Effective Communication in Nursing and Psychotic Disorders
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
92 Terms
What are the key aspects of verbal communication in nursing?
Timing/relevance, pacing, and intonation.
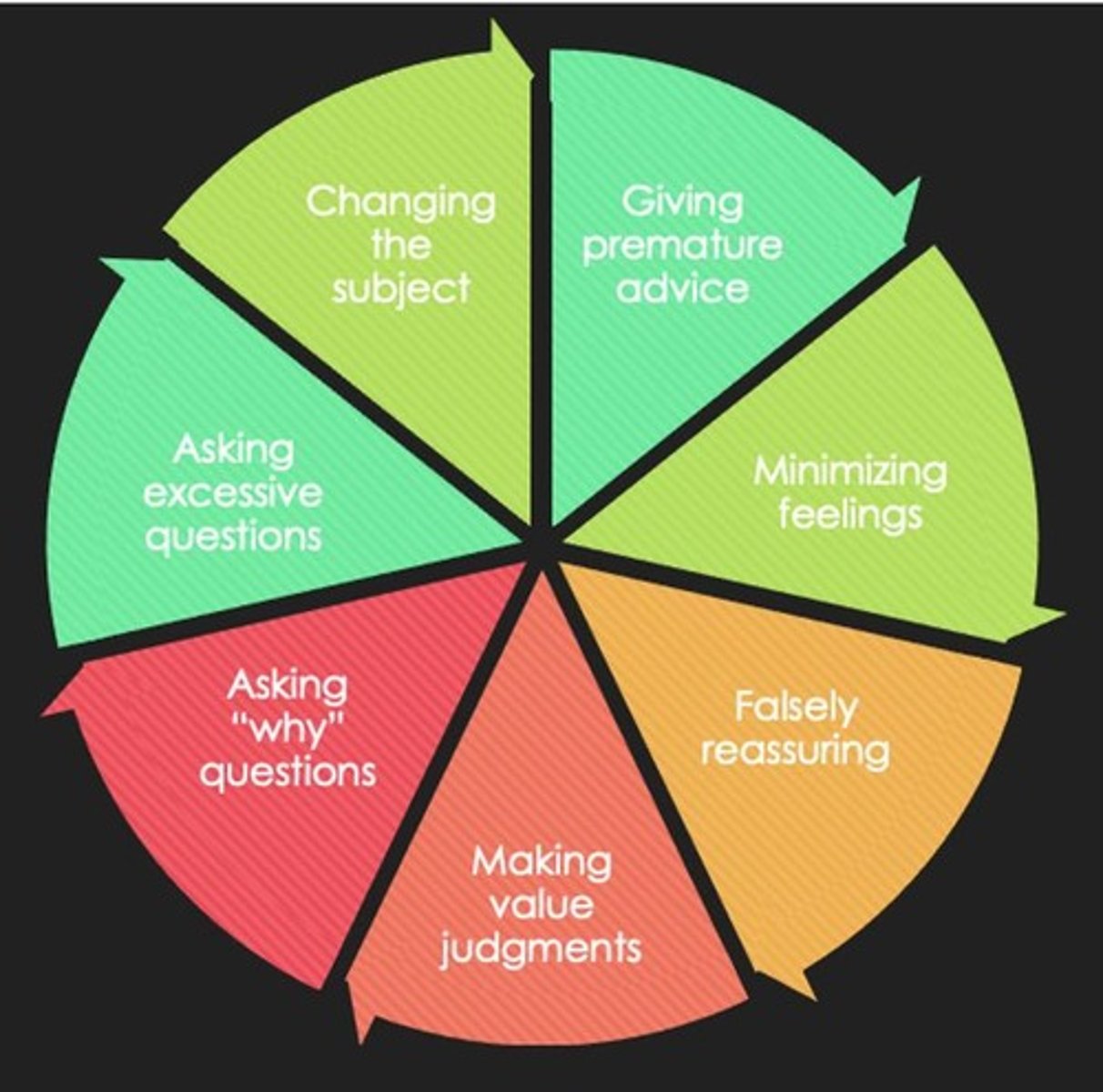
How does timing affect communication in nursing?
Knowing when to communicate allows the receiver to be more attentive to the message.
What impact does pain or distraction have on communication?
It makes it difficult for the nurse to convey the message.
How does pacing influence the perception of a nurse's communication?
A rapid rate of speech can be interpreted as the nurse being in a rush and inattentive.
What does intonation convey in verbal communication?
The tone of voice can communicate a variety of feelings.
What are the keys to therapeutic communication?
Caring attitude, honesty, trust, empathy, and a nonjudgmental attitude.
What is the first strategy in therapeutic communication?
Safety: Stay with the client, protect the client from injury, and assess what the voices are telling the client.
What is the significance of Maslow's hierarchy in therapeutic application for mania?
It serves as a rule of thumb for understanding client needs.
What are some positive symptoms of psychosis?
Hallucinations, delusions, alterations in speech, alterations in behavior, and personal boundary difficulties.
What are hallucinations?
Sensory experiences that appear real but are created by the mind.
What are delusions?
Strongly held false beliefs that are resistant to reasoning.
What is associative looseness in alterations in speech?
Disconnected thoughts that have no cohesive message when expressed.
What is flight of ideas?
Speech moving rapidly from one thought to another, making it impossible to comprehend.
What are neologisms?
Made-up words that have meaning only to the client.
What is echolalia?
Pathological repeating of words spoken to them.
What is clang association?
Choosing words for communication based solely on their sound.
What does 'word salad' refer to?
Words jumbled together with little to no meaning.
What are some alterations in behavior associated with positive symptoms?
Extreme agitation, pacing, rocking, stereotyped behaviors, automatic obedience, negativism, echopraxia, catatonia.
What is catatonia?
Pronounced increase or decrease of movement.
What is waxy flexibility?
Maintaining a specific position for extended periods of time.
What is depersonalization in the context of personal boundary difficulties?
A nonspecific feeling that a client has lost their identity.
What is derealization?
A perception that the environment has changed, such as believing that objects are shrinking.
What are illusions in the context of psychotic disorders?
Misperceptions or misinterpretations of a real experience.
What is the purpose of the Abnormal Involuntary Movement Scale (AIMS)?
To monitor involuntary movements, particularly tardive dyskinesia in clients taking antipsychotic medications.
What does the World Health Organization Disability Assessment Schedule (WHODAS) assess?
It helps determine the client's level of global functioning.
What is milieu therapy?
A therapeutic approach that promotes self-care in a structured and safe environment for clients with psychotic disorders.
What is the Program of Assertive Community Treatment (PACT)?
A treatment approach that includes activities like music and walking to distract from hallucinations.
What should a nurse do when a client reports hallucinations?
Ask the client directly about the hallucinations without arguing or agreeing with their view.
What are command hallucinations and why are they significant?
They are hallucinations that instruct the client to act, which can increase the risk for harm to self or others.
What are first-generation antipsychotics primarily used for?
To control positive symptoms of schizophrenia.
What are the characteristics of low-potency first-generation antipsychotics?
They have low extrapyramidal symptoms (EPS), high sedation, and high anticholinergic side effects.
What complications can arise from first-generation antipsychotics?
Anticholinergic manifestations, agranulocytosis, sedation, and severe dysrhythmias.
What is agranulocytosis and how is it monitored?
A severe reduction in granulocytes, especially neutrophils; monitored by obtaining a CBC and discontinuing medication if WBC is < 3000 mm3.
What nursing actions should be taken for anticholinergic side effects?
Encourage fluid intake, sugarless gum, and high-fiber foods, and educate clients on signs of infection.
What are the signs of neuroleptic malignant syndrome (NMS)?
Symptoms include fever, muscle rigidity, and autonomic instability.
What should be monitored in patients taking high-potency first-generation antipsychotics?
Monitor for high EPS, low sedation, and low anticholinergic side effects.
What are some common side effects of first-generation antipsychotics?
Dry mouth, blurred vision, urinary hesitancy, constipation, and tachycardia.
What precautions should be taken with first-generation antipsychotics?
Avoid concurrent use with anticholinergic medications, alcohol, and opioids; use caution in patients with CNS depression.
What is the significance of teaching clients about potential side effects?
To ensure they recognize and report issues like sedation, sexual dysfunction, and signs of infection.
What role does therapeutic communication play in nursing care for schizophrenia?
It helps establish a trusting relationship and assess discharge needs.
What should a nurse focus on when communicating with a client experiencing paranoid delusions?
Focus on the client's feelings and provide reasonable explanations without arguing.
What are some triggers for hallucinations in clients?
Loud noises and situations that provoke discussions about the client's delusions.
What is the recommended approach when a client is experiencing hallucinations?
Engage in reality-based conversations and identify triggers to manage manifestations.
What nursing actions are recommended for managing sedation from antipsychotics?
Educate clients to take medications at bedtime and avoid driving until sedation subsides.
What are the potential effects of first-generation antipsychotics on weight and metabolism?
They can cause weight gain, gynecomastia, and menstrual irregularities.
What is the importance of monitoring liver function tests (LFTs) in patients on antipsychotics?
To assess for liver impairment and adjust treatment as necessary.
What is the impact of first-generation antipsychotics on sexual function?
They can cause sexual dysfunction, which may require dosage adjustment or switching medications.
What should be done in case of a medical emergency involving fever during antipsychotic treatment?
Go to the ER, stop the antipsychotic, and start aggressive hyperthermia measures.
What is the typical temperature associated with fever in this context?
Often upwards of 105 ℉.
What are some symptoms accompanying fever in antipsychotic treatment emergencies?
Confusion, impaired memory, decreased level of consciousness, and vital sign instability.
What immediate cooling measures should be taken for a patient with fever?
Use cooling blankets, administer antipyretics, and apply ice packs.
What medications may be administered to treat muscle rigidity and cardiac manifestations during a fever emergency?
Dantrolene (muscle relaxer) and Bromocriptine (dopamine agonist).
What should be done after treating a fever emergency in a patient on antipsychotics?
Assist immediate transfer to ICU and wait 2 weeks before resuming therapy.
What is the recommended action if a patient experiences extrapyramidal symptoms (EPS) such as acute dystonia?
Administer anticholinergic/antiparkinsonian medications like Benztropine or antihistamines like Diphenhydramine.
What are the symptoms of acute dystonia?
Severe and painful involuntary contractions/spasms in the tongue, face, neck, and back.
How soon after the first dose should monitoring for acute dystonia begin?
Anywhere between 1 to 5 days after administration.
What is pseudoparkinsonism and its symptoms?
Motor deficits resembling Parkinson's disease, including bradykinesia, tremors, rigidity, drooling, shuffling gait, and pill rolling.
When can pseudoparkinsonism occur after the first dose of antipsychotic medication?
Can occur in 5 to 30 days following the first dose.
What treatments are available for pseudoparkinsonism?
Anticholinergic/antiparkinsonian medications like Benztropine and Trihexyphenidyl.
What is akathisia and its symptoms?
Inability to sit or stand still, characterized by pacing, agitation, anxiety, jitteriness, and feelings of 'crawling out of your skin'.
When does akathisia typically occur after the first dose?
Generally occurs in 5 to 60 days following the first dose.
What treatments are recommended for akathisia?
Beta-blockers like Propranolol, anticholinergic/antiparkinsonian medications like Benztropine, and benzodiazepines like Lorazepam.
What should be monitored in clients with severe akathisia?
Increased risk for suicide.
What characterizes tardive dyskinesia (TD)?
Involuntary movements of perioral muscles and extremities, including tongue fasciculations, lip smacking, and grimacing.
When can tardive dyskinesia appear after starting antipsychotic therapy?
Can occur after months to years, typically years.
How often should patients be evaluated for tardive dyskinesia?
After 12 months of therapy and then every 3 months.
What should be done if tardive dyskinesia appears?
Lower dosage or switch to a second-generation antipsychotic, if applicable.
What is the treatment for tardive dyskinesia?
There is no effective treatment; it is largely permanent, and Benztropine should not be used as it will worsen the condition.
What is the purpose of Valbenazine?
It treats abnormal involuntary movements but is not yet on the ATI.
What scale is used to screen for the presence of EPS?
Abnormal Involuntary Movement Scale (AIMS).
How can a nurse differentiate between EPS and worsening of a psychotic disorder?
By assessing the client for specific symptoms.
When should drugs be administered to control EPS?
Early, to manage early EPS symptoms.
What can be done if adverse effects of antipsychotics are intolerable?
Switch to low-potency or second-generation antipsychotics.
What types of medications can be used to manage EPS?
Anticholinergics/antiparkinsonians, beta-blockers, and benzodiazepines.
What is the recommended administration frequency for depot shots in noncompliant clients?
Every 2 to 4 weeks.
What are some second-generation antipsychotics?
Aripiprazole, Cariprazine, Brexpiprazole, Asenapine, Clozapine, Quetiapine, Olanzapine, Iloperidone, Lurasidone, Paliperidone, Ziprasidone, Risperidone.
What are the therapeutic uses of second-generation antipsychotics?
To treat both negative and positive symptoms of psychosis, psychosis induced by levodopa therapy, and impulse control disorders.
What complications are associated with second/third-generation antipsychotics?
Metabolic syndrome, agitation, sleep disruption, elevated prolactin, diabetes, dyslipidemia, weight gain.
What symptoms should be reported when taking second/third-generation antipsychotics?
Increased thirst, appetite, urination, and signs of hypotension.
What are some sexual side effects of second-generation antipsychotics?
Galactorrhea, gynecomastia, amenorrhea, and sexual dysfunction.
What nursing action should be taken for significant changes in a patient's condition while on antipsychotics?
Hold medication and contact the provider.
What holistic measures can be used to combat anticholinergic effects?
Sip water and use lozenges.
What are the available forms of Lurasidone?
Tablets, orally disintegrating tablets (ODT), oral solution, and long-acting injectable.
What are the nursing actions for administering Risperidone?
Administer with food and monitor for metabolic syndrome and EPS.
What are the adverse effects of Olanzapine?
Weight gain, sedation, prolonged QT interval, and orthostatic hypotension.
What should be monitored after administering extended-release injections of antipsychotics?
The client requires observation for more than 3 hours to monitor for adverse effects.
What is a significant risk associated with Clozapine?
It has the highest risk for agranulocytosis, requiring regular WBC monitoring.
What are the available forms of Quetiapine?
Tablets, extended-release tablets, and ODT.
What are the common adverse effects of Aripiprazole?
Sedation, headache, anxiety, insomnia, and gastrointestinal upset.
What is the mechanism of action for third-generation antipsychotics?
They stabilize dopamine and act as both agonists and antagonists on different receptors.
What should be avoided when taking second-generation antipsychotics?
Alcohol (ETOH) due to increased risk of adverse effects.
What is the recommended nursing action for patients taking antipsychotics with a risk of EPS?
Educate on titration during initial therapy to minimize hypotension.