geography - the living world, tropical rainforests, deserts
1/193
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
194 Terms
producer
an organism that uses light energy and photosynthesis to produce sugars
consumer
an organism that gets its energy by eating other organisms (producers and other consumers)
decomposer
organism that gets it’s energy by decomposing dead organic material in an ecosystem
what are 2 examples of decomposers
bacteria, fungi
what are 6 key biomes
grassland
tundra
tropical rainforest
temperate deciduous forest
polar
hot desert
where are tundras distributed/located (2)
high latitudes, above 60° N
N europe, alaska, N canada
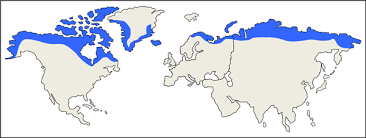
what is the seasonal weather like in Tundra biomes (3)
winters are very cold
summers are brief
little rainfall
how is the environment like in Tundra biomes (3)
barely any trees
vegetation like moss, grass and shrubs
permafrost
what is permafrost
a layer of permanently frozen ground
what are the 2 types of grassland
savannahs and temperate grasslands
where are savannahs located/distributed
found between the tropics
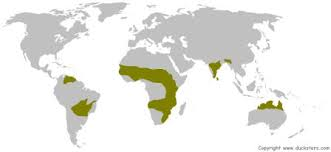
what is the seasonal weather like in a savannah (2)
distinct dry and wet seasons
rainfall is low
what is the environment like in savannahs (2)
grasses
a few scattered trees
where are temperate grasslands located/distributed
higher latitudes (then savannahs)
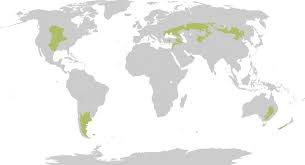
what is the seasonal weather like in temperate grasslands (2)
more variation in temperature
very little rainfall
what is the environment like in temperate grasslands (2)
no trees
only grass
where are temperate deciduous forests found
in the mid latitudes
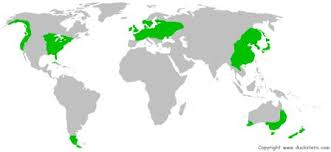
what is the seasonal weather like in temperate deciduous forests (4)
4 distinct seasons
summers are warm
winters are mild
rainfall all year
what is the environment like in temperate deciduous forests (2)
trees (which lose leaves in winter)
lots of vegetation
where are polar biomes located/distributed
around the north and south poles
what is the seasonal weather like in polar regions (4)
very cold
icy
dry
very dark for several months of the year
what is the environment like in polar regions
not much grows
where are hot deserts located/distributed
between 15° and 35° N and S of the equator
what is the seasonal weather like in hot deserts (3)
very hot during day
very cold at night
very little rainfall
what is the environment like in hot deserts (3)
shrubs
cacti
sandy soil
where are tropical rainforests located/distributed (2)
around the equator
between tropics
what is the seasonal weather like in tropical rainforests
hot + wet all year
what is the environment like in tropical rainforests (2)
lush forests
dense vegetation
what latitude is the tropic of cancer at
23.5° North of the equator
what latitude is the tropic of capricorn at
23.5° South of the equator
what is Epping Forest
a temperate deciduous forest located in SW england
Epping forest is a …
SSSI (site of special scientific importance)
example of a food chain in epping forest
shrubs/grasses → worm → rabbit → fox
trees found in epping forest? (4)
oak
breech
hornbeam
elm
how many lakes and ponds are there and why is this important
100+ → provides important habitats for many plants and animals
no. of species of fungi in epping forest?
700 (common due to large amount of deadwood)
how is epping forest sustainably managed
recreation controlled within forest (designated visitor areas e.g. car parks, visitor centre)
paths for walking → protect forest for future gens
vegetation cut back to alert deer of traffic + reduce collisions → protects current + future deer populations
cattle reintroduced in some areas (grazing supports growth of some flora) → helps support flora growth
what is rainfall like in deserts
it varies a lot. it might only rain once every 2/3 years
what is temperature like in deserts
very hot in day (45°C) and very cold at night (5°C)
what is the soil like in deserts (3)
shallow with a coarse, gravelly texture
soil is infertile
soil is dry
what is plant life and vegetation like in deserts (3)
growth is sparse due to lack of rainfall
e.g. of plants are cacti, thornbushes and shrubs
plants have a short life cycle and only appear when it rains
what animals are there in deserts (2)
lots of reptiles, e.g. lizards, snakes, insects, scorpions
mammals tend to be small and nocturnal
people in deserts (2)
tend to be nomads mostly
very few people
how do plants and animals depend on eachother in deserts
plants get nutrients from soil. animals that eat plants digest the nutrients. when animals excrete, their dung contains seeds and nutrients, helping plants reproduce
how is biodiversity in deserts?
very low
there is a sparse number of plants…
so the desert can only support low-density populations of animals
how does the scarce supplies of water affect deserts, animals and plants
the little rainfall is quickly drained away by the coarse desert soil. animals and humans have to find ways of coping, e.g. constantly moving to new places, digging deep wells
how do people grow crops in deserts
through irrigation (artificially watering the land). they draw unsustainable amounts of water from wells.
how does irrigation affect other plant species and animals
it lowers the level of water underground. this reduces the amount available to other plants, so there are less plants for animals to eat
adaptations of plants in deserts? (4)
plant roots
succulent plants
small leaves/spines
seeds only germinate when it rains
how do plant roots help desert plants survive in the conditions (2)
either:
long to reach very deep water supplies
wide to catch lots of rainfall
how do succulent plants survive in the conditions (3)
large, fleshy stems for storing water
thick waxy skin to reduce transpiration
some have sharp spines and toxins to stop animals stealing water from their stems
how does having small leaves or spines help desert plants survive in the conditions (1)
low surface area, reducing transpiration
how does having seeds which only germinate when it rains help desert plants survive in the conditions (1)
the plants grow, flower and release seeds in just a few weeks, making sure they only grow when there’s enough water to survive
adaptations of animals to survive in deserts (4)
nocturnal
have large limbs/ears
able to tolerate high temps
store large amounts of fat
how does being nocturnal help animals to survive in desert conditions (1)
can stay cool by burrowing underground/sitting in shade during day
what is an example of an animal that is nocturnal in deserts
fennec foxes
how does having large limbs/ears help animals to survive in desert conditions
provides a large surface area to lose heat from
how does being able to tolerate high body temperatures help animals to survive in desert conditions (2)
can tolerate higher temps
examples: lizards, snakes, desert iguanas
how does being able to store large amounts of fat help animals to survive in desert conditions
larger mammals can store fat, allowing them to break it down into water when needed
example of animals that store fat
camels (in their humps)
how are camels adapted for deserts? (5)
store fat in their humps
triple eyelids
long eyelashes
they can close their nostrils
large, flat feet
how does having triple eyelids, long eyelashes and being able to close nostrils help camels
keeps sand out of their eyes and nose
how does having large, flat feet help camels
stops them from sinking into the sand
where is biodiversity + human population highest in deserts (2)
small areas around ephemeral (temporary) ponds or rivers
along desert margins
endemic
unique
what do these areas contain
a high proportion of species that are endemic to the desert
what does development around desert margins result in
habitats being divided up by roads. this threatens animals that migrate over large distances to find food and water e.g. desert bighorn sheep
what is the effect of global warming on deserts and animals
makes them hotter and drier
what is the effect of global warming on animals in deserts
animals (e.g. lizards) migrate to cooler areas. animals that can’t migrate are on the decline, or risk of extinction.
what is the world’s largest desert
sahara desert
how big is the sahara desert?
9,000,000 km²
opportunities of economic development in the sahara desert (5)
oil and gas extraction
solar energy
tourism
mineral resources
farming/water irrigation
what is an opportunity of oil and gas extraction? (2)
40,000 jobs
60% of it’s economy comes from this industry