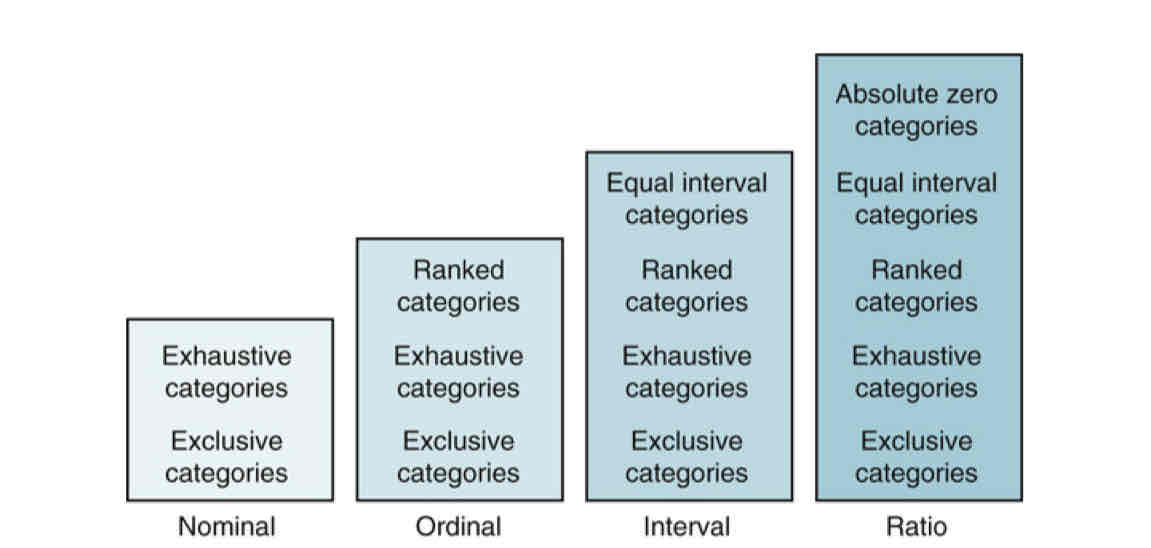
nominal
-lowest form
-exclusive and exhaustive
ex: gender, race, ethnicity
ordinal
-exclusive and exhaustive
-categories that can be rank ordered
-values do NOT have equal distances btwn. them
-ex: pain scale
nonparametric statistics
-used to analyze nominal and ordinal level variables
-values don’t need to be equally distributed
mode
-nominal level data
-most frequently occurring in a data set
median
-ordinal level data
-middle value in a data set
interval
-distance btwn. intervals of the scale are equal
-exclusive and exhaustive
-NO absolute zero (can go below zero)
-ex: temperature
ratio
-highest form of measurement
-exclusive and exhaustive
-numerically equal intervals of a scale
-IS an absolute zero (can’t go below zero)
-ex: pulse, BP, age
parametric statistics
-used on interval and ratio levels of data
-variables are continuous
significant results
-results that align with the outcomes predicted by the researcher/team
-usually identified by an * or p values less than or equal to 0.05