topic 6 psych test
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
66 Terms
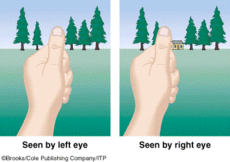
Retinal disparity
binocular cue
By comparing images from two eyes, the greater the distance de between two images, the closer the object
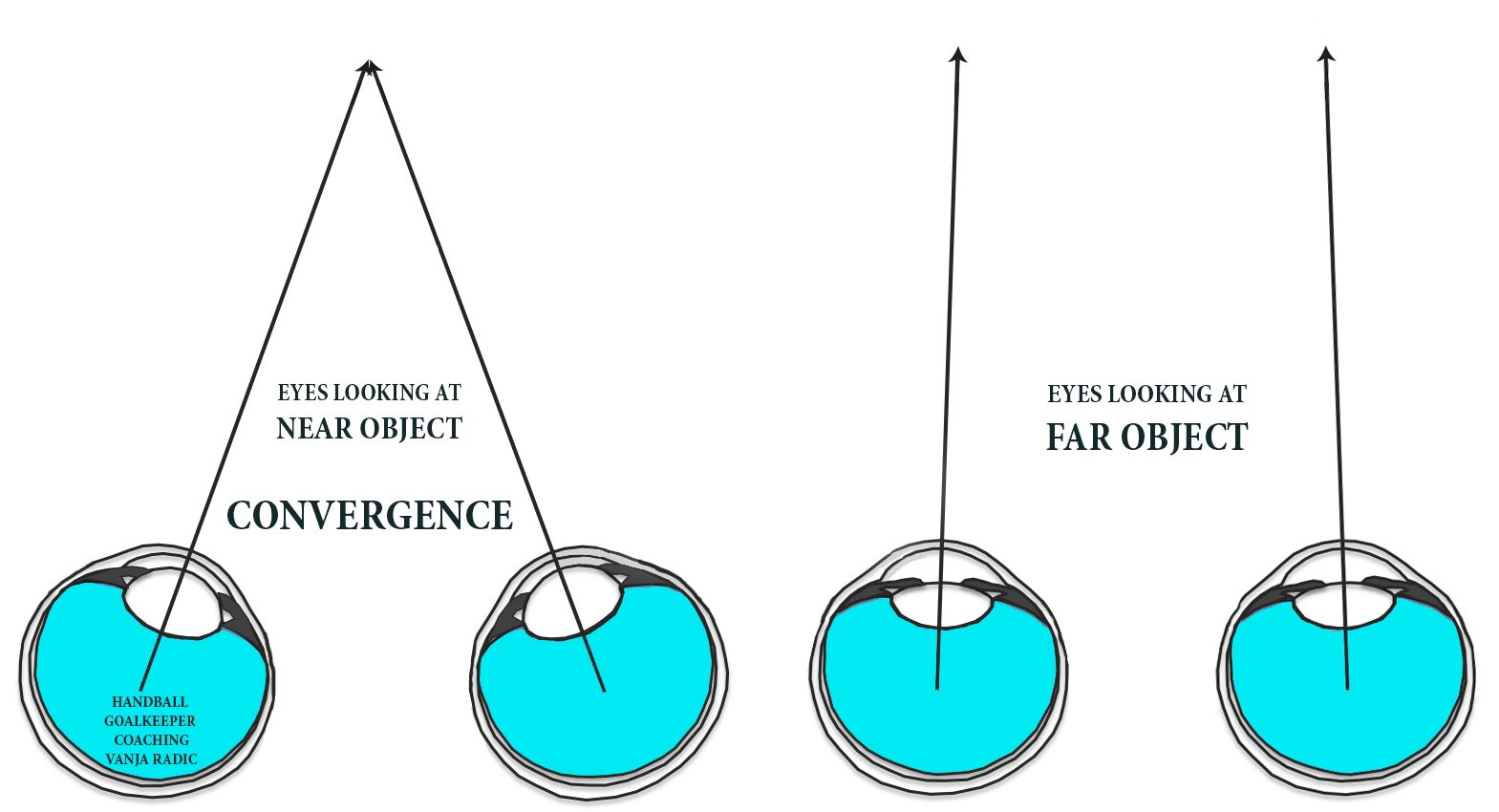
Convergence
binocular cue
Muscles rotate inward when viewing an object nearby; the greater the inward strain, the closer the object
Relative size
monocular cue
If two objects are similar in size, we perceive the one that casts a smaller retinal image to be further away

Interposition
monocular cue
Objects that block other objects tend to be perceived as closer

Relative clarity
Monocular cue
Because the light from distinct objects passes through more light, we perceive hazy objects as farther away than sharp clear objects

Texture gradient
monocular cue
A gradual change in appearance of objects from coarse to fine. The closer, the clearer the detail. The farther away, the smoother/less detailed

Linear Perspective
Monocular cues
Parallel lines appear to converge in the distance. The greater perceived distance

Height in the visual field
monocular cue
Refers to the principle that objects higher in our field of vision are perceived as being farther away

Sensation
detects stimuli
absolute threshold
detecting a stimulus
the minimum amount to notice it
transduction
converting physical energy (sound waves, etc.) into signals that the brain can use to interpret
just-noticeable difference
detecting a change between two stimuli
energy transduced for vision
light waves
energies transduced for touch
Pain, Pressure, Temperature
Retina
where transduction takes place for vision
Blind Spot (Optic disc)
the light insensitive point where the optic nerve leaves the eyeball and there are no receptor cells
Visual/optic nerve
carries visual information (impulses) from the retina to the thalamus/brain
Lens
part of the eye that changes shape and focuses images on our retina
Ocular accommodation
the ability of the lens to change shape and send light back to the retina
Presbyopia (age-related nearsightedness)
a natural result of aging that occurs when lens of the eye hardens and becomes less flexible
Nearsightedness
you are able to see up close
farsightedness
you are able to see far away
Photoreceptors cells
the name of the cells that do the actual transducing of light in the retina
Rods
located in the outer edge of the retina and help with seeing black and white, in the dark, and objects in our peripheral vision
Cones
located near the center of the retina and help with color vision
Blue
Green
Red
Fovea
located in the retina and contains the highest concentration of cones, which leads to the clearest vision that we have
Trichromatic theory
theory of color vision states are the three-color sensitive cones are sensitive to red, green, and blue
Opponent Process Theory
opposing retinal processes enable color vision
Afterimages
visual illusions that occurs when we continue to see an image even after it has been removed from our field of vision
Ganglion Cells
neuron that relay the visual information than our retina to our brain within the optic nerve
Color Vision Deficiency
Dichromatism
Monochromatism
Prosopagnosia
face blindness
either damage to temporal lobe or can be genetic/inherited
Blindsight
-ability to respond to visual stimuli w/o having a conscious awareness of seeing them
Occipital lobe
lobe of the brain that process visual information
Primary visual cortex
Binocular depth cues
2 eyes
size constancy
How we perceive objects moving to us
Our retinas believe that objects grow in size, but we know that the object is only getting close to us.
shape constancy
the phenomenon of perceiving an objects shape as consistent despite changes in its orientation or viewing angle
Apparent movement
term for a visual phenomenon where static images appear to be moving
perception of motion when there is none
Stroboscopic motion
type of apparent movement
still images/ photos (quickly shown) are perceived as moving
Looming
the phenomenon where objects are perceived as having the same size, regardless of their distance from the observer
Phi Phenomenon
visual illusion where stationary object appears to move
Closure
type of gestalt grouping principle
The tendency for the brain to automatically fill in gaps to perceive incomplete shapes, lines, or patterns as a complete, unified whole.
Figure-ground
tendency of the visual system to simplify a scene into the main object we are looking at and everything else that forms the background
Proximity
type of gestalt grouping principle
Tendency to perceive objects that are closer together as belonging to a single, unified group
Similarity
type of gestalt group principle
tendency for people to perceive objects with shared visual characteristics as belonging to the same group
Parietal lobe
body position
Gate control theory
spinal cord either blocks or allows pain to be transmitted to the brain
Phantom limb sensation
continuing to feel sensations after losing a limb
A-delta fibers
“first pain”
C-fibers
“second pain”
Vestibular sense
helps with balance, stability, and spatial orientation
Semicircular canals
they sense and relay information about movement of your head to the brain
kinesthesia
Allows the body to be aware of its position, movement, and actions
Somatic Nervous System
voluntary muscle movements
Ex: “I want to walk around”
Sympathetic nervous system
prepares body for activityEx: increase in adrenaline
“Flight, Fight, Freeze”
Depolarization
Positive ions rushing into the neuron; the action potential occurring
Long-term potentiation
Strength between neurons increase with repeated use (ex: language and muscle memory)
Medulla
inferior part of the brainstemregulates your breathing, heartbeat, and blood pressure
Cerebellum
located in the back of the brain below the occipital and temporal lobes
coordinated and precise movement
Hypothalamus
associated with hunger, sleep, and body temperature
part of limbic system
Hippocampus
helps with the formation of new memories
part of limbic system
Amygdala
associated with emotion and feelings
part of limbic system
Dopamine
Pleasure and reward (Joy), movement, attention, and learning
High Levels:
Schizophrenia
Low Levels
Parkinson’s disease